Soil Microbial Communities and Their Relationship with Soil Nutrients in Different Density Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Plantations in the Mu Us Sandy Land
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Study Area
2.2. Research Methods
2.2.1. Plot Setup and Sample Collection
2.2.2. Soil Nutrient Analysis
2.2.3. Soil Microbial Community Analysis
2.2.4. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Nutrients in Different Density P. sylvestris var. mongolica Plantations
3.2. Composition and Diversity of Soil Microbial Communities in Different Density P. sylvestris var. mongolica Plantations
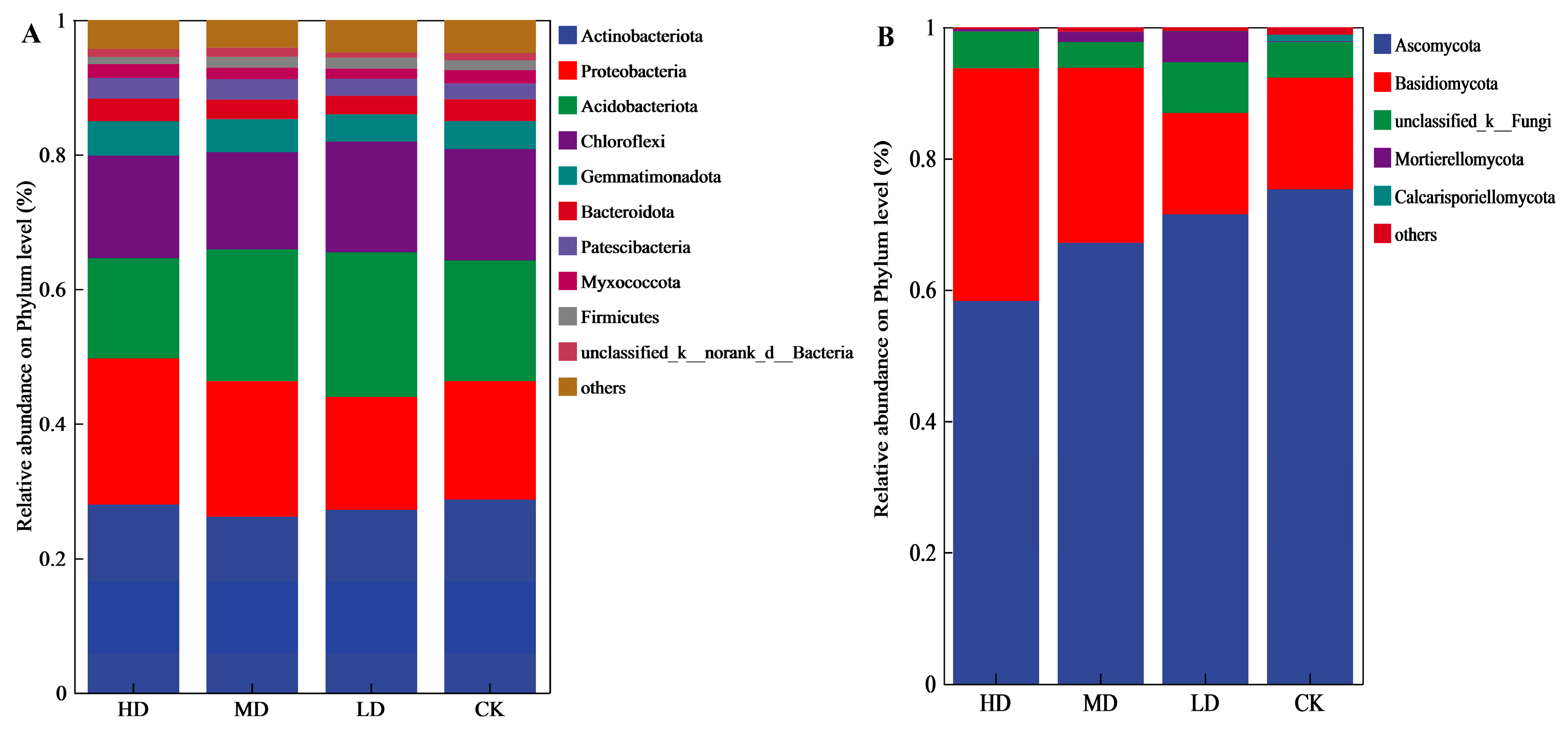
3.2.1. Species Composition at the Phylum Level
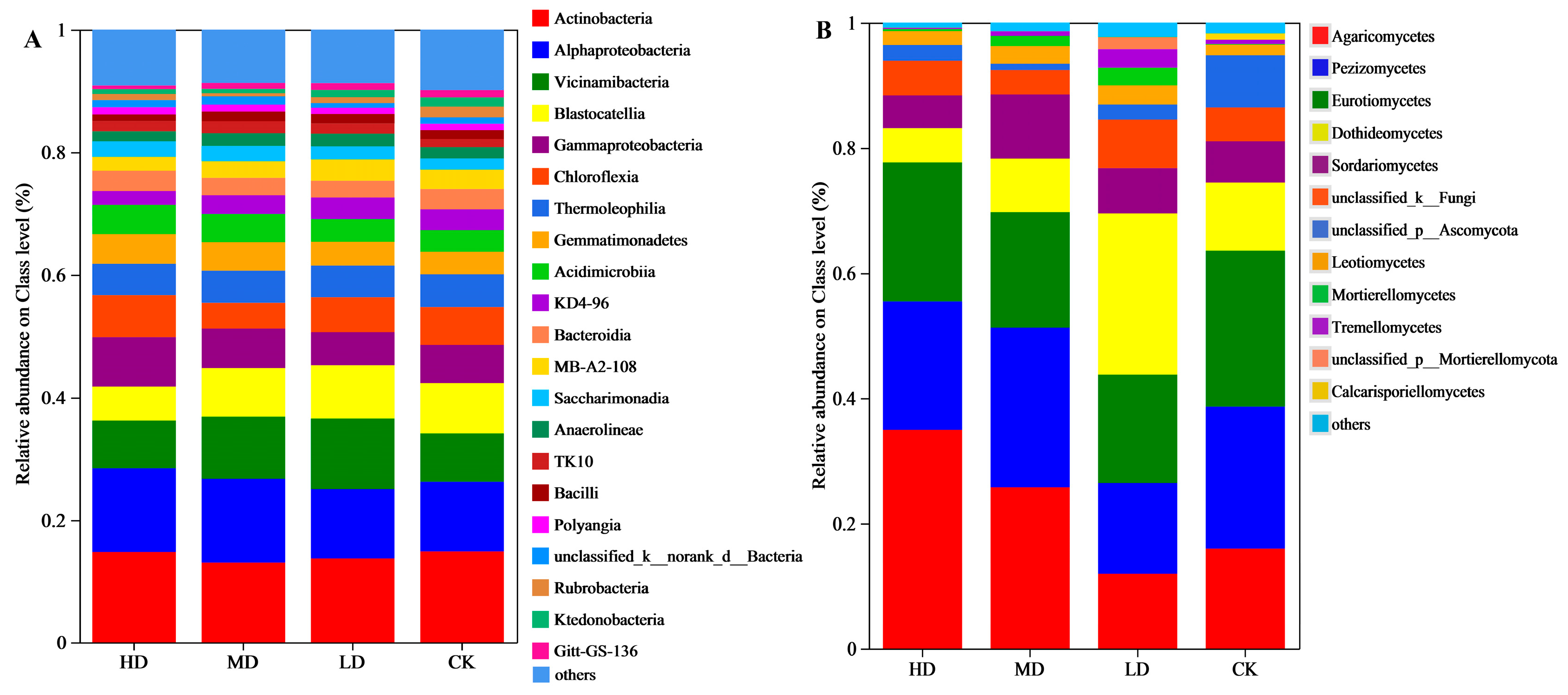
3.2.2. Species Composition at the Class Level
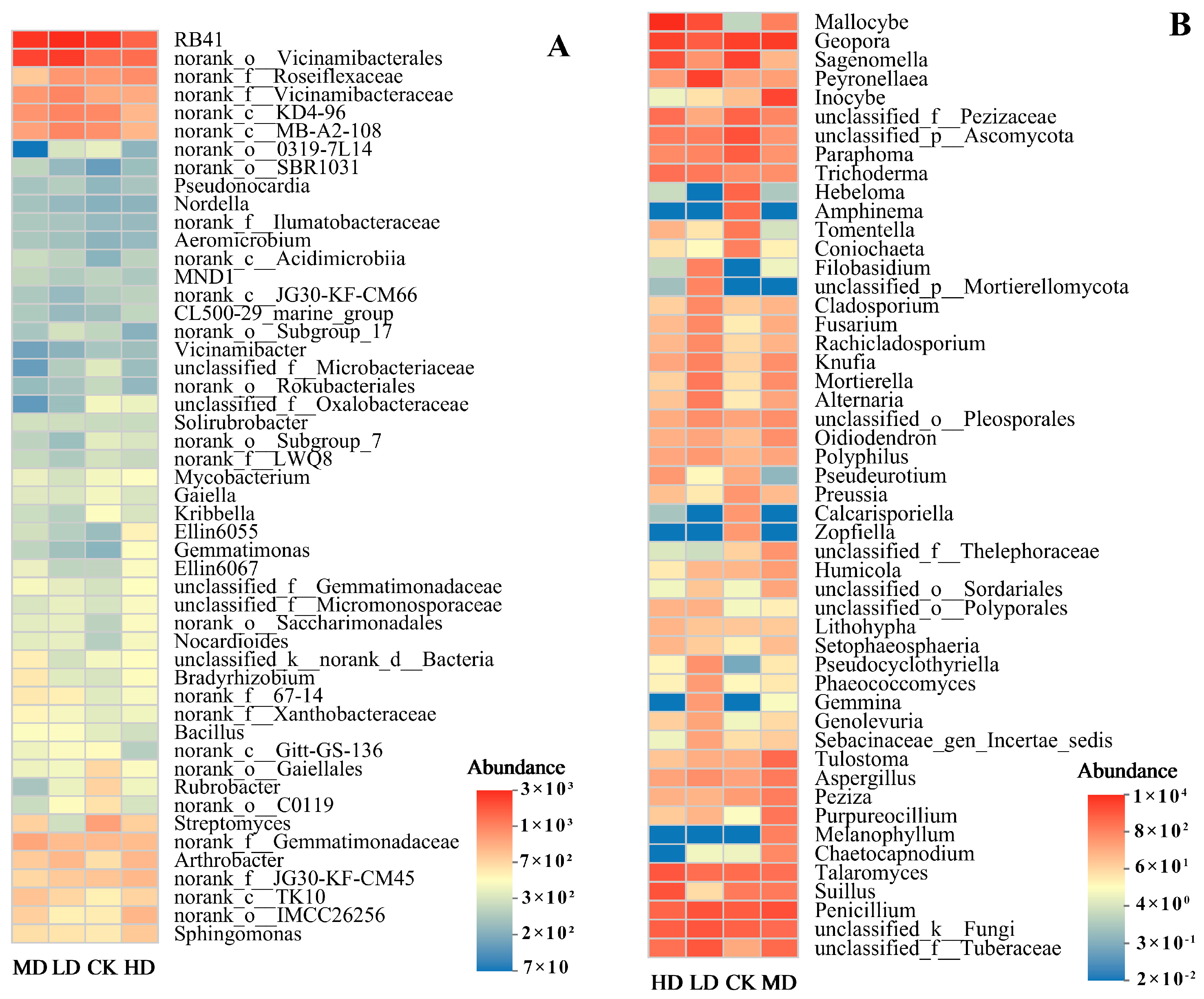
3.2.3. Species Composition at the Genus Level
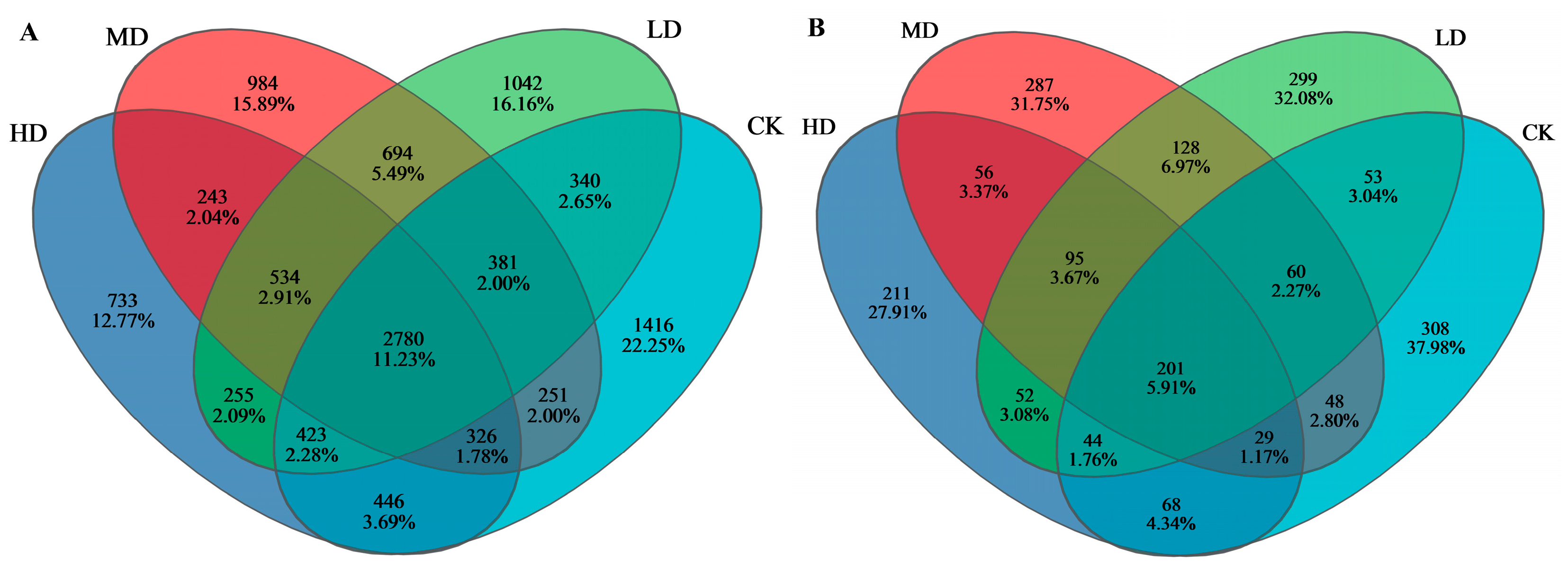
3.2.4. Species Composition at the OTU Level
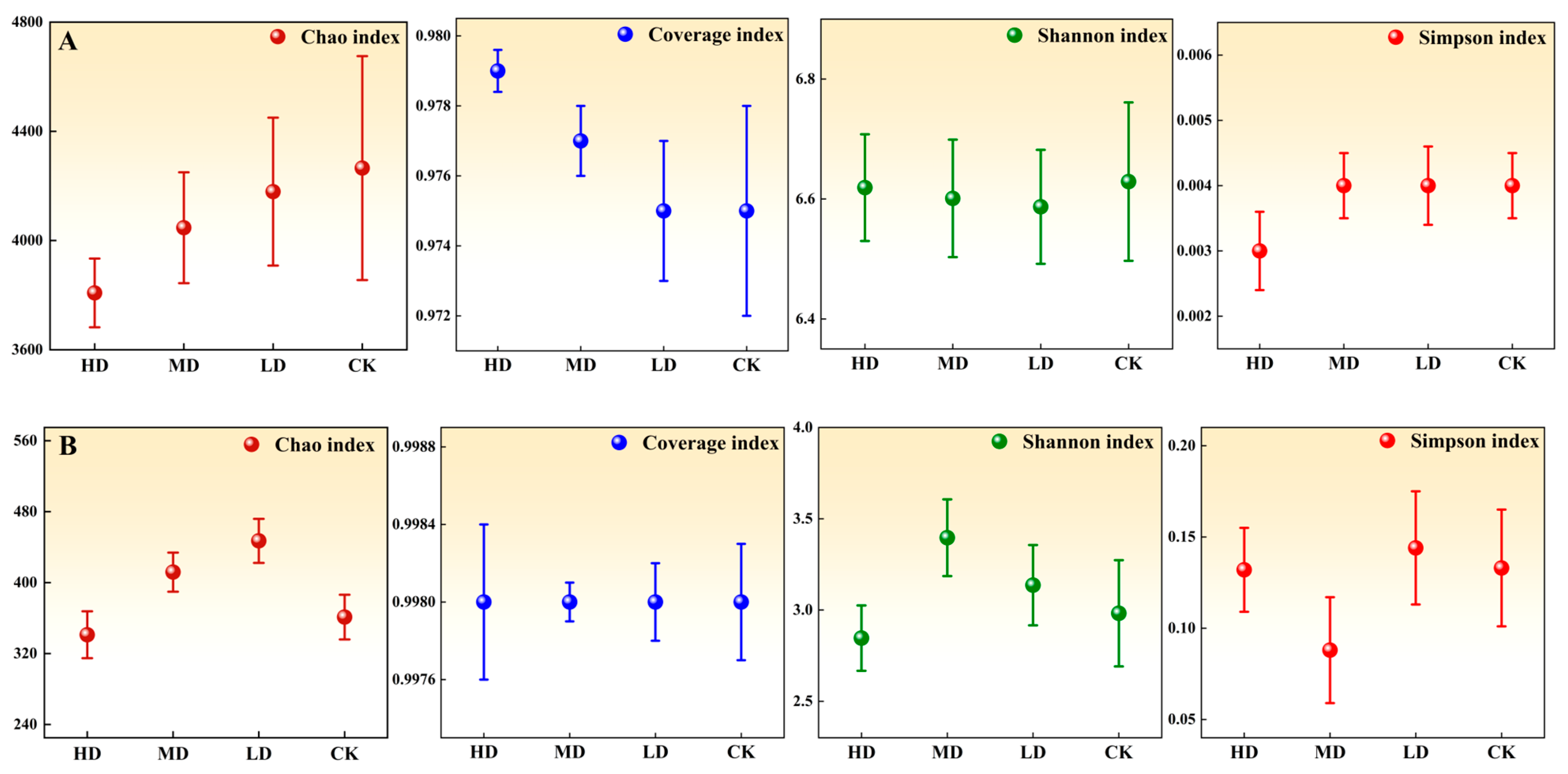
3.2.5. Changes in Soil Microbial Diversity Indices
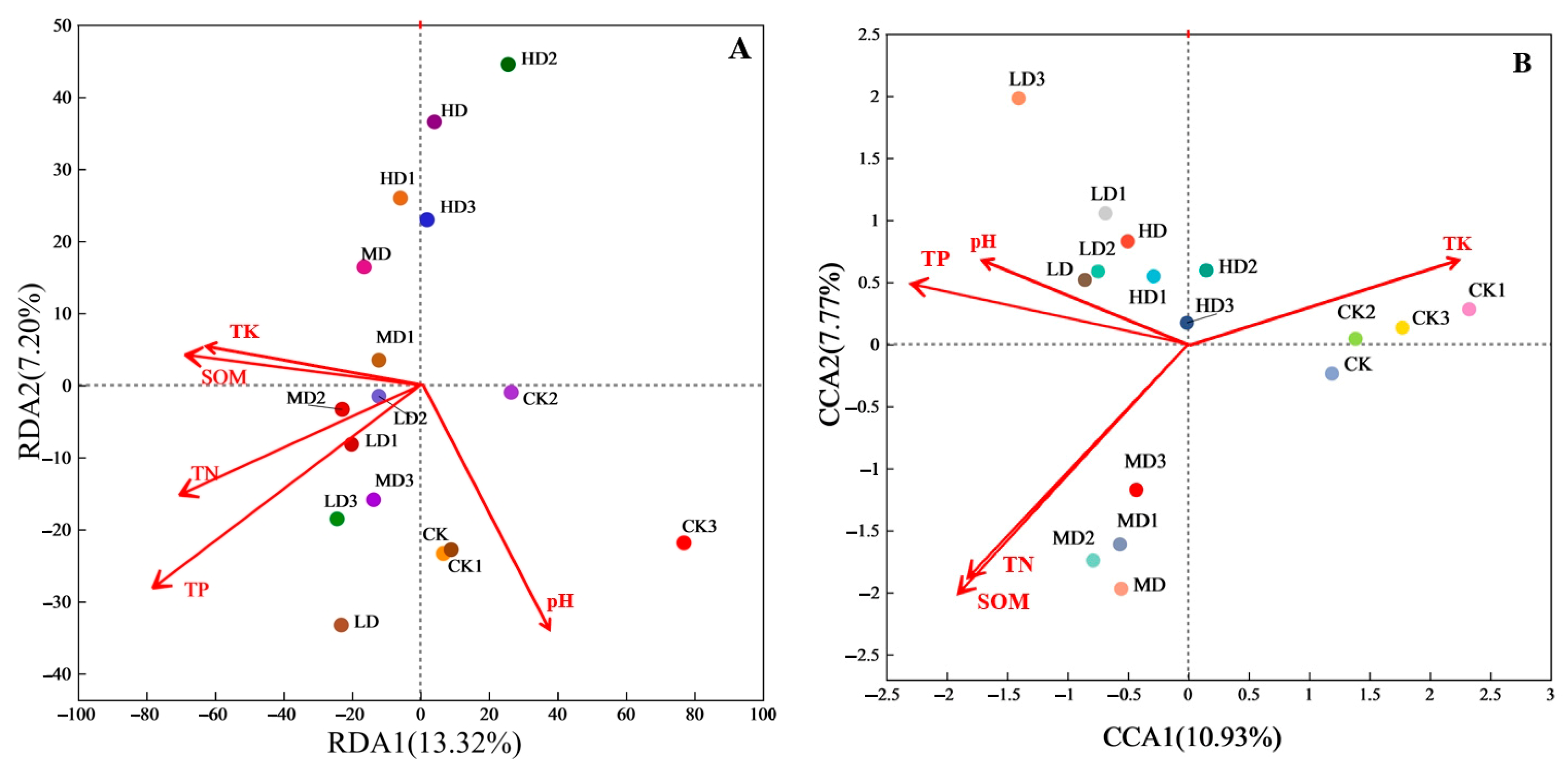
3.3. Main Environmental Factors Affecting Soil Microbial Community Structure
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Density on Soil Nutrients
4.2. Impact of Density on Soil Microbial Community Structure
4.3. Impact of Soil Nutrients on Soil Microorganisms
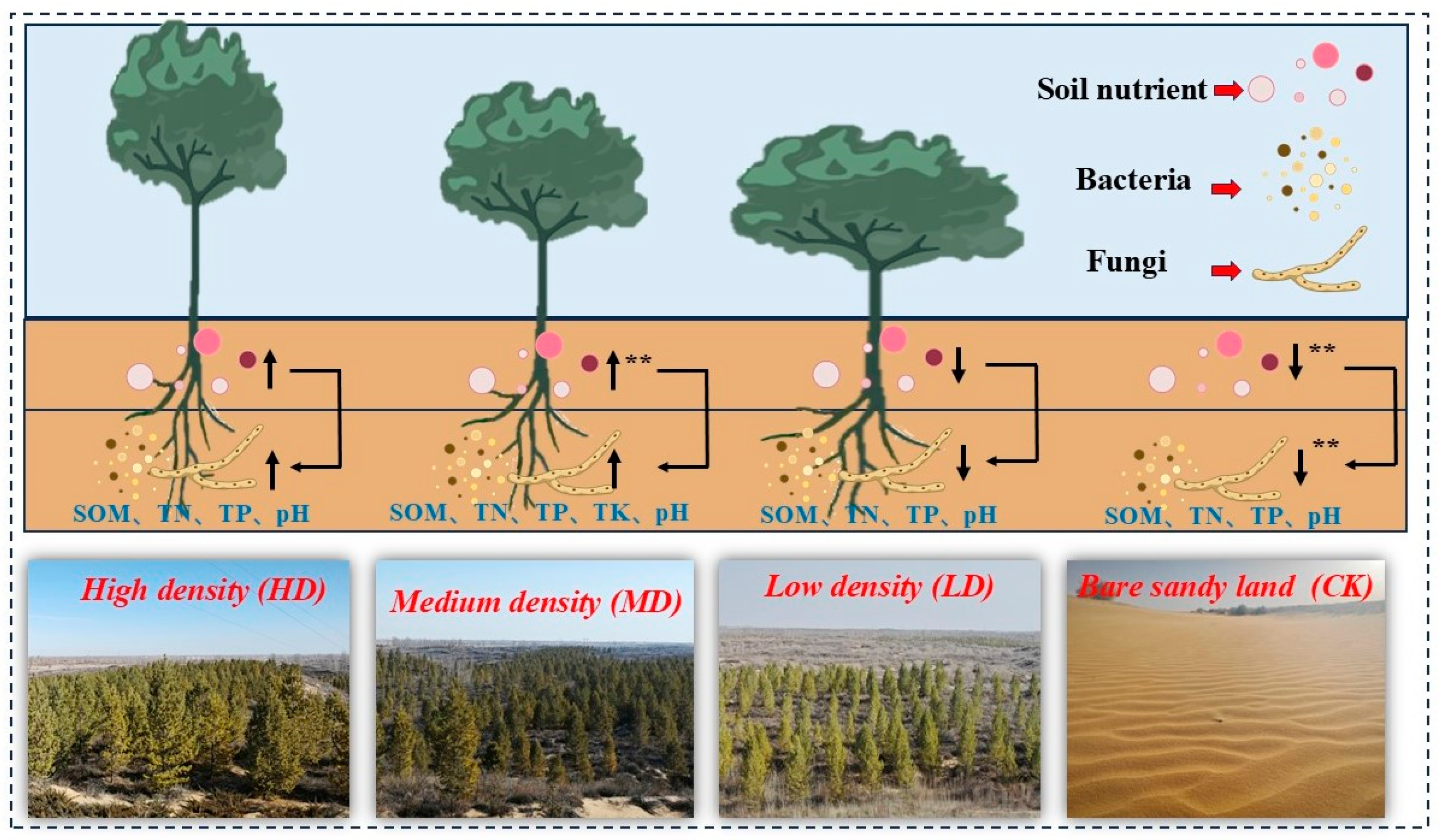
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pascual, J.A.; Garcia, C.; Hernandez, T.; Moreno, J.L.; Ros, M. Soil microbial activity as a biomarker of degradation and remediation processes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1877–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.A. Measurements of the soil microbial community for estimating the success of restoration. