Abstract
Lucky bamboo (Dracaena sanderiana hort. ex. Mast. = Dracaena braunii) is a popular decorative plant in China. In March 2022, a severe outbreak of anthracnose disease occurred on the stems of lucky bamboo plants in a nursery garden in Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China. Thirty-two fungal isolates were obtained from the infected stem tissues and were morphologically identified as Colletotrichum species. A multilocus phylogenetic analysis based on the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region, the actin (ACT) gene, and the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) gene indicated the isolate FGZ-1 as Colletotrichum gloeosporioides (Penz.) Penz. and Sacc. The pathogenicity of isolate FGZ-1 was verified by inoculating mycelial plugs on stem segments and spraying spores on the whole one-year-old lucky bamboo plants. Koch’s postulates were fulfilled via the re-isolation of C. gloeosporioides from the diseased tissues. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of C. gloeosporioides causing anthracnose on lucky bamboo in China. The detection of C. gloeosporioides on lucky bamboo in China expands the range of Colletotrichum species that are associated with anthracnose in this popular ornamental plant. This study lays a solid foundation for future investigations into the pathogenic mechanisms of anthracnose on D. sanderiana and control strategies for this disease, such as biocontrol agents and the construction of resistant cultivars.
1. Introduction
Lucky bamboo (Dracaena sanderiana hort. ex. Mast. = Dracaena braunii) is a popular decorative species and one of the most popular ornamental houseplants in China [1,2]. Lucky bamboo belongs to a different taxonomic order to true bamboos, although the stems have a similar appearance [3]. The history of the lucky bamboo plant can be tracked for more than 4000 years in Chinese culture [4], because they are believed to confer good luck and fortune in life. While lucky bamboo plants are easy to care for and grow well under various indoor conditions, they are inevitably affected by several diseases worldwide, including leaf spots caused by Alternaria alternata in Egypt [5], leaf blight caused by Phytophthora nicotianae in Brazil [6], leaf blight wilt caused by Pantoea stewartii subsp. indologenes in China [7], stem rot caused by Aspergillus niger [8] and Fusarium solani [9] in Iran, stem and root rot caused by Fusarium proliferatum in Iraq [10], and leaf chlorosis caused by pepper mild mottle virus (PMMoV) in Korea [11]. The production of lucky bamboo is significantly impacted by anthracnose, a disease caused by Colletotrichum species, which leads to substantial economic losses globally [12], such as anthracnose caused by Colletotrichum dracaenophilum in Bulgaria [13], Iran [14], the USA [15], Egypt [3], and Brazil [16], as well as Colletotrichum karstii [17] and Colletotrichum truncatum [18] in China. Colletotrichum is a diverse genus of Ascomycete fungi, with species being responsible for anthracnose in numerous economically important plants [19]. Chemical treatments remain a key approach in managing plant diseases. When resistant varieties are not available, the most common method for disease control is the application of fungicides [20].
In March 2022, the typical symptoms of anthracnose were observed on D. sanderiana plants grown in ‘Jiayushan garden’, a nursery garden in Nanjing, China (32°6′27.281″ N, 118°50′24.169″ E). Approximately 40% of the lucky bamboo plants for sale were affected. Decorative plants are expected to maintain a flawless appearance, and anthracnose poses a threat to the ornamental value of lucky bamboo. Therefore, the aims of the present study were to (i) isolate the pathogen causing anthracnose, (ii) identify the causal agent using morphological characterization and molecular analysis, and (iii) assess its pathogenicity. This study is the first to identify that C. gloeosporioides is the cause of anthracnose in D. sanderiana in China via the isolation of the pathogen, morphological characterization, and phylogenetic analysis. These findings enhance our understanding of the disease and provide a basis for future research on its pathogenic mechanisms and control strategies. In particular, more nuanced approaches to contend with diverse pathogens causing anthracnose in D. sanderiana and further exploration of sustainable, environmentally friendly treatments are needed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Isolation
Samples ranging from 10 cm to 15 cm in length were obtained from the diseased stems of five separate lucky bamboo plants exhibiting the characteristic signs of anthracnose in ‘Jiayushan garden’, a nursery garden in Nanjing, China (32°6′27.281″ N, 118°50′24.169″ E). In order to isolate pathogenic fungi, an improved method was used [1]. The stem sections with visible acervuli and spore clusters were sterilized with a 1% sodium hypochlorite solution for 2 min, followed by thorough rinsing with sterilized distilled water, three to four times. Thus, these tissues were then dissected into minute segments (around 0.5 cm in length) under sterile conditions, placed on potato dextrose agar (PDA) amended with rifampicin (100 µg/mL) and streptomycin sulfate (100 µg/mL), and kept at 25 °C in darkness [21]. After a 3-day period, the fungal colonies emerging from the stem tissues were transferred to fresh PDA and maintained at 25 °C in the absence of light. The isolates were purified by isolating single spores, employing a method detailed by Fei et al. [22].
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing
The mycelia of isolates were obtained by inoculating the mycelial plugs into 100 mL of liquid potato dextrose broth (PDB) in a 250 mL baffle flask, culturing them at 25 °C with shaking for at least 3 days, and then harvesting them via filtration [23]. The total genomic DNA of all the 32 single-spore isolates was extracted from the mycelium using the DNeasy Plant Mini Kit (Qiagen, Redwood City, CA, USA). The quantity and purity of the extracted DNA were determined using a NanoDrop ND-3300 fluorospectrometer (Thermo-Fisher Scientific, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The integrity of the DNA was visualized via electrophoresis on 1% (w/v) agarose gels that were stained with ethidium bromide (0.1 mg/L) and viewed under transmitted ultraviolet light using Invitrogen iBright (Thermo-Fisher Scientific, Carlsbad, CA, USA).
The internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region of the ribosomal DNA (rDNA) was amplified using the universal primers ITS1 and ITS4 [24]. The actin (ACT) gene was amplified using the primer pairs ACT-512F and ACT-783R [25]. The glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) gene was amplified using the primers GDF1 and GDR1 [26]. PCR amplification was carried out using 2 PrimeSTAR Max Premix (Takara, Shiga, Japan), 0.3 μM of each primer (GenScript Corporation, Nanjing, China), and 20 ng of genomic DNA. All reactions were performed under the following thermal conditions according to the instruction manual: 30 cycles of ‘98 °C for 10 s, 55 °C for 5 s, and 72 °C for 5 s’. We used a PTC2000 PCR instrument (MJ Research, Celina, O H, USA). Following PCR amplification, the quality and concentration of the PCR products were verified on 1% agarose gels stained with ethidium bromide (0.1 mg/L) and viewed using transmitted ultraviolet light on an E-Gel Imager (Thermo-Fisher Scientific, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The sizes of the PCR products were then determined against Marker II (Tiangen, Beijing, China). Bands of the predicted length were extracted from the agarose gel, purified using the Takara Agarose Gel DNA Extraction Kit, and then inserted into the pMDTM19-T vector (Takara, Shiga, Japan) at a temperature of 16 °C. The DNA, once ligated using the plasmid extraction kit (Tiangen, Beijing, China), was introduced into Escherichia coli DH5α competent cells (Tiangen, Beijing, China) following established protocols [27]. Positive clones were obtained by performing PCR tests on the inserts using the M13 forward primer and the reverse primers of the corresponding targets. Colony PCR tests were conducted using a bacterial suspension in sterilized water for direct amplification. Plasmid DNA was extracted from positive clones using a purification kit (Promega Corporation, Madison, WI, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The inserts were sequenced bi-directionally using the universal primer M13-F/R. Sequencing was performed by the GenScript Corporation (Nanjing, China).
2.3. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
A comparative analysis of the inserted fragments (ITS, ACT, and GAPDH) of all the isolates was performed using ClustalW in BioEdit version 7.0.90 (https://www.bioedit.com/, accessed on 23 January 2021). The sequences of selected isolates were subsequently deposited in GenBank with accession numbers. The ITS, ACT, and GAPDH sequences obtained in this study, together with the sequences of 16 strains representing species that are closely related to Colletotrichum sp. and retrieved from GenBank (Table 1), were aligned using MAFFT version 7 [28] (http://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/server/, accessed on 23 January 2021). For each strain, the sequences of ITS, ACT, and GAPDH were optimized to the same length and concatenated using the SATé-II v.2.2.7 (Simultaneous Alignment and Tree Estimation) high-throughput alignment platform (http://phylo.bio.ku.edu/software/sate/sate.html, accessed on 23 January 2021) [29]. Phylogenetic analyses of the concatenated sequence data of ITS, ACT, and GAPDH were performed using the maximum composite likelihood (ML) method and the Bayesian Inference method (BI) using MEGA version X and MrBayes 3.2.7a [30,31]. Alternaria solani CBS 113403 was included as an outgroup in the phylogenetic analyses. The tree was drawn to scale, with branch lengths being recorded in the same units as those used to record the evolutionary distances, which were used to infer the phylogenetic tree.

Table 1.
Sources of the strains and GenBank accession numbers used in this study.
2.4. Morphology Assay
A pure culture, FGZ-1, was grown on potato dextrose agar (PDA) (200 g of potato, 20 g of dextrose, 15 g of agar powder, and 1000 mL of distilled water) or V8 juice medium (100 mL of V8 tomato juice, 1 g of CaCO3, and 15 g of agar per 1000 mL of distilled water) [32,33] and incubated at 25 ± 2 °C, with the colony morphology being analyzed under the following conditions: alternating 12 h near-UV/12 h dark [34]. The morphology and color of the colony were recorded on day nine. The surface of the PDA culture was flooded with sterilized distilled water and gently scraped to prepare the spore suspension. In order to remove mycelia, the conidial suspension was then filtered with double layers of Miracloth (Calbiochem, San Diego, CA, USA) and placed in darkness and at 25 °C on the hydrophobic surface of a GelBond membrane (Lonza) to facilitate germination and the formation of appressoria [35]. The detailed fungal structures (conidia, germ tube, appressorium, and acervuli) of the obtained isolates were examined in detail under a Zeiss Axio Scope (Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). At least 30 units per structure were measured.
2.5. Pathogenicity Assay
One fungal isolate (FGZ-1) was used as the inoculum. To assess the pathogenicity, healthy one-year-old lucky bamboo plants, ‘lvye fuguizhu’ (Dracaena sanderiana var. virens), were bought from a flower market in Nanjing, China, whose source of goods is the nursery garden in which we determined anthracnose disease. The plants were planted individually in containers with water and placed in a greenhouse, with alternating daily temperatures of 26 °C during the day and 23 °C at night, under a lighting regimen of 16 h of light and 8 h of darkness, for a period of five days, according to the culture manual from the nursery manager, as well as the method described by Abdel-Rahman et al. (2023) [1]. The stems were cut into cylindrical segments (approximately 0.5 cm in width 2 cm in height) and surface-sterilized with sterile gauze, which was soaked using 70% ethanol in advance, to wipe the surface of the segments softly for 20 s. Then, the top and bottom bases were inoculated with mycelial plugs (5 mm diameter from 7-day-old PDA cultures). Sterile PDA plugs were inoculated as a control. The inoculation sites were subsequently covered with Parafilm strips to prevent dehydration and to hold the mycelial plugs in position. In each inoculation procedure, three stem segments were inoculated per treatment. All the pathogenicity tests were repeated at least three times. All treated stem segments were incubated at 25 °C in a moist chamber (relative humidity > 90%) with a 12 h photoperiod, and the infection was checked every three days after inoculation. To assess the pathogenicity on live plants, the conidial suspension was prepared as mentioned above and adjusted to 1 106 conidia/mL using a hemocytometer [35]. Four plants per treatment were spray-inoculated with 10 mL of conidial suspension, sealed with plastic wrap to prevent desiccation, following the method described by Xiong et al. [33], and placed back in a greenhouse. Simultaneously, sterile distilled water was used as a control. All experiments were repeated three times. The surface lesion area was measured and calculated using ImageJ 2.0. Fungi were re-isolated from the lesions, and the morphological characteristics of the isolated fungi were compared with those of the original fungi.
