Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Pinus sylvestris—The First Report in Europe
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wood Sampling and Nematode Extraction
2.2. Morphological Characterization
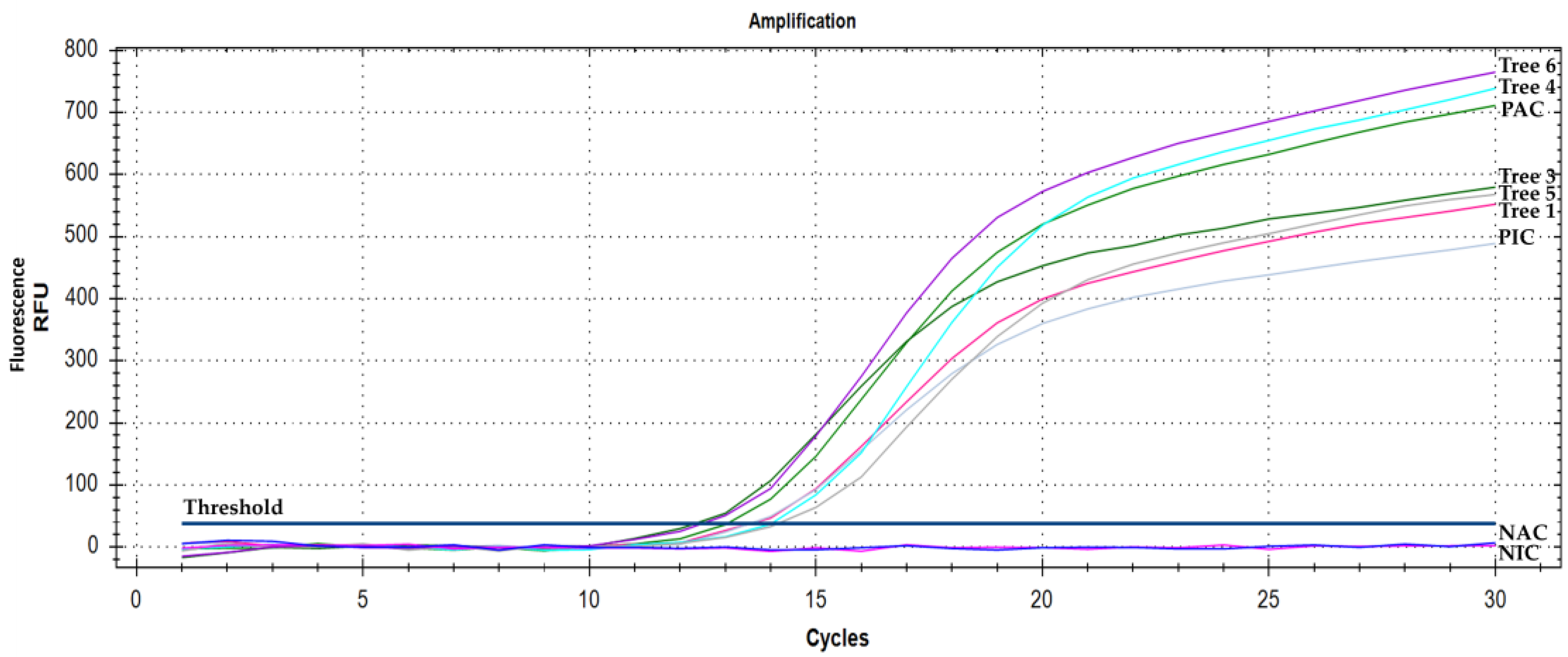
2.3. Real-Time PCR
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EPPO. Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. EPPO Datasheets on Pests Recommended for Regulation. 2024. Available online: https://gd.eppo.int (accessed on 27 May 2024).
