Influence of Tree Species Composition on Leaf and Soil Properties and Soil Enzyme Activity in Mixed and Pure Oak (Quercus variabilis) Stands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Site
2.2. Leaf and Soil Collection
2.3. Measurement of Leaf Indices
2.4. Measurement of Soil Indices
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Leaf Properties Assays
3.2. Soil Properties Assays
3.3. Soil Enzyme Activity Assays
3.4. Correlation Analysis Between Leaf and Soil Indices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, Z.; Ji, K.; Yi, Q.; Cao, S.; Li, P.; Feng, D. Quantitative evaluation of soil erosion in loess hilly area of western Henan based on sampling approach. Water 2024, 16, 2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, Z.; Shi, X.; Yang, X.; Shangguan, Z. Storage of carbon and nitrogen in Quercus and Platycladus orientalis plantations at different ages in the hilly area of western Henan province, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, G.; Delang, C.O.; Lu, X.; Olschewski, R. Optimizing rotation periods of forest plantations: The effects of carbon accounting regimes. For. Policy Econ. 2020, 118, 102263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wang, J.; Lv, D.; Li, S.; Miao, Y.; Hu, M.; Wu, D.; Liu, F.; Wang, D. Effects of cropland-to-orchard conversion on soil multifunctionality, particularly nitrogen cycling in the eastern Loess Plateau. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1471329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shi, X.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Lam, S.K.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Z. Plants, soil properties and microbes directly and positively drive ecosystem multifunctionality in a plantation chronosequence. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 3049–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Li, X. The Grain for green program promotes soil organic matter accumulation and improves soil fungal diversity in the southwestern Karst region. Forests 2025, 16, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Zeng, B.; Jiang, L.; Xu, J. Conservation payments, off-farm labor, and ethnic minorities: Participation and impact of the Grain for green program in China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xie, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. Climate and soil explain contrasting intraspecific trait variability of widespread species over a large environmental gradient. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 56, e03338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Gu, J.; Lu, D.; Yang, J.; Shuai, X.; Li, C.; Chen, H. Mixing with native broadleaf trees modified soil microbial communities of Cunninghamia lanceolata monocultures in South China. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1372128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldea, J.; Ruiz-Peinado, R.; del Río, M.; Pretzsch, H.; Heym, M.; Brazaitis, G.; Jansons, A.; Metslaid, M.; Barbeito, I.; Bielak, K.; et al. Timing and duration of drought modulate tree growth response in pure and mixed stands of Scots pine and Norway spruce. J. Ecol. 2022, 110, 2673–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Halder, I.; Castagneyrol, B.; Ordóñez, C.; Bravo, F.; del Río, M.; Perrot, L.; Jactel, H. Tree diversity reduces pine infestation by mistletoe. Forest Ecol Manag. 2019, 449, 117470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo-Aceves, T.; Toledo-Garibaldi, M. Tree species diversity increases carbon stocks in tropical montane cloud forests across successional stages. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2025, 578, 122480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Zhou, H.; Hu, J.; Yu, H.; Hu, H. A multi-Scale convolution and multi-Layer fusion network for remote sensing forest tree species recognition. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornoff, F.; Klein, A.M.; Blüthgen, N.; Staab, M. Tree diversity increases robustness of multi-trophic interactions. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 286, 20182399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Forestry and Grassland Administration. Available online: https://www.forestry.gov.cn/search/368265 (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Niu, Y.; Jia, G.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. Soil moisture absorption and utilization of Quercus variabilis in Beijing mountain area. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2022, 44, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, C.; Shou, W.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Qiao, Y. Study on adaptation strategies of Quercus variabilis, Robinia pseudoacacia and Platycladus orientalis to drought in Taihang mountain. For. Res. 2022, 35, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Wang, B.; Sun, H. Effects of species mixing on maximum size-density relationships in Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.) Hook.)-dominated mixed forests converted from even-aged pure stands. Front. Plant. Sci. 2024, 15, 1342307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versace, S.; Garfi, V.; Dalponte, M.; Di Febbraro, M.; Frizzera, L.; Gianelle, D.; Tognetti, R. Species interactions in pure and mixed-species stands of silver fir and European beech in Mediterranean mountains. iForest 2021, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik, P.; Filipczak, J. Prognosis of the nutritional status of apple trees based on prebloom leaves and flowers. J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 42, 2003–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Man, X.; Cai, T.; Xiao, R.; Ge, Z. Increasing soil organic carbon and nitrogen stocks along with secondary forest succession in permafrost region of the Daxing’an mountains, northeast China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C. A Preliminary Study on the Effect Mechanism of Tree Species on Soil Carbon Sequestration and Fertility. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Liu, H.; Su, J.; Shen, W. Effects of tree species mixing on bulk and rhizosphere soil microbial resource limitation in stands of Pinus massoniana and Castanopsis hystrix. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 10770–10781. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, C.; Tan, Q.; Liu, G.; Xu, M. Impacts of species mixture on soil nitrogen stocks in the Loess Plateau of China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 491, 119145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Feng, H.; McNie, P.; Liu, Q.; Xu, X.; Pan, C.; Yan, K.; Feng, L.; Goitom, E.A.; Yu, Y. Species mixing improves soil properties and enzymatic activities in Chinese fir plantations: A meta-analysis. Catena 2023, 220, 106723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Tan, Q.; Liu, G.; Xu, M. Mixed-species plantations enhance soil carbon stocks on the loess plateau of China. Plant Soil 2021, 464, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, B.; Qu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Sun, H. Age and species of eucalyptus plantations affect soil microbial biomass and enzymatic activities. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L.; Dong, A. Impacts of tourism disturbance on soil properties at different elevations in Songshan scenic area. J. Henan Agric. Univ. 2016, 50, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. The Geological Features and Tourism Resource Protection Development of Songshan World Geopark. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, C.; Xu, S.; Wei, L. Effects of mixed decomposition of Platycladus orientalis and Quercus variabilis fine roots on soil organic carbon sequestration. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 30, 707–714. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, R. Responses of Functional Traits of Shurbs and Grass of Quercus variabilis Plantation to Thinned and Its Environmental Interpretation. Ph.D. Thesis, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Yan, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Yu, J.; Zheng, Z.; Zhu, H. Developmental changes of okra fruits in cell wall composition, saccharometabolism and related enzymatic activities. Jiangsu J. Agri. Sci. 2023, 39, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Yuan, X.; Ji, C.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Niu, S.; Cui, B. The nutrients and antioxidant activities of eight crabapple cultivars leaves. Food Ferment. Ind. 2022, 48, 196–201. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, H.; Zhi, J.; Zeng, G.; Yue, W. Effects of different induction treatments on contents of nutrient and activities of defense enzymes in the leaves of tomato plant. J. Environ. Entomol. 2019, 41, 405–412. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, B. The Characteristics of Soil Quality, Carbon and Nitrogen Conversion of Double-Cropping Rice with the Application of Exogenous Organic Carbon and Its Microbial Regulatory Pathways. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W. Study on the Effect of Rhizosphere Soil on Medicinal Components of Paeonia ludlowii in Different Areas of Xizang. Ph.D. Thesis, Tibet University, Lhasa, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Cai, H.; Xu, T.; Li, J.; Chen, K. Post-fire changes in soil extracellular enzyme activities and their influencing factors in the permafrost region of the Da Xing’anling Mountains, Northeast China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2025, 36, 497–503. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Jin, D.; Jiang, J.; Li, T. Analysis of bacterial and fungal community composition and soil enzyme activities in the rhizosphere of transgenic Betula platyphylla. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2024, 48, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.; Zhu, N.; Guo, Q.; Zhou, G.; Meng, M.; Wu, S.; Yang, L. Effects of different plantations on soil physical and chemical properties and soil quality evaluation in South subtropical zone. For. Res. 2022, 35, 112–122. [Google Scholar]
- Amoo, A.E.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Babalola, O.O. Forest plantations reduce soil functioning in terrestrial ecosystems from South Africa. Pedobiologia 2021, 89, 150757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, K.; Shen, J.; Zhu, C.; Lin, X.; He, Z.; Ding, G. Effects of slope position and gradient on spatial distribution of soil nutrients in Acacia melanoxylon plantation. JNE For. Univ. 2022, 50, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ojeda-González, P.; Donoso, P.J.; Erlwein, A. Synergy in mixed Nothofagus spp. plantations: The effect of deciduous evergreen neighbourhood on tree growth in the Chilean Andes. N. Z. J. For. Sci. 2020, 50, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Guo, X.; Li, Q.; Ming, A.; Min, H.; Shen, W. Tree species mixing effects on the radial growth of Pinus massoniana and Castanopsis hystrix: A comparison between even-aged and uneven-aged stands. For. Ecol. Manag. 2024, 566, 122058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Dou, X.; Tang, M. Relationship between carbon stock and the structure of coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest in Tianmu Mountains, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 2029–2038. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, Q.; Lei, T.; Cui, G. Coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest has the optimal forest therapy environment among stand types in Xinjiang. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 169, 112950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Fan, Z.; Fu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Sterck, F. Differential determinants of growth rates in subtropical evergreen and deciduous juvenile trees: Carbon gain, hydraulics and nutrient-use efficiencies. Tree Physiol. 