Daily Variation of Soil Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Rubber Plantations Under Different Levels of Organic Fertilizer Substitution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
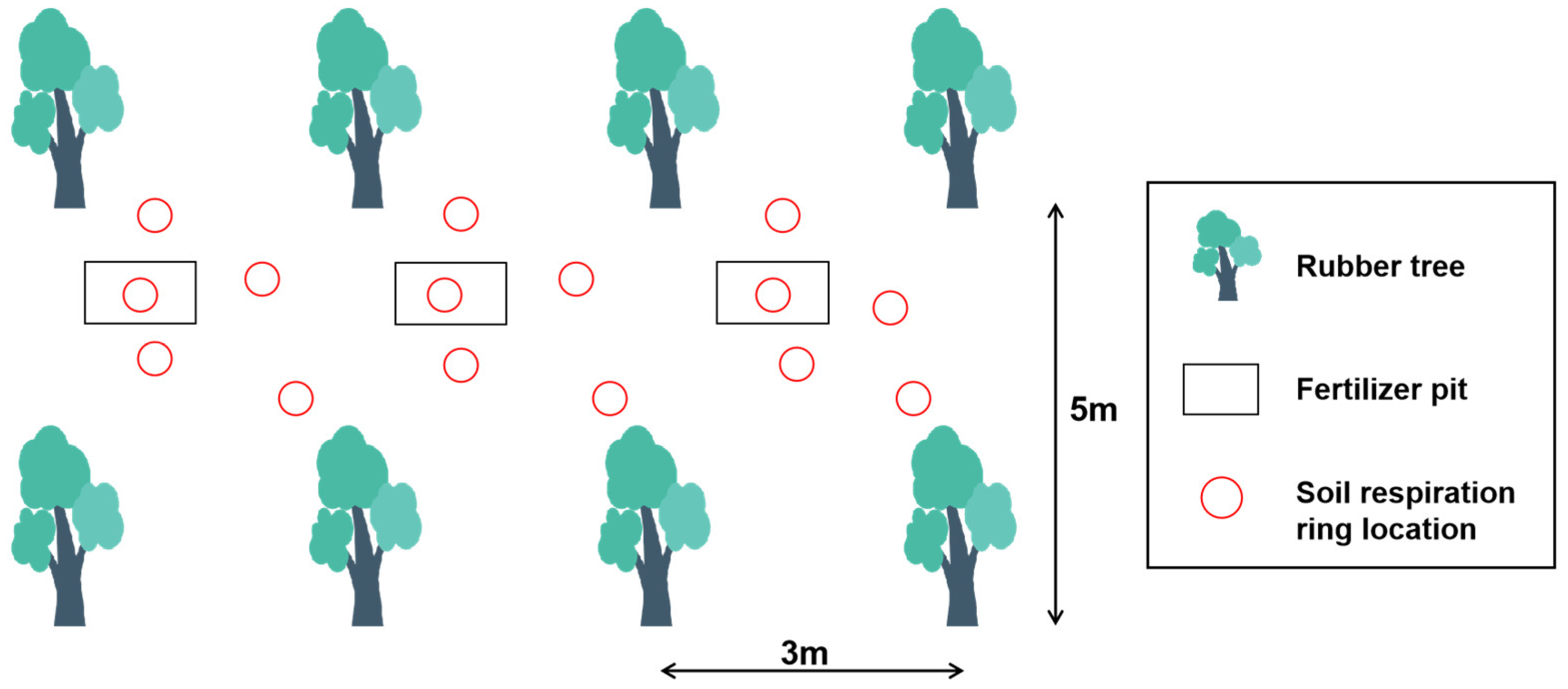
2.2. Experiment Design
2.3. Measurement and Calculation of GHG Fluxes
