Ecological Niche Studies on Hylurgus ligniperda and Its Co-Host Stem-Boring Insects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Experimental Site
2.2. Research Subjects and Sample Collection
Characteristics of Insect Species
2.3. Selection of Predictive Variables
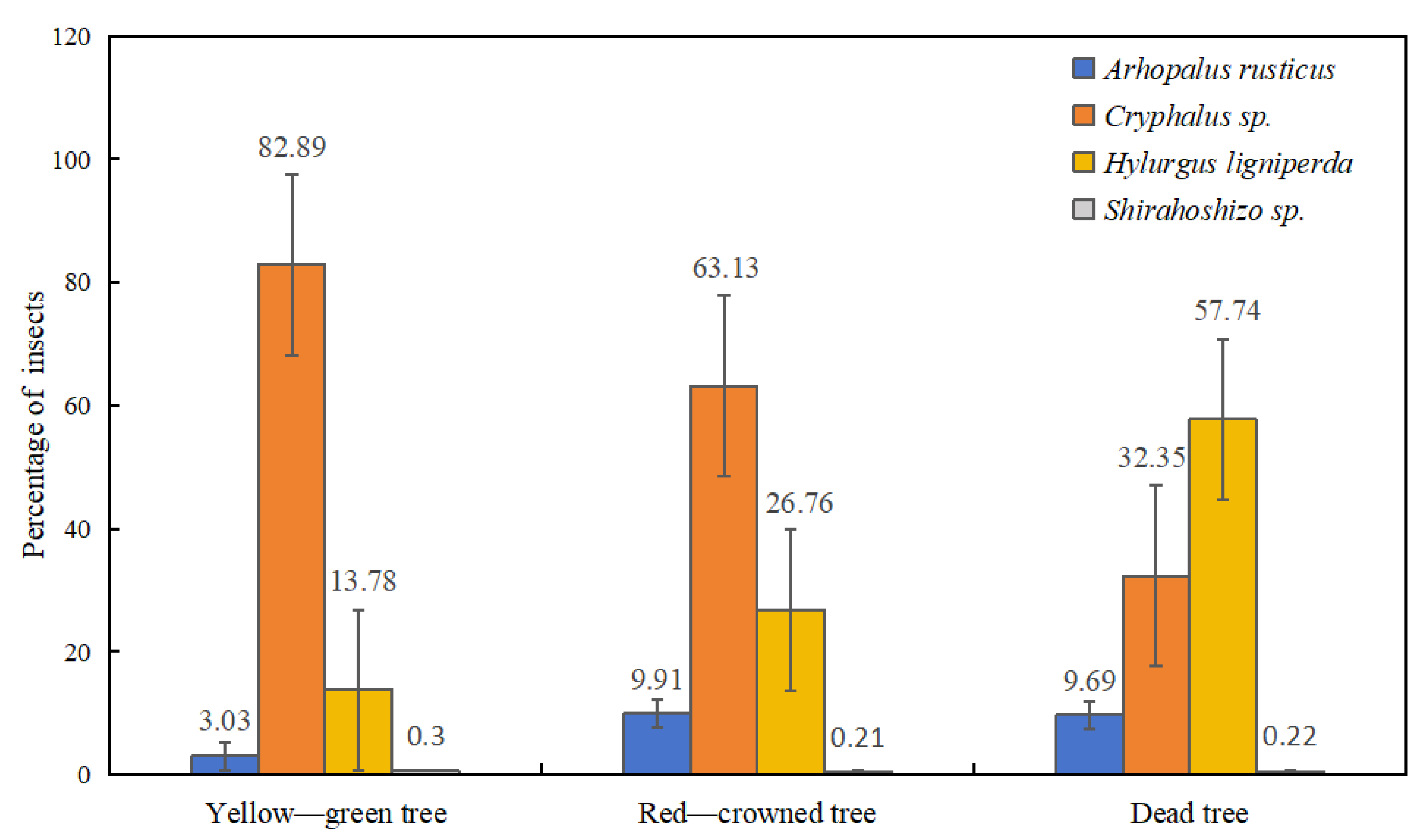
2.4. Statistical Chart of the Quantity Ratio of Various Boring Insects under Different Tree Vigors
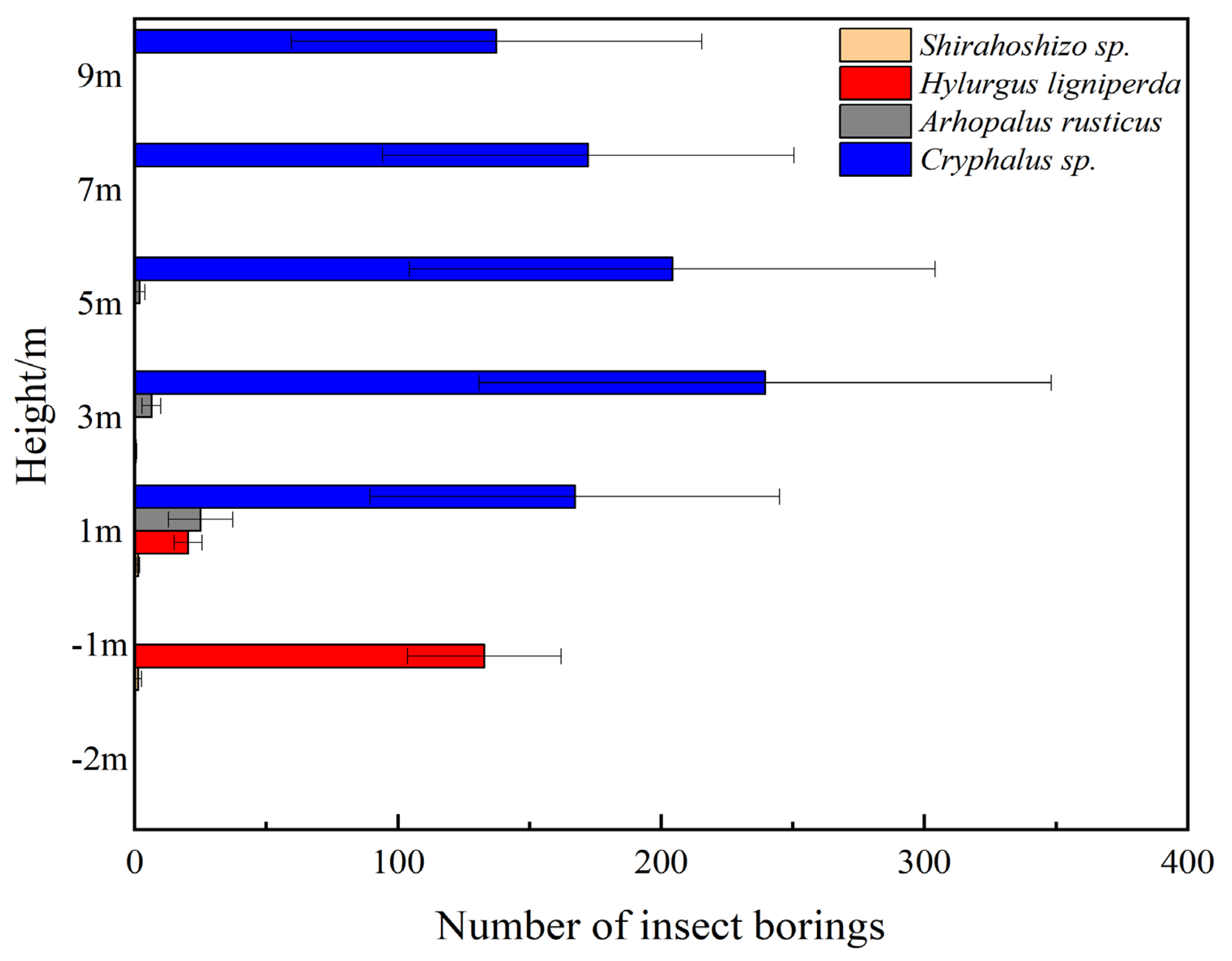
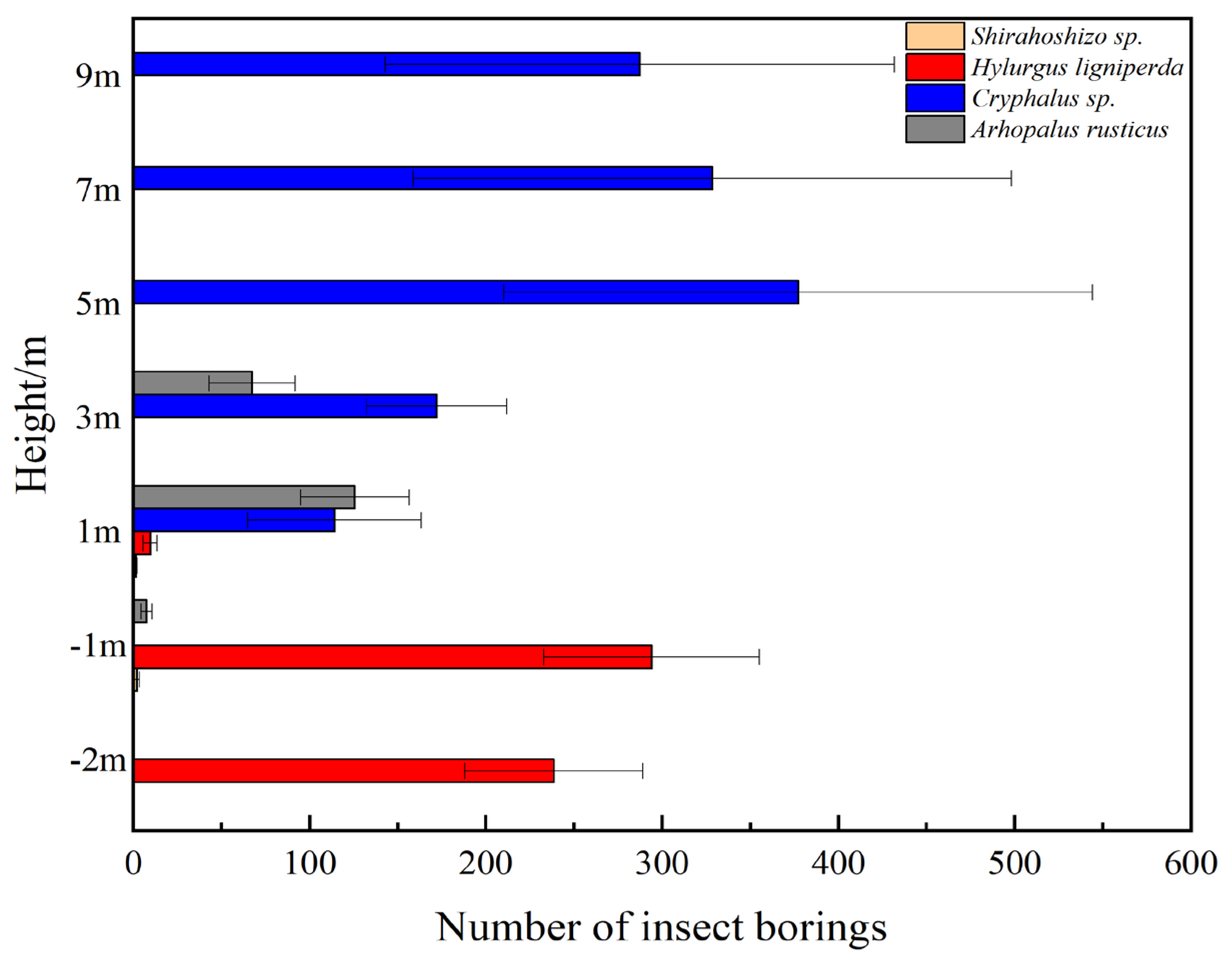
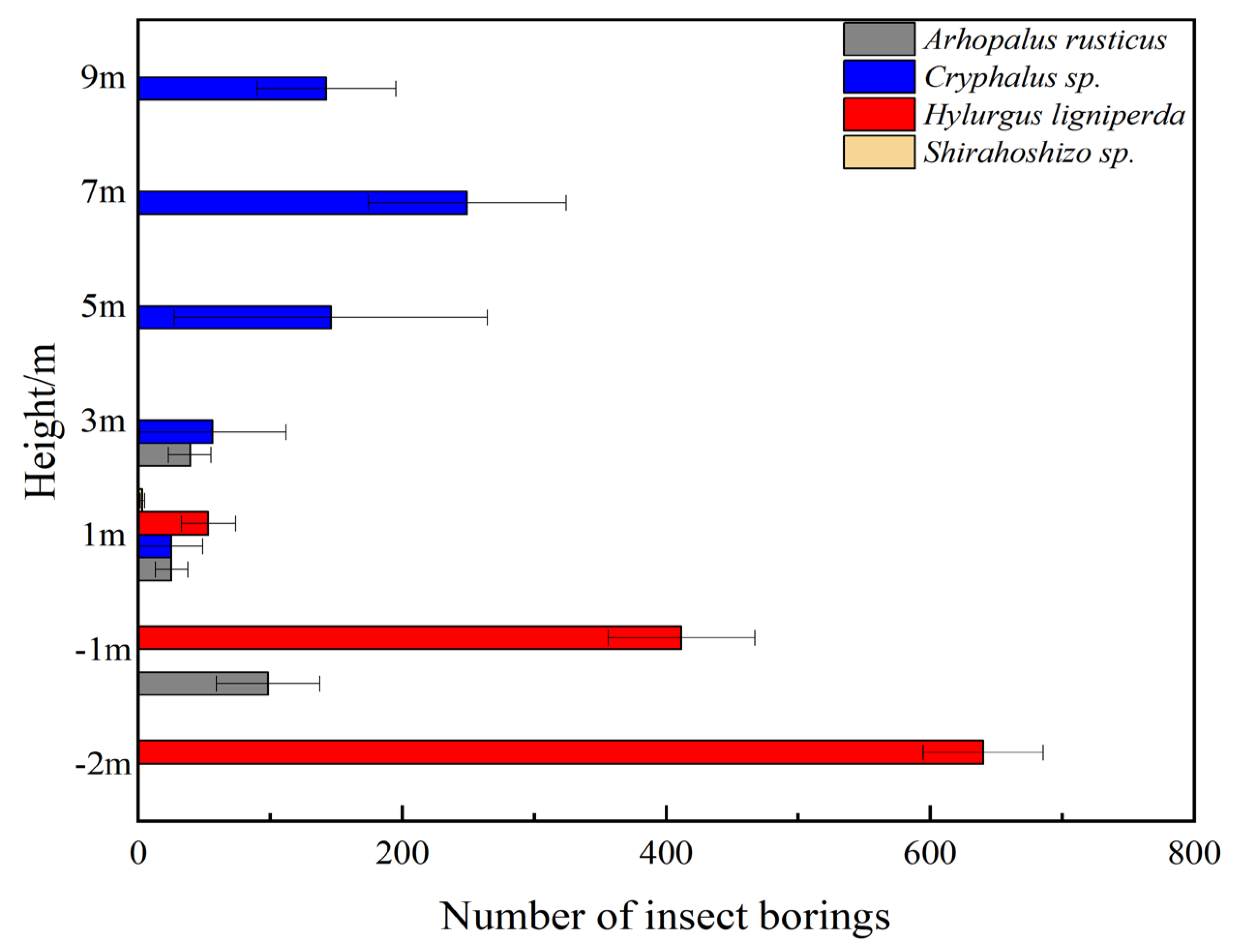
2.5. Statistical Chart of Average Insect Population Density at Different Heights under the Same Tree Vigor
2.6. Generalized Linear Model (GLM) Analysis
2.7. Temporal Niche Analysis
2.8. Niche Value Calculation Formula
2.8.1. Niche Width
2.8.2. Ecological Niche Overlap Index Was Calculated Using the Equation
2.8.3. The Ecological Niche Similarity Coefficient (PS) Was Calculated Using the Equation
2.8.4. Coefficient of Ecological Niche Competition
3. Results
3.1. Species Abundance and Distribution of Boring Insects in P. thunbergii Trees
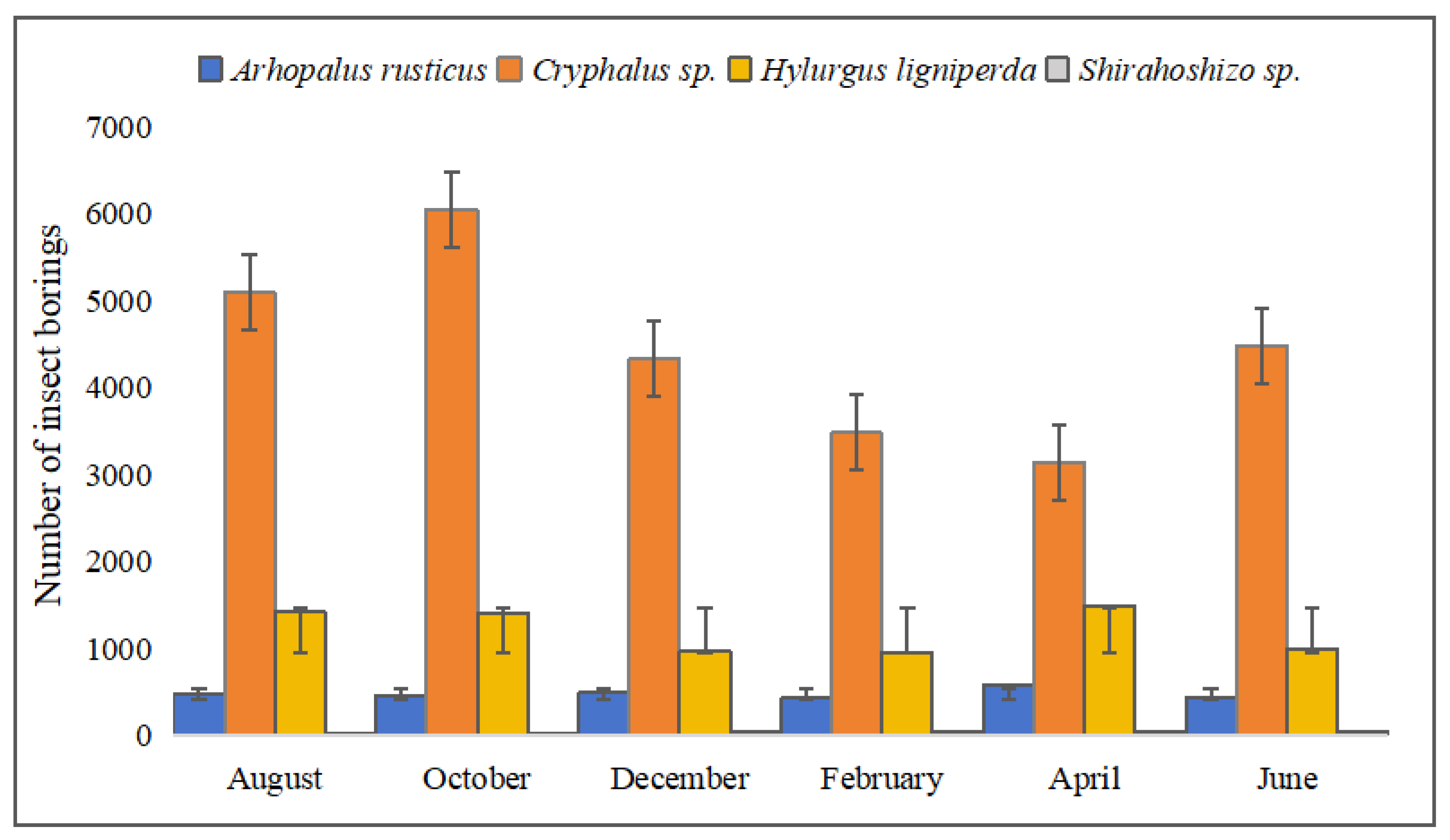
3.2. Temporal Ecological Niche
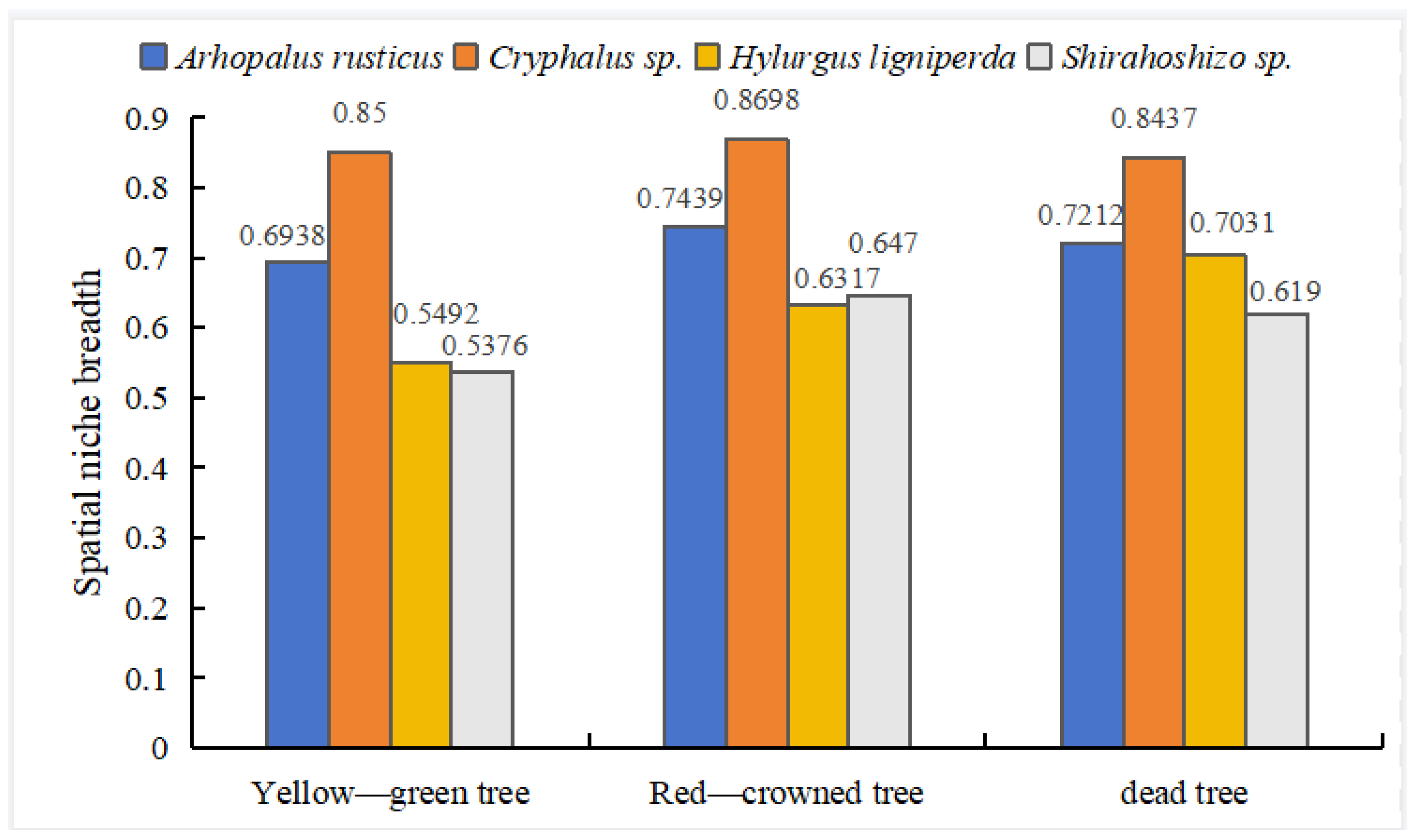
3.3. Spatial Ecological Niche
3.4. Coefficients of Competition between the Boring Insects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, S.L.; Zhou, W.C. Identification of Hylurgus ligniperda. Plant Quar. 2006, 1, 30–31. [Google Scholar]
- Mausel, D.L.; Gara, R.I.; Lanfranco, D.; Ruiz, C.; Ide, S.; Azat, R. The introduced bark beetles Hylurgus ligniperda and Hylastes ater (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) in Chile: Seasonal flight and effect of Pinus radiata log placement on colonization. Can. J. For. Res. 2007, 37, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawson, S.M.; Kerr, J.L.; Somchit, C.; Wardhaugh, C.W. Flight activity of wood-and bark-boring insects at New Zealand ports. N. Z. J. For. Sci. 2020, 50, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, J.P.; Carle, P. Contribution