Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant (B.1.617.2) in Domestic Dogs and Zoo Tigers in England and Jersey during 2021
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Processing
2.2. RNA Extraction
| Submission # | Sample Collection Date 1 | Species, Breed | Age | Sex | Sample Type | E gene RRT-PCR (Cq) | RdRp RRT-PCR (Cq) | Virus Neutralisation Titre (IC50) | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 22 April 2020 | Cat, Ragdoll | 4 months | Female | Lung tissue (formalin fixed paraffin embedded) | No Cq | No Cq | n/a | Negative |
| 2 | 15 May 2020 | Cat, Siamese | 6 years | Female | Oropharyngeal swab | 32.00 | 34.62 | n/a | Positive [27] |
| 10 July 2020 | Oropharyngeal swab | No Cq | No Cq | n/a | |||||
| Rectal swab | No Cq | No Cq | n/a | ||||||
| Serum | n/a | n/a | 128 | ||||||
| 3 | 15 January 2021 | Dog, Pug | Unknown | Unknown | Saliva swab | No Cq | No Cq | n/a | Negative |
| 4 | 29 January 2021 | Cat, unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Nasal, mouth, throat, rectal swabs | No Cq | nt | n/a | Negative |
| 5 | 5 February 2021 | Cat, Sphynx | 10 years, 7 months | Female | Throat, nasal, conjunctival and rectal swab, 28 additional tissues collected post-mortem | No Cq | No Cq | n/a | Negative |
| Serum | n/a | n/a | Negative | ||||||
| 6 | 21 April 2021 | Camel, Bactrian | Unknown | Unknown | Lung tissue | No Cq | No Cq | n/a | Negative |
| 7 | 9 July 2021 | Dog, poodle × shih tzu cross | 8 years | Female | Conjunctival and oropharyngeal swab pooled | 33.42 | 38.65 | n/a | Positive |
| 8 | 7 September 2021 | Gaur Indian Bison | Unknown | Unknown | Lung tissue | No Cq | No Cq | n/a | Negative |
| 9 | 29 October 2021 | Dog, Labrador | 10 years | Male | Pharyngeal swab Rectal swab Conjunctival swab | 24.29 No Cq No Cq | 30.32 No Cq No Cq | n/a | Positive |
| 10 | 3 December 2021 9 December 2021 | Tiger, Amur | 12 years | Male | Sputum swab | 29.08 | 34.59 | n/a | Positive |
| Virus transport medium wash from sputum swab | 27.60 | nt | |||||||
| Oral swab | No Cq | No Cq | |||||||
| Nasal swab | No Cq | No Cq | |||||||
| 11 | 9 December 2021 | Tiger, Amur | 13 years | Female | Nasal swab | 35.83 | No Cq | n/a | Positive |
| 12 | 9 December 2021 | Tiger, Amur | 11 years | Female | Oral swab Nasal swab Faeces | 36.98 31.46 36.99 | No Cq No Cq No Cq | n/a | Positive |
| 13 | 9 December 2021 | Leopard, Amur | 12 years | Male | Oral swab Nasal swab Faeces | No Cq No Cq No Cq | No Cq No Cq No Cq | n/a | Negative |
| 14 | 9 December 2021 | Cat, Burmese | Unknown | Unknown | Oral swab | No Cq | No Cq | n/a | Negative |
| 15 | 6 December 2021 | Dog, Labrador | 4 years 10 months | Male | Pharyngeal swab RNA | 31.46 | nt | n/a | Positive |
| 13 December 2021 | Nasal swab Throat swab BALF Blood Brain tissue Additional 25 tissues | 32.75 34.75 30.50 33.44 31.71 No Cq | 37.01 39.85 35.73 No Cq 35.67 No Cq | ||||||
| 16 | 17 December 2021 | Asian palm civet cat | Adult | Female | Oropharyngeal, conjunctival, nasal, vagina, rectal swab, BALF, additional 25 tissues | No Cq | No Cq | n/a | Negative |
| 17 | 10 February 2022 | Cat, Short hair British | 8 months 4 weeks | Male | Left and right caudal and cranial lung, nasal turbinates, pooled organs (liver, kidney, spleen, thymus) collected at post-mortem | No Cq | No Cq | n/a | Negative |
| 18 | 3 November 2023 | Gorilla | 19 years | Male | Nasal swab | No Cq | No Cq | n/a | Negative |
2.3. Real-Time Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RRT-PCR)
2.4. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. SARS-CoV-2 Virus Neutralisation Test (VNT)
2.6. Virus Isolation
3. Results
3.1. SARS-CoV-2 Investigations in Animals
3.2. Submission 7: Dog from Jersey
3.3. Submission 9: Dog from England
3.4. Submissions 10, 11, and 12: Tigers from England
3.5. Submission 15: Dog from England
3.6. Genome Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucinotta, D.; Vanelli, M. WHO Declares COVID-19 a Pandemic. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 13 February 2024).
