Monitoring Pine Shoot Beetle Damage Using UAV Imagery and Deep Learning Semantic Segmentation Under Different Forest Backgrounds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
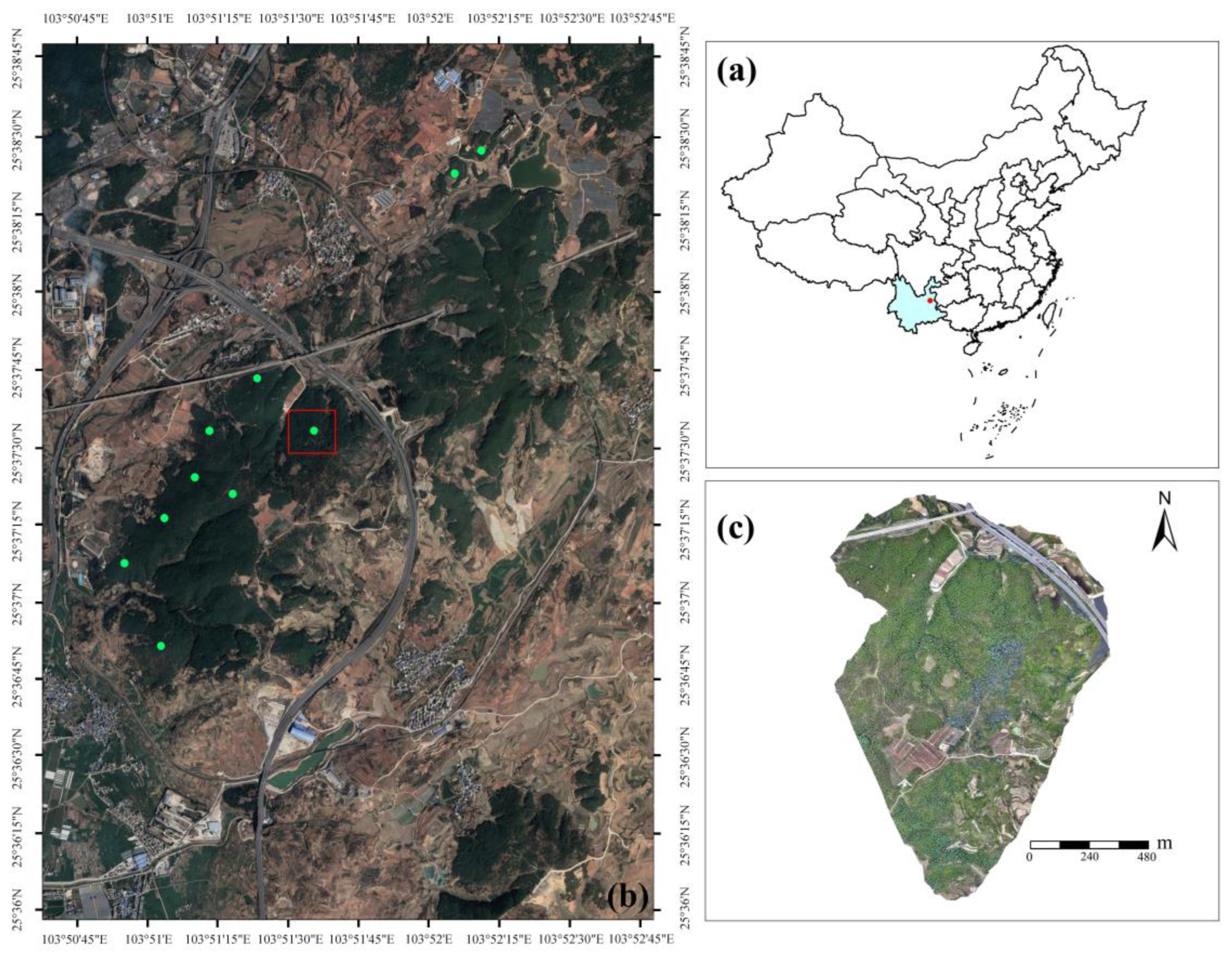
2.1. Study Area
2.2. UAV Image Collection
2.3. Data Annotation and Processing
2.4. Selection of Different Forest Backgrounds
2.5. Models
2.6. Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
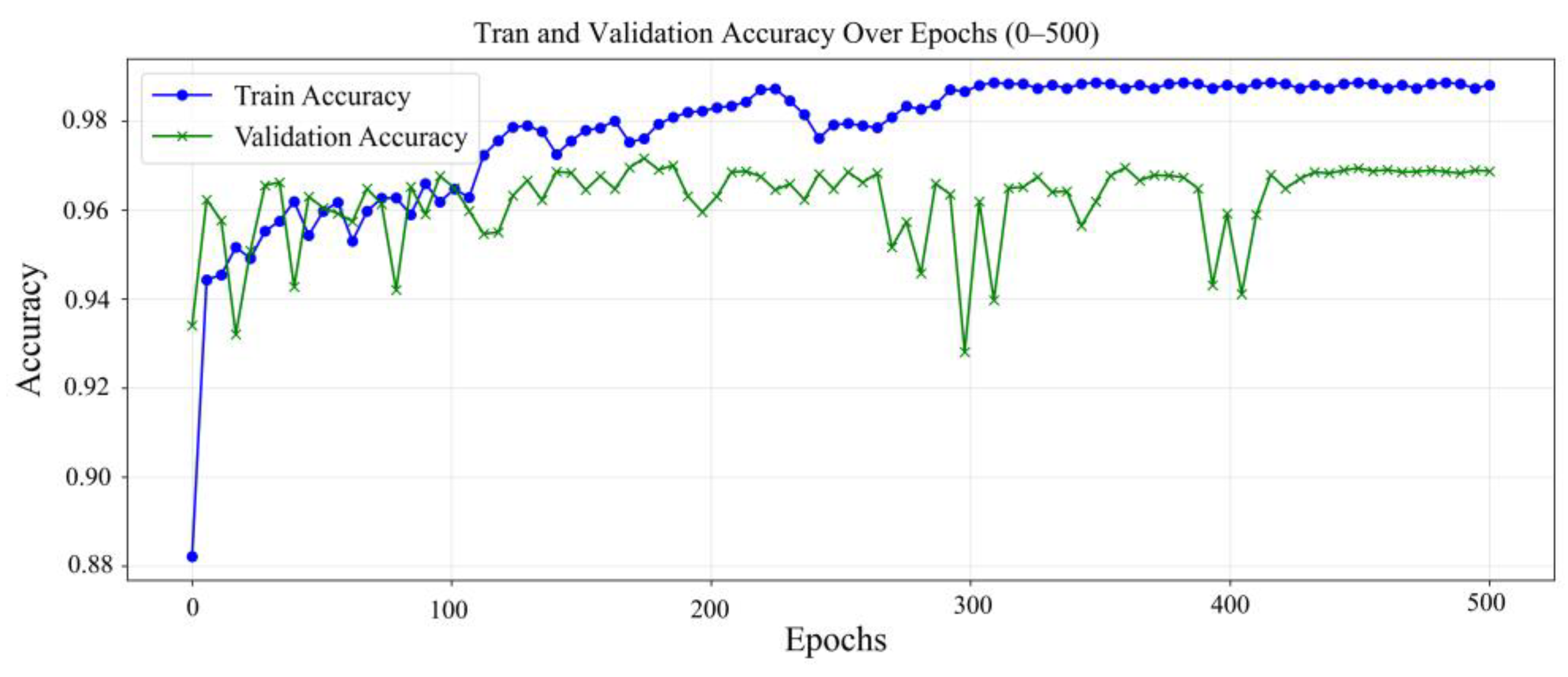
3.1. Comparison of Evaluation Parameters for Different Models
3.2. Detailed Analysis of the FPN Model Performance
3.3. The FPN Model’s Capacity for Identifying Damaged Trees Across Different Forest Backgrounds
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Illarionova, S.; Tregubova, P.; Shukhratov, I.; Shadrin, D.; Kedrov, A.; Burnaev, E. Remote sensing data fusion approach for estimating forest degradation: A case study of boreal forests damaged by Polygraphus proximus. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1412870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.E.M.; Evans, T.; Venter, O.; Williams, B.; Tulloch, A.I.T.; Stewart, C.; Thompson, I.; Ray, J.C.; Murray, K.; Salazar, A.; et al. The Exceptional Value of Intact Forest Ecosystems. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffa, K.F.; Aukema, B.; Bentz, B.J.; Carroll, A.; Erbilgin, N.; Herms, D.A.; Hicke, J.A.; Hofstetter, R.W.; Katovich, S.; Lindgren, B.S.; et al. A Literal Use of “Forest Health” Safeguards Against Misuse and Misapplication. J. For. 2009, 107, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, J.; Sun, H.; Lu, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, S.; Fang, G. Satellite remote sensing identification of discolored standing trees for pine wilt disease based on semi-supervised deep learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Huang, J.; Zong, S.; Huang, H.; Luo, Y. Detecting Shoot Beetle Damage on Yunnan Pine Using Landsat Time-Series Data. Forests 2018, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Huang, H.; Roques, A. Early monitoring of forest wood-boring pests with remote sensing. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2023, 68, 277–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Huo, L.; Zhang, X. Using Only the Red-Edge Bands Is Sufficient to Detect Tree Stress: A Case Study on the Early Detection of PWD Using Hyperspectral Drone Images. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 217, 108665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cong, S.; Zhang, G.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J. Detecting Pest-Infested Forest Damage through Multispectral Satellite Imagery and Improved UNet++. Sensors 2022, 22, 7440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, N.; Khanal, R.; Bhattarai, B.; Lee, J.W. Pine Wilt Disease Segmentation with Deep Metric Learning Species Classification for Early-Stage Disease and Potential False Positive Identification. Electronics 2024, 13, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-Toro, J.; Navarro-Cerrillo, R.M. Analysis of site-dependent Pinus halepensis Mill. defoliation caused by ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma pini’ through shape selection in Landsat time series. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, S.; Olsson, P.O.; Müller, M.; Ghorbanian, A. Kernel-Based Early Detection of Forest Bark Beetle Attack Using Vegetation Indices Time Series of Sentinel-2. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 12868–12877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Ghany, N.M.; Abd El-Aziz, S.E.; Marei, S.S. A review: Application of remote sensing as a promising strategy for insect pests and diseases management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 33503–33515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelcey, J.; Lucieer, A. Sensor correction of a 6-band multispectral imaging sensor for UAV remote sensing. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 1462–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassnacht, F.E.; Latifi, H.; Ghosh, A.; Joshi, P.K.; Koch, B. Assessing the potential of hyperspectral imagery to map bark beetle-induced tree mortality. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Huang, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, K.; Liu, Y. Early Detection of Pine Shoot Beetle Attack Using Vertical Profile of Plant Traits through UAV-Based Hyperspectral, Thermal, and Lidar Data Fusion. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 125, 103549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Huang, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, K.; Liu, Y. Detection of pine shoot beetle (PSB) stress on pine forests at individual tree level using UAV-based hyperspectral imagery and lidar. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Yao, J.; Du, T.; Ma, Y.; Shi, L. Discriminant Analysis of the Damage Degree Caused by Pine Shoot Beetle to Yunnan Pine Using UAV-Based Hyperspectral Images. Forests 2020, 11, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheykhmousa, M.; Mahdianpari, M.; Ghanbari, H.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Ghamisi, P.; Homayouni, S. Support vector machine versus random forest for remote sensing image classification: A meta-analysis and systematic review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 6308–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Yu, L.; Ren, L.; Zhan, Z.; Luo, Y. Early Detection of Dendroctonus valens Infestation at Tree Level with a Hyperspectral UAV Image. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaskie, C.R.; Routhier, M.R.; Fraser, B.T.; Congalton, R.G.; Ayres, M.P.; Garnas, J.R. Early Detection of Southern Pine Beetle Attack by UAV-Collected Multispectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Sun, X.; Sun, Y.; Gao, Y. Text Feature Extraction Based on Deep Learning: A Review. J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2017, 2017, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Wu, Q.; Ding, G.; Xu, H.; Feng, S. A survey of machine learning for big data processing. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2016, 2016, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, K.; Tarabalka, Y.; Angulo, J.; Chanussot, J.; Benediktsson, J.A. Spectral-Spatial Classification of Hyperspectral Data Based on a Stochastic Minimum Spanning Forest Approach. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 2008–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.G.; Cho, H.B.; Youm, S.K.; Kim, S.-W. Detection of pine wilt disease using time series UAV imagery and deep learning semantic segmentation. Forests 2023, 14, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Xu, Q.; Gao, M.; Ning, J.; Jiang, X.; Gao, M. Aerial Image Segmentation of Nematode-Affected Pine Trees with U-Net Convolutional Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Zhang, R.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Yi, T.; Wen, Y.; Ding, C.; Xie, C. Evaluation of Deep Learning Segmentation Models for Detection of Pine Wilt Disease in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H. Study on the damage of pine shoot beetles (Tomicus spp.) to Yunnan pine (Pinus yunnanensis). Acta Entomol. Sin. 1999, 42, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q. Biological characteristics and integrated control of the pine shoot beetle in the Qujing area. West. J. For. Sci. 2003, 1, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zong, S.; Ren, L.; Yu, L.; Gao, B.; Ze, S.; Luo, Y. Relationship Between Canopy Damage Characterization of Yunnan Pine and the Compound Hazards of Harmful Organisms. J. Appl. Entomol. 2017, 54, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet++: A Nested U-Net Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Granada, Spain, 16–20 September 2018; pp. 3–11. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.10165 (accessed on 11 February 2025).
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.02611 (accessed on 11 February 2025).
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path Aggregation Network for Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.01534 (accessed on 11 February 2025).
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, A.; Lerer, A.; Chintala, S.; Chanan, G.; Desmaison, L.; Kopf, A.; Yang, E.; DeVito, Z.; Raison, M.; Tejani, A. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. In Proceedings of the 33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2019), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillov, A.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Panoptic Feature Pyramid Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2019), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 6399–6408. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.02446 (accessed on 11 February 2025).