à l’étude biologique d’Hylurgus ligniperda F. (Coleoptera Scolytidae) dans le Sud-est de la France. For. Sci. 1975, 32, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannemann, W. SCHWENKE (Herausgeber): Die Forstschädlinge Europas. Ein Handbuch in fünf Bänden. Autorenkollektiv: Band 3. Schmetterlinge. 1978. VIII. 467 S., 244 Abb., Format 25.5× 17 cm DM 355.—(Subskriptionspreis DM 296.—). Verlag PAUL PAREY Hamburg und Berlin. Dtsch. Entomol. Z. 1979, 26, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguang, L.; Mary, L.F.; Steven, J.S. A secondary sexual character in the redhaired pine bark beetle, Hylurgus ligniperda Fabricius (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Pan-Pac. Entomol. 2008, 84, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoebeke, E.R. Hylurgus ligniperda: A new exotic pine bark beetle in the United States. Newsl. Mich. Entomol. Soc. 2001, 46, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.l.; Tao, J.; Wu, H.w.; Zong, S.x.; Wang, C.z.; Hua, D.; Shi, J.; Liu, Y.z.; Luo, Y.q. The first discovery and infective characteristics of a major invasive pest Hylurgus ligniperda (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) in China. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2021, 57, 140–150. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.J.; An, Y.L. Quarantine and identification of Hylurgus ligniperda (Fabricius) intercepted from imported Pinus radiata logs. Plant Quar. 2002, 16, 288–289. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.; Park, S.; Jiang, Z.R.; Ji, Y.C.; Ernstsons, A.S.; Li, J.J.; Li, Y.; Hulcr, J. Native or Invasive? The Red-Haired Pine Bark Beetle Hylurgus ligniperda (Fabricius) (Curculionidae: Scolytinae) in East Asia. Forests 2021, 12, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Gao, T.; Luo, Y.; Shi, J. Prediction of the global potential geographical distribution of Hylurgus ligniperda using a maximum entropy model. For. Ecosyst. 