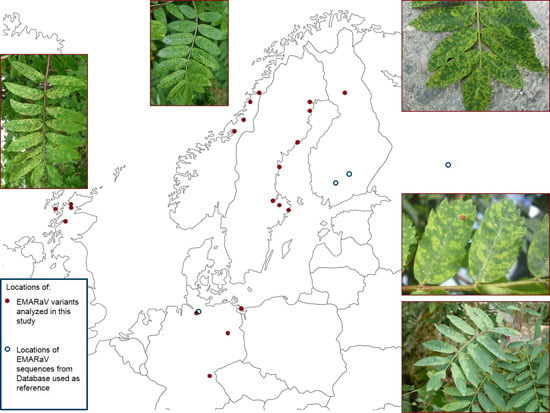
Genetic Variability and Phylogeny of European mountain ash ringspot-associated virus RNA3 and RNA4
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Experimental Section
| EMARaV Variants | Location of Sampled Rowans | RNA3 | RNA4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sweden (S) | E51605 | Lulea | HG799707 | HG799749 |
| E51586 | Pitea | HG799704 | HG799746 | |
| E51587 | Pitea | HG799705 | HG799747 | |
| E51594 | Örnsköldsvik | HG799706 | HG799748 | |
| E53016 | Skärsa | HG799711 | HG799753 | |
| E53011 | Östa | HG799710 | HG799752 | |
| E53009 | Heby | HG799709 | HG799751 | |
| E52165 | Stockholm, Vasa | HG799708 | HG799750 | |
| Finland (FIN) | E51607 | Rovaniemi | HG799712 | HG799754 |
| E52278 | Rovaniemi | HG799713 | HG799755 | |
| E52279 | Rovaniemi | HG799714 | HG799756 | |
| E52280 | Rovaniemi | HG799715 | HG799757 | |
| Scotland (GB) | E52284 | Ullapool Hill | HG799717 | HG799759 |
| E52286 | Ullapool Hill | HG799718 | HG799760 | |
| E52287 | Corrieshalloch | HG799719 | HG799761 | |
| E52283 | Dunvegan | HG799716 | HG799758 | |
| E52288 | Kinlochleven | HG799720 | HG799762 | |
| Germany (D) | E52895 | Benz | HG799732 | HG799774 |
| E52991 | Hamburg | HG799739 | HG799781 | |
| E52992 | Hamburg | HG799740 | HG799782 | |
| E52993 | Hamburg | HG799741 | HG799783 | |
| E52994 | Hamburg | HG799742 | HG799784 | |
| E52995 | Hamburg | HG799743 | HG799785 | |
| E52996 | Hamburg | HG799744 | HG799786 | |
| E52997 | Hamburg | HG799745 | HG799787 | |
| E51609 | Berlin | HG799730 | HG799772 | |
| E52897 | Berlin | HG799733 | HG799775 | |
| E52900 | Berlin | HG799734 | HG799776 | |
| E52901 | Berlin | HG799735 | HG799777 | |
| E52905 | Berlin | HG799736 | HG799778 | |
| E52907 | Berlin | HG799737 | HG799779 | |
| E52990 | Berlin | HG799738 | HG799780 | |
| E52293 | Fichtelgebirge | HG799731 | HG799773 | |
| Norway (N) | E53111 | Mo i Rana | HG799721 | HG799763 |
| E53112 | Mo i Rana | HG799722 | HG799764 | |
| E53113 | Mo i Rana | HG799723 | HG799765 | |
| E53114 | Mo i Rana | HG799724 | HG799766 | |
| E53116 | Mosjoen | HG799725 | HG799767 | |
| E53117 | Mosjoen | HG799726 | HG799768 | |
| E53118 | Formofossen | HG799727 | HG799769 | |
| E53119 | Formofossen | HG799728 | HG799770 | |
| E53120 | Skatval | HG799729 | HG799771 |
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sequence Variability of EMARaV RNA3 and the Deduced p4 Protein
| Genome Region | Compared EMARaV Variants | Nucleotide Sequence Identity | Amino Acid Sequence Identity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variants from GB, S, FIN, D, and 3 from N (E53116–E53118) | 6 of 9 Variants from N (E53111–E53114, E53119–E53120) | Variants from GB, S, FIN, D, and 3 from N (E53116–E53118) | 6 of 9 Variants from N (E53111–E53114, E53119–E53120) | ||
| RNA3 5′ UTR (94 nt) | 33 (42) variants from GB, S, FIN, D and 3 from N (E53116–E53118) | 95.7% to 100% | 84% to 91.4% | - | - |
| 6 (9) variants from N (E53111–E53114, E53119, E53120) | 84% to 91.4% | 96.8% to 100% | - | - | |
| p3 (945 nt; 315 aa) | 33 (42) variants from GB, S, FIN, D and 3 from N (E53116–E53118) | 95.3% to 100% | 85.7% to 86.9% | 97.4% to 100% | 92.6% to 94.9% |
| 6 (9) variants from N (E53111–E53114, E53119, E53120) | 85.7% to 86.9% | 98.5% to 100% | 92.6% to 94.9% | 97.1% to 100% | |