2.4. Soil Sample Collection and Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
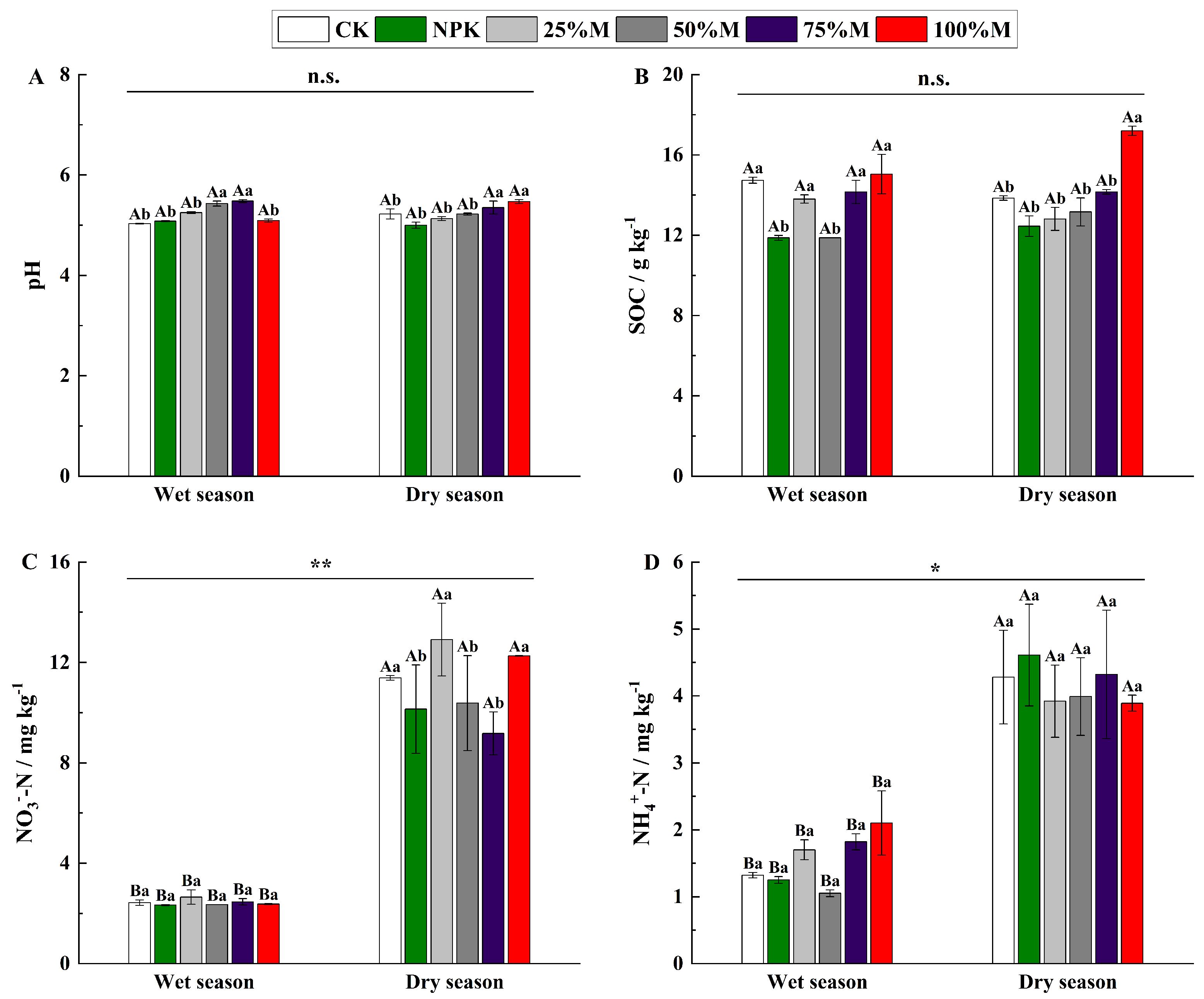
3.1. Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
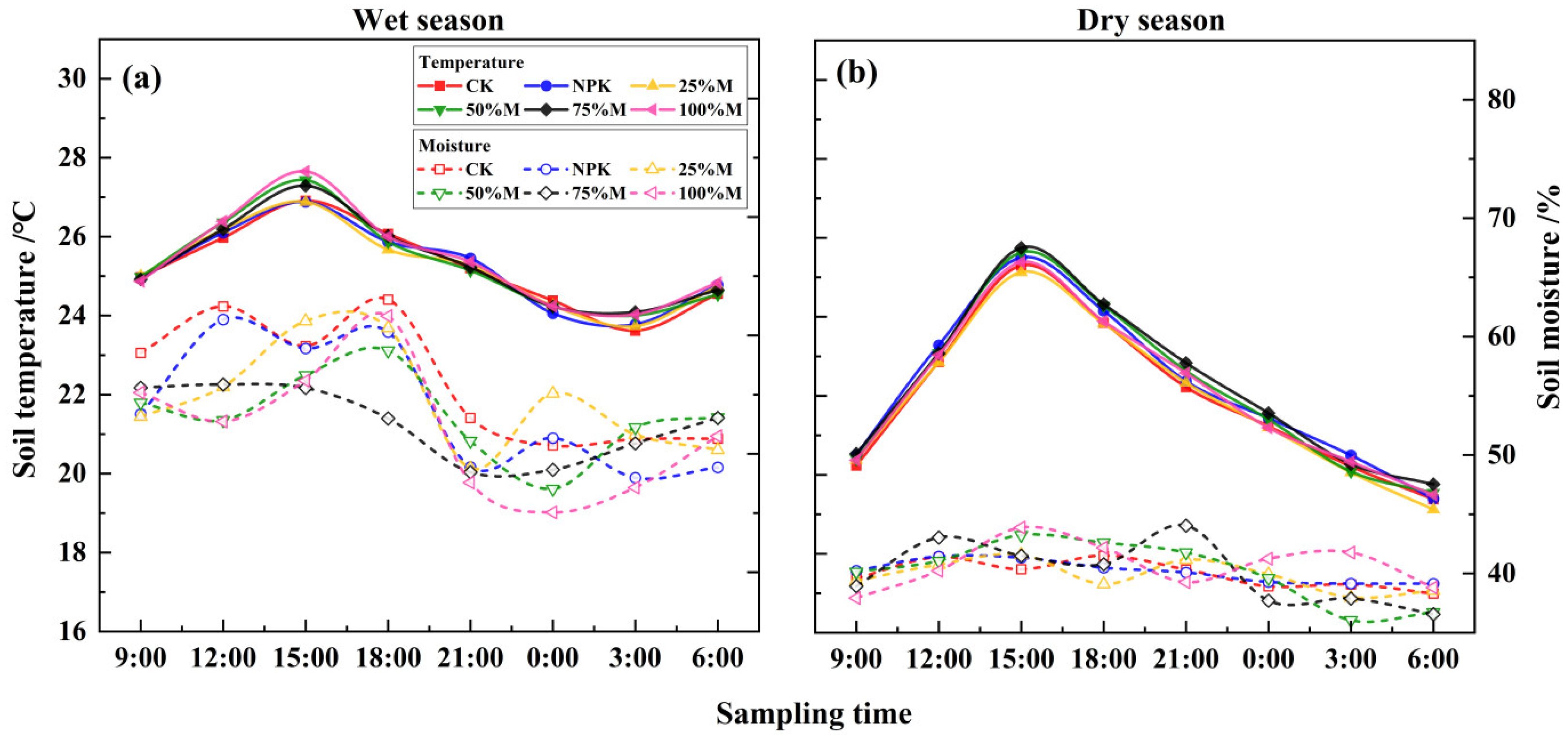
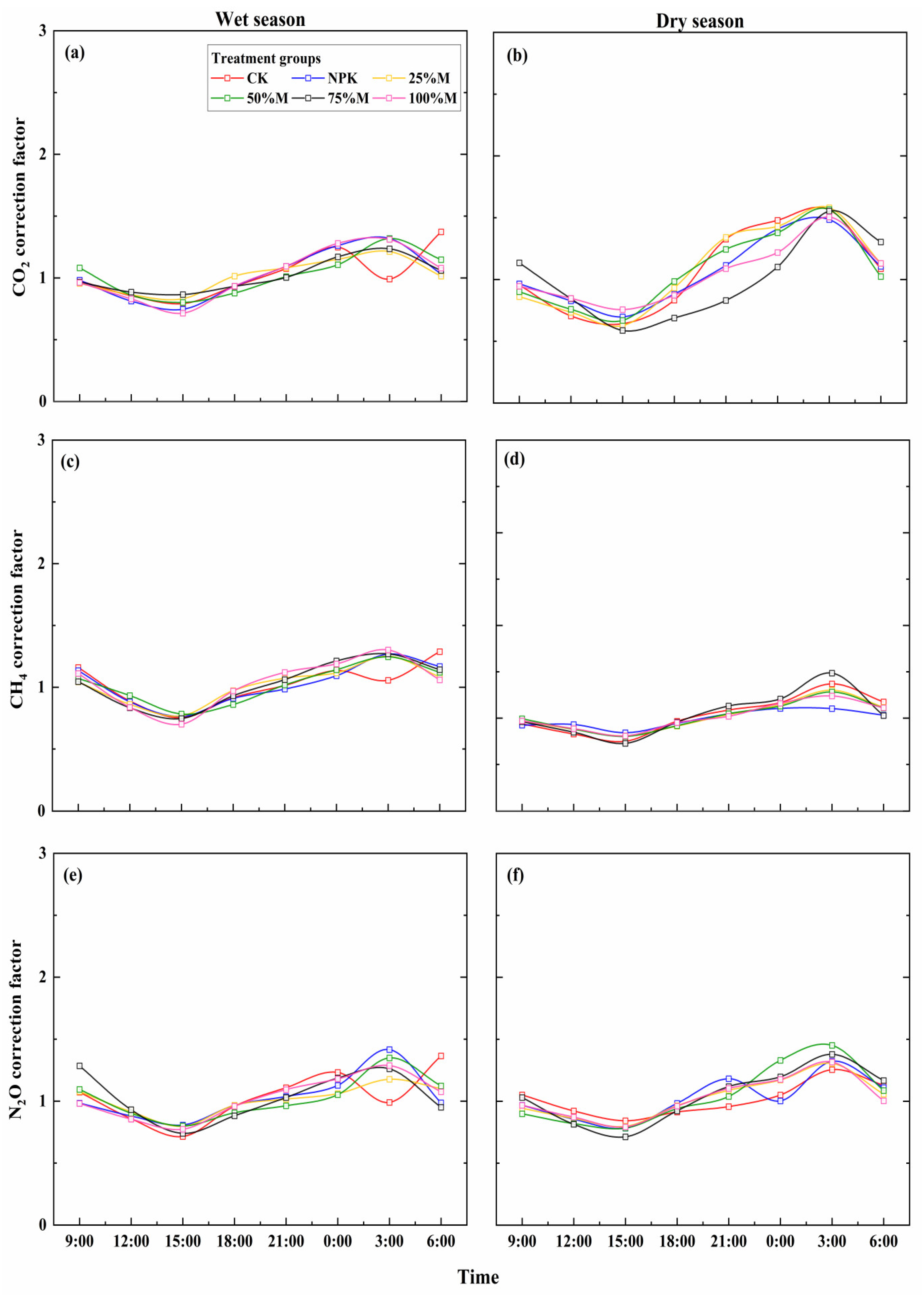
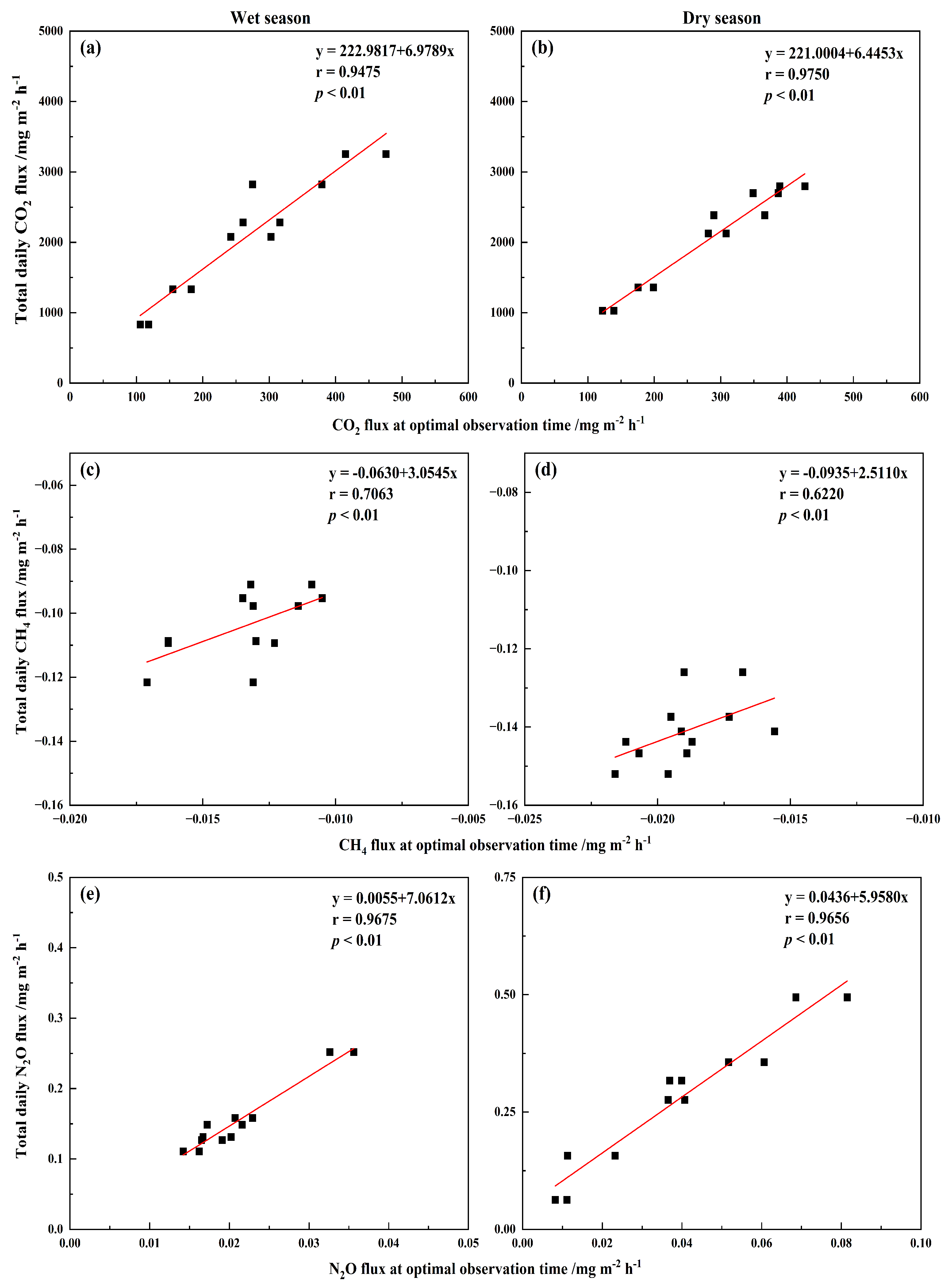
