Results of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus (TBEV) Diagnostics in an Endemic Area in Southern Germany, 2007 to 2022
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Patient Samples
2.2. Determination of TBEV IgM and IgG Antibodies
2.3. Detection of TBEV RNA by Real-Time PCR
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Laboratory-Confirmed Acute TBEV Infections
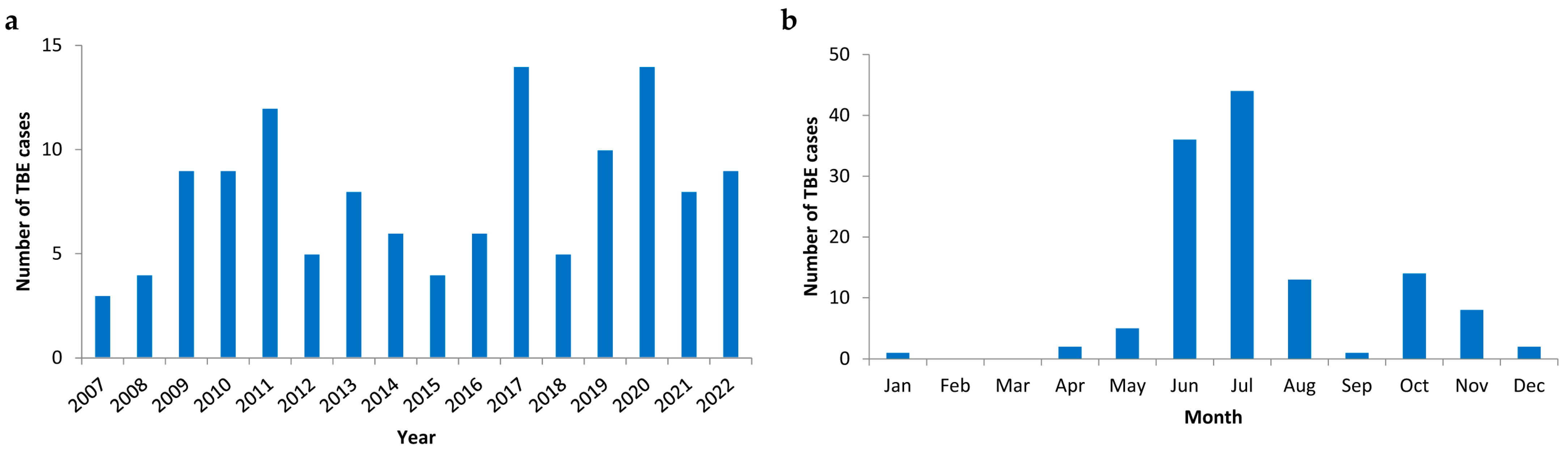
3.2. Temporal Distribution of TBE Cases
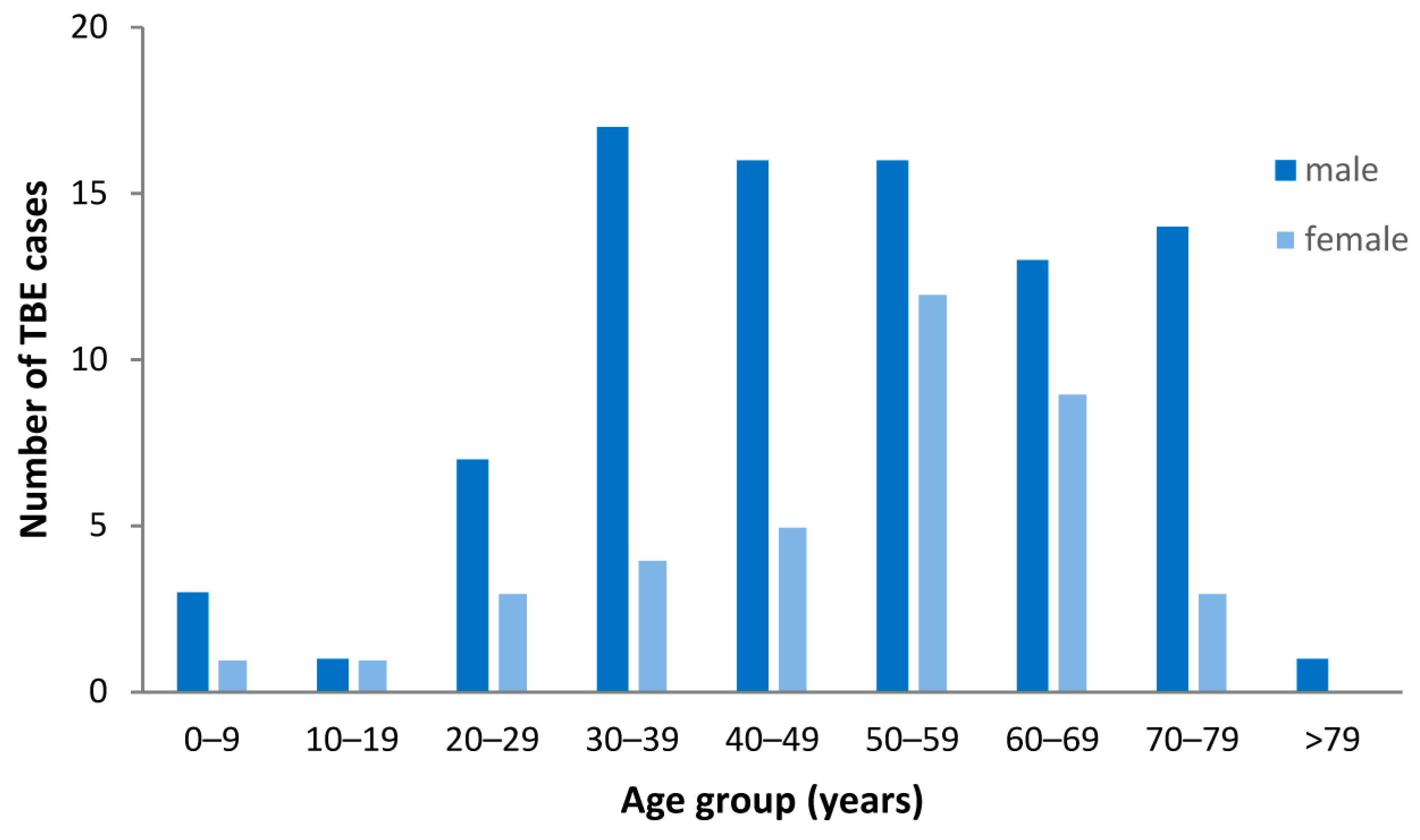
3.3. Demographic Characteristics of TBE Patients
3.4. Positive Rates in TBEV Diagnostics
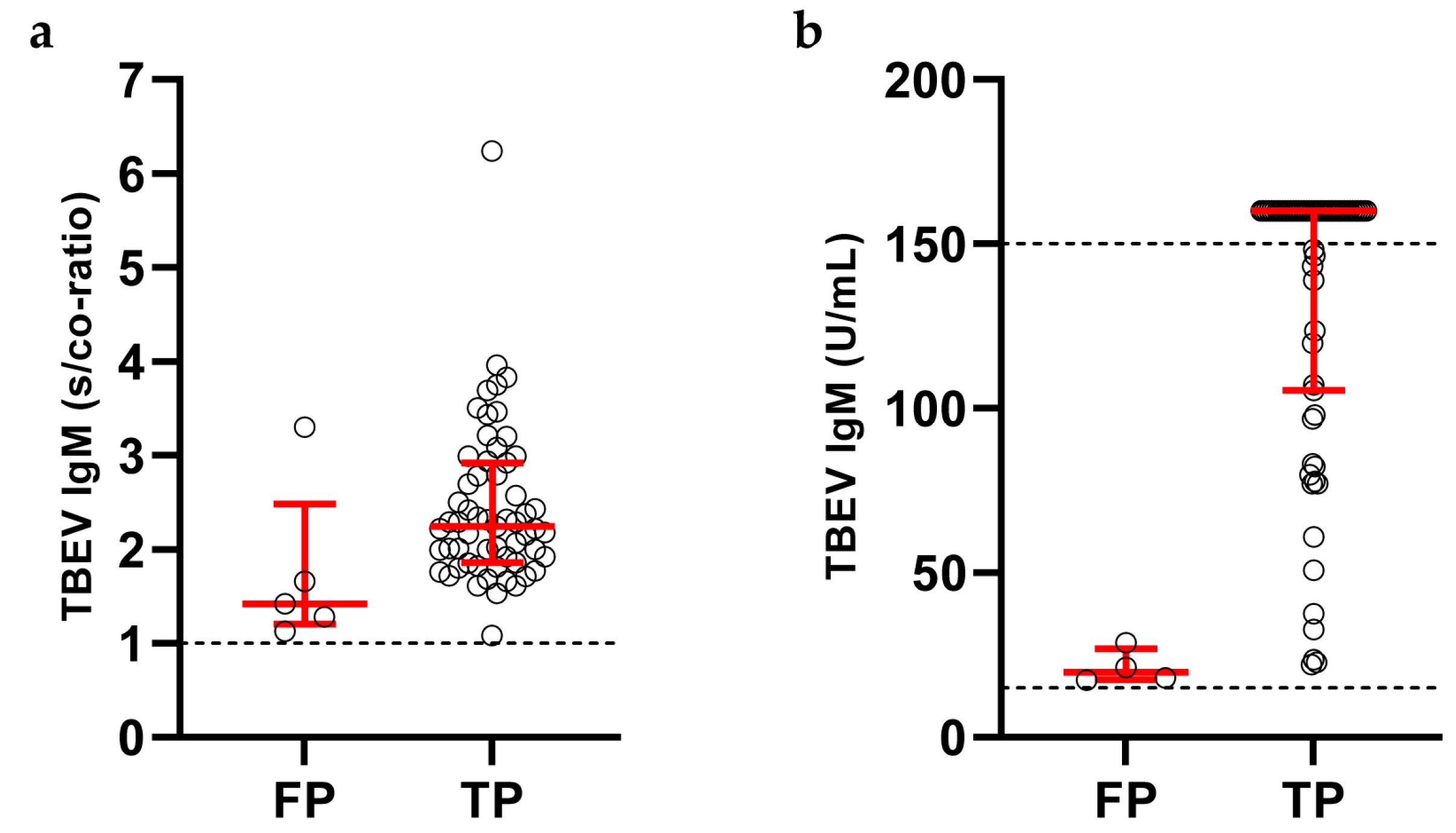
3.5. Clinical Performance of TBEV Antibody Detection in Serum
3.6. Clinical Performance of TBEV IgG Detection in Paired Serum-CSF Samples
3.7. Clinical Performance of TBEV Real-Time PCR
3.8. Seroprevalence of TBEV IgG Antibodies in Non-TBE Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lindquist, L.; Vapalahti, O. Tick-borne encephalitis. Lancet 2008, 371, 1861–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pustijanac, E.; Bursic, M.; Talapko, J.; Skrlec, I.; Mestrovic, T.; Lisnjic, D. Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus: A Comprehensive Review of Transmission, Pathogenesis, Epidemiology, Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, and Prevention. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagostin, F.; Tagliapietra, V.; Marini, G.; Cataldo, C.; Bellenghi, M.; Pizzarelli, S.; Cammarano, R.R.; Wint, W.; Alexander, N.S.; Neteler, M.; et al. Ecological and environmental factors affecting the risk of tick-borne encephalitis in Europe, 2017 to 2021. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2300121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Heuverswyn, J.; Hallmaier-Wacker, L.K.; Beauté, J.; Dias, J.G.; Haussig, J.M.; Busch, K.; Kerlik, J.; Markowicz, M.; Mäkelä, H.; Nygren, T.M.; et al. Spatiotemporal spread of tick-borne encephalitis in the EU/EEA, 2012 to 2020. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2200543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelitsch, A.; Wernike, K.; Klaus, C.; Dobler, G.; Beer, M. Exploring the Reservoir Hosts of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockmann, S.O.; Oehme, R.; Buckenmaier, T.; Beer, M.; Jeffery-Smith, A.; Spannenkrebs, M.; Haag-Milz, S.; Wagner-Wiening, C.; Schlegel, C.; Fritz, J.; et al. A cluster of two human cases of tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) transmitted by unpasteurised goat milk and cheese in Germany, May 2016. Eurosurveillance 2018, 23, 17–0036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martello, E.; Gillingham, E.L.; Phalkey, R.; Vardavas, C.; Nikitara, K.; Bakonyi, T.; Gossner, C.M.; Leonardi-Bee, J. Systematic review on the non-vectorial transmission of Tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEv). Ticks Tick. Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 102028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, A.K.; Springer, A.; Dobler, G.; Bestehorn-Willmann, M.; Monazahian, M.; Strube, C. New and Confirmed Foci of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus (TBEV) in Northern Germany Determined by TBEV Detection in Ticks. Pathogens 2022, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiffi, G.; Grandgirard, D.; Leib, S.L.; Chrdle, A.; Ruzek, D. Tick-borne encephalitis: A comprehensive review of the epidemiology, virology, and clinical picture. Rev. Med. Virol. 2023, 33, e2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygren, T.M.; Pilic, A.; Bohmer, M.M.; Wagner-Wiening, C.; Wichmann, O.; Hellenbrand, W. Recovery and sequelae in 523 adults and children with tick-borne encephalitis in Germany. Infection 2023, 51, 1503–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemieniako-Werszko, A.; Czupryna, P.; Moniuszko-Malinowska, A.; Dunaj-Małyszko, J.; Pancewicz, S.; Grygorczuk, S.; Zajkowska, J. Anti-TBE Intrathecal Synthesis as a Prediction Marker in TBE Patients. Pathogens 2022, 11, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwaiger, M.; Cassinotti, P. Development of a quantitative real-time RT-PCR assay with internal control for the laboratory detection of tick borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) RNA. J. Clin. Virol. 2003, 27, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreier, J.; Stormer, M.; Kleesiek, K. Use of bacteriophage MS2 as an internal control in viral reverse transcription-PCR assays. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4551–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellenbrand, W.; Kreusch, T.; Böhmer, M.M.; Wagner-Wiening, C.; Dobler, G.; Wichmann, O.; Altmann, D. Epidemiology of Tick-Borne Encephalitis (TBE) in Germany, 2001–2018. Pathogens 2019, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert Koch-Institut. FSME: Risikogebiete in Deutschland [TBE: Risk Areas in Germany]. Epid. Bull 2023, 9, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert Koch-Institut: SurvStat@RKI 2.0. Available online: https://survstat.rki.de (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- Nygren, T.M.; Pilic, A.; Böhmer, M.M.; Wagner-Wiening, C.; Wichmann, O.; Harder, T.; Hellenbrand, W. Tick-Borne Encephalitis Risk Increases with Dog Ownership, Frequent Walks, and Gardening: A Case-Control Study in Germany 2018–2020. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert Koch-Institut. Infektionsepidemiologisches Jahrbuch Meldepflichtiger Krankheiten für 2020, Page 34/35. Berlin 2021. Available online: https://www.rki.de/DE/Content/Infekt/Jahrbuch/Jahrbuch_2020.html?nn=2374622 (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- Friedsam, A.M.; Brady, O.J.; Pilic, A.; Dobler, G.; Hellenbrand, W.; Nygren, T.M. Geo-Spatial Characteristics of 567 Places of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Infection in Southern Germany, 2018–2020. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Tick-borne encephalitis. In ECDC Annual Epidemiological Report for 2020; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Semenza, J.C.; Paz, S. Climate change and infectious disease in Europe: Impact, projection and adaptation. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2021, 9, 100230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slunge, D.; Jore, S.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Jepsen, M.T.; Boman, A. Who is afraid of ticks and tick-borne diseases? Results from a cross-sectional survey in Scandinavia. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, M.T.; Jokelainen, P.; Jore, S.; Boman, A.; Slunge, D.; Krogfelt, K.A. Protective practices against tick bites in Denmark, Norway and Sweden: A questionnaire-based study. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reusken, C.; Boonstra, M.; Rugebregt, S.; Scherbeijn, S.; Chandler, F.; Avšič-Županc, T.; Vapalahti, O.; Koopmans, M.; GeurtsvanKessel, C.H. An evaluation of serological methods to diagnose tick-borne encephalitis from serum and cerebrospinal fluid. J. Clin. Virol. 2019, 120, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velay, A.; Solis, M.; Barth, H.; Sohn, V.; Moncollin, A.; Neeb, A.; Wendling, M.J.; Fafi-Kremer, S. Comparison of six commercial tick-borne encephalitis IgM and IgG ELISA kits and the molecular characterization of their antigenic design. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 90, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobler, G.; Kaier, K.; Hehn, P.; Bohmer, M.M.; Kreusch, T.M.; Borde, J.P. Tick-borne encephalitis virus vaccination breakthrough infections in Germany: A retrospective analysis from 2001 to 2018. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1090.e7–1090.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunther, G.; Haglund, M.; Lindquist, L.; Skoldenberg, B.; Forsgren, M. Intrathecal IgM, IgA and IgG antibody response in tick-borne encephalitis. Long-term follow-up related to clinical course and outcome. Clin. Diagn. Virol. 1997, 8, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grygorczuk, S.; Dunaj-Małyszko, J.; Czupryna, P.; Sulik, A.; Toczyłowski, K.; Siemieniako-Werszko, A.; Żebrowska, A.; Pancewicz, S.; Moniuszko-Malinowska, A. The Detectability of the Viral RNA in Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Tick-Borne Encephalitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, A.; Nagy, O.; Tarcsai, K.; Farkas, A.; Takacs, M. First detection of tick-borne encephalitis virus RNA in clinical specimens of acutely ill patients in Hungary. Ticks Tick. Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchhammer-Stockl, E.; Kunz, C.; Mandl, C.W.; Heinz, F.X. Identification of tick-borne encephalitis virus ribonucleic acid in tick suspensions and in clinical specimens by a reverse transcription-nested polymerase chain reaction assay. Clin. Diagn. Virol. 