2022, 9, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.Y.; Zhang, J.H.; Yang, D.; Chen, N.Z. Potential geographical distributions of Hylurgus ligniperda (Coleoptera: Scolytinae) in China. Plant Quar. 2018, 32, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuting, Z.; Xuezhen, G.; Ya, Z.; Siwei, G.; Tao, W.; Jing, T.; Shixiang, Z. Prediction of the potential geographical distribution of Hylurgus ligniperda at the global scale and in China using the MaxEnt model. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2022, 44, 90–99. [Google Scholar]
- Pugh, A.R.; Romo, C.M.; Clare, G.K.; Meurisse, N.; Bader, M.K.F.; Pawson, S.M. Temperature Effects on the Survival and Development of Two Pest Bark Beetles Hylurgus ligniperda F. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) and Hylastes ater Paykull (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Environ. Entomol. 2023, 52, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davydenko, K.; Vasaitis, R.; Meshkova, V.; Menkis, A. Fungi associated with the red-haired bark beetle, Hylurgus ligniperda (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in the forest-steppe zone in eastern Ukraine. Eur. J. Entomol. 2014, 111, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribe, G.D. Phenology of Pinus radiata log colonization by the red-haired pine bark beetle Hylurgus ligniperda (Fabricius)(Coleoptera: Scolytidae) in the south-western Cape Province. J. Entomol. Soc. S. Afr. 1991, 54, 01–07. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Ge, S.; Li, J.; Ren, L.; Wang, C.; Luo, Y. Composition and Diversity of the Endobacteria and Ectobacteria of the Invasive Bark Beetle Hylurgus ligniperda (Fabricius) (Curculionidae: Scolytinae) in Newly Colonized Areas. Insects 2024, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Harrington, T.C.; Lee, J.C.; Seybold, S.J. Leptographium tereforme sp. nov. and other Ophiostomatales isolated from the root-feeding bark beetle Hylurgus ligniperda in California. Mycologia 