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Morphological Characteristics of Isolates
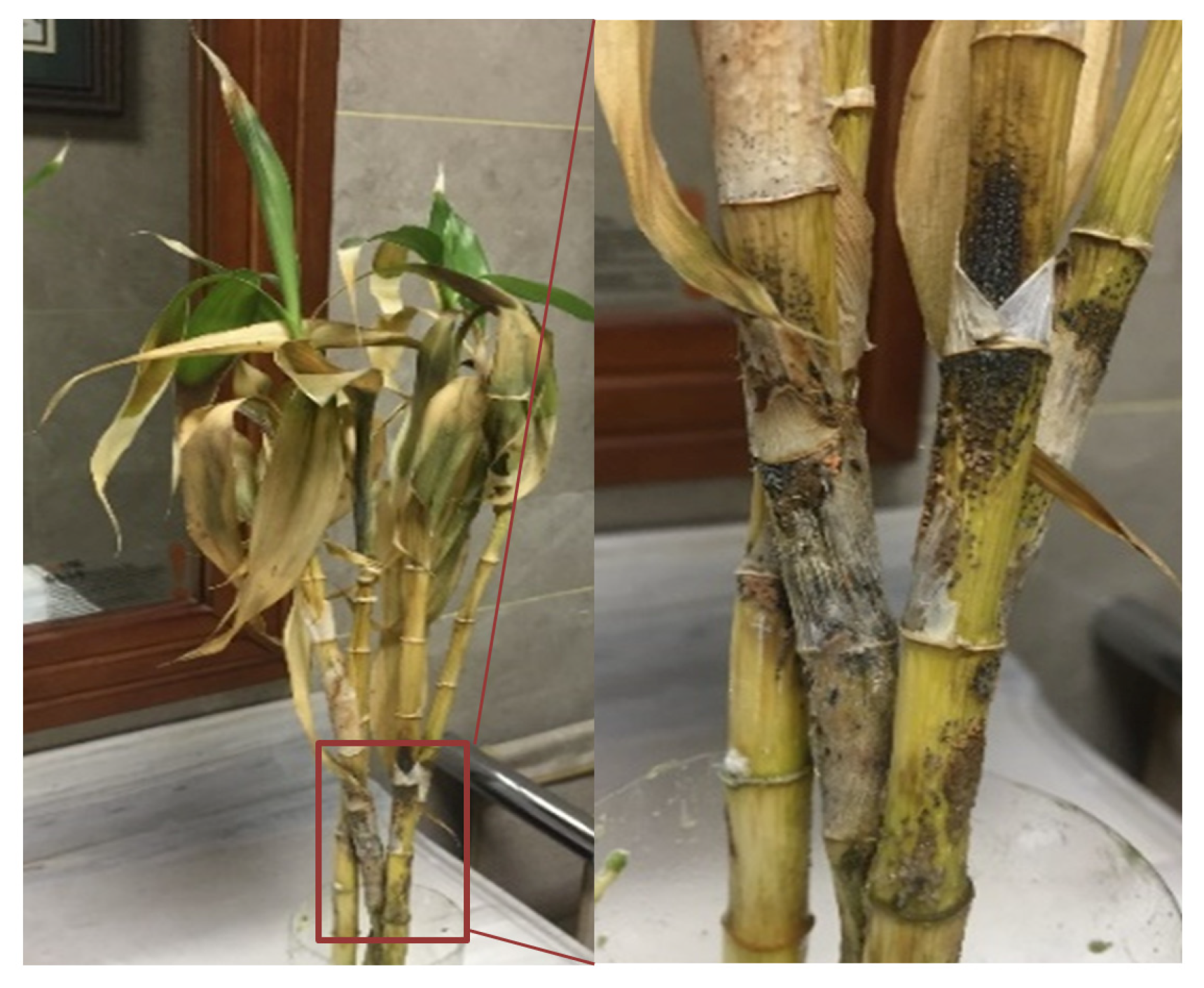
The symptoms of disease on the stems initially appeared as large, sunken, black lesions, covered with numerous black acervuli. Orange-to-pink spore masses were visible within the senescent and dead plants. Symptomatic stem tissues gradually became necrotic and turned soft, and several leaves wilted and eventually abscised from the plants (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
Natural anthracnose symptoms of lucky bamboo plants. A close-up of anthracnose lesions crowded with acervuli and pink spores is indicated with a red box.
