HIV-1 Antiretroviral Drug Resistance in Mozambique: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Electronic Databases
2.2. Search Strategy for Study Identification
2.3. Study Selection and Inclusion Criteria
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Sources of HIV Sequences and Identification of DRMs
2.6. Statistical Analyses
2.7. Risk of Bias Assessment
3. Results
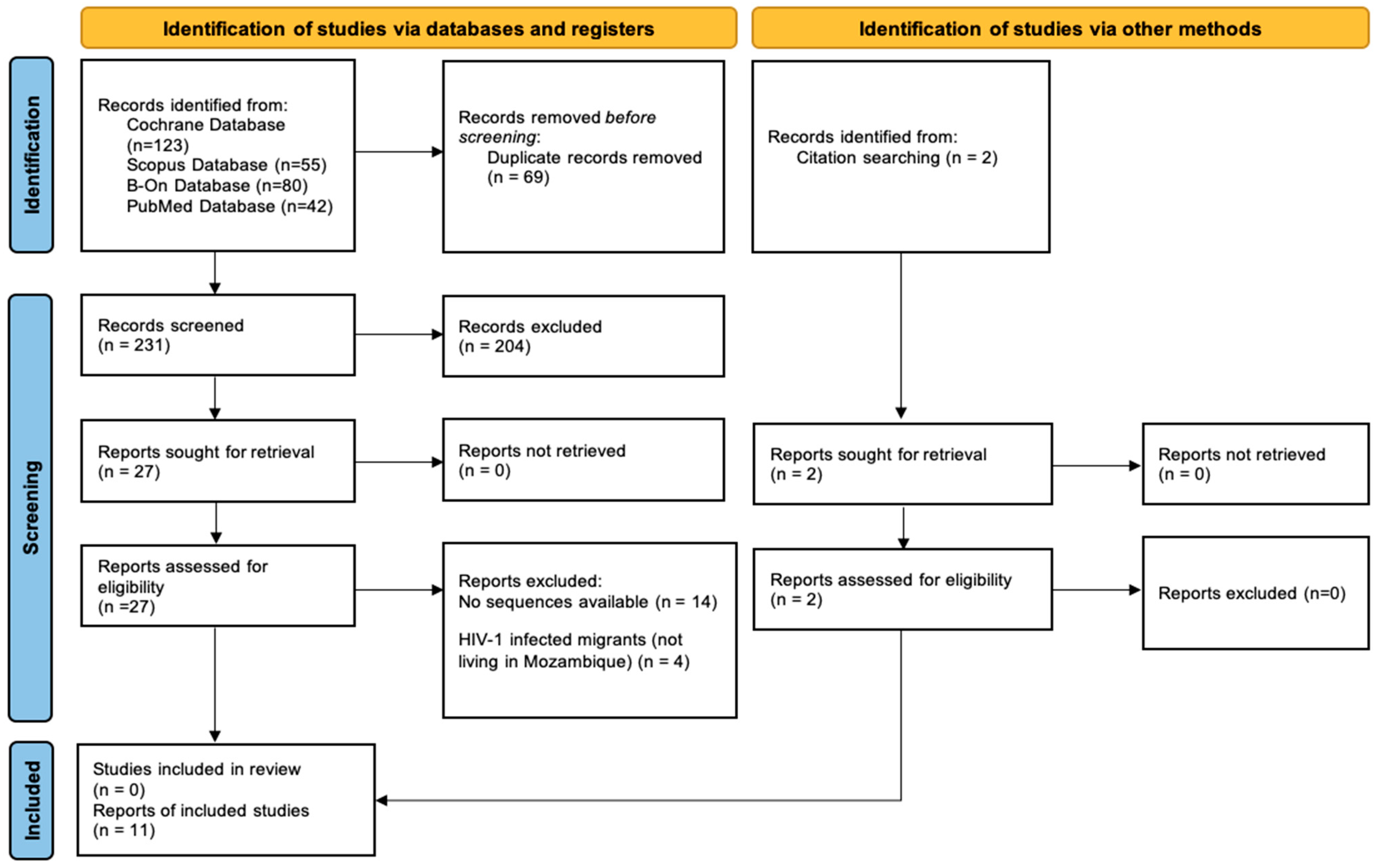
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Studies Characteristics
3.3. Risk of Bias Within Studies
3.4. Results of the Meta-Analysis
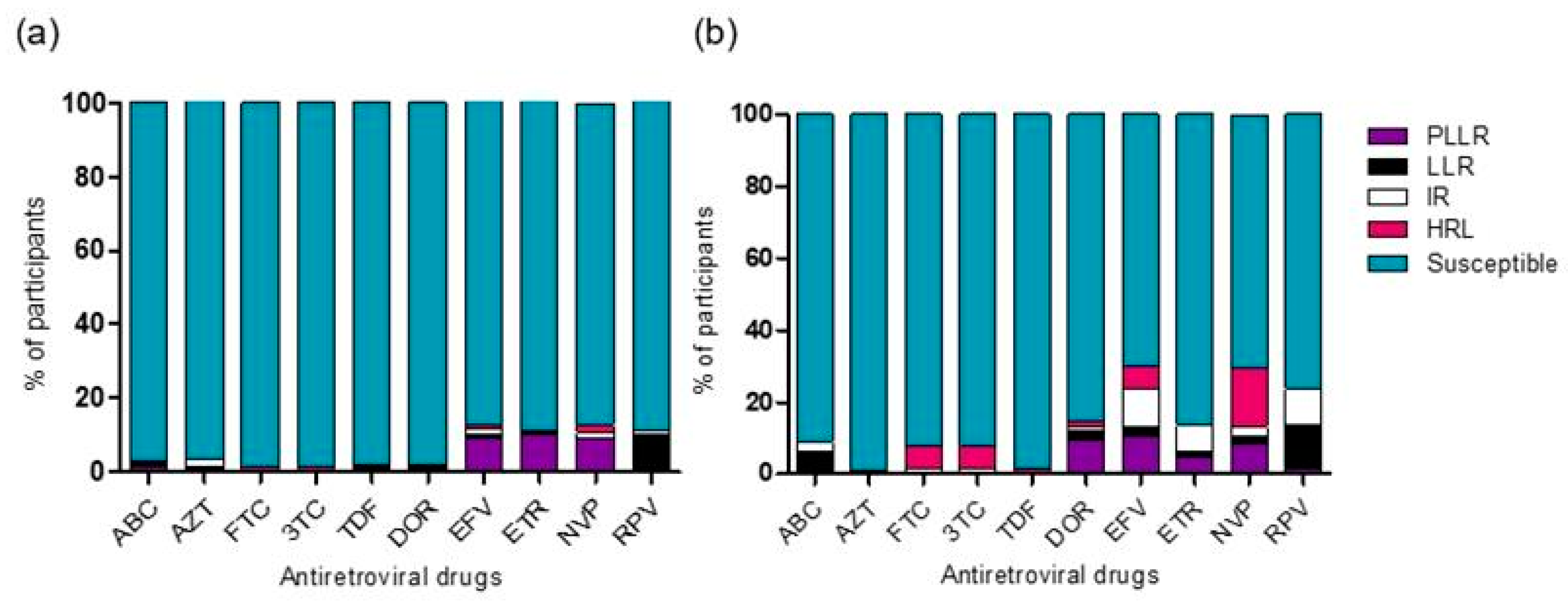
3.5. Genotypic Drug Resistance Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNAIDS. UNAIDS Data 2021; The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV and AIDS: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- GBD 2019 HIV Collaborators. Global, regional, and national sex-specific burden and control of the HIV epidemic, 1990–2019, for 204 countries and territories: The Global Burden of Diseases Study 2019. Lancet HIV 2021, 8, e633–e651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNAIDS. Evaluation of the Un Joint Programme on HIV Mozambique 2016–2020; The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV and AIDS: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- UNAIDS. Country Factsheets—Mozambique 2021; UNAIDS: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bellocchi, M.C.; Forbici, F.; Palombi, L.; Gori, C.; Coelho, E.; Svicher, V.; D’Arrigo, R.; Emberti-Gialloreti, L.; Ceffa, S.; Erba, F.; et al. Subtype analysis and mutations to antiviral drugs in HIV-1-infected patients from Mozambique before initiation of antiretroviral therapy: Results from the DREAM programme. J. Med. Virol. 2005, 76, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parreira, R.; Piedade, J.; Domingues, A.; Lobão, D.; Santos, M.; Venenno, T.; Baptista, J.L.; Mussa, S.A.; Barreto, A.T.; Baptista, A.J.; et al. Genetic characterization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 from Beira, Mozambique. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 2442–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, S.Y.; Kantor, R.; Katzenstein, D.A.; Camacho, R.; Morris, L.; Sirivichayakul, S.; Jorgensen, L.; Brigido, L.F.; Schapiro, J.M.; Shafer, R.W. HIV-1 pol mutation frequency by subtype and treatment experience: Extension of the HIVseq program to seven non-B subtypes. Aids 2006, 20, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, C.M.; Brindeiro, P.A.; Martins, A.N.; Arruda, M.B.; Bule, E.; Stakteas, S.; Tanuri, A.; de Moraes Brindeiro, R. Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates circulating in pregnant women from Mozambique. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 2013–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahuerta, M.; Aparicio, E.; Bardaji, A.; Marco, S.; Sacarlal, J.; Mandomando, I.; Alonso, P.; Martinez, M.A.; Menendez, C.; Naniche, D. Rapid spread and genetic diversification of HIV type 1 subtype C in a rural area of southern Mozambique. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2008, 24, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreotti, M.; Galluzzo, C.M.; Guidotti, G.; Germano, P.; Altan, A.D.; Pirillo, M.F.; Marazzi, M.C.; Vella, S.; Palombi, L.; Giuliano, M. Comparison of HIV type 1 sequences from plasma, cell-free breast milk, and cell-associated breast milk viral populations in treated and untreated women in Mozambique. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2009, 25, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bártolo, I.; Casanovas, J.; Bastos, R.; Rocha, C.; Abecasis, A.B.; Folgosa, E.; Mondlane, J.; Manuel, R.; Taveira, N. HIV-1 genetic diversity and transmitted drug resistance in health care settings in Maputo, Mozambique. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2009, 51, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, D.E.; Camacho, R.J.; Otelea, D.; Kuritzkes, D.R.; Fleury, H.; Kiuchi, M.; Heneine, W.; Kantor, R.; Jordan, M.R.; Schapiro, J.M.; et al. Drug resistance mutations for surveillance of transmitted HIV-1 drug-resistance: 2009 update. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.F.; Ramalho, D.B.; Abreu, C.M.; Vubil, A.; Mabunda, N.; Ismael, N.; Francisco, C.; Jani, I.V.; Tanuri, A. Genetic diversity and naturally polymorphisms in HIV type 1 integrase isolates from Maputo, Mozambique: Implications for integrase inhibitors. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2012, 28, 1788–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bila, D.C.; Young, P.; Merks, H.; Vubil, A.S.; Mahomed, M.; Augusto, A.; Abreu, C.M.; Mabunda, N.J.; Brooks, J.I.; Tanuri, A.; et al. Evolution of primary HIV drug resistance in a subtype C dominated epidemic in Mozambique. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vubil, A.; VI, J.; Mabunda, N.; Ismael, N.; Ramalho, D.; Morgado, M.G.; Couto-Fernandez, J.C. Genetic Diversity and Transmitted Drug Resistance of HIV-1 Subtypes in Blood Donors Candidates in Northern Mozambique. J. AIDS Clin. Res. 2016, 7, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Ismael, N.; Wilkinson, E.; Mahumane, I.; Gemusse, H.; Giandhari, J.; Bauhofer, A.; Vubil, A.; Mambo, P.; Singh, L.; Mabunda, N.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology and Trends in HIV-1 Transmitted Drug Resistance in Mozambique 1999–2018. Viruses 2022, 14, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bbosa, N.; Kaleebu, P.; Ssemwanga, D. HIV subtype diversity worldwide. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2019, 14, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auld, A.F.; Mbofana, F.; Shiraishi, R.W.; Sanchez, M.; Alfredo, C.; Nelson, L.J.; Ellerbrock, T. Four-year treatment outcomes of adult patients enrolled in Mozambique’s rapidly expanding antiretroviral therapy program. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palladino, C.; Briz, V.; Bellón, J.M.; Bártolo, I.; Carvalho, P.; Camacho, R.; Muñoz-Fernández, M.; Bastos, R.; Manuel, R.; Casanovas, J.; et al. Predictors of attrition and immunological failure in HIV-1 patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy from different healthcare settings in Mozambique. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, A.D.; Keiser, O.; Balestre, E.; Brown, S.; Bissagnene, E.; Chimbetete, C.; Dabis, F.; Davies, M.A.; Hoffmann, C.J.; Oyaro, P.; et al. Monitoring and switching of first-line antiretroviral therapy in adult treatment cohorts in sub-Saharan Africa: Collaborative analysis. Lancet HIV 2015, 2, e271–e278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, A.; Sidumo, Z.J.; Zanelli, G.; Magid, N.A.; Luhanga, R.; Brambilla, D.; Liotta, G.; Mancinelli, S.; Marazzi, M.C.; Palombi, L.; et al. Accumulation of HIV-1 drug resistance in patients on a standard thymidine analogue-based first line antiretroviral therapy after virological failure: Implications for the activity of next-line regimens from a longitudinal study in Mozambique. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riou, J.; Dupont, C.; Bertagnolio, S.; Gupta, R.K.; Kouyos, R.D.; Egger, M.; Althaus, C.L. Drivers of HIV-1 drug resistance to non-nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) in nine southern African countries: A modelling study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1042, Erratum in BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, P.; Augusto, O.; Bila, D.; Macassa, E.; Vubil, A.; Jani, I.V.; Pillon, R.; Sandstrom, P.; Sutherland, D.; Giaquinto, C.; et al. Surveillance of HIV drug resistance in children receiving antiretroviral therapy: A pilot study of the World Health Organization’s generic protocol in Maputo, Mozambique. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54 (Suppl. S4), S369–S374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. HIV Drug Resistance Report 2021; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; p. 138. [Google Scholar]
- Carnimeo, V.; Pulido Tarquino, I.A.; Fuentes, S.; Vaz, D.; Molfino, L.; Tamayo Antabak, N.; Cuco, R.M.; Couto, A.; Lobo, S.; de Amaral Fidelis, J.; et al. High level of HIV drug resistance informs dolutegravir roll-out and optimized NRTI backbone strategy in Mozambique. JAC Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 3, dlab050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Consolidated Guidelines on HIV Prevention, Testing, Treatment, Service Delivery and Monitoring: Recommendations for Public Health Approach 2021; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; p. 594. [Google Scholar]
- República de Moçambique; Ministério da Saúde. Relatório Anual das Atividades Relacionadas ao HIV/SIDA; Moçambique, Africa. 2021. Available online: https://pesquisa.bvsalud.org/portal/resource/pt/biblio-1344371 (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- Lain, M.G.; Vaz, P.; Sanna, M.; Ismael, N.; Chicumbe, S.; Simione, T.B.; Cantarutti, A.; Porcu, G.; Rinaldi, S.; de Armas, L.; et al. Viral Response among Early Treated HIV Perinatally Infected Infants: Description of a Cohort in Southern Mozambique. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swannet, S.; Decroo, T.; de Castro, S.; Rose, C.; Giuliani, R.; Molfino, L.; Torrens, A.W.; Macueia, W.; Perry, S.; Reid, T. Journey towards universal viral load monitoring in Maputo, Mozambique: Many gaps, but encouraging signs. Int. Health 2017, 9, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, E.L.; Nhampossa, T.; Clouse, K.; Carlucci, J.G.; Fernández-Luis, S.; Fuente-Soro, L.; Nhacolo, A.; Sidat, M.; Naniche, D.; Moon, T.D. Patterns of mobility and its impact on retention in care among people living with HIV in the Manhiça District, Mozambique. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muwanguzi, M.; Lugobe, H.M.; Ssemwanga, E.; Lule, A.P.; Atwiine, E.; Kirabira, V.; Stella, A.K.; Ashaba, S.; Rukundo, G.Z. Retention in HIV care and associated factors among youths aged 15–24 years in rural southwestern Uganda. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinyandura, C.; Jiyane, A.; Tsalong, X.; Struthers, H.E.; McIntyre, J.A.; Rees, K. Supporting retention in HIV care through a holistic, patient-centred approach: A qualitative evaluation. BMC Psychol. 2022, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuente-Soro, L.; Iniesta, C.; López-Varela, E.; Cuna, M.; Guilaze, R.; Maixenchs, M.; Bernardo, E.L.; Augusto, O.; Gonzalez, R.; Couto, A.; et al. Tipping the balance towards long-term retention in the HIV care cascade: A mixed methods study in southern Mozambique. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FigTree v1.4.4—Molecular Evolution, Phylogenetics Epidemiology. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 7 January 2024).