2011, 103, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clare, G.K.; George, E.M. Life cycle and massrearing of Hylurgus ligniperda using a novel eggcollection method. N. Z. Plant Prot. 2016, 69, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romo, C.M.; Bader, M.K.F.; Pawson, S.M. Comparative Growth and Survival of Hylurgus ligniperda (Coleoptera: Scolytinae) and Arhopalus ferus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) Reared on Artificial or Natural Diet at 15 or 25 °C. J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrice, T.R.; Haack, R.A.; Poland, T.M. Evaluation of three trap types and five lures for monitoring Hylurgus ligniperda (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) and other local scolytids in New York. Gt. Lakes Entomol. 2004, 37, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, W. A Discussion on Some Aspects of Niche Theory. J. Lanzhou Univ. 1990, 5, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, L.; Jinzhao, Z.; Qingke, Z. A review on niche theory and niche metrics. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2003, 25, 100–107. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Liu, K.; Zang, R.; Wang, X.; Sheng, L.; Zhu, Z.; Shi, Q.; Wang, C.a. Development of the modern niche theory and its main representative genres. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2007, 42, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Ju, R.; Li, Y. Niche concept and its application in insect ecology. Chin. J. Ecol. 2006, 25, 1280–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G. On the definition of niche and the improved formula for measuring niche overlap. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1984, 4, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Tang, M.; Ye, H.; Yuan, F. Niche of bark beetles within Pinus armandi ecosystem in inner Qinling Mountains. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2000, 35, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Yan, W.; Luo, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Ma, J. Spatial niches of bark beetle population in Picea crassifolia natural forests. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2007, 29, 165–169. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, F.; Luo, Y.; Shi, J.; Kari, H. Spatial ecological niche of main insect borers in larch of Aershan. Sheng Tai Xue Bao Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 4342–4349. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, B.; Li, Z. Studies on the genus Cryphalus Er. in China and descriptions of new species. Chin. J. Insect Sci. 1963, 12, 597–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, X. Occurrence and damage status of Arhopalus rusticus in China and its control countermeasures. Shandong For. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Z. Spatial Pattren and lts Time Series Dynamics of Shirahoshizo patruelis Adults in Forest. Shandong For. Sci. Technol. 2013, 41, 111–114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y. Fauna Sinica, Insecta (Coleoptera: Curculionidae); Science Press: Beijing, China, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H. Fauna Sinica, Insecta (Coleoptera: Scolytidae); Science Press: Beijing, China, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Lu, J. An Outline of the Classification of Scolytidae in China; Tongji University Press: Shanghai, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S. Chinese Cerambycid Larvae; Chongqing Press: Chongqing, China, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, S.; Luo, Y.; Yu, L.; Lu, W.; Han, X.; Ren, L. Temporal and spatial niches of two sympatric Tomicus species pests of Pinus yunnanensis Faranch. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2018, 55, 279–287. [Google Scholar]