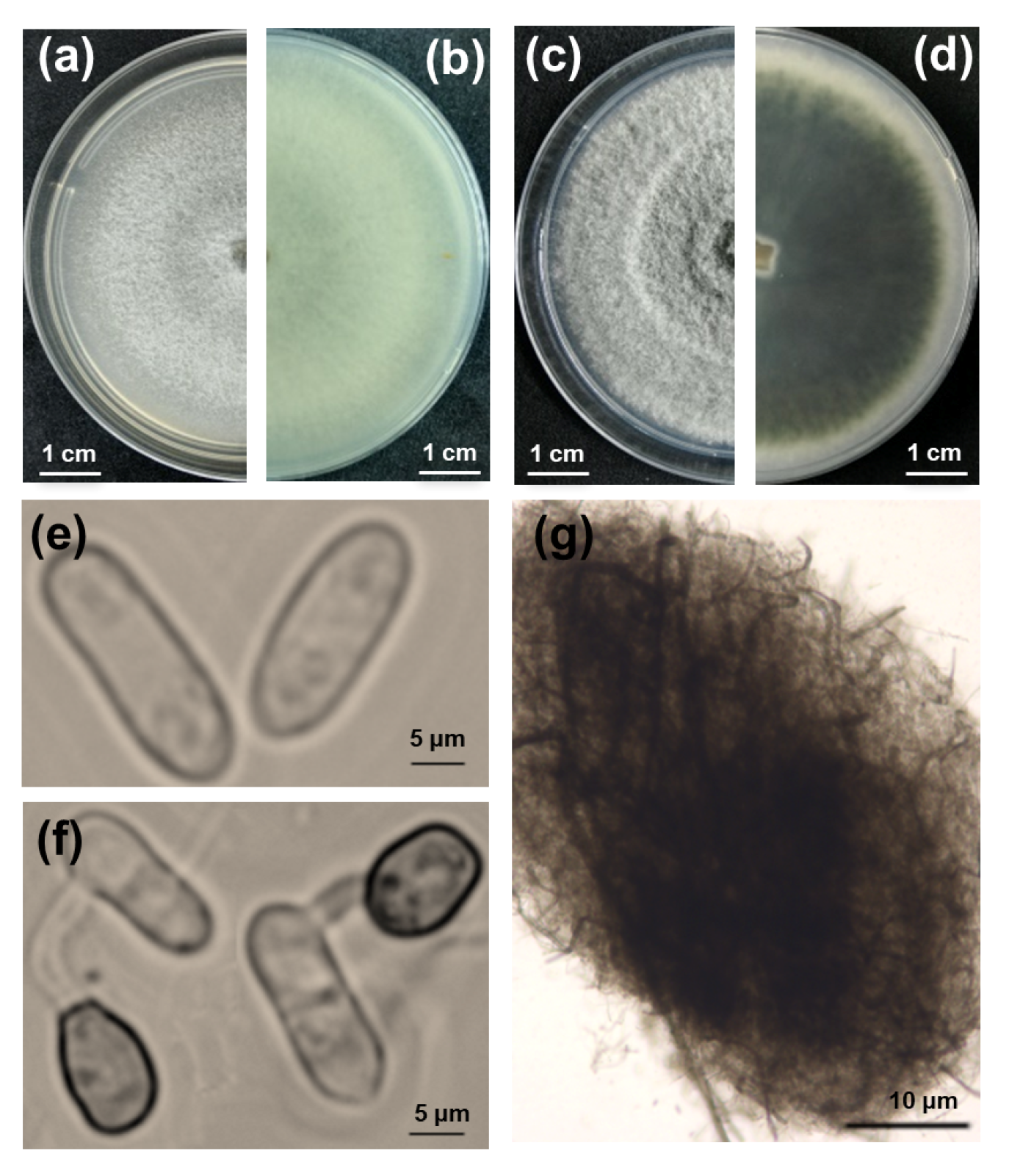
Thirty-two fungal isolates with a notable colony morphology for the Colletotrichum taxon were obtained from five different symptomatic lucky bamboo plants. Then, pure cultures of the 32 isolates were obtained via single-spore isolation. The colonies grown on V8 agar plates in the dark initially produced white, thin, and flat mycelia and eventually became pale gray in the center, exhibiting concentric rings (Figure 2a,b). The colonies grown on potato dextrose agar (PDA) had fluffy mycelia, pale white margins with concentric rings, and an olive-green center, which gradually turned dark green with age and extended to the margins after seven days of incubation in the dark. The reverse side of the colonies completely turned dark green, and the production of crystals on the PDA was observed when the colonies were incubated at 25 °C with a 12 h photoperiod for nine days (Figure 2c,d). Microscopically, the conidia were hyaline, unicellular, and cylindrical with rounded ends, measuring 10.8 to 18.5 × 2.8 to 6.9 μm (Figure 2e). The acervuli were circular to elliptical with no setae (Figure 2g). The appressoria were formed at the tip of the germ tube and were brown and ovate to obovate, measuring 6 to 10 × 4.5 to 7.5 μm (Figure 2f).
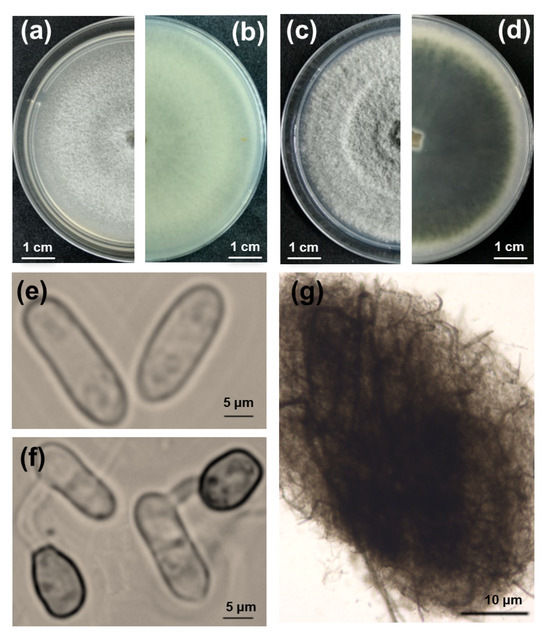
Figure 2.
Morphological characteristics, colony morphology, and microscopic examination of fungi isolated from lucky bamboo. (a–d) Nine-day-old colonies grown on V8 (a,b) and potato dextrose agar (c,d), viewed from the top and bottom, respectively; (e) conidia; (f) germ tube and appressorium; (g) acervuli. Scale bars: (a–d) = 1 cm; (e,f) = 5 μm; (g) = 10 μm.
3.2. Molecular Characterization
Fragments of the 573 bp internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region, 282 bp actin (ACT), and 277 bp glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) were amplified from the genomic DNA of all 32 single-spore isolates. Many of the sequence alignments, performed using ClustalW, showed that the sequences of ITS, ACT, and GAPDH for the 32 isolates shared 100% sequence similarity with each other. One representative single-spore isolate, named FGZ-1, was deposited in the China Center of Industrial Culture Collection (CICC) under the number CICC 41715. The Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) search in GenBank revealed that the sequences obtained from FGZ-1 (GenBank accession nos. MH752444.1-ITS, MH757114.1-ACT, and MH757113.1-GAPDH) had a 99%–100% similarity with the related sequences of C. gloeosporioides in Genbank (strain Sour8-accession no. KX227593.1, strain BWH1-accession no. KF712382.1, and strain TAX-1-accession no. HM575314.1, respectively).