- O’Toole, Á.; Scher, E.; Underwood, A.; Jackson, B.; Hill, V.; McCrone, J.T.; Colquhoun, R.; Ruis, C.; Abu-Dahab, K.; Taylor, B.; et al. Assignment of epidemiological lineages in an emerging pandemic using the pangolin tool. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veab064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern as of 29 June 2023. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/covid-19/variants-concern (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Rambaut, A.; Loman, N.; Pybus, O.; Barclay, W.; Barrett, J.; Carabelli, A.; Connor, T.; Peacock, T.; Robertson, D.L.; Volz, E.; et al. Preliminary Genomic Characterisation of an Emergent SARS-CoV-2 Lineage in the UK Defined by a Novel Set of Spike Mutations. Virological. Available online: https://virological.org/t/563 (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Tegally, H.; Wilkinson, E.; Giovanetti, M.; Iranzadeh, A.; Fonseca, V.; Giandhari, J.; Doolabh, D.; Pillay, S.; San, E.J.; Msomi, N.; et al. Detection of a SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern in South Africa. Nature 2021, 592, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, N.R.; Mellan, T.A.; Whittaker, C.; Claro, I.M.; Candido, D.D.S.; Mishra, S.; Crispim, M.A.E.; Sales, F.C.S.; Hawryluk, I.; McCrone, J.T.; et al. Genomics and epidemiology of the P.1 SARS-CoV-2 lineage in Manaus, Brazil. Science 2021, 372, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ECDC. ECDC Threat Assessment Brief. Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 B. 1.617 Variants in India and Situation in the EU/EEA. 2021. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/threat-assessment-emergence-sars-cov-2-b1617-variants (accessed on 13 May 2021).
- Li, M.; Lou, F.; Fan, H. SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern Delta: A great challenge to prevention and control of COVID-19. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlcochova, P.; Kemp, S.A.; Dhar, M.S.; Papa, G.; Meng, B.; Ferreira, I.A.T.M.; Datir, R.; Collier, D.A.; Albecka, A.; Singh, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 Delta variant replication and immune evasion. Nature 2021, 599, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UKHSA. Delta Remains the Predominant Variant in England. Technical Briefing 33. 23 December 2021. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/1043807/technical-briefing-33.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Worobey, M.; Levy, J.I.; Malpica Serrano, L.; Crits-Christoph, A.; Pekar, J.E.; Goldstein, S.A.; Rasmussen, A.L.; Kraemer, M.U.G.; Newman, C.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; et al. The Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market in Wuhan was the early epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic. Science 2022, 377, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crits-Christoph, A.; Gangavarapu, K.; Pekar, J.E.; Moshiri, N.; Singh, R.; Levy, J.I.; Goldstein, S.A.; Suchard, M.A.; Popescu, S.; Robertson, D.L.; et al. Genetic Evidence of Susceptible Wildlife in SARS-CoV-2 Positive Samples at the Huanan Wholesale Seafood Market, Wuhan: Analysis and Interpretation of Data Released by the Chinese Center for Disease Control. Zenodo. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/7754299 (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Animal and Plant Health Agency. APHA Briefing Note 09/21. SARS-CoV-2 in Animals—Case Definition, Testing and International Reporting Obligations. Available online: http://apha.defra.gov.uk/documents/ov/Briefing-Note-0921.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- World Organisation for Animal Health. SARS-CoV-2 in Animals—Situation Report 22. 2023. Available online: https://www.woah.org/app/uploads/2023/07/sars-cov-2-situation-report-22.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2024).
