Wood Species Differentiation: A Comparative Study of Direct Analysis in Real-Time and Chromatography Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.1.1. Extraction Method for LC-MS
2.1.2. Extraction Method for GC-MS
2.2. Sample Analysis
2.2.1. LC-MS Analysis Method
2.2.2. GC-MS Analysis Method
2.2.3. DART-TOF-MS Analysis Method
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. LC-MS and GC-MS Data Processing
2.3.2. DART-TOF-MS Data Processing
2.3.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Wood Extractives by LC-MS and GC-MS Analysis
3.2. DART-TOF-MS Analysis
3.3. Chemometric Analysis
3.3.1. Principal Component Analysis
3.3.2. Orthogonal Partial Least Squared Discriminant Analysis
3.3.3. Markers for the Wood Species Differentiation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scion. Diversifying Commercial Forestry. Available online: https://www.scionresearch.com/science/growing-the-value-of-forests/diversifying-commercial-forestry (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- Pilot, T.I. Tōtara Industry Pilot Project 2020. Available online: https://www.totaraindustry.co.nz/ (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- Dormontt, E.E.; Boner, M.; Braun, B.; Breulmann, G.; Degen, B.; Espinoza, E.; Gardner, S.; Guillery, P.; Hermanson, J.C.; Koch, G.; et al. Forensic timber identification: It’s time to integrate disciplines to combat illegal logging. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 191, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa da Silva, N.; Deklerck, V.; Baetens, J.M.; Van den Bulcke, J.; De Ridder, M.; Rousseau, M.; Bruno, O.M.; Beeckman, H.; Van Acker, J.; De Baets, B.; et al. Improved wood species identification based on multi-view imagery of the three anatomical planes. Plant Methods 2022, 18, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassold, S.; Lowry, P.P., 2nd; Bauert, M.R.; Razafintsalama, A.; Ramamonjisoa, L.; Widmer, A. DNA Barcoding of Malagasy Rosewoods: Towards a Molecular Identification of CITES-Listed Dalbergia Species. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D. bold: The Barcode of Life Data System (http://www.barcodinglife.org). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, T.C.M.; Braga, J.W.B.; Coradin, V.T.R.; Magalhães, W.L.E.; Okino, E.Y.A.; Camargos, J.A.A.; de Muñiz, G.I.B.; Bressan, O.A.; Davrieux, F. Near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) as a potential tool for monitoring trade of similar woods: Discrimination of true mahogany, cedar, andiroba, and curupixá. Holzforschung 2011, 65, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfullah, L.J.; Sadowski, E.M.; Schmidt, A.R. Species-level determination of closely related araucarian resins using FTIR spectroscopy and its implications for the provenance of New Zealand amber. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, E.; Franca, T.; Calvani, C.; Lacerda, M.; Goncalves, D.; Oliveira, S.L.; Marangoni, B.; Cena, C. Making wood inspection easier: FTIR spectroscopy and machine learning for Brazilian native commercial wood species identification. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 7283–7289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cody, R.B.; Laramée, J.A.; Durst, H.D. Versatile new ion source for the analysis of materials in open air under ambient conditions. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 2297–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wu, W.Y.; Guo, D.A. DART-MS: A new research tool for herbal medicine analysis. World J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2016, 2, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deklerck, V.; Mortier, T.; Goeders, N.; Cody, R.B.; Waegeman, W.; Espinoza, E.; Van Acker, J.; Van den Bulcke, J.; Beeckman, H. A protocol for automated timber species identification using metabolome profiling. Wood Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edison, S.E.; Lin, L.A.; Gamble, B.M.; Wong, J.; Zhang, K. Surface swabbing technique for the rapid screening for pesticides using ambient pressure desorption ionization with high-resolution mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deklerck, V.; Finch, K.; Gasson, P.; Van den Bulcke, J.; Van Acker, J.; Beeckman, H.; Espinoza, E. Comparison of species classification models of mass spectrometry data: Kernel Discriminant Analysis vs Random Forest; A case study of Afrormosia (Pericopsis elata (Harms) Meeuwen). Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 31, 1582–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza, E.O.; Lancaster, C.A.; Kreitals, N.M.; Hata, M.; Cody, R.B.; Blanchette, R.A. Distinguishing wild from cultivated agarwood (Aquilaria spp.) using direct analysis in real time and time of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 28, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, R.; Djidrovska, D.; Ledic, A.; Brzica, S.; Antikj, V.; Hofer, R.; Almirall, J. Characterization and identification of luminescent components in inks using various analytical techniques for the study of crossed-line intersections. Forensic Chem. 2017, 3, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Sun, J.; Chen, P.; Frazier, J.; Benefield, V.; Zhang, M. Chemical analysis and classification of black pepper (Piper nigrum L.) based on their country of origin using mass spectrometric methods and chemometrics. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 109877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, G.; Guo, J.; Wiedenhoeft, A.C.; Liu, C.C.; Yin, Y. Timber species identification from chemical fingerprints using direct analysis in real time (DART) coupled to Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (FTICR-MS): Comparison of wood samples subjected to different treatments. Holzforschung 2019, 73, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Seo, Y.T.; Park, S.-i.; Jeong, S.H.; Kim, M.K.; Jang, Y.P. DART–TOF–MS based metabolomics study for the discrimination analysis of geographical origin of Angelica gigas roots collected from Korea and China. Metabolomics 2014, 11, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cody, R.B.; Dane, A.J.; Dawson-Andoh, B.; Adedipe, E.O.; Nkansah, K. Rapid classification of White Oak (Quercus alba) and Northern Red Oak (Quercus rubra) by using pyrolysis direct analysis in real time (DART™) and time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 95, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, C.; Espinoza, E. Analysis of select Dalbergia and trade timber using direct analysis in real time and time-of-flight mass spectrometry for CITES enforcement. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 26, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, P.D.; Mundo, I.A.; Wiemann, M.C.; Chavarria, G.D.; McClure, P.J.; Voin, D.; Espinoza, E.O. Identification of selected CITES-protected Araucariaceae using DART TOFMS. IAWA J. 2017, 38, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, K.; Espinoza, E.; Jones, F.A.; Cronn, R. Source identification of western Oregon Douglas-fir wood cores using mass spectrometry and random forest classification. Appl. Plant Sci. 2017, 5, 1600158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, E.R.; McClure, P.J.; Huffman, A.N.; Voin, D.; Espinoza, E.O. Reliability of wood identification using DART-TOFMS and the ForeST© database: A validation study. Forensic Sci. Int. Anim. Environ. 