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
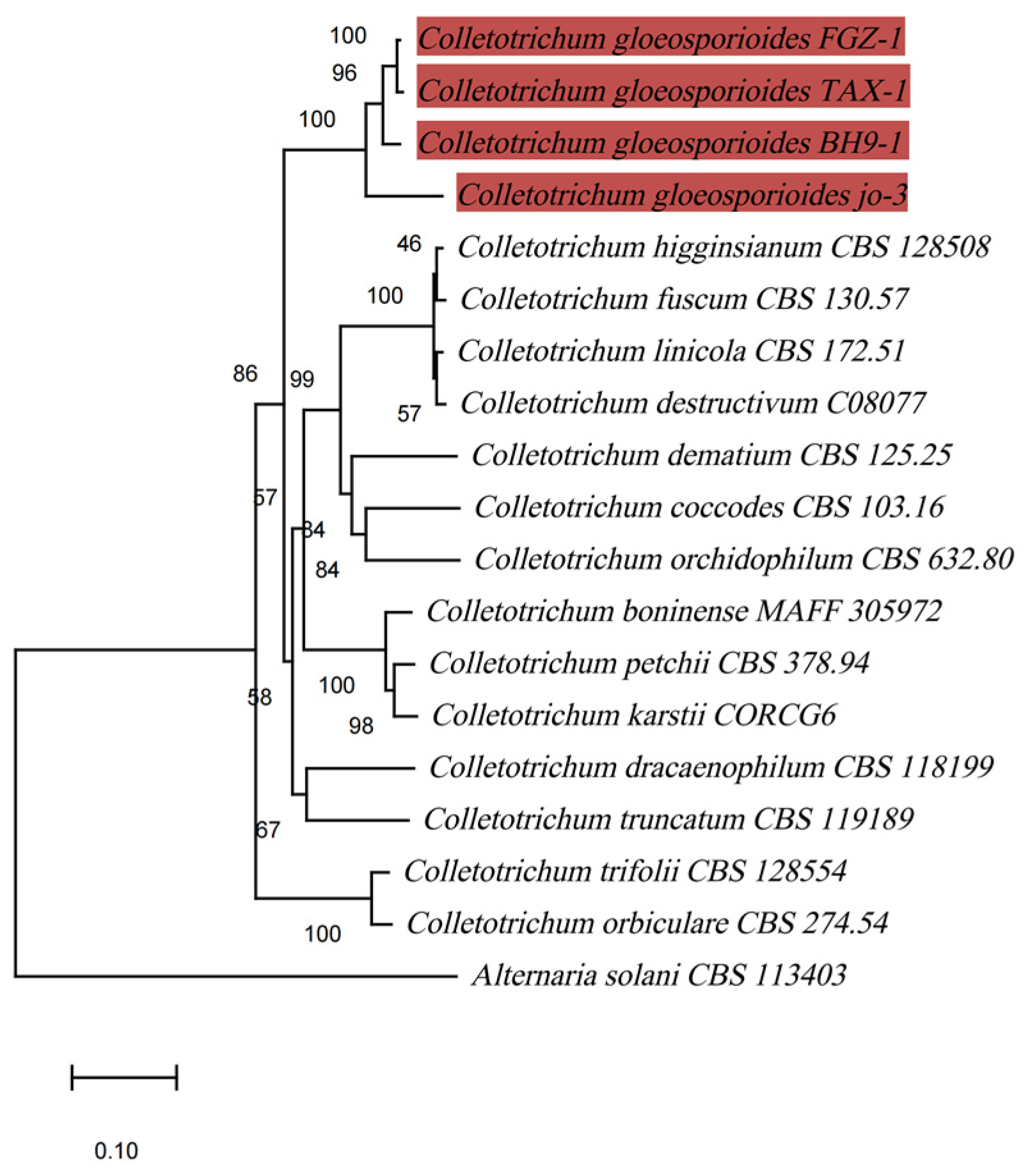
In the phylogenetic tree that was established based on the concatenated ITS, ACT, and GAPDH sequences, the isolate FGZ-1 belonged to the monophyletic clade that comprised three reference isolates of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides with a robust bootstrap and formed a clade that was obviously distinct from other Colletotrichum species (Figure 3). Isolate FGZ-1 was separated from C. dracaenophilum, which has been reported to cause anthracnose on lucky bamboo in Bulgaria, Iran, USA, Egypt, and Brazil [3,13,14,15,16]. In addition to C. dracaenophilum, another three species of Colletotrichum have been associated with the development of anthracnose on lucky bamboo, namely, C. petchii [36], C. karstii [17], and C. truncatum [18]; these were also clearly separated from the C. gloeosporioides isolate FGZ-1 (Figure 3). The phylogenetic tree based on the Bayesian method also confirmed these results (Figure S1).
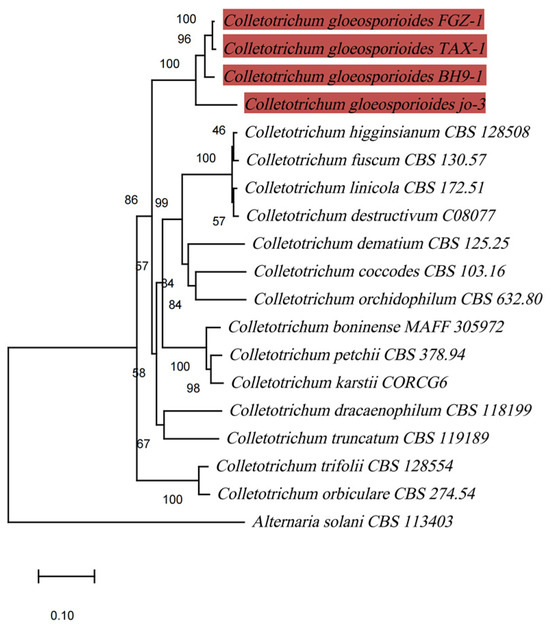
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic maximum-likelihood tree, computed from the concatenated sequences of ITS, ACT, and GAPDH of 19 fungal strains using MEGA software (version X). Alternaria solani CBS 113403 was chosen as an outgroup. Bootstrap support values higher than 50% are shown above the branches. The scale bar indicates the number of nucleotide substitutions per site. The branches highlighted in red represent C. gloeosporioides sequences.