- Evans, H.F.; McNamara, D.G.; Braasch, H.; Chadoeuf, J.; Magnusson, C. Pest Risk Analysis (PRA) for the territories of the European Union (as PRA area) on Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and its vectors in the genus Monochamus. EPPO Bull. 1996, 26, 199–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, M.M.; Braasch, H.; Bravo, M.A.; Penas, A.C.; Burgemeister, W.; Metge, K.; Sousa, E. First report of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Portugal and in Europe. Nematology 1999, 1, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelleira, A.; Picoaga, A.; Mansilla, J.P.; Aguin, O. Detection of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, causal agent of pine wilt disease on Pinus pinaster in Northwestern Spain. Plant Dis. 2011, 95, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, L.; Arcos, S.C.; Escuer, M.; Merino, R.S.; Esparrago, G.; Abelleira, A.; Navas, A. Incidence of the pinewood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophlius Steiner & Buhrer, 1934 (Nickle, 1970) in Spain. Nematology 2011, 13, 755–757. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, L.; Cardoso, J.M.S.; Lopes, A.; Pestana, M.; Abreu, F.; Nunes, N.; Mota, M.; Abrantes, I. The pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, in Madeira Island. Helminthologia 2012, 49, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, P.; Rodríguez, V.; Renedo, F.; Sanz, A.V.; Domínguez, J.C.; Pérez-Escolar, G.; Miranda, J.; Álvarez, B.; González-Casas, A.; Mayor, E.; et al. First report of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus causing pine wilt disease on Pinus radiata in Spain. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inácio, M.L.; Nóbrega, F.; Vieira, P.; Bonifácio, L.; Naves, P.; Sousa, E.; Mota, M. First detection of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus associated with Pinus nigra in Portugal and in Europe. For. Pathol. 2015, 45, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skilling, D.D. Pinus sylvestris (Scotch pine). In Silvics of North America, 1st ed.; Burns, R.M., Honkala, B.H., Eds.; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1990; pp. 489–496. [Google Scholar]
- Houston, D.T.; de Rigo, D.; Caudullo, G. Pinus sylvestris in Europe: Distribution, habitat, usage, and threats. In European Atlas of Forest Tree Species; San-Miguel-Ayanz, J., de Rigo, D., Caudullo, G., Houston Durrant, T., Mauri, A., Eds.; European Union Official Publication: Luxembourg, 2016; pp. 132–133. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, C.; Gaspar, M.J.; Pires, J.; Alves, A.; Simões, R.; Rodrigues, J.C.; Silva, M.E.; Carvalho, A.; Brito, J.E.; Lousada, J.L. Physical, chemical and mechanical properties of Pinus sylvestris wood at five sites in Portugal. IForest 2017, 10, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dropkin, V.H.; Foudin, A.S. Report of the occurrence of Bursaphelenchus lignicolus induced pine wilt disease in Missouri. Plant Dis. Rep. 1979, 63, 904–905. [Google Scholar]
- Dropkin, V.H.; Foudin, A.; Kondo, E.; Linit, M.; Smith, M.; Robbins, K. Pinewood nematode: A threat to U.S. forests? Plant Dis. 1981, 65, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.C.; Morehart, A.L. Decline, and death of Pinus spp. in Delaware caused by Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. J. Nematol. 1982, 14, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carling, D.E. Some insects associate of the pinewood nematode in eastern Virgínia. Can. J. Forest Res. 1984, 14, 826–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, R.B.; Appleby, J.E. Epidemiology of pine wilt in Illinois. Plant Dis. 1984, 68, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryss, A.; Vieira, P.; Mota, M.; Kulinich, O. A synopsis of the genus Bursaphelenchus Fuchs, 1937 (Aphelenchida: Parasitaphelenchidae) with key to species. Nematology 2005, 7, 393–458. [Google Scholar]
- Braasch, H. Bursaphelenchus species in conifers in Europe: Distribution and morphological relationships. EPPO Bull. 2001, 31, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polomski, J.; Schönfeld, U.; Braasch, H.; Dobbertin, M.; Burgermeister, W.; Rigling, D. Occurrence of Bursaphelenchus species in declining Pinus sylvestris in a dry Alpine valley in Switzerland. For. Pathol. 2006, 36, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errico, G.; Carletti, B.; Schröder, T.; Mota, M.; Vieira, P.; Roversi, P.F. An update on the occurrence of nematodes belonging to the genus Bursaphelenchus in the Mediterranean area. Forestry 2008, 88, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldeias do Xisto. Available online: https://www.aldeiasdoxisto.pt/pt/aldeias/lousa/ (accessed on 6 June 2024).
- Whitehead, A.G.; Hemming, J.R. A comparison of some quantitative methods of extracting small vermiform nematodes from soil. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1965, 55, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, L.; Santos, M.C.V.; Santos, M.S.; Curtis, R.H.C.; Abrantes, I.M.O. Morpho-biometrical characterisation of Portuguese Bursaphelenchus xylophilus isolates with mucronate, digitate or round tailed females. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2008, 47, 223–233. [Google Scholar]
- Nickle, W.R.; Golden, A.M.; Mamiya, Y.; Wergin, W.P. On the taxonomy and morphology of pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner & Buhrer, 1934) Nickle, 1970. J. Nematol. 1981, 13, 385–392. [Google Scholar]
- EPPO. PM 7/44(4) Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. EPPO Bull. 2023, 53, 156–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagnone, S.; Abad, P.; Castagnone-Sereno, P. Satellite DNA-based species-specific identification of single individuals of the pinewood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae). Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2005, 112, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, C.; Castagnone, C.; Boonham, N.; Tomlinson, J.; Lawson, R.; Hockland, S.; Quill, J.; Vieira, P.; Mota, M.; Castagnone-Sereno, P. Satellite DNA as a target for Taqman real-time PCR detection of the pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2007, 8, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodda, M. Phylum Nematoda: A classification, catalogue, and index of valid genera, with a census of valid species. Zootaxa 2022, 5114, 1–289. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, J.M.; Sousa, E.; Abrantes, I. Pine Wilt Disease: Historical Review. In Pine Wil Disease in Europe: Biological Interactions and Integrated Management, 1st ed.; Sousa, E., Vale, F., Abrantes, I., Eds.; FNAPF: Oeiras, Portugal, 2015; pp. 13–32. [Google Scholar]