2022, 2, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rodríguez, P.; Bautista-Ortín, A.B.; Gómez-Plaza, E. Increasing wine quality through the use of oak barrels: Factors that will influence aged wine color and aroma. In Wine: Types, Production and Health; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 301–317. [Google Scholar]
- Blazenovic, I.; Kind, T.; Ji, J.; Fiehn, O. Software Tools and Approaches for Compound Identification of LC-MS/MS Data in Metabolomics. Metabolites 2018, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worley, B.; Powers, R. PCA as a practical indicator of OPLS-DA model reliability. Curr. Metabolomics 2016, 4, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, E.D.; Gonçalves, J.F.; Marques, A.; Martins, N.d.S.; Pena, C.; Laia, M.L.d. Physical and chemical properties of wood from Eucalyptus and Corymbia clones in different planting densities. Ciênc. Florest. 2023, 33, e64965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, T.A.S.; Arriel, T.G.; Zanuncio, A.J.V.; Carvalho, A.G.; Branco-Vieira, M.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Trugilho, P.F. Determination of the Chemical Composition of Eucalyptus spp. for Cellulosic Pulp Production. Forests 2021, 12, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, J.A. Distribution of extractives in pinus radiata earlywood and latewood. N. Z. J. For. Sci. 1978, 8, 288–294. [Google Scholar]
- Hemingway, R.W.; Hillis, W.E. Changes in fats and resins of Pinus radiata associated with heartwood formation. Appita 1971, 4, 439–443. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, X.; Chang, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ran, S.; Huang, Z.; Li, P.