2021, 41, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Ge, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Huang, H.; Tong, Z.; Zhang, J. Forest conversion from pure to mixed Cunninghamia lanceolata plantations enhances soil multifunctionality, stochastic processes, and stability of bacterial networks in subtropical southern China. Plant Soil 2023, 488, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qi, S.; Li, P.; Zhou, P. Influence of stand and environmental factors on forest productivity of Platycladus orientalis plantations in Beijing’s mountainous areas. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Shen, F.; Meng, J.; Yang, L. Dynamic characteristics of litter decomposition and nutrient release in 4 species of Larix plantations. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2024, 44, 119–129. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Cui, N.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, J. Mixed Effects on Cellulose, Total phenols and Condensed Tannins Degradation in the Litter Leaves of Pinus massoniana and Native Broad-leaved Tree Species. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2023, 31, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.; Zhu, B.; Zhu, J.; Ji, C.; Yang, W. Review on the study of forest coarse woody debris decomposition. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2024, 48, 541–560. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Latitudinal Variation Pattern of Defense Strategies of Quercus variabilis Blume. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Forestry, Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, P. Coupling of Carbon-Nitrogen Cycles and Hydrological Process of Typical Forest Ecosystems in Beijing Mountainous Area. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, M.; Cheng, Z.; Jia, Z. Analyses on phylogenetic structures and interspecific associations between main tree species in natural regeneration communities of three plantations in Xiaoxishan of Beijing. J. Plant Res. Environ. 2023, 32, 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K. The Influence of Site Conditions and Stand Structure on the Damage Degree of Leaf-Eating Insect in Quercus variabilis Pure Forest and Quercus variabilis–Platycladus orientalis Mixed Forest. Master’s Thesis, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Yu, X.; Jia, G. Water uptake by coniferous and broad-leaved forest in a rocky mountainous area of northern China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 265, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yu, X.; Jia, G. Water utilization characteristics of typical vegetation in the rocky mountain area of Beijing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 91, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Han, L.; Liu, K.; Hu, X.; Fu, Z.; Chen, L. Water source of Robinia pseudoacacia and Platycladus orientalis plantations under different soil moisture conditions in the Loess Plateau of Western Shanxi, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 588–596. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, X.; Ding, B.; Liu, Z.; Jia, G. Water Storage and Use by Platycladus orientalis under different rainfall conditions in the rocky mountainous area of northern China. Forests 2022, 13, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Jia, G.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Huang, J.; Wen, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Jia, J.; Peng, S. Long-term study on the seasonal water uptake of Platycladus orientalis in the Beijing mountain area, northern China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 307, 108531. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Huang, G.; Lv, K.; Su, T. Soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry of different vegetation types in tropical and subtropical forests. Chin. J. App. Environ. Biol. 2023, 29, 423–431. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, S.; Xia, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wu, S.; Zhang, N.; Yue, X.; Deng, Y.; Xia, Y. Improvement and the relationship between chemical properties and microbial communities in secondary salinization of soils induced by rotating vegetables. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 921, 171019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, W.; Gu, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, S. Comparison of soil chemical and microbial properties in monoculture larch and mixed plantations in a temperate forest ecosystem in Northeast China. Ecol. Process. 2022, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.; Chowdhary, S.; Koksch, B.; Murphy, C.D. Biodegradation of amphipathic fluorinated peptides reveals a new bacterial defluorinating activity and a new source of natural organofluorine compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 9762–9772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.; Hof, C.; Niemcová, P.; Murphy, C.D. Recent advances in fungal xenobiotic metabolism: Enzymes and applications. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, M.; Chen, X.; Yu, X.; Yan, J.; Zhang, X.; Hamel, C.; Sheng, Y.; Tang, M. Neighborhood effects on soil properties, mycorrhizal attributes, tree growth, and nutrient status in afforested zones. Restor. Ecol. 2020, 28, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharker, B.; Islam, M.A.; Hossain, M.A.A.; Ahmad, I.; Al Mamun, A.; Ghosh, S.; Rahman, A.; Hossain, M.S.; Ashik, M.A.; Hoque, M.R.; et al. Characterization of lignin and hemicellulose degrading bacteria isolated from cow rumen and forest soil: Unveiling a novel enzymatic model for rice straw deconstruction. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
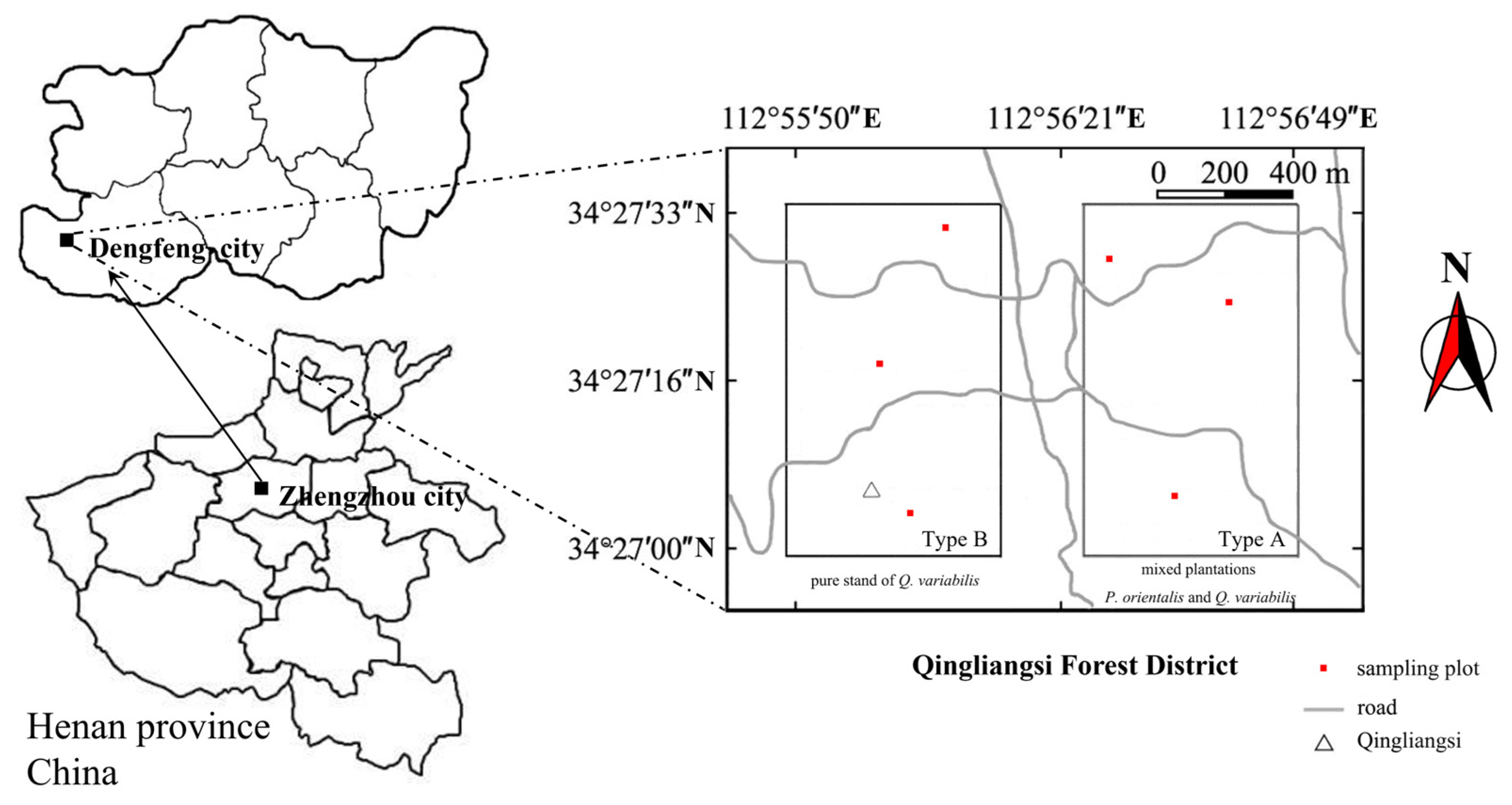
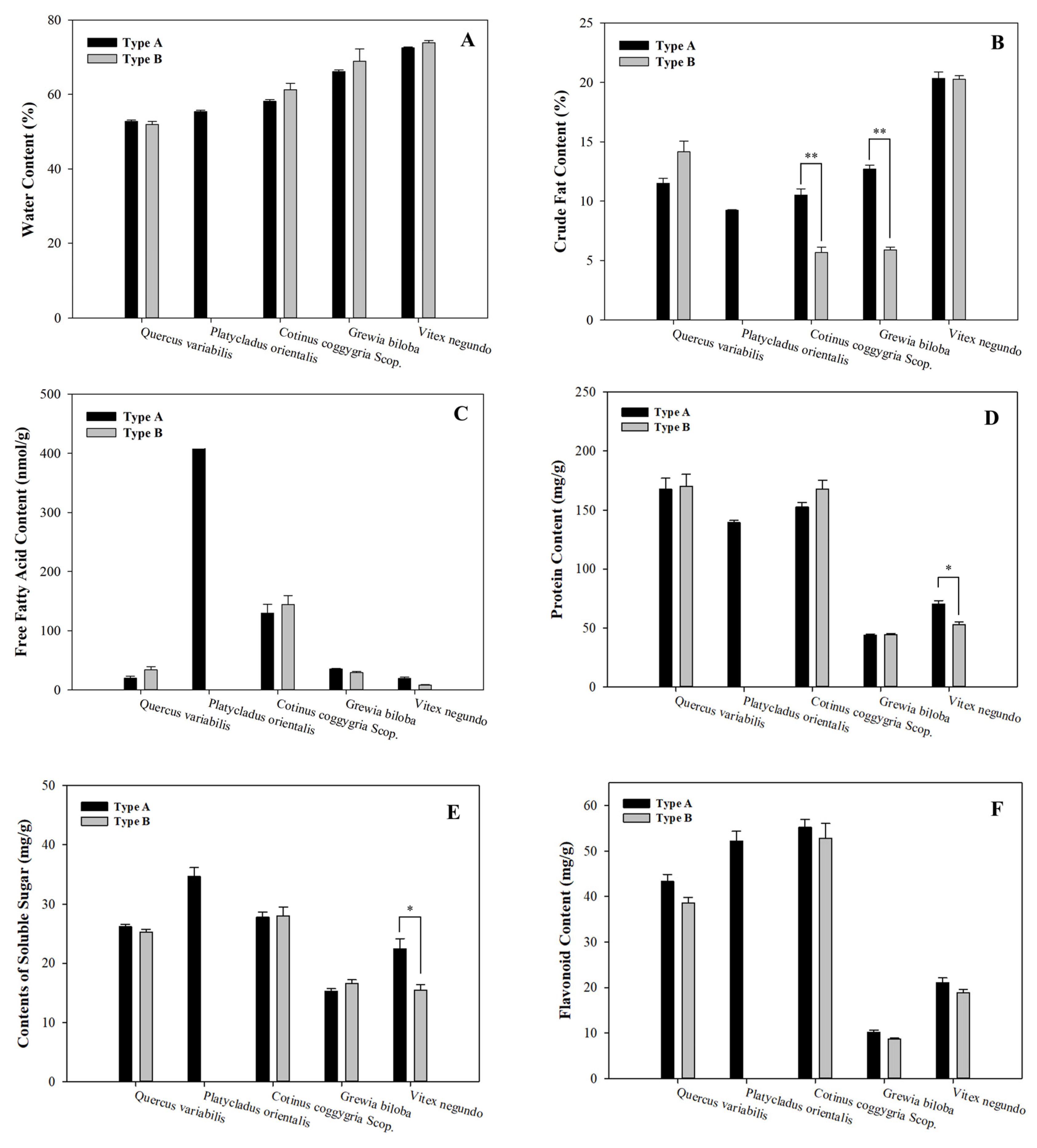


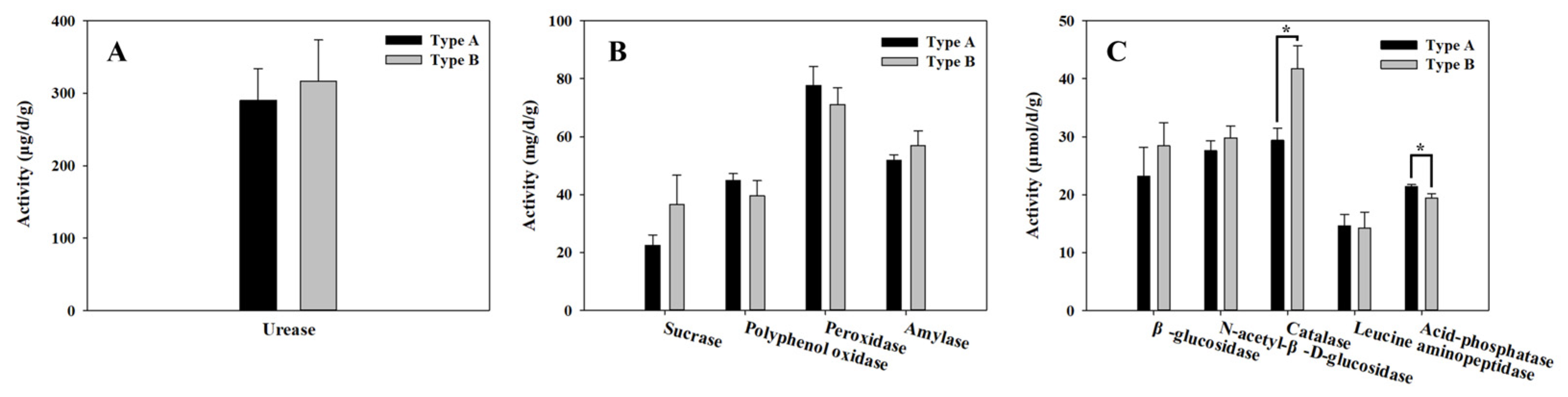
| Stand Type | Altitude (m) | Slope (°) | Aspect | Canopy Density (%) | Stand Density (Plants·hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type A (mixed plantations of P. orientalis and Q. variabilis) | 639.74 | 9.74 | Sunny slope | 76.91 | 1423 |
| Type B (pure stands of Q. variabilis) | 602.14 | 8.97 | Sunny slope | 74.68 | 1426 |
