Seasonal Water Use Patterns of Eucalyptus with Different Ages in Southern Subtropical China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.2.1. Collection of Rainfall Samples
2.2.2. Collection of Tree Stem (Xylem) Samples
2.2.3. Collection of Soil Samples
2.3. Sample Processing and Isotope Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
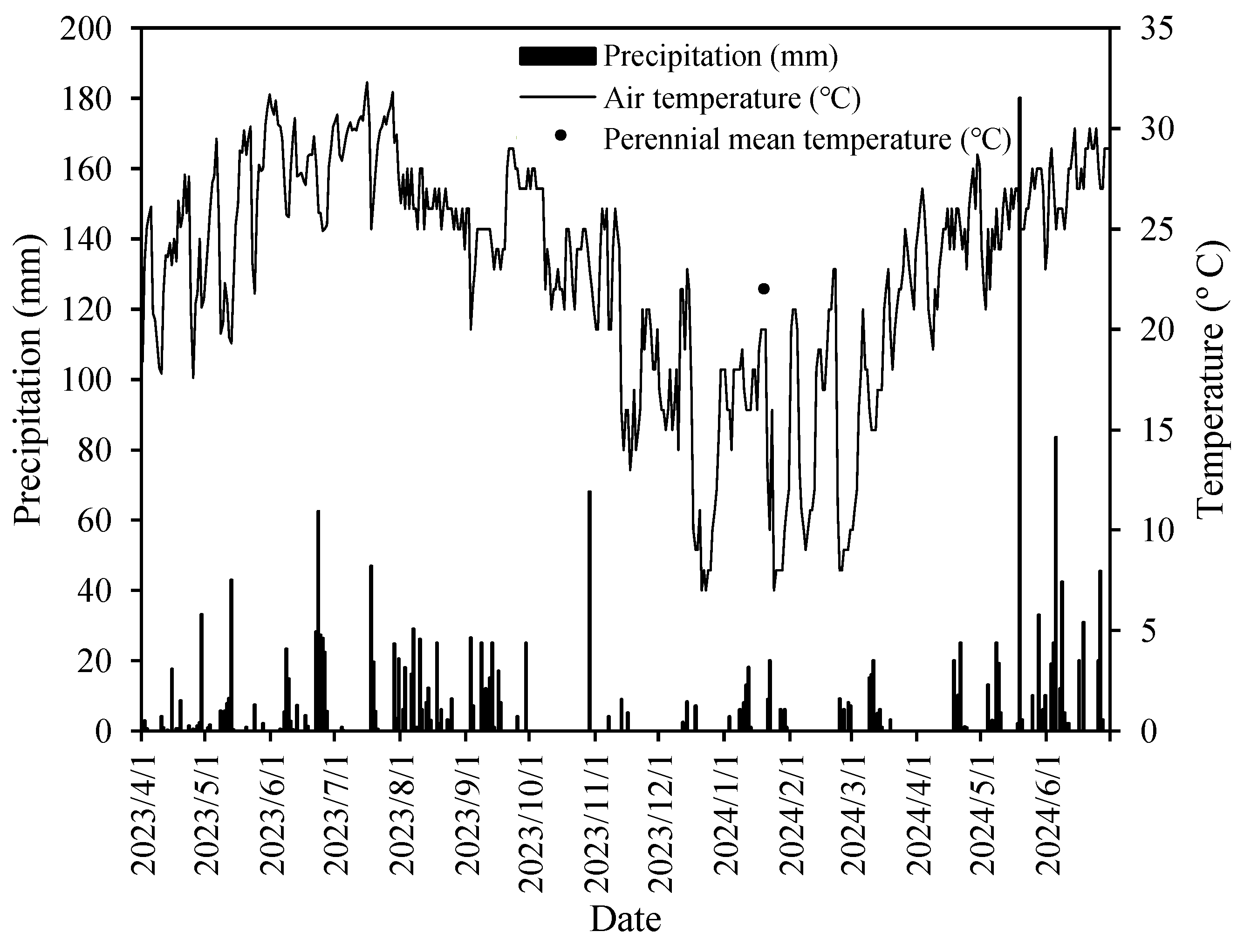
3.1. Meteorological and Environmental Conditions
3.2. Variation in Soil Water Content in Stands of Different Ages During Dry and Wet Seasons
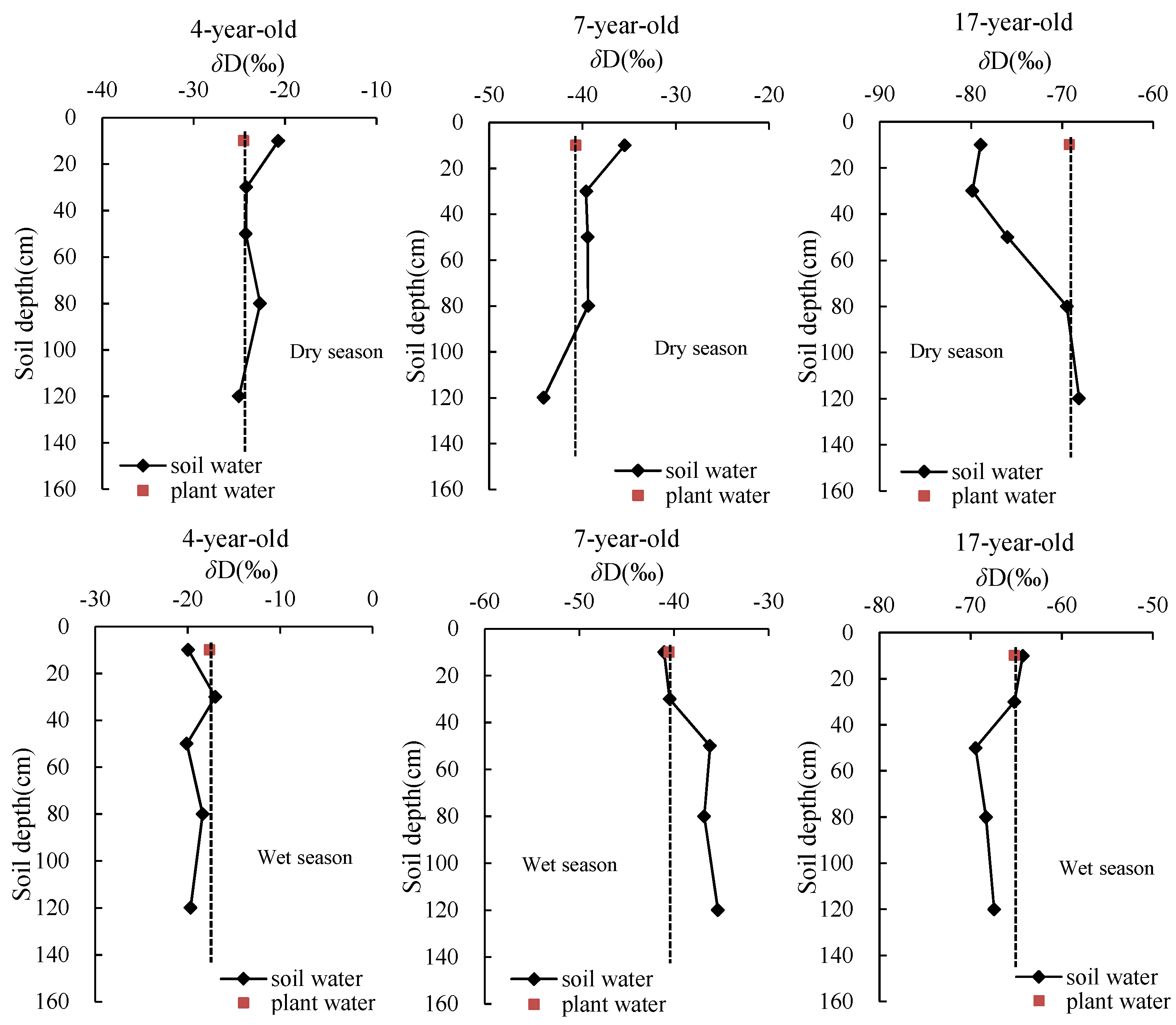
3.3. δD in Soil and Xylem Water
3.4. Water Use Patterns of Eucalyptus of Different Ages
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Water Content and Hydrogen Isotopes of Soil Water in Eucalyptus Plantations of Different Ages During Dry and Wet Seasons
4.2. Water Use Patterns of Eucalyptus of Different Ages During Dry and Wet Seasons
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosado, B.H.P.; Joly, C.A.; Burgess, S.S.O.; Oliveira, R.S.; Aidar, M.P.M. Changes in plant functional traits and water use in Atlantic rainforest: Evidence of conservative water use in spatio-temporal scales. Trees 2016, 30, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossiord, C.; Sevanto, S.; Dawson, T.E.; Adams, H.D.; Collins, A.D.; Dickman, L.T.; McDowell, N.G. Warming combined with more extreme precipitation regimes modifies the water sources used by trees. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.F.; Hui, D.F.; Liu, H.; Wang, F.M.; Yao, K.C.; Lu, H.F.; Ren, H.; Wang, J. Responses of plant water uptake sources to altered precipitation patterns in a tropical secondary forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 355, 110138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.Q.; Wu, Y.H.; Li, Y.J.; Liu, Y.Q. Effects of meteorological droughts on agricultural water resources in southern China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 548, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein, G.; Tayebeh, A.A.; Alireza, E.; Mohammad, B. The spatial-temporal changes in water balance components under future climate change in the Gorganroud Watershed, Iran. Water Cycle 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socha, J.; Hawryło, P.; Tymińska-Czabańska, L.; Reineking, B.; Lindner, M.; Netzel, P.; Grabska-Szwagrzyk, E.; Vallejos, R.; Reyer, C.P.O. Higher site productivity and stand age enhance forest susceptibility to drought-induced mortality. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 341, 109680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangi, E.; Dalmonech, D.; Cioccolo, E.; Marano, G.; Bianchini, L.; Puchi, P.F.; Grieco, E.; Cescatti, A.; Colantoni, A.; Chirici, G.; et al. Stand age diversity (and more than climate change) affects forests’ resilience and stability, although unevenly. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerhoulas, L.; Kolb, T.; Koch, G. Tree size, stand density, and the source of water used across seasons by ponderosa pine in northern Arizona. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 289, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.N.; Liu, W.J.; Chen, C.F. How do plants share water sources in a rubber-tea agroforestry system during the pronounced dry season? Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 236, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zhou, O.; Sun, Y.M.; Li, X.M.; Di, N.; Li, D.D.; Yilihamu, G.; Wang, Y.F.; Fu, J.Y.; Xi, B.Y.; et al. Effects of stand age and structure on root distribution and root water uptake in fast-growing poplar plantations. J. Hydrol. 2023, 616, 128831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.F.; An, J.; Zhao, X.N.; Gao, X.D.; Wu, P.; Huo, G.P.; Robinson, B.H. Age- and climate-related water use patterns of apple trees on China’s Loess Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voltas, J.; Lucabaugh, D.; Chambel, M.R.; Ferrio, J.P. Intraspecific variation in the use of water sources by the Circum-Mediterranean conifer Pinus halepensis. New Phytol. 2015, 208, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Zheng, X.J.; Yin, X.W.; Yue, Y.M.; Liu, R.; Xu, G.Q.; Li, Y. Seasonal variation in the groundwater dependency of two dominant woody species in a desert region of Central Asia. Plant Soil 2019, 444, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.W.; Huang, L.M.; Shao, M.A.; Zhang, Y.L.; Pan, Y.H. Water use pattern and transpiration of Mongolian pine plantations in relation to stand age on northern Loess Plateau of China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 330, 109320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, B.J.; Jiao, L.; Lu, N.; Li, J.Y.; Chen, W.L.; Wang, L.X. Age-related water use characteristics of Robinia pseudoacacia on the Loess Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 301–302, 108344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Forestry and Grassland Administration. Comprehensive Monitoring and Evaluation Report on Forest and Grassland Ecology in China; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2021. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gándara, J.; Ross, S.; Quero, G.; Gonzalo, D.; Figarola, G.; Viega, L. Differential water-use efficiency and growth among Eucalyptus grandis hybrids under two different rainfall conditions. For. Syst. 2020, 29, e006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campoe, O.C.; Alvares, C.A.; Carneiro, R.L.; Binkley, D.; Ryan, M.G.; Hubbard, R.M.; Stahl, J.; Moreira, G.; Moraes, L.F.; Stape, J.L. Climate and genotype influences on carbon fluxes and partitioning in Eucalyptus plantations. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 475, 118445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Du, A.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, J. Factors limiting the growth of Eucalyptus and the characteristics of growth and water use under water and fertilizer management in the dry season of Leizhou Peninsula, China. Agronomy 2019, 9, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehleringer, J.R.; Roden, J.; Dawson, T.E. Assessing ecosystem-level water relations through stable isotope ratio analyses. In Methods in Ecosystem Science; Sala, O.E., Jackson, R.B., Mooney, H.A., Howarth, R.W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 181–198. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.L.; Helliker, B.R.; Tang, X.H.; Li, F.; Zhou, Y.P.; Song, X. Stem water cryogenic extraction biases estimation in deuterium isotope composition of plant source water. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 33345–33350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehleringer, J.R.; Dawson, T.E. Water uptake by plants: Perspectives from stable isotope composition. Plant Cell Environ. 1992, 15, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, B.J.; Wang, L.X.; Lu, N.; Li, J.Y. Water use characteristics of the common tree species in different plantation types in the Loess Plateau of China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 288–289, 108020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, B.C.; Semmens, B.X. MixSIAR GUI User Manual, version 3.1; GitHub: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2013.