- Browne, F.G. Pests and Diseases of Forest Plantation Trees: An Annotated List of the Principal Species Occurring in the British Commonwealth; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, R.; Zhao, X.; Huang, S.; Hua, J.; Sun, S. Vertical Distribution of Wood-boring Pests and Its Parasitic Wasp in Pinus tabulaeformis. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2021, 37, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N. Researches on Biological Characteristics and Adult Emergence Period Prediction of Arhopalus rusticus. D. Shandong Agric. Univ. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Omkar; Afaq, U. Food consumption, utilization and ecological efficiency of Parthenium beetle, Zygogramma bicolorata pallister (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2011, 14, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Sun, C.; Yang, F. Morphological Characteristics and Feeding Rhythm of Hypera sp. Sci. Anhui Agric. 2021, 49, 136–139. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Hu, J.; Song, C. Oviposition Ecological Niche of Monochamus alternatus and Arhopalus rusticus on Pinus thunbergia Infected with Pine Wood. J. Shandong Agric. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2023, 54, 670–675. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lu, P.; Zhang, Y. Geostatistical analysis of the spatial distribution of Arhopalus rusticus larvae and adults. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qu, H.; Wang, J.; Pan, Y.; Qi, S.a.; Qu, H. Investigation of two stem-borers on Pinus thunbergii in Yantai. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2018, 46, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.x.; Liu, F.; Kong, X.b.; Zhang, S.f.; Zhang, Z. Spatiotemporal niche of competition and coexistence of three Tomicus spp. infesting Pinus yunnanensis during the transferring stage from shoots to trunk. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2020, 56, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Bao, M.; Ao, T.; Ren, L.; Luo, Y. Population distribution patterns and ecological niches of two Sirex species damaging Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2017, 54, 924–932. [Google Scholar]