| RNA3 3′ UTR (435–445 nt) | 33 (42) variants from GB, S, FIN, D and 3 from N (E53116–E53118) | 93.7% to 100% | 69.6% to 77.5% | - | - |
| 6 (9) variants from N (E53111–E53114, E53119, E53120) | 69.6% to 77.5% | 90.1% to 100% | - | - | |
| p4 coding region, primer sequences removed (656 nt; 218 aa) | 33 (42) variants from GB, S, FIN, D and 3 from N (E53116–E53118) | 97.4% to 100% | 97.5% to 100% | 97.2% to 100% | 96.7% to 99.5% |
| 6 (9) variants from N (E53111–E53114, E53119, E53120) | 97.5% to 100% | 97.4% to 100% | 96.7% to 99.5% | 97.2% to 99.5% | |
3.2. Phylogenetic Relationships Based on p3 and p4 Protein Sequences

3.3. Selection Pressure on EMARaV Nucleocapsid (p3) and p4 Protein
| dN | sd (dN) | sd (dN)/dN | dS | sd (dS) | sd (dS)/ dS | dN/dS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p3 | 0.013 | 0.007 | 0.492 | 0.266 | 0.034 | 0.128 | 0.050 |
| p4 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.333 | 0.032 | 0.008 | 0.247 | 0.116 |
3.4. Genetic Diversity in the Nucleocapsid Protein of Norwegian Isolates
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Büttner, C.; von Bargen, S.; Bandte, M.; Mühlbach, H.-P. Forest diseases caused by viruses. In Infectious Forest Diseases; Gonthier, P.N.G., Ed.; CABI: Wallingford, Oxfordshire, UK, 2013; pp. 50–75. [Google Scholar]
- Benthack, W.; Mielke, N.; Büttner, C.; Mühlbach, H.P. Double-stranded RNA pattern and partial sequence data indicate plant virus infection associated with the ringspot disease of European mountain ash (Sorbus aucuparia L.). Arch. Virol. 2005, 150, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielke, N.; Mühlbach, H.P. A novel, multipartite, negative-strand RNA virus is associated with the ringspot disease of European mountain ash (Sorbus aucuparia L.). J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kegler, H. Das Ringfleckenmosaik der Eberesche (Sorbus aucuparia L.). J. Phytopathol. 1960, 37, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamberg, L.; Malmivaara-Lämsä, M.; Lehvävirta, S.; Kotze, D. The effects of soil fertility on the abundance of rowan (Sorbus aucuparia L.) in urban forests. Plant Ecol. 2009, 204, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sæbø, A.; Benedikz, T.; Randrup, T.B. Selection of trees for urban forestry in the Nordic countries. Urban For.Urban Green. 2003, 2, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robel, J.; Bandte, M.; Mühlbach, H.-P.; von Bargen, S.; Büttner, C. Ein neuartiges virus in Sorbus aucuparia L.: Nachweis und Verbreitung des European mountain ash ringspot-associated virus (EMARaV). In Jahrbuch der Baumpflege; Dujesiefken, D., Ed.; Haymarket Media: Braunschweig, Germany, 2013; pp. 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Von Bargen, S.; Büttner, T.; Mühlbach, H.P.; Robel, J.; Büttner, C. First Report of European mountain ash ringspot-associated virus in Sorbus aucuparia in Norway. Plant Disease 2014, 98, 700–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimová, L.; Marek, M.; Konrady, M.; Ryšánek, P. Newly identified host range of European mountain ash ringspot-associated virus (EMARaV) and its distribution in the Czech Republic. For. Pathol. 2015, 45, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, W.A. Transmission of plant viruses. In Virology of Flowering Plants; Stevens, W.A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 41–68. [Google Scholar]