- EFSA Panel on Animal Health and Welfare (AHAW); Nielsen, S.S.; Alvarez, J.; Bicout, D.J.; Calistri, P.; Canali, E.; Drewe, J.A.; Garin-Bastuji, B.; Gonzales Rojas, J.L.; Gortázar, C.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 in animals: Susceptibility of animal species, risk for animal and public health, monitoring, prevention and control. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e07822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delahay, R.J.; de la Fuente, J.; Smith, G.C.; Sharun, K.; Snary, E.L.; Flores Girón, L.; Nziza, J.; Fooks, A.R.; Brookes, S.M.; Lean, F.Z.X.; et al. Assessing the risks of SARS-CoV-2 in wildlife. One Health Outlook 2021, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenollar, F.; Mediannikov, O.; Maurin, M.; Devaux, C.; Colson, P.; Levasseur, A.; Fournier, P.E.; Raoult, D. Mink, SARS-CoV-2, and the Human-Animal Interface. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 663815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oude Munnink, B.B.; Sikkema, R.S.; Nieuwenhuijse, D.F.; Molenaar, R.J.; Munger, E.; Molenkamp, R.; van der Spek, A.; Tolsma, P.; Rietveld, A.; Brouwer, M.; et al. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 on mink farms between humans and mink and back to humans. Science 2021, 371, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, V.L.; Dennis, P.M.; McBride, D.S.; Nolting, J.M.; Madden, C.; Huey, D.; Ehrlich, M.; Grieser, J.; Winston, J.; Lombardi, D.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection in free-ranging white-tailed deer. Nature 2022, 602, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchipudi, S.V.; Surendran-Nair, M.; Ruden, R.M.; Yon, M.; Nissly, R.H.; Vandegrift, K.J.; Nelli, R.K.; Li, L.; Jayarao, B.M.; Maranas, C.D.; et al. Multiple spillovers from humans and onward transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in white-tailed deer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2121644119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caserta, L.C.; Martins, M.; Butt, S.L.; Hollingshead, N.A.; Covaleda, L.M.; Ahmed, S.; Everts, M.R.R.; Schuler, K.L.; Diel, D.G. White-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) may serve as a wildlife reservoir for nearly extinct SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2215067120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, D.; Garushyants, S.; Franks, J.; Magee, A.; Overend, S.; Huey, D.; Williams, A.; Faith, S.; Kandeil, A.; Trifkovic, S.; et al. Accelerated evolution of SARS-CoV-2 in free-ranging white-tailed deer. Res. Sq. 2023. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lean, F.Z.X.; Lamers, M.M.; Smith, S.P.; Shipley, R.; Schipper, D.; Temperton, N.; Haagmans, B.L.; Banyard, A.C.; Bewley, K.R.; Carroll, M.W.; et al. Development of immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridisation for the detection of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded specimens. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosie, M.J.; Epifano, I.; Herder, V.; Orton, R.J.; Stevenson, A.; Johnson, N.; MacDonald, E.; Dunbar, D.; McDonald, M.; Howie, F.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in respiratory samples from cats in the UK associated with human-to-cat transmission. Vet. Rec. 2021, 188, e247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.; Bleicker, T.; Brunink, S.; Schneider, J.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro. Surveill. 2020, 25, 2000045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toussaint, J.F.; Sailleau, C.; Breard, E.; Zientara, S.; De Clercq, K. Bluetongue virus detection by two real-time RT-qPCRs targeting two different genomic segments. J. Virol. Methods 2007, 140, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, M.; Hagag, I.T.; Balzer, J.; Beyer, K.; Kersebohm, J.C.; Sadeghi, B.; Wernike, K.; Höper, D.; Wylezich, C.; Beer, M.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 variant B.1.1.7 in a cat in Germany. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 140, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huddleston, J.; Hadfield, J.; Sibley, T.R.; Lee, J.; Fay, K.; Ilcisin, M.; Harkins, E.; Bedford, T.; Neher, R.A.; Hodcroft, E.B. Augur: A bioinformatics toolkit for phylogenetic analyses of human pathogens. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the Ultrafast Bootstrap Approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, J.; Rhodes, S.; Ross, C.S.; Skinner, P.; Smith, S.P.; Shipley, R.; Warren, C.J.; Goharriz, H.; McElhinney, L.M.; Temperton, N.; et al. Comparison of Serological Assays for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies. Viruses 2021, 13, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, J.; Byrne, A.M.P.; Goharriz, H.; Golding, M.; Cuesta, J.M.A.; Mollett, B.C.; Shipley, R.; McElhinney, L.M.; Fooks, A.R.; Brookes, S.M. Infectious droplet exposure is an inefficient route for SARS-CoV-2 infection in the ferret model. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DEFRA; APHA. COVID-19 Confirmed in Pet Cat in the UK. 2020. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/news/covid-19-confirmed-in-pet-cat-in-the-uk (accessed on 6 July 2023).