3.2. Daily Changes in Soil GHG Fluxes
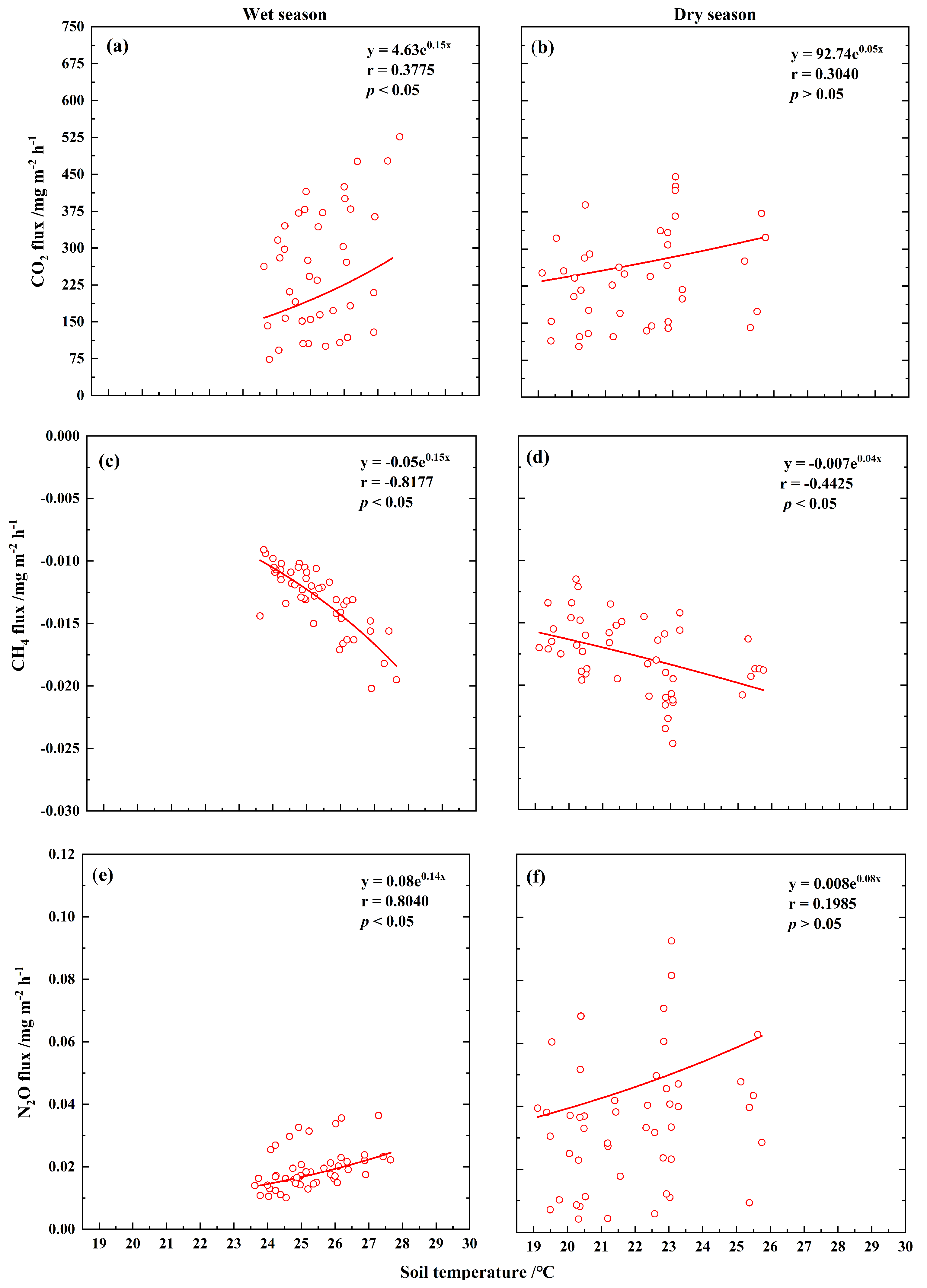
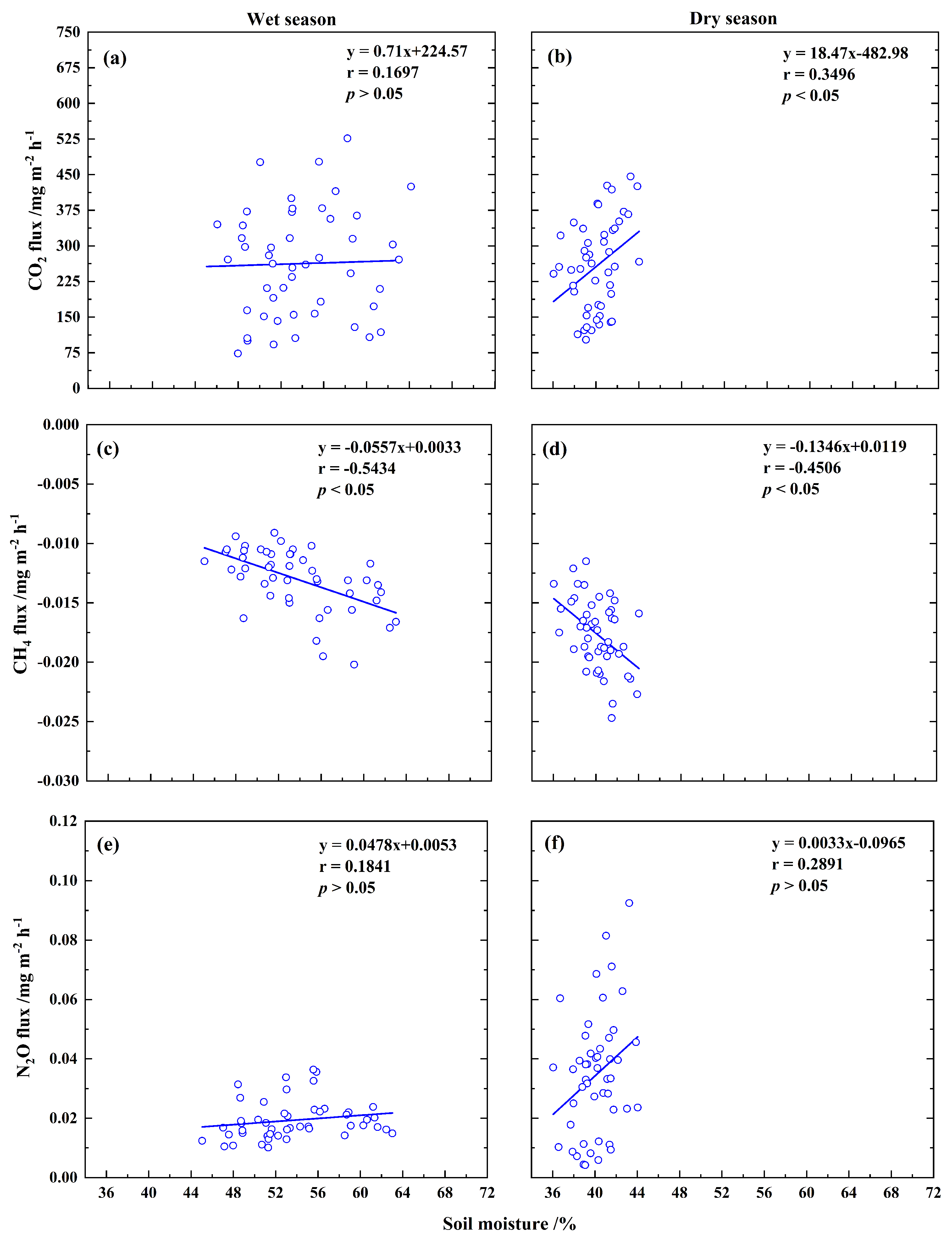
3.3. Relationships Between Soil GHG Fluxes and Soil Temperature or Moisture
3.4. Correction Factor for GHG Fluxes
4. Discussion
4.1. Daily Variation of Soil GHG Fluxes
4.2. Effects of Organic Fertilizer Substitution on GHG Fluxes in Rubber Plantation Soils
4.3. Effects of Soil Temperature and Soil Moisture on Soil GHG Fluxes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mandloi, S.; Bangre, J.; Aher, B.S.; Sharma, O.P.; Prajapati, S.; Singh, S. Conservation Agriculture as a Climate Change Mitigation Strategy: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Change 2023, 13, 3230–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report; Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1–34. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/sixth-assessment-report-cycle/ (accessed on 24 July 2024).