| Water | Crude Fat | Free Fatty Acid | Protein | Soluble Sugar | Tannin | Flavonoid | Lignin | Cellulose | Hemicellulose | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 1.000 | 0.943 | 0.409 | −0.336 | −0.803 | −1.000 * | 0.454 | 0.852 | −0.295 | −0.219 |
| Crude fat | 0.525 | 1.000 | 0.690 | −0.003 | −0.559 | −0.949 | 0.725 | 0.978 | 0.040 | 0.118 |
| 0.474 | ||||||||||
| Free fatty acid | −0.562 | 0.409 | 1.000 | 0.722 | 0.215 | −0.425 | 0.999 * | 0.826 | 0.751 | 0.801 |
| 0.311 | 0.984 | |||||||||
| Protein | −0.976 | −0.699 | 0.366 | 1.000 | 0.831 | 0.319 | 0.687 | 0.207 | 0.999 * | 0.993 |
| −0.952 | −0.180 | −0.003 | ||||||||
| Soluble sugar | −0.076 | −0.889 | −0.782 | 0.293 | 1.000 | 0.793 | 0.166 | −0.373 | 0.806 | 0.757 |
| −0.325 | 0.679 | 0.798 | 0.600 | |||||||
| Tannin | 0.751 | −0.169 | −0.968 | −0.587 | 0.602 | 1.000 | −0.470 | −0.861 | 0.278 | 0.202 |
| −0.102 | −0.924 | −0.977 | −0.209 | −0.908 | ||||||
| Flavonoid | −0.844 | 0.015 | 0.918 | 0.705 | −0.472 | −0.988 | 1.000 | 0.853 | 0.718 | 0.770 |
| 0.715 | −0.277 | −0.277 | −0.895 | −0.893 | 0.623 | |||||
| Lignin | 0.571 | 0.998 * | 0.358 | −0.738 | −0.862 | −0.114 | −0.041 | 1.000 | 0.249 | 0.324 |
| −0.234 | −0.967 | −0.997 | −0.076 | −0.844 | 0.991 | 0.512 | ||||
| Cellulose | 0.805 | −0.082 | −0.943 | −0.655 | 0.530 | 0.996 | −0.998 * | −0.027 | 1.000 | 0.997 * |
| −0.694 | 0.305 | 0.469 | 0.882 | 0.906 | −0.646 | −1.000 * | −0.537 | |||
| Hemicellulose | −0.23 | 0.708 | 0.934 | 0.01 | −0.953 | −0.816 | 0.717 | 0.667 | −0.762 | 1.000 |
| 0.984 | −0.975 | −0.999 * | −0.043 | −0.825 | 0.986 | 0.483 | 0.999 * | −0.509 |
| Water | Crude Fat | Free Fatty Acid | Protein | Soluble Sugar | Tannin | Flavonoid | Lignin | Cellulose | Hemicellulose | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 1.000 | 0.422 | 0.526 | 0.333 | −0.925 | 0.456 | −0.446 | −0.829 | 0.084 | 0.985 |
| Crude fat | −0.919 | 1.000 | 0.993 | −0.715 | −0.047 | 0.999 * | −1.000 * | −0.857 | 0.939 | 0.574 |
| Free fatty acid | 0.806 | −0.974 | 1.000 | −0.627 | −0.165 | 0.997 | −0.996 | −0.912 | 0.891 | 0.667 |
| Protein | 0.22 | −0.587 | 0.755 | 1.000 | −0.665 | −0.688 | 0.696 | 0.252 | −0.912 | 0.162 |
| Soluble sugar | −0.572 | 0.849 | −0.947 | −0.926 | 1.000 | −0.084 | 0.073 | 0.555 | 0.300 | −0.845 |
| Tannin | 1.000 * | −0.908 | 0.79 | 0.194 | −0.55 | 1.000 | −1.000 ** | −0.876 | 0.925 | 0.605 |
| Flavonoid | 0.967 | −0.787 | 0.627 | −0.037 | −0.343 | 0.973 | 1.000 | 0.870 | −0.929 | −0.596 |
| Lignin | −0.789 | 0.483 | −0.272 | 0.426 | −0.052 | −0.805 | −0.92 | 1.000 | −0.627 | −0.914 |
| Cellulose | −0.994 | 0.956 | −0.865 | −0.324 | 0.657 | −0.991 | −0.933 | 0.718 | 1.000 | 0.257 |
| Hemicellulose | 0.988 | −0.847 | 0.705 | 0.066 | −0.438 | 0.992 | 0.995 | −0.875 | −0.966 | 1.000 |
| Water | pH | Total Nitrogen | Total Phosphorus | Organic Matter | Organic Carbon | Ammonium Nitrogen | Nitrate Nitrogen | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 1.000 | 0.514 | 0.448 | 0.324 | 0.301 | 0.301 | −0.315 | 0.420 |