- Zheng, W.B.; Wang, S.Q.; Sprenger, M.; Liu, B.X.; Cao, J.S. Response of soil water movement and groundwater recharge to extreme precipitation in a headwater catchment in the North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2019, 576, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, N.E.; Froend, R.H. How important is groundwater availability and stream perenniality to riparian and floodplain tree growth? Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.F.; Yong, L.L.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.W.; Zhang, Z.X.; Xu, Y.X.; Sun, Z.G.; Sang, L.Y.; Wang, L. Evaporation, infiltration and storage of soil water in different vegetation zones in the Qilian Mountains: A stable isotope perspective. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 3771–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.H.; Xiao, B.; Ghanbarian, B. Increasing effect of biocrusts on evaporation is evidenced by simulating evaporation and diffusion experiments and water stable isotope analysis. J. Hydrol. 2024, 637, 131427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, L.L.; Zhu, G.F.; Wan, Q.Z.; Xu, Y.X.; Zhang, Z.X.; Sun, Z.G.; Ma, H.Y.; Sang, L.Y.; Liu, Y.W.; Guo, H.W.; et al. The soil water evaporation process from mountains based on the stable isotope composition in a headwater basin and northwest China. Water 2020, 12, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huo, S.Y.; Guo, J.; Sun, J.; Pan, J.; Wang, D.; Tan, Q.K.; Pei, B.B. Using hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes to estimate soil water evaporation loss under continuous evaporation conditions. Hydrol. Process. 2023, 37, e14885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, S.R.; Wan, X.C.; Jiang, C.Q.; Song, X.F.; Wang, J.X. Effects of rainfall on soil moisture and water movement in a subalpine dark coniferous forest in southwestern China. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 3800–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazis, C.; Feng, X. A stable isotope study of soil water: Evidence for mixing and preferential flow paths. Geoderma 2004, 119, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benettin, P.; Volkmann, T.H.M.; von Freyberg, J.; Frentress, J.; Penna, D.; Dawson, T.E.; Kirchner, J.W. Effects of climatic seasonality on the isotopic composition of evaporating soil waters. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 2881–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.Z.; Qiu, Z.J.; Zhou, G.Y.; Zuecco, G.; Liu, Y.; Wen, Y. Soil water hydraulic redistribution in a subtropical monsoon evergreen forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.T.; Zhu, G.F.; Bai, W.W.; Yuan, R.P.; Zhang, Y. Root distribution and water uptake applied by hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes for lianas in northwest China. Forests 2024, 15, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, M.; Leistert, H.; Gimbel, K.; Weiler, M. Illuminating hydrological processes at the soil-vegetation-atmosphere interface with water stable isotopes. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 674–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCole, A.A.; Stern, L.A. Seasonal water use patterns of Juniperus ashei on the Edwards Plateau, Texas, based on stable isotopes in water. J. Hydrol. 2007, 342, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.P.; Chen, H.S.; Wang, K.L.; Tan, W.; Deng, P.Y.; Yang, J. Seasonal water use patterns of woody species growing on the continuous dolostone outcrops and nearby thin soils in subtropical China. Plant Soil 2011, 341, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wen, X.F.; Sun, X.M. Seasonal variations in depth of water uptake for a subtropical coniferous plantation subjected to drought in an East Asian monsoon region. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 201, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.Q.; Xu, Q.; Zuo, H.J.; Xu, W.B.; Diao, K.; Zhang, B.B. Changes in water uptake patterns of trees in forests across a successional gradient in southern China. Forests 2024, 15, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.C.; Zheng, X.T.; He, W.; Lin, W.; Yan, G.Z.; Zhu, H.; Peng, C.L. Different responses of macro- and microelement contents of 41 subtropical plants to environmental changes in the wet and dry seasons. J. Plant Ecol. 2023, 16, rtad027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Zhang, X.D.; Liu, M.; Wang, C.T.; Manuel, L.; Hu, L. Precipitation-induced soil properties and plant communities mediate root strategies in an alpine meadow. J. Plant Ecol. 2024, 17, rtae072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Zhao, P.; McCarthy, H.R.; Ouyang, L.; Niu, J.F.; Zhu, L.W.; Ni, G.Y.; Huang, Y.Q. Hydraulic balance of a Eucalyptus urophylla plantation in response to periodic drought in low subtropical China. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schume, H.; Hailu, Z.; Hailu, T.; Sieghardt, M.; Godbold, D.L. Spatial analysis of soil water depletion and biomass production in the transition zone between a Eucalyptus camaldulensis stand and a maize field in Ethiopia. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 320, 108956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Wu, Z.Y.; He, H. Interpreting seasonal droughts over the Yangtze River Basin utilizing anomalies of local-scale atmospheric circulation. J. Hydrol. 2025, 58, 102231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Hui, W.K.; Zhao, F.Y.; Wang, P.Y.; Su, C.Y.; Gong, W. Physiology of plant responses to water stress and related genes: A review. Forests 2022, 13, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Stand Age (a) | Geographic Location | Altitude (m) | Average DBH (cm) | Average Height (m) | Density (Tree∙ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 108°11′46″ E 22°43′58″ N | 176–187 | 12 | 19 | 1248 |
| 7 | 108°11′54″ E 22°41′24″N | 201–208 | 17 | 24 | 1112 |
| 17 | 108°11′43″ E 22°44′27″ N | 174–181 | 34 | 37 | 735 |
| Stand Age (a) | Soil Texture (%) | Soil Depth (cm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–20 | 20–40 | 40–60 | 60–90 | 90–150 | ||
| 4 | Clay | 23.7 | 34.5 | 32.6 | 24.4 | 26.5 |
| Silt | 46.8 | 35.4 | 26.1 | 38.9 | 34.3 | |
| Sand | 29.5 | 30.1 | 41.3 | 36.7 | 39.2 | |
| 7 | Clay | 26.2 | 32.1 | 24.9 | 22.8 | 25.4 |
| Silt | 38.5 | 37.2 | 40.5 | 36.3 | 30.5 | |
| Sand | 35.3 | 30.7 | 34.6 | 40.9 | 44.1 | |
| 17 | Clay | 24.8 | 35.2 | 30.1 | 26.9 | 20.2 |
| Silt | 33.9 | 40.2 | 36.5 | 38.4 | 47.5 | |
| Sand | 41.3 | 24.6 | 33.4 | 34.7 | 32.3 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuo, H.; Xu, Q.; Gao, D.; Xu, W.; Diao, K.; Zhang, B. Seasonal Water Use Patterns of Eucalyptus with Different Ages in Southern Subtropical China. Forests 2025, 16, 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040708
Zuo H, Xu Q, Gao D, Xu W, Diao K, Zhang B. Seasonal Water Use Patterns of Eucalyptus with Different Ages in Southern Subtropical China. Forests. 2025; 16(4):708. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040708
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuo, Haijun, Qing Xu, Deqiang Gao, Wenbin Xu, Ke Diao, and Beibei Zhang. 2025. "Seasonal Water Use Patterns of Eucalyptus with Different Ages in Southern Subtropical China" Forests 16, no. 4: 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040708
APA StyleZuo, H., Xu, Q., Gao, D., Xu, W., Diao, K., & Zhang, B. (2025). Seasonal Water Use Patterns of Eucalyptus with Different Ages in Southern Subtropical China. Forests, 16(4), 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040708