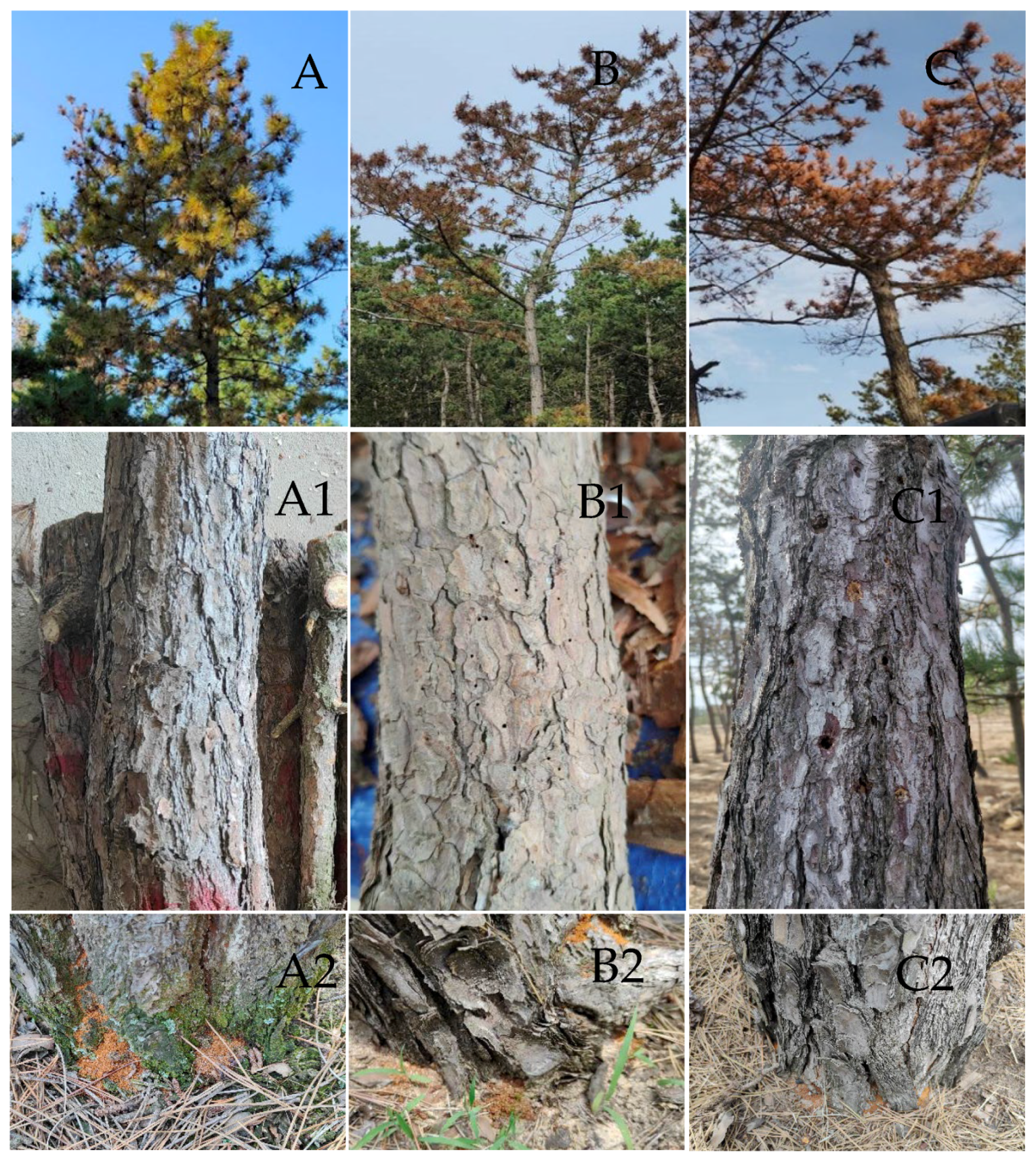


| Quantity | Mean Height (m) | Mean DBH (cm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yellow–green tree | 6 | 9.92 ± 1.32 | 16.73 ± 2.57 |
| Red-crowned tree | 6 | 9.83 ± 1.63 | 18.87 ± 3.54 |
| Dead tree | 6 | 9.42 ± 1.86 | 16.52 ± 3.53 |
| Omnibus Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| LR χ2 | Df | Sig | |
| H. ligniperda | 289.166 | 20 | 0.000 |
| Cryphalus sp. | 149.551 | 20 | 0.000 |
| A. rusticus | 106.408 | 20 | <0.001 |
| Shirahoshizo sp. | 67.540 | 20 | <0.001 |
| Test of Model Effects | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Wald χ2 | Df | Sig | |
| H. ligniperda | Intercept | 296.365 | 1 | 0.000 |
| Tree vigor | 124.614 | 2 | 0.000 | |
| Height | 651.848 | 6 | 0.000 | |
| Tree vigor × Height | 347.974 | 12 | 0.000 | |
| Cryphalus sp. | Intercept | 387.698 | 1 | 0.000 |
| Tree vigor | 31.966 | 2 | <0.001 | |
| Height | 201.794 | 6 | 0.000 | |
| Tree vigor × Height | 53.136 | 12 | <0.001 | |
| A. rusticus | Intercept | 70.116 | 1 | <0.001 |
| Tree Vigor | 20.364 | 2 | <0.001 | |
| Height | 106.173 | 6 | 0.000 | |
| Tree vigor × Height | 40.643 | 12 | <0.001 | |
| Shirahoshizo sp. | Intercept | 35.458 | 1 | <0.001 |
| Tree vigor | 0.436 | 2 | 0.804 | |
| Height | 71.043 | 6 | <0.001 | |
| Tree vigor × Height | 17.880 | 12 | 0.119 | |
| Hylurgus ligniperda | Cryphalus sp. | Shirahoshizo sp. | Arhopalus rusticus | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hylurgus ligniperda | 0.733 | 0.008 | 0.289 | |
| Cryphalus sp. | 0.733 | 0.005 | 0.267 | |
| Shirahoshizo sp. | 0.008 | 0.005 | 0.014 | |
| Arhopalus rusticus | 0.289 | 0.267 | 0.014 |
| Health Status of Pine Tree | Species | Niche Overlap (Proportion of Niche Similarity) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cryphalus sp. | A. rusticus | H. ligniperda | ||
| Yellow–green tree | A. rusticus | 0.1565 (0.6834) | ||
| H. ligniperda | 0.1118 (0.6111) | 0.1210 (0.5348) | ||