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; et al. Totarol prevents neuronal injury in vitro and ameliorates brain ischemic stroke: Potential roles of Akt activation and HO-1 induction. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 289, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendall, J.G.; Cambie, R.C. Totarol a Non-Conventional Diterpenoid. Aust. J. Chem. 1995, 48, 883–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webby, R.F.; Markham, K.R.; Molloy, B.P.J. The characterisation of New Zealand Podocarpus hybrids using flavonoid markers. N. Z. J. Bot. 1987, 25, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, D.B.; Hinkley, S.F.R.; Weavers, R.T. Waihoensene. A new laurenene-related diterpene from Podocarpus totara var waihoensis. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 4297–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-E.; Park, E.-K.; Kim, J.-G. A mosquito larvicidal diterpenoid isolated from Podocarpus totara D. Don ex Lambert. J. Entomol. Sci. 2000, 35, 474–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.; Miranda, I.; Knapic, S.; Quilhó, T.; Pereira, H. Chemical and anatomical characterization, and antioxidant properties of barks from 11 Eucalyptus species. Eur. J. Wood Prod. 2017, 76, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller Da Silva, P.H.; Brito, J.O.; Da Silva, F.G., Jr. Potential of eleven Eucalyptus species for the production of essential oils. Sci. Agric. 2006, 63, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, F.M.; Fathy, M.M.; Salama, M.M.; Saber, F.R. Chemical composition and bioactivity of the volatile oil from leaves and stems of Eucalyptus cinerea. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwa, K.; Ismail, A.; Souihi, M.; Yassine, M.; Dhaouadi, F.; Mohsen, H.; Lamia, H. Chemical composition and herbicidal potential of essential oil of Eucalyptus maculata Hook. Sci. Afr. 2023, 21, e01751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