- Stanford University—HIV Drug Resistance Database (HIVdb Program: Sequence Analysis) 2023. Available online: https://hivdb.stanford.edu/ (accessed on 23 January 2024).
- Shafer, R.W.; Jung, D.R.; Betts, B.J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase and protease mutation search engine for queries. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 1290–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, B.C.; Dahabreh, I.J.; Trikalinos, T.A.; Lau, J.; Trow, P.; Schmid, C.H. Closing the Gap between Methodologists and End-Users: R as a Computational Back-End. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 49, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joanna Briggs Institute. The Joanna Briggs Institute Critical Appraisal Tools for Use in JBI Systematic Reviews Checklist for Prevalence Studies. 2017, p. 7. Available online: https://jbi.global/sites/default/files/2019-05/JBI_Critical_Appraisal-Checklist_for_Prevalence_Studies2017_0.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- Risk of Bias Tools—Robvis (Visualization Tool). Available online: https://www.riskofbias.info/welcome/robvis-visualization-tool (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- Micek, M.A.; Dross, S.; Blanco, A.J.; Beck, I.A.; Matunha, L.; Seidel, K.; Montoya, P.; Matediana, E.; Gantt, S.; Gloyd, S.; et al. Transmission of nevirapine-resistant HIV type 1 via breast milk to infants after single-dose nevirapine in Beira, Mozambique. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouamou, V.; Mavetera, J.; Manasa, J.; Ndhlovu, C.E.; Katzenstein, D.; McGregor, A.M. Pretreatment HIV Drug Resistance Among Adults Initiating or Re-Initiating First-Line Antiretroviral Therapy in Zimbabwe: Fast-Tracking the Transition to Dolutegravir-Based First-Line Regimens? AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2021, 37, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta-Wright, A.; Fielding, K.; van Oosterhout, J.J.; Alufandika, M.; Grint, D.J.; Chimbayo, E.; Heaney, J.; Byott, M.; Nastouli, E.; Mwandumba, H.C.; et al. Virological failure, HIV-1 drug resistance, and early mortality in adults admitted to hospital in Malawi: An observational cohort study. Lancet HIV 2020, 7, e620–e628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, A.; Goldstein, F.; Reichmuth, M.L.; Kouyos, R.D.; Wandeler, G.; Egger, M.; Riou, J. Acquired HIV drug resistance mutations on first-line antiretroviral therapy in Southern Africa: Systematic review and Bayesian evidence synthesis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2022, 148, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etta, E.M.; Mavhandu, L.; Manhaeve, C.; McGonigle, K.; Jackson, P.; Rekosh, D.; Hammarskjold, M.L.; Bessong, P.O.; Tebit, D.M. High level of HIV-1 drug resistance mutations in patients with unsuppressed viral loads in rural northern South Africa. AIDS Res. Ther. 2017, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, C.; Ulenga, N.; Liu, E.; Aboud, S.; Mugusi, F.; Chalamilla, G.; Sando, D.; Aris, E.; Carpenter, D.; Fawzi, W. HIV virological failure and drug resistance in a cohort of Tanzanian HIV-infected adults. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 1966–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabona, G.; Mahiti, M.; Masoud, S.; Mbelele, P.; Mgunya, A.S.; Minja, L.; Sunguya, B.; Shigemi, U.; Matsuda, M.; Hachiya, A.; et al. Pre-treatment and acquired HIV drug resistance in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania in the era of tenofovir and routine viral load monitoring. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 3016–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhann, F.; de Forest, A.; Heger, E.; Nhlema, A.; Scheller, C.; Kaiser, R.; Steffen, H.M.; Tweya, H.; Fätkenheuer, G.; Phiri, S. Pretreatment resistance mutations and treatment outcomes in adults living with HIV-1: A cohort study in urban Malawi. AIDS Res. Ther. 2020, 17, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimukangara, B.; Lessells, R.J.; Rhee, S.Y.; Giandhari, J.; Kharsany, A.B.M.; Naidoo, K.; Lewis, L.; Cawood, C.; Khanyile, D.; Ayalew, K.A.; et al. Trends in Pretreatment HIV-1 Drug Resistance in Antiretroviral Therapy-naive Adults in South Africa, 2000–2016: A Pooled Sequence Analysis. EClinicalMedicine 2019, 9, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henerico, S.; Mikasi, S.G.; Kalluvya, S.E.; Brauner, J.M.; Abdul, S.; Lyimo, E.; Desderius, B.; Korn, K.; van Zyl, G.; Jacobs, G.B.; et al. Prevalence and patterns of HIV drug resistance in patients with suspected virological failure in North-Western Tanzania. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seu, L.; Mulenga, L.B.; Siwingwa, M.; Sikazwe, I.; Lambwe, N.; Guffey, M.B.; Chi, B.H. Characterization of HIV drug resistance mutations among patients failing first-line antiretroviral therapy from a tertiary referral center in Lusaka, Zambia. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo, S.; Hunt, G.; Zuma, K.; Zungu, M.; Marinda, E.; Mabaso, M.; Kana, V.; Kalimashe, M.; Ledwaba, J.; Naidoo, I.; et al. HIV drug resistance profile in South Africa: Findings and implications from the 2017 national HIV household survey. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, N.I.; Musaazi, J.; Kityo, C.; Walimbwa, S.; Hoppe, A.; Balyegisawa, A.; Kaimal, A.; Mirembe, G.; Tukamushabe, P.; Ategeka, G.; et al. Dolutegravir or Darunavir in Combination with Zidovudine or Tenofovir to Treat HIV. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, S.Y.; Grant, P.M.; Tzou, P.L.; Barrow, G.; Harrigan, P.R.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Shafer, R.W. A systematic review of the genetic mechanisms of dolutegravir resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 3135–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCluskey, S.M.; Pepperrell, T.; Hill, A.; Venter, W.D.F.; Gupta, R.K.; Siedner, M.J. Adherence, resistance, and viral suppression on dolutegravir in sub-Saharan Africa: Implications for the TLD era. Aids 2021, 35 (Suppl. 2), S127–S135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboud, M.; Kaplan, R.; Lombaard, J.; Zhang, F.; Hidalgo, J.A.; Mamedova, E.; Losso, M.H.; Chetchotisakd, P.; Brites, C.; Sievers, J.; et al. Dolutegravir versus ritonavir-boosted lopinavir both with dual nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor therapy in adults with HIV-1 infection in whom first-line therapy has failed (DAWNING): An open-label, non-inferiority, phase 3b trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuco, R.M.; Loquiha, O.; Juga, A.; Couto, A.; Meggi, B.; Vubil, A.; Sevene, E.; Osman, N.; Temermam, M.; Degomme, O.; et al. Nevirapine hair and plasma concentrations and HIV-1 viral suppression among HIV infected ante-partum and post-partum women attended in a mother and child prevention program in Maputo city, Mozambique. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.J.; Chunda-Liyoka, C.; Poppe, L.K.; Meinders, K.; Chileshe, C.; West, J.T.; Wood, C. High nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor resistance levels in HIV-1-infected Zambian mother-infant pairs. Aids 2020, 34, 1833–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, C.L.; Sils, T.; Ko, D.; Wong-On-Wing, A.; Beck, I.A.; Styrchak, S.M.; DeMarrais, P.; Tierney, C.; Stranix-Chibanda, L.; Flynn, P.M.; et al. Maternal Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Drug Resistance Is Associated With Vertical Transmission and Is Prevalent in Infected Infants. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 2001–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dow, D.E.; Schimana, W.; Nyombi, B.M.; Mmbaga, B.T.; Shayo, A.M.; Bartlett, J.A.; Massambu, C.G.; Kifaro, E.G.; Turner, E.L.; DeMarco, T.; et al. HIV Resistance and Prevention of Mother-to-Child Transmission Regimen in HIV-Infected Infants in Northern Tanzania. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2017, 33, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, L.; Gholamin, S.; White, E.; Zijenah, L.; Katzenstein, D.A. Comparing Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell DNA and Circulating Plasma viral RNA pol Genotypes of Subtype C HIV-1. J. AIDS Clin. Res. 2012, 3, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicenti, I.; Razzolini, F.; Saladini, F.; Romano, L.; Zazzi, M. Use of peripheral blood DNA for genotype antiretroviral resistance testing in drug-naive HIV-infected subjects. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 1657–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, S.G.; Boldrin, C.; Cruciani, M.; Nicolini, G.; Cerbaro, I.; Manfrin, V.; Dal Bello, F.; Franchin, E.; Franzetti, M.; Rossi, M.C.; et al. Both human immunodeficiency virus cellular DNA sequencing and plasma RNA sequencing are useful for detection of drug resistance mutations in blood samples from antiretroviral-drug-naive patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 1783–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessôa, R.; Sanabani, S.S. High prevalence of HIV-1 transmitted drug-resistance mutations from proviral DNA massively parallel sequencing data of therapy-naïve chronically infected Brazilian blood donors. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huruy, K.; Mulu, A.; Liebert, U.G.; Maier, M. Correction: HIV-1C proviral DNA for detection of drug resistance mutations. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derache, A.; Shin, H.S.; Balamane, M.; White, E.; Israelski, D.; Klausner, J.D.; Freeman, A.H.; Katzenstein, D. HIV drug resistance mutations in proviral DNA from a community treatment program. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, K.E.; Nawas, G.T.; Chan, C.; York, L.; Fisher, J.; Connick, E.; Zangeneh, T.T. Clinical Outcomes Following the Use of Archived Proviral HIV-1 DNA Genotype to Guide Antiretroviral Therapy Adjustment. Open Forum. Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofz533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Armenia, D.; Walworth, C.; Santoro, M.M.; Shafer, R.W. Genotypic Resistance Testing of HIV-1 DNA in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 35, e0005222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, M.M.; Perno, C.F. HIV-1 Genetic Variability and Clinical Implications. ISRN Microbiol. 2013, 2013, 481314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, E.; White, E.; Clark, D.; Churchill, D.; Zhang, H.; Collins, S.; Pillay, D.; Sabin, C.; Nelson, M.; Winston, A.; et al. An association between K65R and HIV-1 subtype C viruses in patients treated with multiple NRTIs. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2075–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainberg, M.A.; Brenner, B.G. The Impact of HIV Genetic Polymorphisms and Subtype Differences on the Occurrence of Resistance to Antiretroviral Drugs. Mol. Biol. Int. 2012, 2012, 256982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Lebedev, A.; Gromov, K.; Kazennova, E.; Zazzi, M.; Incardona, F.; Sönnerborg, A.; Bobkova, M. Pre-existing singleton E138A mutations in the reverse transcriptase gene do not affect the efficacy of first-line antiretroviral therapy regimens using rilpivirine in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. Clin. Case Rep. 2022, 10, e05373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sluis-Cremer, N.; Jordan, M.R.; Huber, K.; Wallis, C.L.; Bertagnolio, S.; Mellors, J.W.; Parkin, N.T.; Harrigan, P.R. E138A in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase is more common in subtype C than B: Implications for rilpivirine use in resource-limited settings. Antivir. Res. 2014, 107, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novitsky, V.; Wester, C.W.; DeGruttola, V.; Bussmann, H.; Gaseitsiwe, S.; Thomas, A.; Moyo, S.; Musonda, R.; Van Widenfelt, E.; Marlink, R.G.; et al. The reverse transcriptase 67N 70R 215Y genotype is the predominant TAM pathway associated with virologic failure among HIV type 1C-infected adults treated with ZDV/ddI-containing HAART in southern Africa. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2007, 23, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantor, R.; Smeaton, L.; Vardhanabhuti, S.; Hudelson, S.E.; Wallis, C.L.; Tripathy, S.; Morgado, M.G.; Saravanan, S.; Balakrishnan, P.; Reitsma, M.; et al. Pretreatment HIV Drug Resistance and HIV-1 Subtype C Are Independently Associated With Virologic Failure: Results From the Multinational PEARLS (ACTG A5175) Clinical Trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Authors [Year of Publication] | Information | Main Findings | Funding | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. Sequences | Sample Collection Date | HIV Viral Population from | Participants | Age in Years [Mean (SD); Median (IQR) or Range)] | Male/ Female | Region | Antiretroviral Drugs | |||
| Andreotti et al. (2009) [10] | 101 | 2009 | Plasma Breast milk PBMC | Pregnant | [26.2 (+/−4.5); 26 (17–39)] | 0/53 | Maputo | AZT (or d4T) + 3TC + NVP | Almost all strains were subtype C (exceptions: 1 subtype A and 1 subtype G). DRMs:
| Drug Resource Enhancement against AIDS in Mozambique (DREAM Program) |
| Oliveira et al. (2012) [13] | 57 | December 2009 to August 2010 | Plasma | Adult | >18 (NA) | 18/39 | Maputo | AZT (or d4T) + 3TC + NVP | 92.9% of sequences were subtype C (exceptions: 1.7% subtype A and 5.4% URF_CG). DRMs:
| Brazilian National Research Council, (471299/2009-0) and National AIDS Program/Ministery of Health, Brazil, and Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ), Brazil |