1995, 4, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saksida, A.; Duh, D.; Lotric-Furlan, S.; Strle, F.; Petrovec, M.; Avsic-Zupanc, T. The importance of tick-borne encephalitis virus RNA detection for early differential diagnosis of tick-borne encephalitis. J. Clin. Virol. 2005, 33, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saksida, A.; Jakopin, N.; Jelovšek, M.; Knap, N.; Fajs, L.; Lusa, L.; Lotrič-Furlan, S.; Bogovič, P.; Arnež, M.; Strle, F.; et al. Virus RNA Load in Patients with Tick-Borne Encephalitis, Slovenia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veje, M.; Studahl, M.; Johansson, M.; Johansson, P.; Nolskog, P.; Bergstrom, T. Diagnosing tick-borne encephalitis: A re-evaluation of notified cases. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steininger, P.A.; Bobinger, T.; Dietrich, W.; Lee, D.H.; Knott, M.; Bogdan, C.; Korn, K.; Lang, R. Two Cases of Severe Tick-Borne Encephalitis in Rituximab-Treated Patients in Germany: Implications for Diagnosis and Prevention. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2017, 4, ofx204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, A.; Pauksens, K.; Nordmark, G.; Kumlien, E. Fatal outcome of tick-borne encephalitis in two patients with rheumatic disease treated with rituximab. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 855–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunze, M.; Banović, P.; Bogovič, P.; Briciu, V.; Čivljak, R.; Dobler, G.; Hristea, A.; Kerlik, J.; Kuivanen, S.; Kynčl, J.; et al. Recommendations to Improve Tick-Borne Encephalitis Surveillance and Vaccine Uptake in Europe. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girl, P.; Bestehorn-Willmann, M.; Zange, S.; Borde, J.P.; Dobler, G.; von Buttlar, H. Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Nonstructural Protein 1 IgG Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Differentiating Infection versus Vaccination Antibody Responses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e01783-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euringer, K.; Girl, P.; Kaier, K.; Peilstöcker, J.; Schmidt, M.; Müller-Steinhardt, M.; Rauscher, B.; Bressau, E.; Kern, W.V.; Dobler, G.; et al. Tick-borne encephalitis virus IgG antibody surveillance: Vaccination- and infection-induced seroprevalences, south-western Germany, 2021. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 200408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erber, W.; Schmitt, H.J. Self-reported tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) vaccination coverage in Europe: Results from a cross-sectional study. Ticks Tick. Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


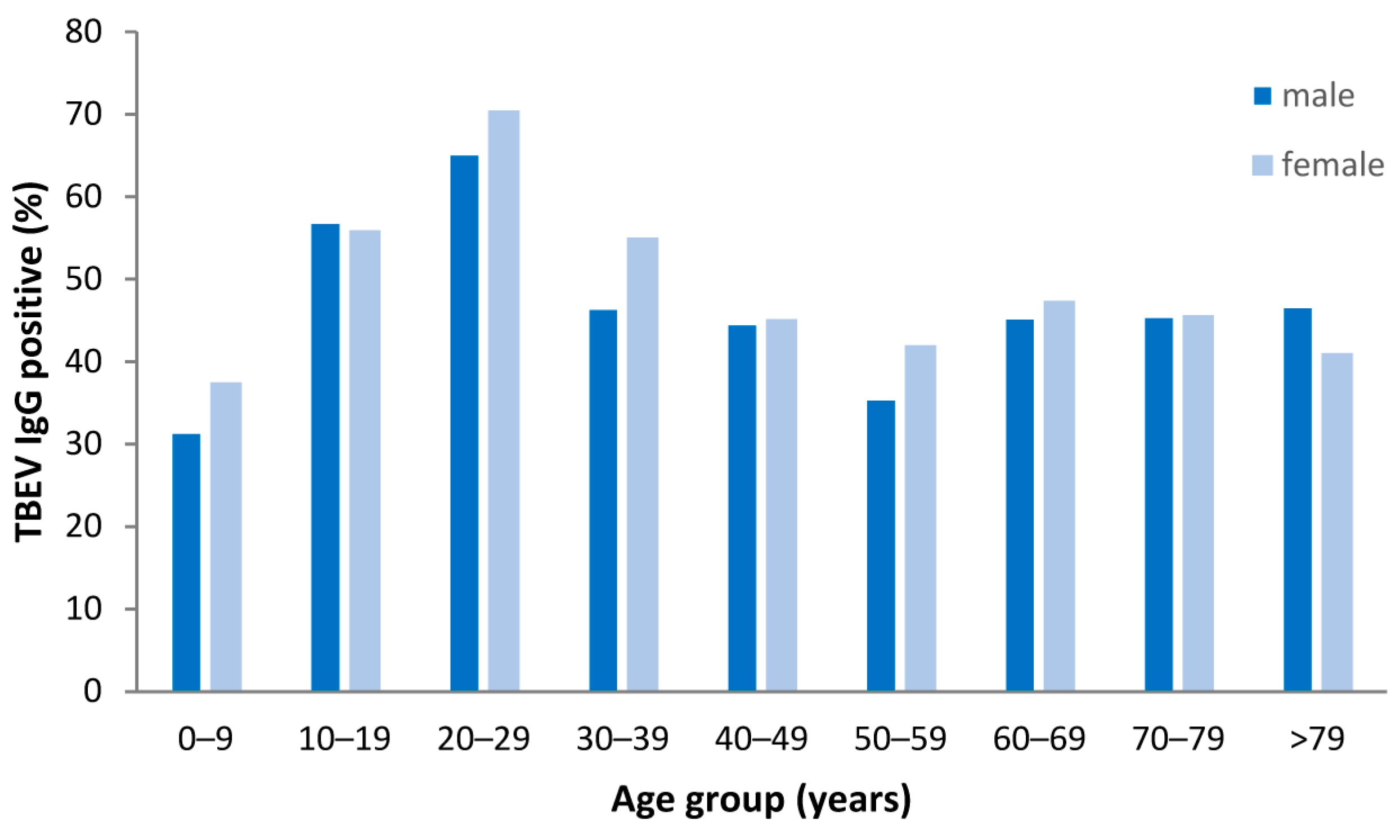
| No TBE | Confirmed TBE | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| TBEV IgM negative | 3578 | 4 | 3582 |
| TBEV IgM positive | 9 | 122 | 131 |
| 3587 | 126 | 3713 |
| Patient | Age | Sex | Disease | Immunosuppressive Medication | Real-Time PCR Result (Ct Value) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSF | Serum | Urine | |||||
| 1 | 54 y | f | Rheumatoid arthritis | RTX | 33.4 | negative | negative |
| 2 | 74 y | m | B-NHL | RTX, bendamustine | 33.4 | negative | 35.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Steininger, P.; Ensser, A.; Knöll, A.; Korn, K. Results of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus (TBEV) Diagnostics in an Endemic Area in Southern Germany, 2007 to 2022. Viruses 2023, 15, 2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15122357
Steininger P, Ensser A, Knöll A, Korn K. Results of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus (TBEV) Diagnostics in an Endemic Area in Southern Germany, 2007 to 2022. Viruses. 2023; 15(12):2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15122357
Chicago/Turabian StyleSteininger, Philipp, Armin Ensser, Antje Knöll, and Klaus Korn. 2023. "Results of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus (TBEV) Diagnostics in an Endemic Area in Southern Germany, 2007 to 2022" Viruses 15, no. 12: 2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15122357
APA StyleSteininger, P., Ensser, A., Knöll, A., & Korn, K. (2023). Results of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus (TBEV) Diagnostics in an Endemic Area in Southern Germany, 2007 to 2022. Viruses, 15(12), 2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15122357