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2003, 54, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, L.A.; Degens, B.P.; Sparling, G.P.; Duncan, L.C. Changes in microbial heterotrophic diversity along five plant successional sequences. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 2093–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Xiang, W.; Ouyang, S.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Luo, G.; Kuzyakov, Y. Forest conversion to plantations: A meta-analysis of consequences for soil and microbial properties and functions. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 5643–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossio, D.A.; Scow, K.M.; Gunapala, N.; Graham, K.J. Determinants of soil microbial communities: Effects of agricultural management, season, and soil type on phospholipid fatty acid profiles. Microb. Ecol. 1995, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panikov, N.S. Understanding and prediction of soil microbial community dynamics under global change. Appl. Soil Ecol. 1999, 11, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.D.; van der Putten, W.H. Belowground biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Nature 2014, 515, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayston, S.J.; Wang, S.; Campbell, C.D.; Edwards, A.C. Selective influence of plant species on microbial diversity in the rhizosphere. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Zhu, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, J. Water use patterns of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica trees of different ages in a semiarid sandy lands of Northeast China. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2016, 129, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D. Soil Enzyme Activity Changes and Influencing Factors of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Plantation in Sandy Land. Master’s Thesis, Liaoning University of Engineering and Technology, Shenyang, China, 2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.N.; Liao, C.Y.; Li, X.M.; Yang, X.J. Changes of soil enzyme activity in different forest ages of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantation in Mu Us Sandy Land. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2014, 2, 1–5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iddrisu, A.Q.; Hao, Y.; Issifu, H.; Getnet, A.; Sakib, N.; Yang, X.; Zhang, P. Effects of Stand Density on Tree Growth, Diversity of Understory Vegetation, and Soil Properties in a Pinus koraiensis Plantation. Forests 2024, 15, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girvan, M.S.; Bullimore, J.; Pretty, J.N.; Osborn, A.M.; Ball, A.S. Soil type is the primary determinant of the composition of the total and active bacterial communities in arable soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 1800–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, C.W.; Moorman, T.B.; Beare, M. Role of microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in soil quality. Methods Assess. Soil Qual. 1997, 49, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, B. Analysis of the characteristics of climate change in the ecologically vulnerable area of the Mu Us dune field under the background of global warming. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- . Cheng, Y.; Zhan, H.; Yang, W.; Feng, W.; Lu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hao, R. Redistribution process of precipitation in ecological restoration activity of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica in Mu Us Sandy Land, China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2023, 11, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, W.; Ta, F.; Meng, X.; Dong, Z.; Xiao, N. Effects of age and density of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica on soil moisture in the semiarid Mu Us Dunefield, northern China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 473, 118313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, B.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Han, F. Dynamic changes of soil microbial community in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantations in the Mu Us Sandy Land. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoc, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. Available online: https://pascal-francis.inist.fr/vibad/index.php?action=getRecordDetail&idt=24797598 (accessed on 5 September 2024). [CrossRef]
- Çömez, A.; Güner, Ş.T.; Tolunay, D. The effect of stand structure on litter decomposition in Pinus sylvestris L. stands in Turkey. Ann. For. Sci. 2021, 78, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabtai, I.A.; Hafner, B.D.; Schweizer, S.A.; Höschen, C.; Possinger, A.; Lehmann, J.; Bauerle, T. Root exudates simultaneously form and disrupt soil organo-mineral associations. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, C.P. Effects of root exudates of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica on soil environment and microorganisms under different stands. J. Shandong Agric. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2022, 3, 380–385. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, T.; Wu, D.; Shen, H.O.; Ren, X.Y.; Wang, D.L.; Wang, K. Root and soil nutrient distribution characteristics of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantation in sandy land. Chin. Soil Water Conserv. Sci. 2020, 4, 84–93. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.S.; Chi, L.L.; Xiao, W.; Song, G. Variation characteristics of soil nutrients in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantations with different densities. Liaoning For. Sci. Technol. 