| Lahuerta et al. (2008) [9] | 51 | 1999 and 2004 | Plasma | Adult | Means: 33 (IQR 25–48) and 23 (IQR 20–30) | 0/81 | Maputo | Naive | All sequences were subtype C. No DRMs. | Spanish Ministry of Education and Science (SAF-05845) (BFU2006-01066/BMC) (FIPSE project 36549/06); Vizcaya Argentaria foundation (BBVA 02-0); Spanish Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria (FIS01/1236). |
| Micek et al. (2014) [43] | 33 | Between June 2005 and May 2008 | PBMC | Neonates/Infants | 0–2 (NA) | NA | Beira | NVP (after birth) and AZT (first week of life) | All sequences were subtype C. NVP resistance was detected in 37.5% of infants infected via breast milk. DRMs:
| National Institutes of Health (R01 AI058723 and STD/AIDS T32 AI07140) and the University of Washington/Fred Hutch Center for AIDS Research (CFAR) (P30 AI027757). |
| Bila et al. (2013) [14] | 112 | March to June in 2007 and in 2009 | PBMC | Pregnant | 15–25 (NA) | 0:234 | Maputo and Beira | Naive | All sequences were subtype C. TDR was classified as <5% in Maputo and 5–15% in Beira. DRMs:
| NA |
| Vubil et al. (2016) [15] | 95 | November 2009 and June 2010 | Plasma | Adult | 29 (NA) | 120:0 | Nampula and Pemba | Naive | 80% of strains were subtype C (exceptions: 10.5% subtype A, 3.2% subtype D and 2.1% subtype G). DRMs:
| Instituto Nacional de Saúde, Mozambique; Fundo Nacional de Investigação, Mozambique (IOC-FIOCRUZ) |
| Bellocchi et al. (2005) [5] | 58 | First months of 2003 | Plasma | Adult | NA | - | Maputo | Naive | All virus strains were subtype C. DRMs:
| Drug Resource Enhancement against AIDS in Mozambique (DREAM Program) |
| Parreira et al. (2006) [6] | 43 | August and October 2003 | PBMC | Adult | Mean: 28.8 (1–63) | 34:96 | Beira | Naive | All virus strains were subtype C. DRMs:
| Fundacão GlaxoSmithKline das Ciências de Saúde, Portugal |
| Bártolo et al. (2009) [11] | 186 | Between 2002–2004 | Plasma | Adult | Mean: 41 (+/−12) | 82:62 | Maputo | Naive | Most strains were to subtype C (exceptions: 3.8% subtype G, 6.7% CRF37_cpx and 7.7% of other CRFs). DRMs:
| NA |
| Vaz et al. (2012) [23] | 112 | October 2007 and June 2008 | Plasma | Infants/Child | Median: 2 (1.3–5.9) | 43:76 | Maputo | ZDV or d4T + 3TC + NVP (or EFV) | All virus strains were subtype C. DRMs:
| The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (K23 AI074423-05) European Community’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007–2013) |
| Abreu et al. (2008) [8] | 76 | 2002 | Plasma | Pregnant | NA | - | Multicenter | Naive | Northern: 64.3% of isolates were subtype C (exceptions: 18% subtype A, 11% subtype D and 7.1% others CRFs). Southern: 95% isolates were subtype C (exceptions: 5% subtype D). Central: 100% of isolates were subtype C. DRMs:
| Programa de Cooperação em Ciência, Tecnologia e Inovação com Países da África-PROAFRICA (Proc# 491367/2005-8) with Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil |
| Variable | No. Studies | Total No. of DRMs/Total No. of Sequences | DRM Rate (95% CI) a | Heterogeneity Index I2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Localization: | ||||
| Maputo | 5 | 78/511 | 0.095 (0.024; 0.207) | 91.4 * |
| Maputo/Beira | 1 | 25/112 | 0.233 (0.151; 0.305) | NA |
| Nampula/Pemba | 1 | 19/95 | 0.200 (0.126; 0.286) | NA |
| Beira | 1 | 23/43 | 0.535 (0.386; 0.680) | NA |
| Multicentric | 1 | 17/76 | 0.224 (0.138; 0.324) | NA |
| Sequence origin: | ||||
| Plasma | 7 | 114/682 | 0.126 (0.056; 0.218) | 90.0 * |
| Cells | 2 | 48/155 | 0.367 (0.105; 0.683) | 92.5 * |
| Participant’s group: | ||||
| Pregnant women | 3 | 56/364 | 0.166 (0.077; 0.281) | 85.4 * |
| Adults | 6 | 106/473 | 0.169 (0.048; 0.344) | 93.2 * |
| Variable | No. Studies | Total No. of DRMs/Total No. of Sequences | DRM Rate (95% CI) a | Heterogeneity Index I2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Localization (sequence origin): | ||||
| Maputo (Plasma) | 3 | 101/248 | 0.318 (0.059; 0.664) | 96.3 * |
| Beira (Cells) | 1 | 28/33 | 0.848 (0.708; 0.948) | NA |
| Participant’s group: | ||||
| Pregnant women | 1 | 26/118 | 0.220 (0.151; 0.299) | NA |
| Adults | 1 | 2/18 | 0.111 (0.012; 0.292) | NA |
| Neonates/Infants/Children | 2 | 101/145 | 0.747 (0.533; 0.912) | 81.7 * |
| Treatment Regimen | No. Studies | Total No. of DRMs/Total No. of Sequences | DRM Rate (95% CI) a | Heterogeneity Index I2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug-naive | 9 | 162/837 | 0.169 (0.082; 0.280) | 93.3 * |
| AZT (or d4T) + 3TC + NVP | 2 | 28/136 | 0.192 (0.105; 0.298) | 27.7 |