- Jones, S.; Tyson, G.B.; Orton, R.J.; Smollett, K.; Manna, F.; Kwok, K.; Suárez, N.M.; Logan, N.; McDonald, M.; Bowie, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 in Domestic UK Cats from Alpha to Omicron: Swab Surveillance and Case Reports. Viruses 2023, 15, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooruzzaman, M.; Diel, D.G. Infection Dynamics, Pathogenesis, and Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in Naturally Susceptible Animal Species. J. Immunol. 2023, 211, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sit, T.H.C.; Brackman, C.J.; Ip, S.M.; Tam, K.W.S.; Law, P.Y.T.; To, E.M.W.; Yu, V.Y.T.; Sims, L.D.; Tsang, D.N.C.; Chu, D.K.W.; et al. Infection of dogs with SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 586, 776–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lean, F.Z.X.; Nunez, A.; Spiro, S.; Priestnall, S.L.; Vreman, S.; Bailey, D.; James, J.; Wrigglesworth, E.; Suarez-Bonnet, A.; Conceicao, C.; et al. Differential susceptibility of SARS-CoV-2 in animals: Evidence of ACE2 host receptor distribution in companion animals, livestock and wildlife by immunohistochemical characterisation. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 2275–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, A.; Smith, D.; Ghai, R.R.; Wallace, R.M.; Torchetti, M.K.; Loiacono, C.; Murrell, L.S.; Carpenter, A.; Moroff, S.; Rooney, J.A.; et al. First Reported Cases of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Companion Animals—New York, March-April 2020. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 710–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrs, V.R.; Peiris, M.; Tam, K.W.S.; Law, P.Y.T.; Brackman, C.J.; To, E.M.W.; Yu, V.Y.T.; Chu, D.K.W.; Perera, R.; Sit, T.H.C. SARS-CoV-2 in Quarantined Domestic Cats from COVID-19 Households or Close Contacts, Hong Kong, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 3071–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudd, J.M.; Tamil Selvan, M.; Cowan, S.; Kao, Y.-F.; Midkiff, C.C.; Narayanan, S.; Ramachandran, A.; Ritchey, J.W.; Miller, C.A. Clinical and Histopathologic Features of a Feline SARS-CoV-2 Infection Model Are Analogous to Acute COVID-19 in Humans. Viruses 2021, 13, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaus, J.; Meli, M.L.; Willi, B.; Nadeau, S.; Beisel, C.; Stadler, T.; Eth Sars-Co, V.S.T.; Egberink, H.; Zhao, S.; Lutz, H.; et al. Detection and Genome Sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 in a Domestic Cat with Respiratory Signs in Switzerland. Viruses 2021, 13, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotstein, D.S.; Peloquin, S.; Proia, K.; Hart, E.; Lee, J.; Vyhnal, K.K.; Sasaki, E.; Balamayooran, G.; Asin, J.; Southard, T.; et al. Investigation of SARS-CoV-2 infection and associated lesions in exotic and companion animals. Vet. Pathol. 2022, 59, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, A.; Ghai, R.R.; Gary, J.; Ritter, J.M.; Carvallo, F.R.; Diel, D.G.; Martins, M.; Murphy, J.; Schroeder, B.; Brightbill, K.; et al. Determining the role of natural SARS-CoV-2 infection in the death of domestic pets: 10 cases (2020–2021). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2021, 259, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvallo, F.R.; Martins, M.; Joshi, L.R.; Caserta, L.C.; Mitchell, P.K.; Cecere, T.; Hancock, S.; Goodrich, E.L.; Murphy, J.; Diel, D.G. Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Cat with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Viruses 2021, 13, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva-Saz, S.; Giner, J.; Tobajas, A.P.; Pérez, M.D.; González-Ramírez, A.M.; Macías-León, J.; González, A.; Verde, M.; Yzuel, A.; Hurtado-Guerrero, R.; et al. Serological evidence of SARS-CoV-2 and co-infections in stray cats in Spain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Tholoth, M.; Hussein, M.; Mohammed, D.; Al-Rasheedi, M.; Al-Qubaisi, H.; Al-Blooshi, A.; Al-Ahbabi, M.; Al-Dhaheri, Z.; Al-Blooshi, K.; Al-Herbawi, M.; et al. Serological Investigation on the Presence of Feline Coronavirus (FCoV) and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in Domestic Cats Living with COVID-19 Positive Owners in the UAE, 2022. Animals 2023, 13, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudreault, N.N.; Trujillo, J.D.; Carossino, M.; Meekins, D.A.; Morozov, I.; Madden, D.W.; Indran, S.V.; Bold, D.; Balaraman, V.; Kwon, T.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection, disease and transmission in domestic cats. Emerg. Microbes. Infect. 2020, 9, 2322–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhards, N.M.; Gonzales, J.L.; Vreman, S.; Ravesloot, L.; van den Brand, J.M.A.; Doekes, H.P.; Egberink, H.F.; Stegeman, A.; Oreshkova, N.; van der Poel, W.H.M.; et al. Efficient Direct and Limited Environmental Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 Lineage B.1.22 in Domestic Cats. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0255322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosco-Lauth, A.M.; Hartwig, A.E.; Porter, S.M.; Gordy, P.W.; Nehring, M.; Byas, A.D.; VandeWoude, S.; Ragan, I.K.; Maison, R.M.; Bowen, R.A. Experimental infection of domestic dogs and cats with SARS-CoV-2: Pathogenesis, transmission, and response to reexposure in cats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 26382–26388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). SARS-CoV-2 in Animals Situation Update 5 December 2023. 2023. Available online: https://www.fao.org/animal-health/situation-updates/sars-cov-2-in-animals/en (accessed on 13 February 2024).
- Kuroda, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Suzuki, H.; Park, E.-s.; Ishijima, K.; Tatemoto, K.; Virhuez-Mendoza, M.; Inoue, Y.; Harada, M.; et al. Pet Animals Were Infected with SARS-CoV-2 from Their Owners Who Developed COVID-19: Case Series Study. Viruses 2023, 15, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colitti, B.; Bertolotti, L.; Mannelli, A.; Ferrara, G.; Vercelli, A.; Grassi, A.; Trentin, C.; Paltrinieri, S.; Nogarol, C.; Decaro, N.; et al. Cross-Sectional Serosurvey of Companion Animals Housed with SARS-CoV-2-Infected Owners, Italy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1919–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalife, S.; Abdallah, M. High seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in household cats and dogs of Lebanon. Res. Vet. Sci. 2023, 157, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelitsch, A.; Allendorf, V.; Conraths, F.J.; Gethmann, J.; Schulz, J.; Wernike, K.; Denzin, N. SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Clinical Signs in Cats and Dogs from Confirmed Positive Households in Germany. Viruses 2023, 15, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadi, H.; Kurucay, H.N.; Elhag, A.E.; Dogan, F.; Yildirim, S.; Tutuncu, H.; Muftuoglu, B.; Tamer, C.; Okur Gumusova, S.; Yazici, Z.; et al. A one-year extensive molecular survey on SARS-CoV-2 in companion animals of Turkey shows a lack of evidence for viral circulation in pet dogs and cats. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2023, 19, 100280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, Y.Y.; Carrai, M.; Choi, Y.R.; Brackman, C.J.; Tam, K.W.S.; Law, P.Y.T.; Woodhouse, F.; Gray, J.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.; et al. Low Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Canine and Feline Serum Samples Collected during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Hong Kong and Korea. Viruses 2023, 15, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Wolff, C.; Prada, J.M.; Mughini-Gras, L. When COVID-19 sits on people’s laps: A systematic review of SARS-CoV-2 infection prevalence in household dogs and cats. One Health 2023, 16, 100497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, T.J.; Hickman, P.; Kazerooni, N.; Kennedy, M.; Kania, S.A.; Dennis, M.; Szafranski, N.; Gerhold, R.; Su, C.; Masi, T.; et al. Possible Cross-Reactivity of Feline and White-Tailed Deer Antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0025022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, J.K.; Edison, L.K.; Rowe-Haas, D.K.; Takano, T.; Gilor, C.; Crews, C.D.; Tuanyok, A.; Arukha, A.P.; Shiomitsu, S.; Walden, H.D.S.; et al. Both Feline Coronavirus Serotypes 1 and 2 Infected Domestic Cats Develop Cross-Reactive Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain: Its Implication to Pan-CoV Vaccine Development. Viruses 2023, 15, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.S.; Parthasarathy, K.; Sounderrajan, V.; Neelagandan, K.; Anbazhagan, P.; Chandramouli, V. Susceptibility of SARS Coronavirus-2 infection in domestic and wild animals: A systematic review. 3 Biotech 2023, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero, R.; Garay, E.; Botero, Y.; Serrano-Coll, H.; Gastelbondo, B.; Muñoz, M.; Ballesteros, N.; Castañeda, S.; Patiño, L.H.; Ramirez, J.D.; et al. Human-to-dog transmission of SARS-CoV-2, Colombia. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agopian, R.G.; da Luz, S.C.G.; Zebral, A.G.B.; de Sousa, G.F.; de Oliveira, I.A.V.; Lima, L.S.; Sechi, M.A.; de Oliveira, M.C.; Rudiniski, V.F.; Brandespim, D.F.; et al. First reported cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection in pets in São Paulo, Brazil. Vet. World 2022, 15, 2593–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molini, U.; Coetzee, L.M.; Engelbrecht, T.; de Villiers, L.; de Villiers, M.; Mangone, I.; Curini, V.; Khaiseb, S.; Ancora, M.; Cammà, C.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 in Namibian Dogs. Vaccines 2022, 10, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Bastit, L.; Rodon, J.; Pradenas, E.; Marfil, S.; Trinite, B.; Parera, M.; Roca, N.; Pou, A.; Cantero, G.; Lorca-Oro, C.; et al. First Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Delta (B.1.617.2) Variant of Concern in a Dog with Clinical Signs in Spain. Viruses 2021, 13, 2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meekins, D.A.; Gaudreault, N.N.; Richt, J.A. Natural and Experimental SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Domestic and Wild Animals. Viruses 2021, 13, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAloose, D.; Laverack, M.; Wang, L.; Killian, M.L.; Caserta, L.C.; Yuan, F.; Mitchell, P.K.; Queen, K.; Mauldin, M.R.; Cronk, B.D.; et al. From People to Panthera: Natural SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Tigers and Lions at the Bronx Zoo. mBio 2020, 11, e02220-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allender, M.C.; Adkesson, M.J.; Langan, J.N.; Delk, K.W.; Meehan, T.; Aitken-Palmer, C.; McEntire, M.M.; Killian, M.L.; Torchetti, M.; Morales, S.A.; et al. Multi-species outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant in a zoological institution, with the detection in two new families of carnivores. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e3060–e3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmeier, E.; Chan, T.; Agüí, C.V.; Willi, B.; Wolfensberger, A.; Beisel, C.; Topolsky, I.; Beerenwinkel, N.; Stadler, T.; Swiss Sars-Co, V.S.C.; et al. Detection and Molecular Characterization of the SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant and the Specific Immune Response in Companion Animals in Switzerland. Viruses 2023, 15, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Kang, M.; Wu, H.; Sun, B.; Baele, G.; He, W.T.; Lu, M.; Suchard, M.A.; Ji, X.; He, N.; et al. Risk assessment of SARS-CoV-2 replicating and evolving in animals. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 32, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Morales, L.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M.; Pérez-Sancho, M.; Domínguez, L.; Barroso-Arévalo, S. The Omicron (B.1.1.529) SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern also affects companion animals. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 940710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piewbang, C.; Poonsin, P.; Lohavicharn, P.; Wardhani, S.W.; Dankaona, W.; Puenpa, J.; Poovorawan, Y.; Techangamsuwan, S. SARS-CoV-2 Transmission from Human to Pet and Suspected Transmission from Pet to Human, Thailand. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2022, 60, e0105822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyson, G.B.; Jones, S.; Montreuil-Spencer, C.; Logan, N.; Scott, S.; Sasvari, H.; McDonald, M.; Marshall, L.; Murcia, P.R.; Willett, B.J.; et al. Increase in SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence in UK Domestic Felids Despite Weak Immunogenicity of Post-Omicron Variants. Viruses 2023, 15, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Wan, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, F. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Recent progress and future perspectives. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantin, K.; Anna, M.; Valerie, A.; Franz Josef, C.; Martin, B.; Nicolai, D.; Kerstin, W. Dogs and cats are less susceptible to the omicron variant of concern of SARS-CoV-2—A field study. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.; do Nascimento, G.M.; Nooruzzaman, M.; Yuan, F.; Chen, C.; Caserta, L.C.; Miller, A.D.; Whittaker, G.R.; Fang, Y.; Diel, D.G. The Omicron Variant BA.1.1 Presents a Lower Pathogenicity than B.1 D614G and Delta Variants in a Feline Model of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0096122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohandas, S.; Yadav, P.D.; Sapkal, G.; Shete, A.M.; Deshpande, G.; Nyayanit, D.A.; Patil, D.; Kadam, M.; Kumar, A.; Mote, C.; et al. Pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (R346K) variant in Syrian hamsters and its cross-neutralization with different variants of concern. eBioMedicine 2022, 79, 103997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, E.R.; Ryan, K.A.; Bewley, K.R.; Coombes, N.S.; Salguero, F.J.; Carnell, O.T.; Biddlecombe, S.; Charlton, M.; Challis, A.; Cross, E.S.; et al. The Omicron Sub-Variant BA.4 Displays a Remarkable Lack of Clinical Signs in a Golden Syrian Hamster Model of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Viruses 2023, 15, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