- Brichta, J.; Stanislav Vacek, S.; Vacek, Z.; Cukor, J.; Mikeska, M.; Bílek, L.; Šimůnek, V.; Josef Gallo, J.; Brabec, P. Importance and potential of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) in 21st century. Cent. Eur. For. J. 2023, 69, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegamia, M.; Jenkins, T.A.R. Estimate global risks of a forest disease under current and future climates using species distribution model and simple thermal model—Pine Wilt disease as a model case. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 409, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panesar, T.S.; Sutherland, J.R. Pathogenicity of canadian isolates of the Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (pinewood nematode) to provenances of Pinus sylvestris and Pinus contorta as grown in Finland: A greenhouse study. Scand. J. Forest Res. 1989, 4, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melakeberhan, H.; Webster, J.M. Relationship of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus population density to mortality of Pinus sylvestris. J. Nematol. 1990, 22, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Filipiak, A. Pathogenicity of selected isolates of the quarantine pinewood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus to Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.). J. Plant Prot. Res. 2015, 55, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes da Silva, M.; Solla, A.; Sampedro, L.; Zas, R.; Vasconcelos, M.W. Susceptibility to the pinewood nematode (PWN) of four pine species involved in potential range expansion across Europe. Tree Physiol. 2015, 35, 987–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-García, A.; Martín, J.A.; Gil, L.; Menéndez-Gutiérrez, M.; Díaz, R. Resin canal traits variation in Pinus spp. with different susceptibility to the pine wood nematode. Forests 2023, 14, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulinich, O.A.; Elena, N.; Arbuzova, E.N.; Chalkin, A.A.; Kozyreva, N.I. Experimental confirmation of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus survival and propagation in birch logs. Russ. J. Nematol. 2024, 32, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Arbuzova, E.N.; Kulinich, O.A.; Chalkin, A.A.; Kozyreva, N.I.; Gorbach, V.V.; Ryss, A.Y. Infestation of pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) seedlings with the pinewood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus Steiner and Buhrer (Nickle) through wood sawdust. Ann. For. Sci. 2023, 80, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halik, S.; Bergdahl, D.R. Long-term survival of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in living Pinus sylvestris in an established plantation. Eur. J. For. Pathol. 1984, 24, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naves, P.M.; Sousa, E.M.; Quartau, J.M. Feeding and oviposition preferences of Monochamus galloprovincialis for certain conifers under laboratory conditions. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2006, 120, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutroumpa, F.A.; Vincent, B.; Roux-Morabito, G.; Martin, C.; Lieutier, F. Fecundity and larval development of Monochamus galloprovincialis (Coleoptera Cerambycidae) in experimental breeding. Ann. For. Sci. 2008, 65, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szmigielski, R.; Cieslak, M.; Rudziński, K.J.; Maciejewska, B. Identification of volatiles from Pinus sylvestris attractive for Monochamus galloprovincialis using a SPME-GC/MS platform. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 19, 2860–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Husillos, E.; Álvarez-Baz, G.; Etxebeste, I.; Pajares, J.A. Shoot feeding, oviposition, and development of Monochamus galloprovincialis on Pinus pinea relative to other pine species. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2013, 149, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| P. sylvestris | Wood Sample (g) | B. xylophilus/100 g | Other Nematodes/100 g | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Juveniles | Females | Males | |||
| Tree 1 | 140 | 3 * | ---- | ---- | 185 |
| Tree 2 | 145 | ---- | ---- | ---- | 131 |
| Tree 3 | 134 | 212 ** | 345 | 370 | 376 |
| Tree 4 | 136 | 4 * | ---- | ---- | 52 |
| Tree 5 | 133 | 5 * | ---- | ---- | 79 |
| Tree 6 | 139 | 91 ** | 29 | 28 | 286 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fonseca, L.; Silva, H.; Cardoso, J.M.S.; Esteves, I.; Maleita, C.; Lopes, S.; Abrantes, I. Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Pinus sylvestris—The First Report in Europe. Forests 2024, 15, 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15091556
Fonseca L, Silva H, Cardoso JMS, Esteves I, Maleita C, Lopes S, Abrantes I. Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Pinus sylvestris—The First Report in Europe. Forests. 2024; 15(9):1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15091556
Chicago/Turabian StyleFonseca, Luís, Hugo Silva, Joana M. S. Cardoso, Ivânia Esteves, Carla Maleita, Sónia Lopes, and Isabel Abrantes. 2024. "Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Pinus sylvestris—The First Report in Europe" Forests 15, no. 9: 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15091556
APA StyleFonseca, L., Silva, H., Cardoso, J. M. S., Esteves, I., Maleita, C., Lopes, S., & Abrantes, I. (2024). Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Pinus sylvestris—The First Report in Europe. Forests, 15(9), 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15091556