3.4. Pathogenicity Tests
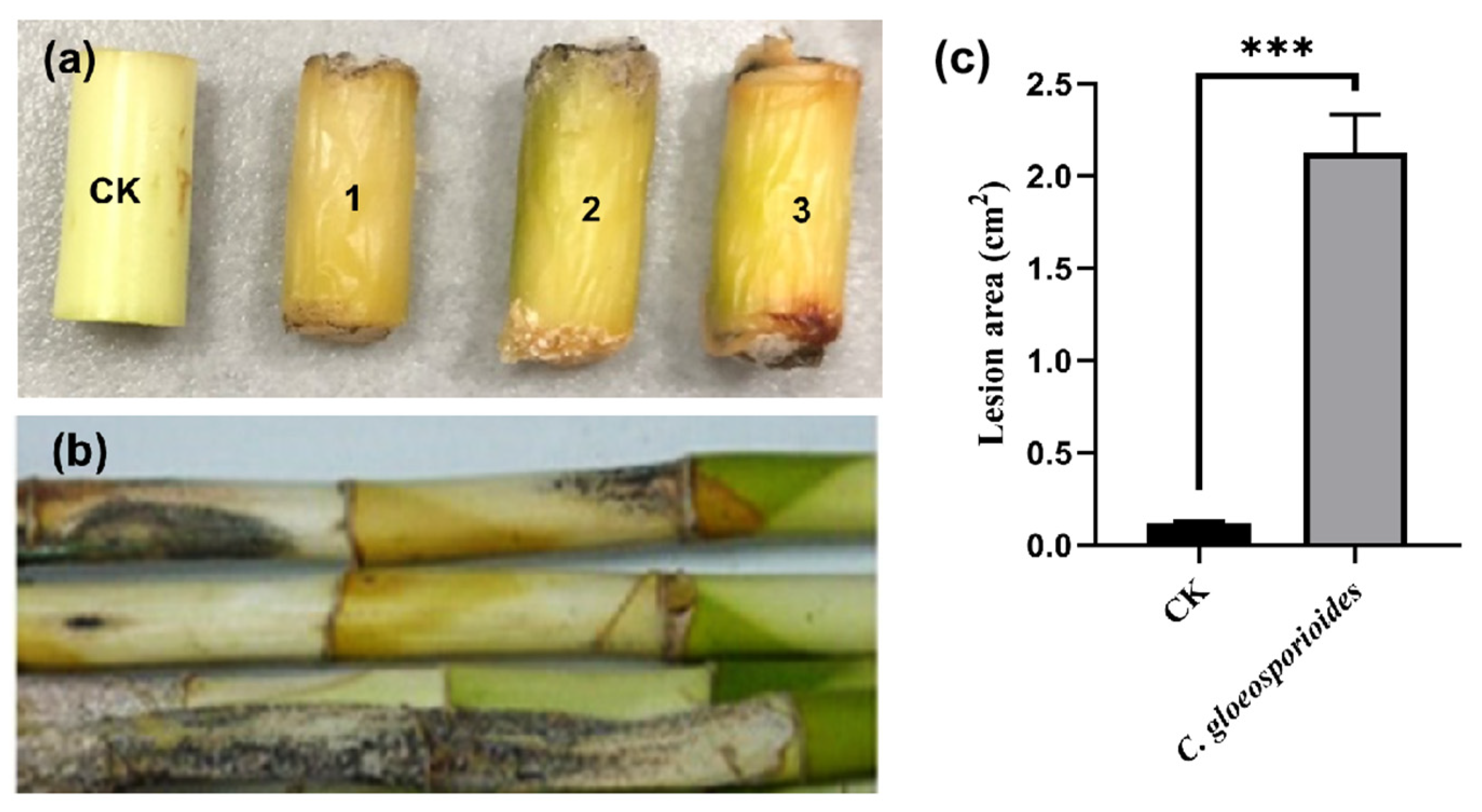
Symptoms of black spots and stem rot were observed on segments of the lucky bamboo three weeks after being artificially inoculated with mycelial plugs of isolate FGZ-1, and the disease severity reached 100%; meanwhile, the controls, which were inoculated with pure agar plugs, remained symptomless (Figure 4a). Similar disease symptoms were observed on the whole one-year-old plants eight weeks after inoculation (Figure 4b). All of the inoculated stem segments and whole plants showed anthracnose symptoms that were similar to those of naturally diseased lucky bamboo plants (Figure 1). Koch’s postulates were fulfilled by the re-isolation of fungal colonies from all symptomatic stems and plants, but not from those of the controls. In addition, these isolates had the same colony morphology, microscopic morphology, and molecular characteristics as described above. The experiment was repeated three times, and similar results were obtained.
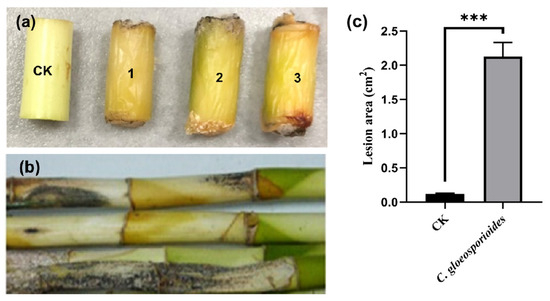
Figure 4.
The symptoms of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides FGZ-1 inoculated on lucky bamboo segments (a) and live plants (b). CK, inoculated with pure PDA plugs as controls; 1–3, inoculated with C. gloeosporioides FGZ-1 mycelial plugs. The surface lesion area was measured and calculated using ImageJ 2.0 (c). The data are expressed as the mean ± SD from three biological replicates (one-way ANOVA, Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test; *** p < 0.001).