- Führling, M.; Büttner, C. Transmission experiments of viruses to woody seedlings (Quercus robur L. and Sorbus aucuparia L.) by grafting and mechanical inoculation. Eur. J. For. Pathol. 1995, 25, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke-Ehret, N.; Thoma, J.; Schlatermund, N.; Mühlbach, H.P. Detection of European mountain ash ringspot-associated virus-specific RNA and protein P3 in the pear leaf blister mite Phytoptus pyri (Eriophyidae). Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielke-Ehret, N.; Mühlbach, H.-P. Emaravirus: A novel genus of multipartite, negative strand RNA plant viruses. Viruses 2012, 4, 1515–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mühlbach, H.-P.; Mielke-Ehret, N. Emaravirus. In Virus Taxonomy, 9th ed.; King, A.M.Q., Adams, M.J., Carstens, E.B., Lefkowitz, E.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 767–770. [Google Scholar]
- Laney, A.G.; Keller, K.E.; Martin, R.R.; Tzanetakis, I.E. A discovery 70 years in the making: Characterization of the Rose rosette virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 1727–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGavin, W.J.; Mitchell, C.; Cock, P.J.; Wright, K.M.; Macfarlane, S.A. Raspberry leaf blotch virus, a putative new member of the genus Emaravirus, encodes a novel genomic RNA. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbeaino, T.; Digiaro, M.; Martelli, G.P. Complete nucleotide sequence of four RNA segments of fig mosaic virus. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 1719–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbeaino, T.; Digiaro, M.; Uppala, M.; Sudini, H. Deep sequencing of pigeonpea sterility mosaic virus discloses five RNA segments related to emaraviruses. Virus Res. 2014, 188, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatineni, S.; McMechan, A.J.; Wosula, E.N.; Wegulo, S.N.; Graybosch, R.A.; French, R.; Hein, G.L. An eriophyid mite-transmitted plant virus contains eight genomic RNA segments with unusual heterogeneity in the nucleocapsid protein. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11834–11845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Sabanadzovic, S.; Keller, K.; Martin, R.; Tzanetakis, I. A putative new emaravirus associated with blackberry yellow vein disease. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Virus and Other Transmissible Fruit Crop Diseases, Rome, Italy, 3–8 June 2012; pp. 360–364.
- Elbeaino, T.; Digiaro, M.; Uppala, M.; Sudini, H. Deep sequencing of dsRNAs recovered from mosaic-diseased pigeonpea reveals the presence of a novel Emaravirus: Pigeonpea sterility mosaic virus 2. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 2019–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laney, A.G. Characterization of the Causal Agents of Rose Rosette and Redbud Yellow Ringspot; University of Arkansas: Fayetteville, NC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Y.; Tugume, A.K.; Valkonen, J.P.T. Small-RNA deep sequencing reveals Arctium tomentosum as a natural host of Alstroemeria virus X and a new putative Emaravirus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melzer, M.; Sugano, J.; Uchida, J.; Kawate, M.; Borth, W.; Hu, J. Partial characterization of a novel emara-like virus from Cordyline fruticosa (L.) with ti ringspot disease. In Proceedings of 2014 APS-CPS Joint Meeting, Minneapolis, MA, USA, 9–13 August 2014; pp. 79–79.