- Chen, C.; Yang, X.; Chen, R.; Yu, J.; Du, L.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ni, D. FFPN: Fourier Feature Pyramid Network for Ultrasound Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–12 October 2023; pp. 234–245. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.13790 (accessed on 11 February 2025).
- Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. E-FPN: An Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network for UAV Scenarios Detection. Vis. Comput. 2024, 41, 675–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.P.; Sauter, T.; Maier, A.K. Towards a guideline for evaluation metrics in medical image segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 80, 102420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Sun, J.; Ding, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, G. Robust liver vessel extraction using 3D U-Net with variant dice loss function. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 101, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.C.; Wulder, M.A.; Brooks, D.; Reich, R.; Wheate, R.D. Detection of Red Attack Stage Mountain Pine Beetle Infestation with High Spatial Resolution Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Bentz, B.; Alvarez, M.F.; Coops, N.C. Estimating the probability of mountain pine beetle red-attack damage. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 101, 150–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubin, A.; Kozhoridze, G.; Zabihi, K.; Modlinger, R.; Singh, V.V.; Surový, P.; Jakuš, R. Detection of Susceptible Norway Spruce to Bark Beetle Attack Using PlanetScope Multispectral Imagery. Front. For. Glob. Change 2023, 6, 1130721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalponte, M.; Solano-Correa, Y.T.; Frizzera, L.; Gianelle, D. Mapping a European spruce bark beetle outbreak using Sentinel-2 remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshev, A.; Taskar, B.; Daniilidis, K. Object detection via boundary structure segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F.; Liu, J. Medical image segmentation algorithm based on multilayer boundary perception-self attention deep learning model. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 15017–15039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maninis, K.K.; Pont-Tuset, J.; Arbelaez, P.; Van Gool, L. Convolutional oriented boundaries: From image segmentation to high-level tasks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 819–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; You, J.; Lee, J. Detecting Pine Trees Damaged by Wsilt Disease Using Deep Learning Techniques Applied to Multi-Spectral Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Sun, F.; Shen, W.; Dong, B.; Ma, S.; Huo, X.; Lan, P. Deep Learning-Based Pine Nematode Trees’ Identification Using Multispectral and Visible UAV Imagery. Drones 2022, 6, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minarik, R.; Langhammer, J.; Lendzioch, T. Detection of Bark Beetle Disturbance at Tree Level Using UAS Multispectral Imagery and Deep Learning. Forests 2021, 12, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Flight Height | 50 m |