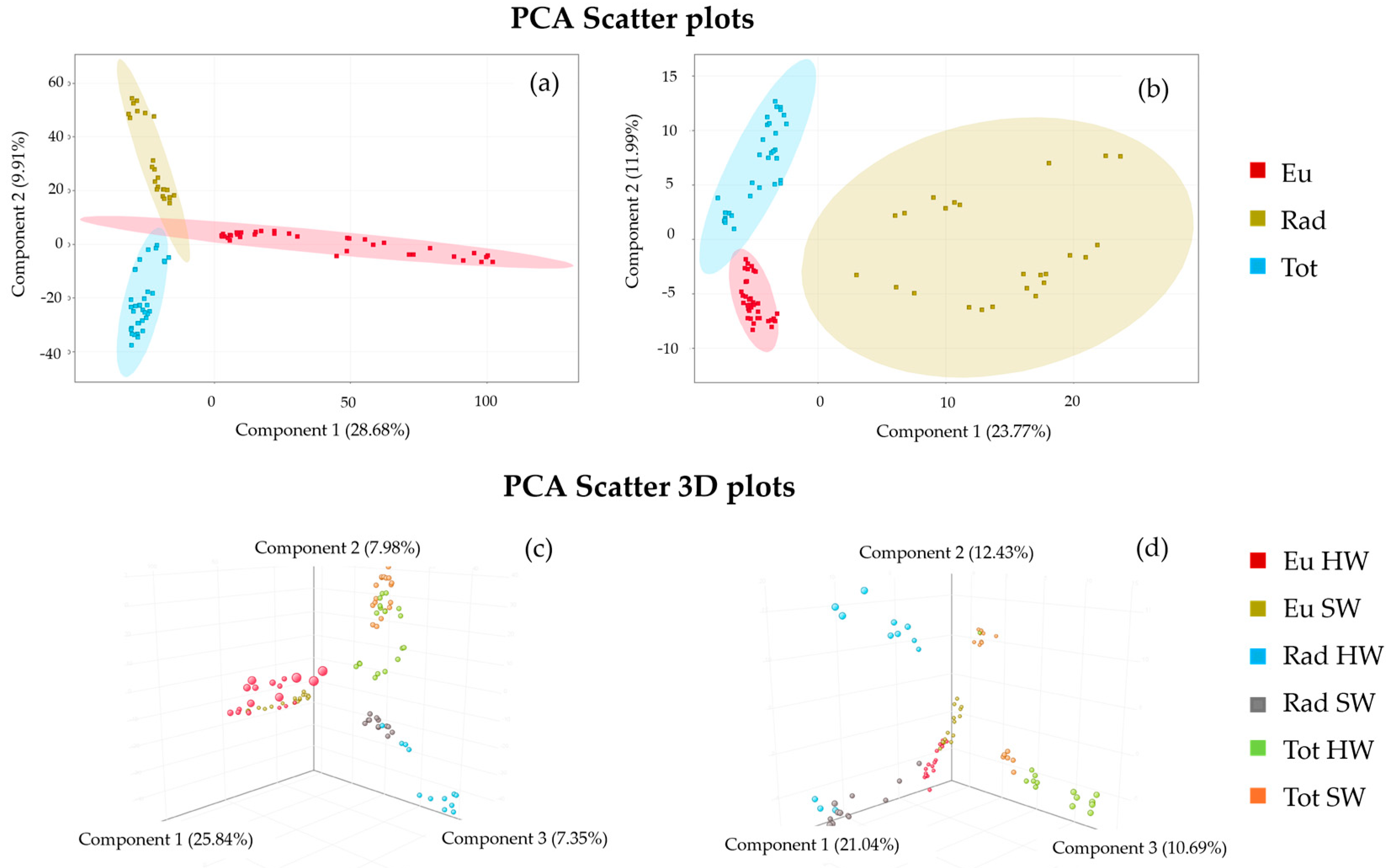
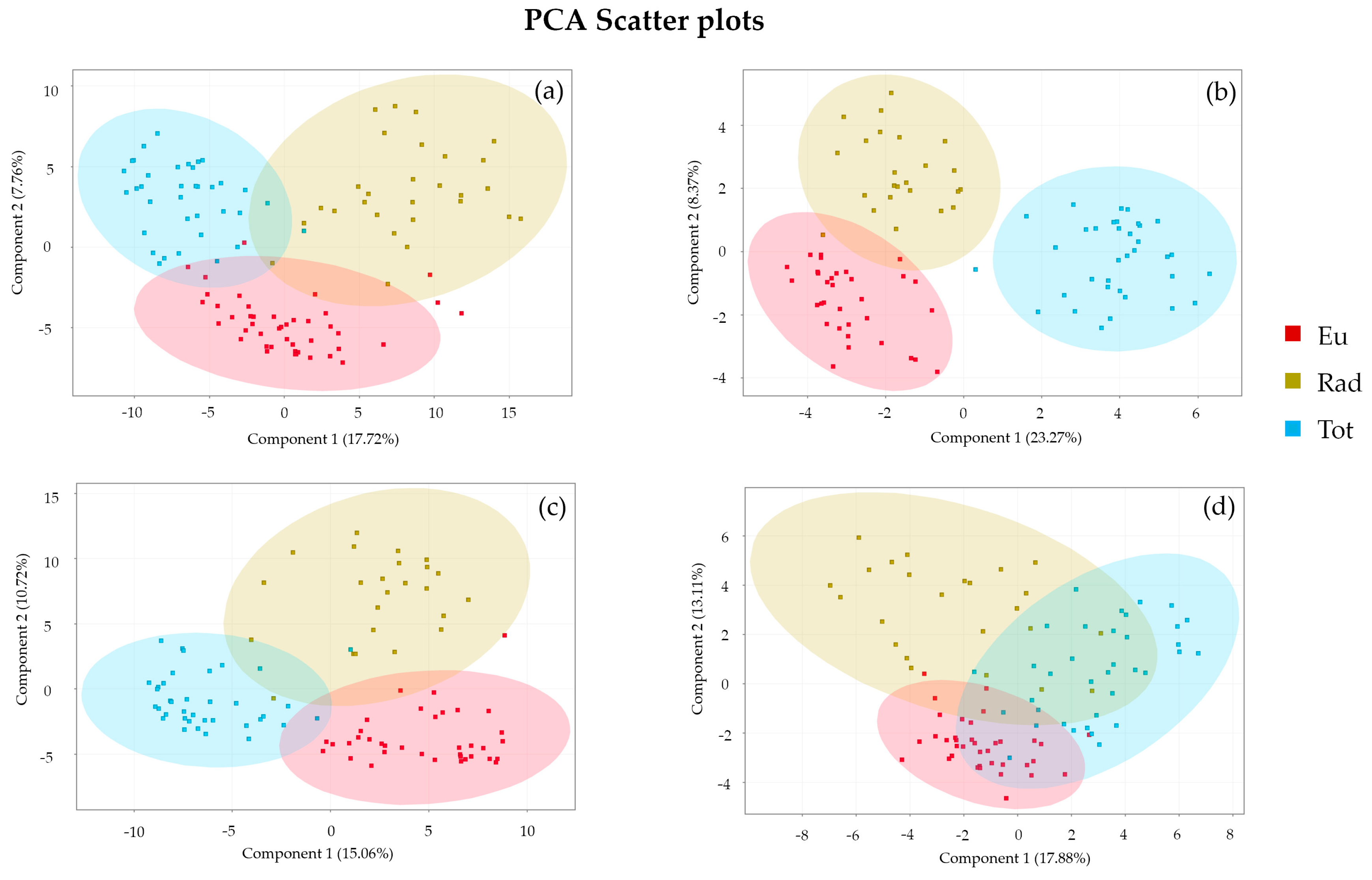
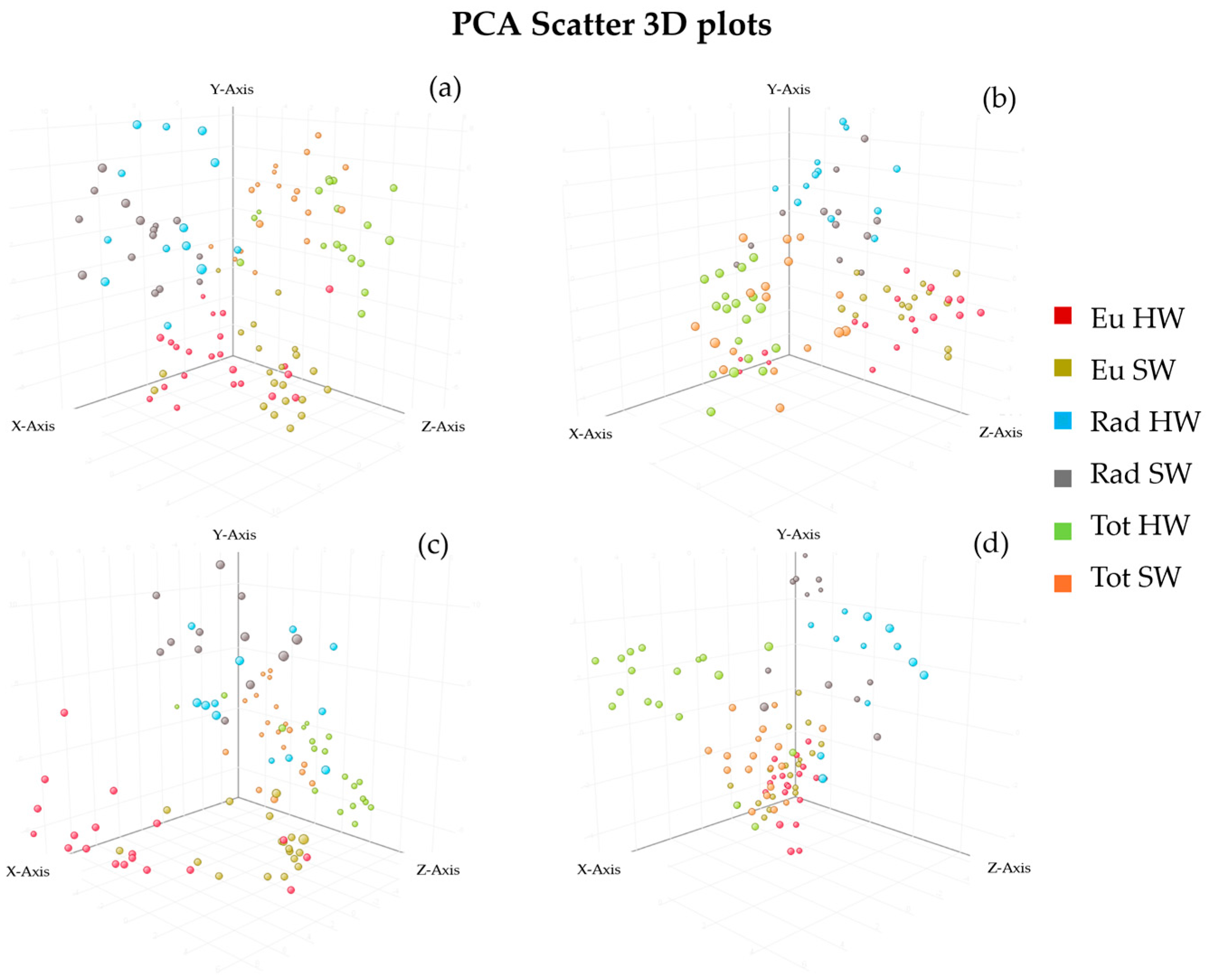
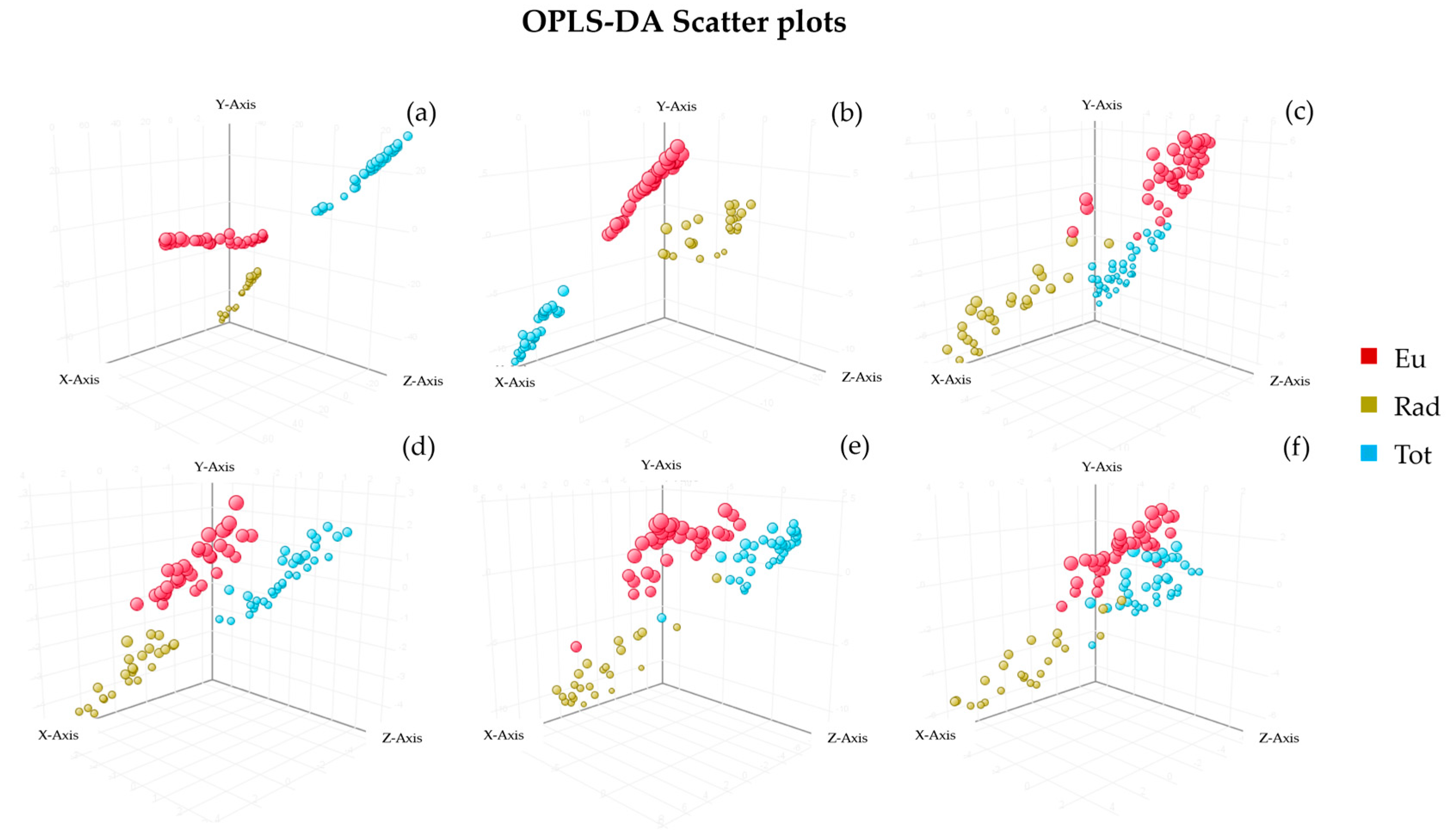
| Models | R2X | R2Y | Q2 | Accuracy % | Components |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCMS | 0.3796 | 0.8513 | 0.7167 | 100 | 2 |
| GCMS | 0.3521 | 0.8990 | 0.8026 | 100 | 2 |
| DART Acetonitrile | 0.3046 | 0.6971 | 0.5057 | 91.75 | 2 |
| DART Methanol | 0.2562 | 0.8452 | 0.6388 | 95.918 | 2 |
| DART Dichloromethane | 0.3140 | 0.8372 | 0.6177 | 100 | 2 |
| DART without Solvent | 0.2529 | 0.8023 | 0.6423 | 95.37 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Isak, I.; Newson, H.L.; Singh, T. Wood Species Differentiation: A Comparative Study of Direct Analysis in Real-Time and Chromatography Mass Spectrometry. Forests 2025, 16, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16020255
Isak I, Newson HL, Singh T. Wood Species Differentiation: A Comparative Study of Direct Analysis in Real-Time and Chromatography Mass Spectrometry. Forests. 2025; 16(2):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16020255
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsak, Ilena, Harriet Laura Newson, and Tripti Singh. 2025. "Wood Species Differentiation: A Comparative Study of Direct Analysis in Real-Time and Chromatography Mass Spectrometry" Forests 16, no. 2: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16020255
APA StyleIsak, I., Newson, H. L., & Singh, T. (2025). Wood Species Differentiation: A Comparative Study of Direct Analysis in Real-Time and Chromatography Mass Spectrometry. Forests, 16(2), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16020255