2021, 6, 1–4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Liu, T.R.; Tan, Z.J.; Guo, J.P.; Zhang, Y.X. Characterization of soil physicochemical properties and microbiomass carbon and nitrogen in natural forests of oil pine with different stand densities. J. Ecol. Environ. 2019, 28, 8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, E.H. Effects of Silvicultural Density on Nutrient Element Distribution in Sandy Camphor Pine Plantation Forests. Master’s Thesis, Liaoning University of Engineering and Technology, Shenyang, China, 2021. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Tuo, F.; Qi, H.B.; Nan, W.G.; Dong, Z.B. Study on soil nutrients in camphor pine plantation forests at the southeastern edge of the Mu Us Sandy. Henan Sci. 2019, 37, 8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.W. Characteristics of Soil C, N, P Changes in Zhanggutai Sandy Camphor Pine Plantation Forests of Different Stand Ages. Ph.D. Thesis, Liaoning University of Engineering and Technology, Shenyang, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Vaziriyeganeh, M.; Zwiazek, J.J. Effects of pH and mineral nutrition on growth and physiological responses of trembling aspen (Populus tremuloides), jack pine (Pinus banksiana), and white spruce (Picea glauca) seedlings in sand culture. Plants 2020, 9, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.N. Changes of Soil pH and Its Influencing Factors in Sand Fixation Forest Land of Sylvestris Pine. Master’s Thesis, Liaoning University of Engineering and Technology, Shenyang, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.L. Effects of different density regulation on forest growth in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantation. Liaoning For. Sci. Technol. 