| NVP (after birth) + AZT (first week of life) | 1 | 28/33 | 0.848 (0.708; 0.948) | NA |
| AZT (or d4T) + 3TC + NVP (or EFV) | 1 | 73/112 | 0.652 (0.561; 0.737) | NA |
| Treatment Regimen | MRR a | 95% CI b | Std. Error | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug-naive | 1 | - | - | - |
| AZT (or d4T) + 3TC + NVP | 0.586 | 0.1670; 1.0058 | 0.2140 | 0.2301 |
| AZT (or d4T) + 3TC + NVP (or EFV) | 2.883 | 2.5829; 3.1839 | 0.1533 | <0.00001 |
| NVP (after birth) + AZT (first week of life) | 3.754 | 3.3274; 4.1797 | 0.2174 | <0.00001 |
| Index Specimen | Coefficient | Std. Error | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | |||
| Intercept | 16.28 | 5.17 | 0.0016 |
| Male (%) | 5.58 | 6.89 | 0.4183 |
| Subtype C | −17.31 | 5.36 | 0.0012 |
| Treatment (AZT or d4T + 3TC + NVP as reference) | |||
| Drug-naïve | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.3229 |
| AZT (or d4T) + 3TC+ NVP (or EFV) | 1.95 | 0.60 | 0.0011 |
| NVP (after birth) + AZT (first week of life) | 0.86 | 0.54 | 0.1133 |
| Sequence origin (cells) | |||
| Plasma | −4.45 | 1.13 | <0.0001 |
| Localization (Nampula/Pemba as reference) | |||
| Mozambique multicentric | 1.21 | 0.47 | 0.0104 |
| Maputo | 2.23 | 0.71 | 0.0016 |
| Maputo and Beira | −0.73 | 0.51 | 0.1505 |
| Participant group (Adult as reference) | |||
| Pregnant women | −0.14 | 0.38 | 0.7057 |
| Neonates/Infants/Children | 0.86 | 0.54 | 0.1133 |
| Treatment Regimen | No. Studies | Viral Load (log10 HIV-1 RNA Copies) | 95% CI a | I2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug-naive | 3 | 4.373 | 4.053; 4.694 | 86.5 * |
| AZT (or d4T) + 3TC + NVP | 1 | 3.100 | 2.778; 3.422 | NA |
| Index Specimen | Studies | Coefficient | Std. Error | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | ||||
| Intercept | 21.13 | 4.31 | <0.001 | |
| Subtype C | −17.03 | 4.36 | <0.001 | |
| Treatment (Drug-naïve as reference) | 3 | - | - | - |
| AZT/d4T + 3TC + NVP | 1 | −2.24 | 0.32 | <0.001 |
| Model 2 | ||||
| Intercept | 4.60 | 0.18 | <0.001 | |
| Treatment (Drug-naïve as reference) | 3 | - | - | - |
| AZT/d4T + 3TC + NVP | 1 | −1.50 | 0.27 | <0.001 |
| Participant group (pregnant as reference) | 2 | - | - | - |
| Adults | 2 | −0.35 | 0.21 | 0.098 |
| Index Specimen | Studies | Coefficient | Std. Error | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 374.00 | 35.24 | <0.001 | |
| Participant group (pregnant as reference) | 2 | - | - | - |
| Adults | 2 | 12.40 | 49.05 | 0.800 |
| Treatment (Drug-naive as reference) | 3 | - | - | - |
| AZT/d4T + 3TC + NVP | 1 | 244.00 | 64.06 | <0.001 |
| Resistance Mutations | Naive, No (%) (n = 837) | Treated, No. (%) (n = 281) | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| NRTI resistance mutations | |||
| K65R | 0 (0) | 3 (1.1) | 0.002 |
| M184V | 9 (1.1) | 17 (6.0) | <0.0001 |
| NNRTI resistance mutations | |||
| K103N | 8 (0.96) | 11 (3.9) | 0.001 |
| V106M | 0 (0) | 3 (1.1) | 0.002 |
| Y181C | 2 (0.24) | 21 (7.5) | <0.0001 |
| G190A | 5 (0.60) | 8 (2.8) | 0.002 |
| H221Y | 0 (0) | 4 (1.4) | 0.0005 |
| PI resistance mutations | |||
| Q58E | 2 (0.24) | 7 (2.49) | 0.0003 |
| G73S | 0 (0) | 3 (1.1) | 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonçalves, P.; Mascarenhas, P.; Marcelino, R.; Mabunda, N.; Kroidl, A.; Buck, W.C.; Jani, I.; Palladino, C.; Taveira, N. HIV-1 Antiretroviral Drug Resistance in Mozambique: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Viruses 2024, 16, 1808. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16121808
Gonçalves P, Mascarenhas P, Marcelino R, Mabunda N, Kroidl A, Buck WC, Jani I, Palladino C, Taveira N. HIV-1 Antiretroviral Drug Resistance in Mozambique: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Viruses. 2024; 16(12):1808. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16121808
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonçalves, Paloma, Paulo Mascarenhas, Rute Marcelino, Nédio Mabunda, Arne Kroidl, W. Chris Buck, Ilesh Jani, Claudia Palladino, and Nuno Taveira. 2024. "HIV-1 Antiretroviral Drug Resistance in Mozambique: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Viruses 16, no. 12: 1808. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16121808
APA StyleGonçalves, P., Mascarenhas, P., Marcelino, R., Mabunda, N., Kroidl, A., Buck, W. C., Jani, I., Palladino, C., & Taveira, N. (2024). HIV-1 Antiretroviral Drug Resistance in Mozambique: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Viruses, 16(12), 1808. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16121808