4. Discussion
Considering the morphological features described earlier, along with the multi-gene phylogenetic studies and pathogenicity evaluations that were subsequently performed, the isolates were identified as C. gloeosporioides [37] and were determined to be a pathogenic fungus of anthracnose on lucky bamboo in China.
C. gloeosporioides is one of the most common Colletotrichum sp. pathogens, infecting many economically important plants throughout the world, including citrus, yam, papaya, avocado, coffee, eggplant, loquat, sweet pepper, and tomato [38]. So far, C. dracaenophilum is the Colletotrichum species that has been most widely reported to cause anthracnose disease on D. sanderiana plants [3,13,14,15,16]. In the United States, Sharma et al. [15] previously reported that an isolate of the C. gloeosporioides species complex caused anthracnose disease in lucky bamboo but was less pathogenic than isolates of C. dracaenophilum. Moreover, in China, Li et al. [17] and Liu et al. [18], respectively, reported that anthracnose in lucky bamboo could be caused by C. truncatum and C. karstii.
Colletotrichum is a large genus containing many species that cause anthracnose in a wide range of economically significant plants [19]. Chemical control continues to be the primary method used for disease prevention, as the absence of resistant varieties necessitates fungicide application [20]. Several strategies for the control of anthracnose in lucky bamboo have been reported [39]. For example, the growth of C. dracaenophilum on lucky bamboo can be inhibited by the fungicide Kemazed 50% WP or by biocontrol agents such as Trichoderma harzianum, Trichoderma viride, Bacillus subtilis, and Bacillus Pumilus [3]. A novel regeneration protocol for D. sanderiana has also been reported, which contributes to breeding for disease resistance for D. sanderiana against Colletotrichum sp. [40]. Based on these strategies, we believe that testing biological control agents on the new causal agent C. gloeosporioides for D. sanderiana would also be highly beneficial and provide additional insights into their efficacy against anthracnose, contributing to more targeted and sustainable disease management approaches. Also, resistant cultivars of D. sanderiana for C. gloeosporioides could be constructed based on the D. sanderiana regeneration system. This combined approach of biological control and tissue culture would pave the way for more effective, integrated solutions to manage anthracnose in lucky bamboo cultivation.
The accurate identification of the causal agent is crucial for effective disease management, as few distinctive morphological traits can be solely relied on for identifying Colletotrichum sp. [41]. Currently, species identification of this genus typically employs multilocus phylogenetic analysis of DNA sequences [42]. In our study, C. gloeosporioides was identified as the causal agent of anthracnose in D. sanderiana based on pathogen isolation, morphological characterization, and phylogenetic analysis. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to find that anthracnose symptoms are caused by C. gloeosporioides on D. sanderiana in China. The report of C. gloeosporioides on lucky bamboo in China widens the range of Colletotrichum species that are involved in the development of anthracnose in this popular ornamental houseplant. The occurrence and spread of C. gloeosporioides might pose a significant threat to lucky bamboo cultivation in China. Further research on the development of molecular diagnostic techniques and control measures for anthracnose disease is needed. In future studies, we will focus more on the biological control of C. gloeosporioides on D. sanderiana.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this study identified the cause of anthracnose in D. sanderiana plants. By observing the symptoms on stems, diseased tissue was isolated, and the pathogen was characterized based on the morphology of the colony, conidia, appressorium, and acervuli. Phylogenetic analysis, using multi-gene sequences of ITS, ACT, and GAPDH, led to the identification of C. gloeosporioides as the causal agent. These findings contribute to a deeper and more systematic understanding of the disease. The detailed descriptions, molecular data, and pathogenicity tests offer valuable resources for pathologists and mycologists who are interested in C. gloeosporioides. Furthermore, this research provides a foundation for future studies on the pathogenic mechanisms of this disease and control measures for D. sanderiana.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/f16010128/s1: Figure S1. Phylogenetic tree based on Bayesian inference computed from the concatenated sequences of ITS, ACT and GAPDH of 19 fungal strains using MrBayes 3.2.7a. Alternaria solani CBS 113403 was chosen as an outgroup.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Q. and Q.X.; methodology, Y.Q., Q.X., X.W., X.H., T.L., and Y.L.; analysis of results, Y.Q., Q.X., and X.Z.; resources, Y.Q., X.W., and X.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Q. and Q.X.; writing—review and editing, Y.Q. and X.W.; supervision, Y.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX23_1114); China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M691605); Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (2021K641C); Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (SJCX23_0350); Students Practice Innovation and Training Program of Nanjing Forestry University under Grant nos. 2022NFUSPITP0364; and Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Kai Tao from Oregon Health and Science University for the English revision of the text.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Abdel-Rahman, T.F.; Abdel-Megeed, A.; Salem, M.Z. Characterization and control of Rhizoctonia solani affecting lucky bamboo (Dracaena sanderiana hort. ex. Mast.) using some bioagents. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junaid, A.; Mujib, A.; Sharma, M. Cell and tissue culture of Dracaena sanderiana Sander ex Mast: A review. Hamdard Med. 2009, 52, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Morsy, A.A.; Elshahawy, I.E. Anthracnose of lucky bamboo Dracaena sanderiana caused by the fungus Colletotrichum dracaenophilum in Egypt. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chongtham, N.; Bisht, M.S. Bamboo Shoot: Superfood for Nutrition, Health and Medicine; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hilal, A.; El-Argawy, E.; Korany, A.E.; Fekry, T. Chemical and biological control of Dracaena marginata leaf spots in northern Egypt. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2016, 18, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.V.O.D.; Luz, E.D.M.N.; de Souza, J.T. First record of Phytophthora nicotianae causing leaf blight on Dracaena sanderiana. New Dis. Rep. 2011, 24, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, Z.Y.; Le, R.; Hu, H.Q. First Report of Leaf Blight Wilt on Dracaena sanderiana by Pantoea stewartii subsp. indologenes in China. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Aliabadi, F. First report of stem rot of Dracaena caused by Aspergillus niger in Iran. Plant Health Prog. 2008, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi-Tizaki, M.; Zafari, D.; Sadeghi, J. First report of Fusarium solani causing stem rot of Dracaena in Iran. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2016, 56, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahuf, A.A. First report of causing stem and root rot on lucky bamboo (Dracaena braunii) in Iraq. Hell. Plant Prot. J. 2019, 12, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-W.; Jeong, Y.; Yang, K.-Y.; Jeong, R.-D. First report of natural infection of Dracaena braunii by pepper mild mottle virus in Korea. J. Plant Pathol. 2022, 104, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiwan, N.; Tibpromma, S.; Jayawardena, R.; Mapook, A.; Wanasinghe, D.; Mortimer, P.; Lumyong, S.; Hyde, K. Colletotrichum dracaenigenum, a new species on Dracaena fragrans. Phytotaxa 2021, 491, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobev, S.G.; Castlebury, L.A.; Rossman, A.Y. First report of Colletotrichum dracaenophilum on Dracaena sanderiana in Bulgaria. Plant Dis. 2008, 92, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komaki, A.M.; Aghapour, B.; Aghajani, M.A. First report of Colletotrichum dracaenophilum on Dracaena sanderiana. Rostaniha 2012, 13, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Merritt, J.L.; Palmateer, A.; Goss, E.; Smith, M.; Schubert, T.; Johnson, R.S.; van Bruggen, A.H.C. Isolation, characterization, and management of Colletotrichum spp. causing anthracnose on lucky bamboo (Dracaena sanderiana). HortSci. Horts 2014, 49, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, D.M.; Barreto, R.W. Colletotrichum dracaenophilum causes anthracnose on Dracaena braunii in Brazil. Australas. Plant Dis. Notes 2016, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Yan, Z.B.; Wang, Y.H.; Lin, Q.K.; Wang, S.B.; Zhou, Z. First report of Colletotrichum karstii causing anthracnose on lotus bamboo (Dracaena sanderiana) in China. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Lu, J.N.; Zhou, Y.H. First report of Colletotrichum truncatum causing anthracnose of lucky bamboo in Zhanjiang, China. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, R.; Van Kan, J.A.; Pretorius, Z.A.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; Di, P.A.; Spanu, P.D.; Rudd, J.J.; Dickman, M.; Kahmann, R.; Ellis, J.; et al. The Top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, M.; Peres, N.; Villani, S.; Schnabel, G. Managing Colletotrichum on Fruit Crops: A “Complex” Challenge. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 2301–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.H.; Fan, K.; Li, D.W.; Han, C.M.; Qu, Y.Y.; Qi, Y.K.; Wu, X.Q. Identification, virulence and fungicide sensitivity of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides s.s. responsible for walnut anthracnose disease in China. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, L.; Lu, W.; Xu, X.; Yan, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Bai, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, W.; Yang, J.; et al. A rapid approach for isolating a single fungal spore from rice blast diseased leaves. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 1415–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, K. CtPMK1, a mitogen-activated-protein kinase gene, is required for conidiation, appressorium formation, and pathogenicity of Colletotrichum truncatum on soybean. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2015, 167, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR Protoc. A Guide Methods Appl. 1990, 18, 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, I.; Kohn, L.M. A method for designing primer sets for speciation studies in filamentous ascomycetes. Mycologia 1999, 91, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerber, J.C.; Liu, B.; Correll, J.C.; Johnston, P.R. Characterization of diversity in Colletotrichum acutatum sensu lato by sequence analysis of two gene introns, mtDNA and intron RFLPs, and mating compatibility. Mycologia 2003, 95, 872–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: Multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2017, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Warnow, T.J.; Holder, M.T.; Nelesen, S.M.; Yu, J.; Stamatakis, A.P.; Linder, C.R. SATé-II: Very fast and accurate simultaneous estimation of multiple sequence alignments and phylogenetic trees. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993, 10, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Zhang, L.; Waletich, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, X.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Q. Characterization of the papain-like protease p29 of the Hypovirus CHV1-CN280 in its natural host fungus Cryphonectria parasitica and nonhost fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Phytopathology® 2019, 109, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Xiong, Q.; Xu, J.; Wang, K.J.; Wang, K.R. CpBir1 is required for conidiation, virulence and anti-apoptotic effects and influences hypovirus transmission in Cryphonectria parasitica. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2013, 50, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cai, L.; Hyde, K.; Yu, Z.; McKenzie, E. Colletotrichum anthracnose of Amaryllidaceae. Fungal Divers. 2009, 39, 123–146. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, B.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Xiao, W.; Wu, J.; Yu, H.; Zhang, C. Genetic diversity of Colletotrichum spp. causing grape anthracnose in Zhejiang, China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damm, U.; Sato, T.; Alizadeh, A.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Crous, P.W. The Colletotrichum dracaenophilum, C. magnum and C. orchidearum species complexes. Stud. Mycol. 2019, 92, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, J.P.; Timmer, L.W.; Mitchell, D. Morphological and pathological characteristics of strains of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides from citrus. Phytopathology 1992, 82, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, D.; Rossman, A. Fungal Databases, US National Fungus Collections, ARS, USDA. Retrieved 16 January 2018. Available online: https://fungi.ars.usda.gov/ (accessed on 23 January 2021).
- Elshahawy, I.E.; Darwesh, O.M. Preventive and curative effect of difenoconazole + azoxytrobin and thiophanate-methyl against lucky bamboo anthracnose disease caused by Colletotrichum dracaenophilum. Heliyon 2023, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, J.; Mujib, A.; Sharma, M.P. In vitro micropropagation of Dracaena sanderiana Sander ex Mast: An important indoor ornamental plant. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 20, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayawardena, R.S.; Hyde, K.D.; Damm, U.; Cai, L.; Yan, J.Y. Notes on currently accepted species of Colletotrichum. Mycosphere 2016, 7, 1192–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, M.; Damm, U.; Crous, P.W.; Cai, L. Species boundaries in plant pathogenic fungi: A Colletotrichum case study. BMC Evol. Biol. 2016, 16, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).