2020, 5, 4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Fei, F.; Diao, J.; Chen, B.J.; Guan, Q. Thinning intensity affects microbial functional diversity and enzymatic activities associated with litter decomposition in a Chinese fir plantation. J. For. Res. 2018, 29, 1337–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiser, A.D.; Knoepp, J.D.; Bradford, M.A. Microbial communities may modify how litter quality affects potential decomposition rates as tree species migrate. Plant Soil 2013, 372, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Luo, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, G.; Li, X. Response of plant diversity and soil physicochemical properties to different gap sizes in a Pinus massoniana plantation. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F.N.; Jiang, M.; Li, Y.Y.; Dang, H.L.; Peng, M.W.; Zhuang, L. Analysis of soil fungal community structure and diversity of Tamarix chinensis shrubland in the lower reaches of Tarim River. Arid. Zone Geogr. 2021, 3, 759–768. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Yu, W.; Turak, A.; Chen, D.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Z. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus inputs on soil bacterial abundance, diversity, and community composition in Chinese fir plantations. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoo, A.E.; Babalola, O.O. Impact of land use on bacterial diversity and community structure in temperate pine and indigenous forest soils. Diversity 2019, 11, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, C.; Wu, M.; Li, Z. Shifts in bacterial and fungal diversity in a paddy soil faced with phosphorus surplus. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2018, 54, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Zhou, X.; Guo, D.; Zhao, J.H.; Yan, L.; Feng, G.Z.; Zhao, L.P. Soil pH is the primary factor driving the distribution and function of microorganisms in farmland soils in northeastern China. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Wu, M.; Jiang, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, Z.; Li, Z. Soil pH rather than nutrients drive changes in microbial community following long-term fertilization in acidic Ultisols of southern China. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 1853–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragot, S.A.; Huguenin-Elie, O.; Kertesz, M.A.; Frossard, E.; Bünemann, E.K. Total and active microbial communities and phoD as affected by phosphate depletion and pH in soil. Plant Soil 2016, 408, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Song, M.H. The role of plant and soil microbes in regulating nutrient cycling in ecosystems. Plant Ecol. 2010, 8, 979–988. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Sun, X.M.; Liu, X.Y.; He, N.P.; Yu, Q. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on soil microbial community structure in typical temperate steppe of Inner Mongolia. Ecology 2014, 17, 4943–4949. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, G.D.; Liu, M.J.; Gao, G.L.; Yu, M.H.; Li, X. Effects of different vegetation types on soil microbial community structure in typical forest land in Yulin sandy area. Soil Bull. 2022, 4, 907–918. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Liu, L.; Dou, Y.; An, S. Comparison of soil microbial community between planted woodland and natural grass vegetation on the Loess Plateau. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 460, 117817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Peng, C.; Yang, B.; Song, H.; Li, Q.; Jiang, L.; Wang, M. Contrasting soil bacterial community, diversity, and function in two forests in China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.; Feng, Q.; Li, Y.; Yu, X.; Ren, S. Drivers of soil bacterial diversity in sandy grasslands in China. Environ. Sci. 2021, 12, 141689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type | Longitude | Latitude | Elevation/m | Age/a | Density/hm2 | Average Tree Height/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Density (HD) | 109.239063 | 38.872321 | 1269.56 | 9 | 3600 | 5.8 |