| Shirahoshizo sp. | 0.1542 (0.3987) | 0.1540 (0.3713) | 0.0818 (0.4851) | |
| Red-crowned tree | A. rusticus | 0.1606 (0.6567) | ||
| H. ligniperda | 0.1079 (0.5275) | 0.1178 (0.4275) | ||
| Shirahoshizo sp. | 0.1542 (0.5000) | 0.1233 (0.4850) | 0.1108 (0.3046) | |
| Dead tree | A. rusticus | 0.1558 (0.5903) | ||
| H. ligniperda | 0.0683 (0.5344) | 0.0910 (0.5127) | ||
| Shirahoshizo sp. | 0.1151 (0.5515) | 0.1496 (0.4024) | 0.0689 (0.2784) | |
| Health Status of Pine Tree | Species | Interspecific Competition Coefficients | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cryphalus sp. | A. rusticus | H. ligniperda | ||
| Yellow–green tree | A. rusticus | 0.8177 | ||
| H. ligniperda | 0.6373 | 0.4942 | ||
| Shirahoshizo sp. | 0.4661 | 0.4394 | 0.4914 | |
| Red-crowned tree | A. rusticus | 0.7673 | ||
| H. ligniperda | 0.5480 | 0.4445 | ||
| Shirahoshizo sp. | 0.5460 | 0.4946 | 0.3432 | |
| Dead tree | A. rusticus | 0.6866 | ||
| H. ligniperda | 0.6260 | 0.5177 | ||
| Shirahoshizo sp. | 0.5717 | 0.4128 | 0.2632 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bi, L.; Tao, J.; Ren, L.; Wang, C.; Zhong, K. Ecological Niche Studies on Hylurgus ligniperda and Its Co-Host Stem-Boring Insects. Forests 2024, 15, 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050792
Bi L, Tao J, Ren L, Wang C, Zhong K. Ecological Niche Studies on Hylurgus ligniperda and Its Co-Host Stem-Boring Insects. Forests. 2024; 15(5):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050792
Chicago/Turabian StyleBi, Lihong, Jing Tao, Lili Ren, Chuanzhen Wang, and Kai Zhong. 2024. "Ecological Niche Studies on Hylurgus ligniperda and Its Co-Host Stem-Boring Insects" Forests 15, no. 5: 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050792
APA StyleBi, L., Tao, J., Ren, L., Wang, C., & Zhong, K. (2024). Ecological Niche Studies on Hylurgus ligniperda and Its Co-Host Stem-Boring Insects. Forests, 15(5), 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050792