| pH | 0.813 ** | 1.000 | 0.506 | 0.698 * | 0.400 | 0.400 | 0.229 | 0.712 * |
| Total nitrogen | 0.942 ** | 0.802 ** | 1.000 | 0.369 | 0.944 ** | 0.944 ** | 0.221 | 0.505 |
| Total phosphorus | 0.766 * | 0.827 ** | 0.651 | 1.000 | 0.203 | 0.203 | 0.063 | 0.550 |
| Organic matter | 0.911 ** | 0.847 ** | 0.972 ** | 0.711 * | 1.000 | 1.000 ** | 0.329 | 0.387 |
| Organic carbon | 0.911 ** | 0.847 ** | 0.972 ** | 0.711 * | 1.000 ** | 1.000 | 0.329 | 0.387 |
| Ammonium nitrogen | −0.465 | −0.485 | −0.400 | −0.300 | −0.501 | −0.501 | 1.000 | 0.438 |
| Nitrate nitrogen | −0.333 | −0.34 | −0.139 | −0.498 | −0.081 | −0.081 | −0.105 | 1.000 |
| S-PPO | S-POD | S-CAT | S-ACP | S-SC | S-AL | S-β-GC | S-NAG | S-LAP | S-UE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-PPO | 1.000 | −0.434 | 0.635 | 0.574 | 0.521 | −0.018 | 0.032 | −0.039 | 0.010 | 0.652 |
| S-POD | 0.145 | 1.000 | −0.653 | −0.330 | −0.863 ** | 0.576 | −0.088 | −0.039 | 0.191 | −0.818 ** |
| S-CAT | 0.410 | −0.728 * | 1.000 | 0.341 | 0.827 ** | −0.092 | −0.097 | 0.139 | 0.027 | 0.866 ** |
| S-ACP | −0.121 | −0.828 ** | 0.706 * | 1.000 | 0.406 | 0.200 | −0.675 * | −0.656 | 0.674 * | 0.404 |
| S-SC | 0.506 | −0.663 | 0.938 ** | 0.739 * | 1.000 | −0.374 | −0.026 | 0.183 | −0.023 | 0.967 ** |
| S-AL | 0.157 | 0.105 | −0.235 | −0.072 | −0.053 | 1.000 | −0.551 | −0.469 | 0.657 | −0.359 |
| S-β-GC | 0.381 | −0.448 | 0.635 | 0.36 | 0.625 | 0.393 | 1.000 | 0.834 ** | −0.953 ** | 0.027 |
| S-NAG | 0.205 | −0.048 | 0.448 | 0.25 | 0.422 | 0.126 | 0.386 | 1.000 | −0.787 * | 0.210 |
| S-LAP | 0.315 | −0.748 * | 0.882 ** | 0.829 ** | 0.924 ** | 0.098 | 0.58 | 0.547 | 1.000 | −0.097 |
| S-UE | 0.560 | −0.586 | 0.811 ** | 0.632 | 0.923 ** | 0.318 | 0.736 * | 0.479 | 0.918 ** | 1.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Shao, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, X. Influence of Tree Species Composition on Leaf and Soil Properties and Soil Enzyme Activity in Mixed and Pure Oak (Quercus variabilis) Stands. Forests 2025, 16, 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16030471
Wang J, Liu C, Shao X, Song Y, Wang X. Influence of Tree Species Composition on Leaf and Soil Properties and Soil Enzyme Activity in Mixed and Pure Oak (Quercus variabilis) Stands. Forests. 2025; 16(3):471. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16030471
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Juan, Chang Liu, Xinliang Shao, Yiting Song, and Xu Wang. 2025. "Influence of Tree Species Composition on Leaf and Soil Properties and Soil Enzyme Activity in Mixed and Pure Oak (Quercus variabilis) Stands" Forests 16, no. 3: 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16030471
APA StyleWang, J., Liu, C., Shao, X., Song, Y., & Wang, X. (2025). Influence of Tree Species Composition on Leaf and Soil Properties and Soil Enzyme Activity in Mixed and Pure Oak (Quercus variabilis) Stands. Forests, 16(3), 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16030471