- Elbeaino, T.; Whitfield, A.; Sharma, M.; Digiaro, M. Emaravirus-specific degenerate PCR primers allowed the identification of partial RNA-dependent RNA polymerase sequences of Maize red stripe virus and Pigeonpea sterility mosaic virus. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 188, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, C.; Karlin, D.G.; Lu, Y.; Wright, K.; Chen, J.; MacFarlane, S. Experimental and bioinformatic evidence that Raspberry leaf blotch emaravirus P4 is a movement protein of the 30K superfamily. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Arenal, F.; Fraile, A.; Malpica, J.M. Variability and genetic structure of plant virus populations. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2001, 39, 157–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta-Leal, R.; Duffy, S.; Xiong, Z.; Hammond, R.W.; Elena, S.F. Advances in plant virus evolution: Translating evolutionary insights into better disease management. Phytopathology 2011, 101, 1136–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallinen, A.K.; Lindberg, I.L.; Tugume, A.K.; Valkonen, J.P. Detection, distribution, and genetic variability of European mountain ash ringspot-associated virus. Phytopathology 2009, 99, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valkonen, J.P.T.; Rännäli, M. First Report of European mountain ash ringspot-associated virus in Sorbus aucuparia from Eastern Karelia, Russia. Plant Disease 2010, 94, 921–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Bargen, S.; Arndt, N.; Robel, J.; Jalkanen, R.; Büttner, C. Detection and genetic variability of European mountain ash ringspot-associated virus (EMARaV) in Sweden. For. Pathol. 2013, 43, 429–432. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrière, G.; Gouy, M. WWW-query: An on-line retrieval system for biological sequence banks. Biochimie 1996, 78, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korber, B. HIV signature and sequence variation analysis. In Computational and Evolutionary Analysis of HIV Molecular Sequences; Rodrigo, G.A., Learn, G.H., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 55–72. [Google Scholar]
- Nei, M.; Gojobori, T. Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1986, 3, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gonzales, M.J.; Dugan, J.M.; Shafer, R.W. Synonymous-non-synonymous mutation rates between sequences containing ambiguous nucleotides (Syn-SCAN). Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 886–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, S.; Akiyama, M.; Aoki, K.; Sugaya, Y.; Higuchi, K.; Hiraoka, M.; Miki, Y.; Saitoh, N.; Yoshiyama, K.; Ihara, K.; et al. DNA replication errors produced by the replicative apparatus of Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 289, 835–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walia, J.J.; Willemsen, A.; Elci, E.; Caglayan, K.; Falk, B.W.; Rubio, L. Genetic variation and possible mechanisms driving the evolution of worldwide Fig mosaic virus isolates. Phytopathology 2014, 104, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsompana, M.; Abad, J.; Purugganan, M.; Moyer, J.W. The molecular population genetics of the Tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV) genome. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roßbach, J.; Dieckmann, H.L.; Büttner, T.; Mühlbach, H.-P.; Von Bargen, S.; Büttner, C. Genetic Variability and Phylogeny of European mountain ash ringspot-associated virus RNA3 and RNA4. Forests 2015, 6, 4072-4087. https://doi.org/10.3390/f6114072
Roßbach J, Dieckmann HL, Büttner T, Mühlbach H-P, Von Bargen S, Büttner C. Genetic Variability and Phylogeny of European mountain ash ringspot-associated virus RNA3 and RNA4. Forests. 2015; 6(11):4072-4087. https://doi.org/10.3390/f6114072
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoßbach, Jenny, Heike Luisa Dieckmann, Theresa Büttner, Hans-Peter Mühlbach, Susanne Von Bargen, and Carmen Büttner. 2015. "Genetic Variability and Phylogeny of European mountain ash ringspot-associated virus RNA3 and RNA4" Forests 6, no. 11: 4072-4087. https://doi.org/10.3390/f6114072
APA StyleRoßbach, J., Dieckmann, H. L., Büttner, T., Mühlbach, H.-P., Von Bargen, S., & Büttner, C. (2015). Genetic Variability and Phylogeny of European mountain ash ringspot-associated virus RNA3 and RNA4. Forests, 6(11), 4072-4087. https://doi.org/10.3390/f6114072