- Stijn, G.B.; Iris, C.; Márcio, F.A.L.; Gerard, W.K.; Jochen, M.; Mathias, C.; Dirk, R.; Wietse, B.; Paul, L.E.B. Soil aggregate stability governs field greenhouse gas fluxes in agricultural soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 191, 109354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Lu, C.; Ciais, P.; Anna, M.M.; Josep, G.C.; Eri, S.; Deborah, N.H.; Kevin, R.G.; Stephen, S.; Zhang, B.; et al. The terrestrial biosphere as a net source of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. Nature 2016, 531, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren-Thomas, E.M.; Edwards, D.P.; Bebber, D.P.; Phourin, C.; Alex, N.D.; Tom, D.E.; Frances, H.L.; James, F.M.; Menghor, N.; Hannah, J.O.; et al. Protecting tropical forests from the rapid expansion of rubber using carbon payments. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Jing, Y.; Bei, M.; Yang, H.; Cha, Z.; Lin, Q.; Luo, W. Short-Term Effects of Organic Amendments on Soil Fertility and Root Growth of Rubber Trees on Hainan Island, China. J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 2137–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Liu, W.; Wu, Z. Improving soil pH, nutrient concentrations, and enzyme activities by green manure returning in young and mature rubber plantations on Hainan Island, China. Plant Soil 2024, 495, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayama, M.; Kikuchi, S.; Uemura, A.; Takahashi, M. Growth Characteristics of Seven Willow Species Distributed in Eastern Japan in Response to Compost Application. Forests 2023, 14, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidik, B.R.; Sutanto, A.; Zen, S.; Noor, R. Application pineapple liquid waste to increase fruit weight and vitamin C pineapple as biological learning resources. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1567, 022051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Nie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, H.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y. Characteristics of Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Yellow Paddy Soils under Long-Term Organic Fertilizer Application. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, J.; Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Zhang, G.; Xu, H.; Kazuyuki, Y. Methane and nitrous oxide emissions from irrigated lowland rice paddies after wheat straw application and midseason aeration. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2014, 100, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Hu, T.; Ali, M.; Li, J.; Zhu, R.; Jiao, X.; Jing, P. A quantitative review of the effects of biochar application on rice yield and nitrogen use efficiency in paddy fields: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Zhu, B.; Wang, S. Stimulation of N2O emission by manure application to agricultural soils may largely offset carbon benefits: A global meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 4068–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, M.; Hui, R.; Sui, T.; Yang, L.; Du, W.; Dong, Z. A 4-year field measurement of N2O emissions from a maize-wheat rotation system as influenced by partial organic substitution for synthetic fertilizer. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 263, 110384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andréa, S.B.E.; Leonardo, M.P.; Carolina, B.B.; Acacio, A.N.; Camila, B.B.; Janaina, B.C. Organic management increases soil nitrogen but not carbon content in a tropical citrus orchard with pronounced N2O emissions. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 234, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Qi, J.; Yu, H.; Hu, C.; Mu, Y.; Qu, J. Dynamic chamber as a more reliable technique for measuring methane emissions from aquatic ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851 Pt 1, 158147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.M.; Jasdeep, S.; Sandeep, K. Prediction of greenhouse gas emissions from agricultural fields with and without cover crops. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2022, 86, 1227–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Kong, D. Daily variation patterns of soil N2O and CO2 emissions in rice fields and determination of optimal observation time. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2014, 30, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Yao, P.; Lu, Q.; Chen, S.; Chen, Z.; Wu, H.; Ye, X. Effects of continuous overturning of ryegrass on diurnal variation of CO2 in tobacco-growing soil profile in central Henan Province. Acta Tabacaria Sin. 2024, 30, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, J.R.A.; Keith, A.S.; Rilner, A.F.; Abmael, S.C.; Abmael, S.C.; William, R.D.O.; Claudia, P.J.; Segundo, U.; Robert, M.B. Selection of the most suitable sampling time for static chambers for the estimation of daily mean N2O flux from soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 46, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cueva, A.; Bullock, S.H.; López-Reyes, E.; Vargas, R. Potential bias of daily soil CO2 efflux estimates due to sampling time. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Xu, W.X.; Su, T.Y.; Yu, L.; Jiang, Y.M.; Lu, J.L.; Liu, W.J.; Yang, Q. Effects of replacing chemical nitrogen fertilizer with organic fertilizer at different rates on soil nutrients and enzyme activities in Hainan rubber forest. J. Trop. Biol. 2024, 15, 745–755. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1078.S.20240328.1354.005.html (accessed on 13 September 2024).
- Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Yu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, J.; Liu, W.; Yang, Q. Responses of soil greenhouse gas emissions to different application rates of biochar in a subtropical Chinese chestnut plantation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 271, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Wu, J.; Cai, L.; Wang, Z. Study on the daily variation of greenhouse gas emissions from dry-crop farmland under different management modes of straw and biomass charcoal. Territ. Nat. Resour. Study 2024, 6, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.J.; Zhu, J.; Ji, H.; John, G.; Sha, L.; Song, Q.; Liu, Y.; Bai, X.; Lin, Y.; Gao, J.; et al. Drivers of difference in CO2 and CH4 emissions between rubber plantation and tropical rainforest soils. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 304–305, 108391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.; Stefanie, G.; Sergey, B.; Piepho, H.-P.; Rhett, D.H.; Xu, J.; Georg, C. Converting forests into rubber plantations weakened the soil CH4 sink in tropical uplands. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 2311–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xian, Y.; Tang, W.; Fang, M.; Song, B.; Hu, Q.; Wu, Z. Patterns and Drivers of Greenhouse Gas Emissions in a Tropical Rubber Plantation from Hainan, Danzhou. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.J.; Ji, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.P.; Sha, L.Q.; Liu, Y.T.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.; Dong, Y.; Bai, X.L.; et al. The effects of nitrogen fertilization on N2O emissions from a rubber plantation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammirato, C.; Wallman, M.; Weslien, P.; Klemedtsson, L.; Rütting, T. Measuring frequency and accuracy of annual nitrous oxide emission estimates. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 310, 108624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lun, X. Characteristics of daily changes in CO2, CH4, and N2O emissions from wheat fields under fertilizer and no-fertilizer measures. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2014, 23, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.Z.; Ning, T.Y.; Chi, S.Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.W.; Han, H.F.; Li, C.Q.; Li, Z.J. Diurnal variations of the greenhouse gases emission and their optimal observation duration under different tillage systems. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, J.; Li, R.; Yang, H.; Ma, J.; Sa, R. Characterization of daily changes of N2O and CO2 in spring maize fields under different irrigation measures and the influencing factors. Ecol. Sci. 2023, 42, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, E.; Vaneeckhaute, C. Greenhouse gas emissions from inorganic and organic fertilizer production and use: A review of emission factors and their variability. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 276, 111211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, N.A.; Madramootoo, C.A.; Zhang, T.; Tan, C.S. Soil nutrients and plant uptake parameters as related to greenhouse gas emissions. J. Environ. Qual. 2022, 51, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Q.; Ding, C.; Abubakari, S.M.; Feng, J.; Lei, M.; Gan, Z.; Zhu, B.; Hu, Y.-L. Contrasting impacts of fertilization on topsoil and subsoil greenhouse gas fluxes in a thinned Chinese fir plantation. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 359, 121055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Shi, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, T.; Ma, L.; Zheng, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhai, B. Responses of environmental and soil enzyme stoichiometric characteristics of wheat cropping system to fertilizer management in rain-fed areas of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 41520–41533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carla, C.P.; Dániel, T.; Johannes, R. Can moisture affect temperature dependences of microbial growth and respiration? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 156, 108223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, Q.; Xu, X.; Huang, G. Impact of irrigation and fertilization regimes on greenhouse gas emissions from the soil of mulching cultivated maize (Zea mays L.) field in the upper reaches of Yellow River, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Ma, W.; Yang, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, T. Effects of different fertilizer application modes on greenhouse gas emissions of watermelon in facilities. J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2025, 44, 527–536. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/12.1347.S.20240620.0853.002.html (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- Feng, Y.; Wang, N.; Xie, H.; Li, J.; Li, G.; Xue, L.; Fu, H.; Feng, Y.; Gerrard, E.J.P.; Chen, D. Livestock manure-derived hydrochar is more inclined to mitigate soil Global Warming Potential than raw materials based on soil stoichiometry analysis. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2023, 59, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Xing, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Di, H.; Tang, C.; Xu, J.; Li, Y. Soil acidification induced variation of nitrifiers and denitrifiers modulates N2O emissions in paddy fields. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-G.; Thomas, A.D.; Pelster, D.; Todd, S.R.; Alberto, S.-C. Greenhouse gas emissions in natural and agricultural lands in sub-Saharan Africa: Synthesis of available data and suggestions for further studies. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 4789–4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Z. Effects of Organic Substitution and Staged Application of Nitrogen Fertilizer on Soil Nitrogen Fate and Nitrogen Efficiency of Spring Wheat. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Song, F.; Yin, Z.; Chen, P.