| Height Mode | real-time terrain following |
| Longitudinal Overlap | 90% |
| Lateral Overlap | 80% |
| Orthophoto GSD | 1.38 cm/pixel |
| Flight Speed | 1.3 m/s |
| Model | No. Parameters | Backbone | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| UNet | 31,030,113 | VGG16 | Symmetric encoder–decoder |
| UNet++ | 34,567,890 | ResNet | Nested skip connections |
| DeepLabV3+ | 74,982,817 | Xception | Atrous pooling with decoder |
| PAN | 28,456,712 | ResNet | Path aggregation and attention |
| FPN | 23,123,567 | ResNet | Top-down feature pyramid |
| Model | Train Loss | Train Acc | Val Loss | Val Acc | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | IoU | mIoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FPN | 0.0579 | 0.9887 | 0.1648 | 0.9687 | 0.8341 | 0.8413 | 0.8352 | 0.7239 | 0.7185 |
| UNet | 0.3305 | 0.9404 | 0.3697 | 0.9318 | 0.6660 | 0.7178 | 0.6738 | 0.5175 | 0.5622 |
| UNet++ | 0.1473 | 0.9699 | 0.2090 | 0.9565 | 0.7212 | 0.8929 | 0.7911 | 0.6624 | 0.6744 |
| DeepLabV3+ | 0.0913 | 0.9820 | 0.2457 | 0.9530 | 0.7566 | 0.7801 | 0.7564 | 0.6163 | 0.6339 |
| PAN | 0.0997 | 0.9802 | 0.2306 | 0.9565 | 0.7870 | 0.7886 | 0.7695 | 0.6361 | 0.6499 |
| Backgrounds | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | IoU | mIoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Backgrounds A (pure Yunnan pine) | 0.9892 | 0.8544 | 0.8663 | 0.8552 | 0.7479 | 0.7235 |
| Backgrounds B (grassland-Yunnan pine) | 0.9816 | 0.8264 | 0.7374 | 0.8013 | 0.7423 | 0.7122 |
| Backgrounds C (bare soil-Yunnan pine) | 0.9721 | 0.7670 | 0.7526 | 0.7695 | 0.6312 | 0.6499 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, L.; Wang, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhan, Z. Monitoring Pine Shoot Beetle Damage Using UAV Imagery and Deep Learning Semantic Segmentation Under Different Forest Backgrounds. Forests 2025, 16, 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040668
Wang L, Gao Y, Liu Y, Zhong L, Wang S, Ma Y, Zhan Z. Monitoring Pine Shoot Beetle Damage Using UAV Imagery and Deep Learning Semantic Segmentation Under Different Forest Backgrounds. Forests. 2025; 16(4):668. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040668
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lixia, Yang Gao, Yujie Liu, Lihui Zhong, Shichunyun Wang, Yunqiang Ma, and Zhongyi Zhan. 2025. "Monitoring Pine Shoot Beetle Damage Using UAV Imagery and Deep Learning Semantic Segmentation Under Different Forest Backgrounds" Forests 16, no. 4: 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040668
APA StyleWang, L., Gao, Y., Liu, Y., Zhong, L., Wang, S., Ma, Y., & Zhan, Z. (2025). Monitoring Pine Shoot Beetle Damage Using UAV Imagery and Deep Learning Semantic Segmentation Under Different Forest Backgrounds. Forests, 16(4), 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040668