| Medium Density (MD) | 109.238535 | 38.871885 | 1270.56 | 9 | 2400 | 5.6 |
| Low Density (LD) | 109.238103 | 38.871497 | 1268.56 | 9 | 1800 | 5.3 |
| Bare Sandy (CK) | 109.293974 | 38.807876 | 1267.04 | / | / | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hai, L.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, K.; Hong, G.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Gao, X.; Li, Z.; Li, F. Soil Microbial Communities and Their Relationship with Soil Nutrients in Different Density Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Plantations in the Mu Us Sandy Land. Forests 2025, 16, 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16030547
Hai L, Zhou M, Zhao K, Hong G, Li Z, Liu L, Gao X, Li Z, Li F. Soil Microbial Communities and Their Relationship with Soil Nutrients in Different Density Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Plantations in the Mu Us Sandy Land. Forests. 2025; 16(3):547. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16030547
Chicago/Turabian StyleHai, Long, Mei Zhou, Kai Zhao, Guangyu Hong, Zihao Li, Lei Liu, Xiaowei Gao, Zhuofan Li, and Fengzi Li. 2025. "Soil Microbial Communities and Their Relationship with Soil Nutrients in Different Density Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Plantations in the Mu Us Sandy Land" Forests 16, no. 3: 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16030547
APA StyleHai, L., Zhou, M., Zhao, K., Hong, G., Li, Z., Liu, L., Gao, X., Li, Z., & Li, F. (2025). Soil Microbial Communities and Their Relationship with Soil Nutrients in Different Density Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Plantations in the Mu Us Sandy Land. Forests, 16(3), 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16030547