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, Z.; Wang, B.; Zheng, E. Organic fertilizer substitutions maintain maize yield and mitigate ammonia emissions but increase nitrous oxide emissions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 53115–53127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priya, E.; Sudipta, S.; Pradip, K.M. A review on slow-release fertilizer: Nutrient release mechanism and agricultural sustainability. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Aili-Buaidi, Y.; Yang, F.; He, Q. Winter soil respiration and its driving factors in the hinterland of Taklamakan Desert. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 6711–6719. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.2031.q.20141218.1100.009 (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- Andressa, U.A.; Daniele, R.C.; Eduardo, A.D.O.; Eduardo, H.; Jana, C.; Marta, P.-M.; Sergi, M.-B.; Carlos, A.M. Adjustments in photosynthetic pigments, PS II photochemistry and photoprotection in a tropical C4 forage plant exposed to warming and elevated [CO2]. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 194, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Hirano, T.; Sakaguchi, K.; Yamashita, S.; Cui, R.; Sun, L.; Liang, N. Spatiotemporal variation in soil methane uptake in a cool-temperate immature deciduous forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 184, 109094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Shen, L.; Su, W. Progress of research on the effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration on CH4 emission and related microbiological processes in rice fields. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 35, 2267–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, R.; Song, C.; Wang, L. Research progress on biochemical processes and influencing factors of wetland methane. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 42, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Li, W. Progress of research on factors affecting methane production and emission in paddy fields and emission reduction measures. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2024, 38, 475–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Zhang, F.; Bo, Q.; Tang, A.; Gao, J.R.; Wei, X.; Yue, S.; Shen, Y.; Li, S. Microbial and isotopomer analysis of N2O production pathways in calcareous film-mulched farmland. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2023, 59, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-F.; Whitaker, J.; Toet, S.; Amy, B.; Christian, A.D.; Niall, P.M. Diurnal variability in soil nitrous oxide emissions is a widespread phenomenon. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 4950–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Hayden, H.L.; Suter, H.; Hu, H.; Lam, S.K.; He, J.; Pauline, M.M.; Chen, D. The effect of temperature and moisture on the source of N2O and contributions from ammonia oxidizers in agricultural soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 53, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Yao, Y.; Guan, Y.; Mahran, S.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Lu, Y.; Xu, G.; Du, M.; Li, G.; et al. Effects of land use patterns on soil properties and nitrous oxide flux on a semi-arid environmental conditions of Loess Plateau China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 51, e02899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Lai, X.; Liao, K. Comparing the variations and controlling factors of soil N2O emissions and NO3−-N leaching on tea and bamboo hillslopes. Catena 2020, 188, 104463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatment Groups | Fertilizer Application in June from a Single Fertilization Pits | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urea (g) | Calcium Superphosphate (g) | Potassium Chloride (g) | Organic Fertilizers (kg) | |
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| NPK | 608.70 | 1166.00 | 300.00 | 0 |
| 25%M | 456.52 | 696.00 | 253.00 | 4.70 |
| 50%M | 304.35 | 236.00 | 207.00 | 9.30 |
| 75%M | 152.17 | 0 | 160.00 | 14.00 |
| 100%M | 0 | 0 | 110.00 | 19.00 |
| Treatment Groups | Average Daily Fluxes (mg m−2 h−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | CH4 | N2O | |
| CK | 194.1 ± 36.8 b | −0.0155 ± 0.0033 a | 0.011 ± 0.002 c |
| NPK | 137.0 ± 29.4 c | −0.0148 ± 0.0030 a | 0.028 ± 0.004 b |
| 25%M | 216.1 ± 36.0 b | −0.0152 ± 0.0023 a | 0.032 ± 0.005 ab |
| 50%M | 317.4 ± 53.2 ab | −0.0147 ± 0.0039 a | 0.040 ± 0.006 a |
| 75%M | 325.5 ± 62.0 ab | −0.0158 ± 0.0035 a | 0.026 ± 0.004 b |
| 100%M | 372.0 ± 70.6 a | −0.0160 ± 0.0043 a | 0.025 ± 0.005 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Chen, Q.; Ran, H.; Lu, W.; Xu, W.; Ali, W.; Yang, Q.; Liu, W.; Fang, M.; Yang, H. Daily Variation of Soil Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Rubber Plantations Under Different Levels of Organic Fertilizer Substitution. Forests 2025, 16, 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040706
Zhang W, Chen Q, Ran H, Lu W, Xu W, Ali W, Yang Q, Liu W, Fang M, Yang H. Daily Variation of Soil Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Rubber Plantations Under Different Levels of Organic Fertilizer Substitution. Forests. 2025; 16(4):706. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040706
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wangxin, Qingmian Chen, Hongyu Ran, Wen Lu, Wenxian Xu, Waqar Ali, Qiu Yang, Wenjie Liu, Mengyang Fang, and Huai Yang. 2025. "Daily Variation of Soil Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Rubber Plantations Under Different Levels of Organic Fertilizer Substitution" Forests 16, no. 4: 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040706
APA StyleZhang, W., Chen, Q., Ran, H., Lu, W., Xu, W., Ali, W., Yang, Q., Liu, W., Fang, M., & Yang, H. (2025). Daily Variation of Soil Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Rubber Plantations Under Different Levels of Organic Fertilizer Substitution. Forests, 16(4), 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040706