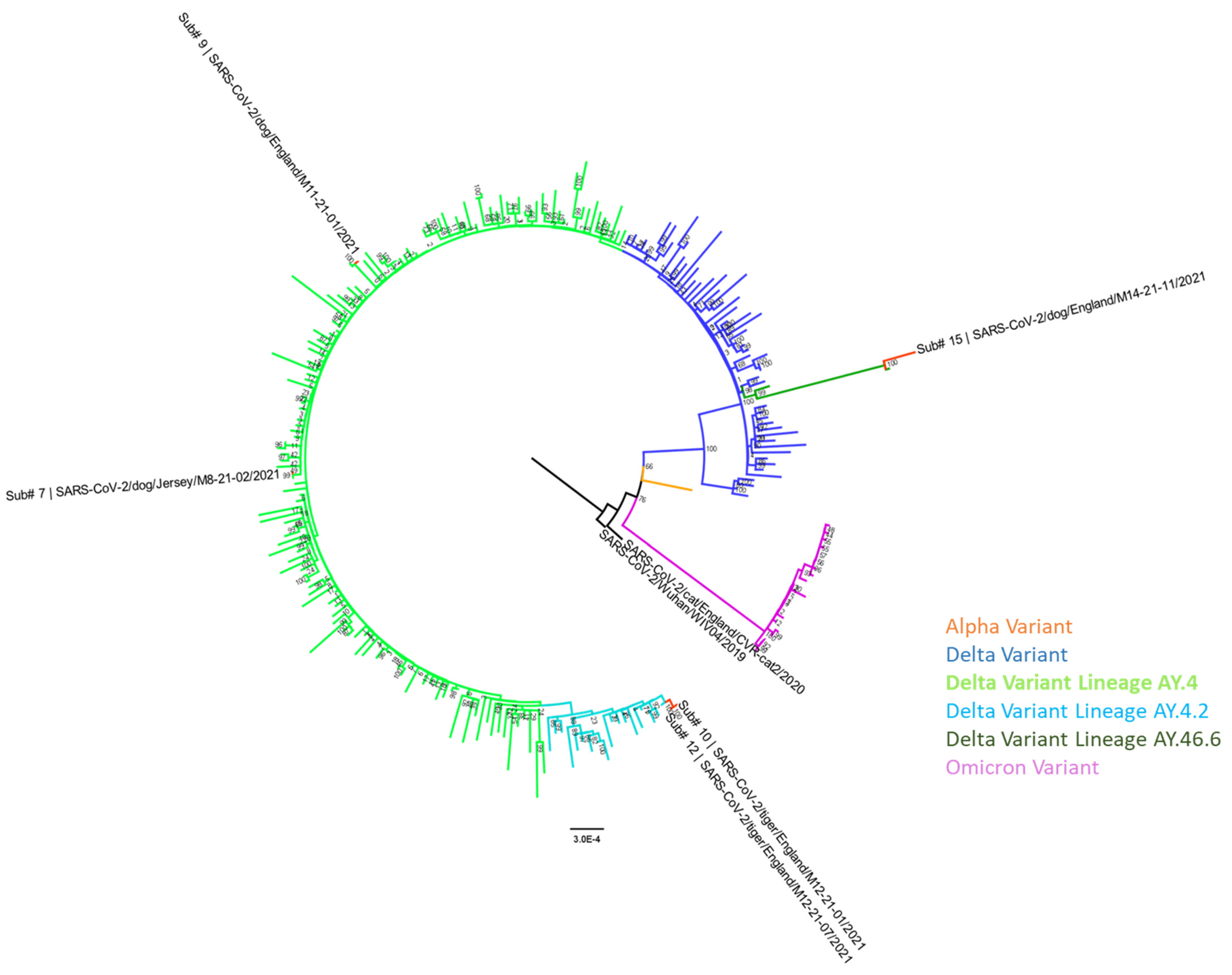
| Submission # | Sequence Name | Sample Type | Sample Collection Date | Accession Numbers GISAID; GenBank | Delta Variant PANGO Sublineage | Most Closely Related Human Sequence | Percentage Nucleotide Similarity (Genome Coverage) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | SARS-CoV-2/dog/Jersey/M8-21-02/2021 | Conjunctival and Oropharyngeal swab pooled | 9 July 2021 | EPI_ISL_18943724; PP515674 | AY.4 | SARS-CoV-2/England/PHEC-3461AE/2021 collection date: 2021 EPI_ISL_3572506 | 99.95% (91%) |
| 9 | SARS-CoV-2/dog/England/M11-21-01/2021 | Pharyngeal swab | 29 October 2021 | EPI_ISL_18943725; PP515675 | AY.4 | SARS-CoV-2/Scotland/QEUH-29B97E4/2021 collection date: 08-11-2021 EPI_ISL_6433530 | 100% (90%) |
| 10 | SARS-CoV-2/tiger/England/M12-21-01/2021 | Sputum swab | 3 December 2021 | EPI_ISL_18943726; PP515676 | AY.4.2 | SARS-CoV-2/England/QEUH-27CC601/2021 collection date: 19-10-2021 EPI_ISL_5529494 | 99.91–99.93% (90–93%) |
| 11 | SARS-CoV-2/tiger/England/M12-21-05/2021 | Nasal swab | 9 December 2021 | EPI_ISL_18943727; PP515677 | AY.4.2 | ||
| 12 | SARS-CoV-2/tiger/England/M12-21-07/2021 | Nasal swab | 9 December 2021 | EPI_ISL_18943728; PP515678 | AY.4.2 | ||
| 15 | SARS-CoV-2/dog/England/M14-21-11/2021 | BALF | 13 December 2021 | EPI_ISL_18943729; PP515679 | AY.46.6 | SARS-CoV-2/England/MILK-2E31E35/2021 collection date: 11-12-2021 EPI_ISL_7815416 | 99.99% (98%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seekings, A.H.; Shipley, R.; Byrne, A.M.P.; Shukla, S.; Golding, M.; Amaya-Cuesta, J.; Goharriz, H.; Vitores, A.G.; Lean, F.Z.X.; James, J.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant (B.1.617.2) in Domestic Dogs and Zoo Tigers in England and Jersey during 2021. Viruses 2024, 16, 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040617
Seekings AH, Shipley R, Byrne AMP, Shukla S, Golding M, Amaya-Cuesta J, Goharriz H, Vitores AG, Lean FZX, James J, et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant (B.1.617.2) in Domestic Dogs and Zoo Tigers in England and Jersey during 2021. Viruses. 2024; 16(4):617. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040617
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeekings, Amanda H., Rebecca Shipley, Alexander M. P. Byrne, Shweta Shukla, Megan Golding, Joan Amaya-Cuesta, Hooman Goharriz, Ana Gómez Vitores, Fabian Z. X. Lean, Joe James, and et al. 2024. "Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant (B.1.617.2) in Domestic Dogs and Zoo Tigers in England and Jersey during 2021" Viruses 16, no. 4: 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040617
APA StyleSeekings, A. H., Shipley, R., Byrne, A. M. P., Shukla, S., Golding, M., Amaya-Cuesta, J., Goharriz, H., Vitores, A. G., Lean, F. Z. X., James, J., Núñez, A., Breed, A., Frost, A., Balzer, J., Brown, I. H., Brookes, S. M., & McElhinney, L. M. (2024). Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant (B.1.617.2) in Domestic Dogs and Zoo Tigers in England and Jersey during 2021. Viruses, 16(4), 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040617










