Cell Culture Models for Hepatitis B and D Viruses Infection: Old Challenges, New Developments and Future Strategies
Abstract
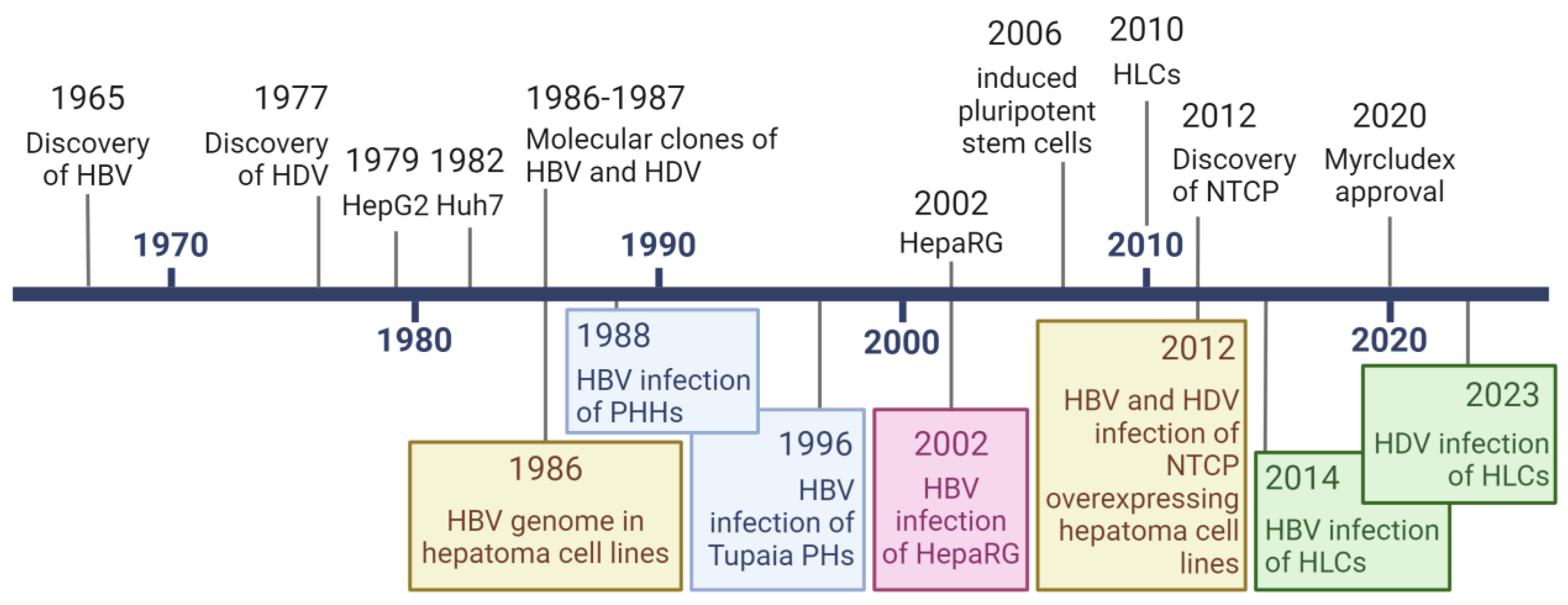
1. Introduction
2. In Vitro Models to Study Virus Infection
2.1. Primary Human Hepatocytes (PHHs)
2.2. Hepatoma-Derived Cell Lines Huh7/HepG2
2.3. HepaRG, dHepaRG
2.4. NTCP Overexpressing Hepatoma Cell Lines
2.5. Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Hepatocyte like Cells (HLCs)
3. Biological Relevance and Specific Questions to Be Answered
3.1. Hepatic Polarity In Vitro: Effect on Expression and Access to NTCP
3.2. Heterogeneity, Differentiation, and Stability of Cell Populations
3.3. Cell Proliferation and How Relevant It Is to Study HDV/HBV In Vitro
3.4. Innate Immunity in Response to Infection
3.5. In Vitro Model of Efficient HBV/HDV Co-Infection
3.6. Co-Culture with Immune Cells
3.7. Genetic Background of the Host Cell and Personalized In Vitro Model
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsukuda, S.; Watashi, K. Hepatitis B virus biology and life cycle. Antiviral Res. 2020, 182, 104925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, R.; Yan, Y.; Shi, S.; Xi, J.; Zou, J.; Yu, G.; Feng, X.; et al. HBV Genome and Life Cycle. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1179, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mentha, N.; Clément, S.; Negro, F.; Alfaiate, D. A review on hepatitis D: From virology to new therapies. J. Adv. Res. 2019, 17, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson-Tsoris, S.; Liang, T.J. Hepatitis Delta Virus–Host Protein Interactions: From Entry to Egress. Viruses 2023, 15, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockdale, A.J.; Kreuels, B.; Henrion, M.Y.R.; Giorgi, E.; Kyomuhangi, I.; de Martel, C.; Hutin, Y.; Geretti, A.M. The global prevalence of hepatitis D virus infection: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asselah, T.; Rizzetto, M. Hepatitis D Virus Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, S.; Neumann-Haefelin, C.; Lampertico, P. Hepatitis D virus in 2021: Virology, immunology and new treatment approaches for a difficult-to-treat disease. Gut 2021, 70, 1782–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Lechón, M.J.; Donato, M.T.; Castell, J.V.; Jover, R. Human hepatocytes in primary culture: The choice to investigate drug metabolism in man. Curr. Drug Metab. 2004, 5, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gripon, P.; Diot, C.; Thézé, N.; Fourel, I.; Loreal, O.; Brechot, C.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C. Hepatitis B virus infection of adult human hepatocytes cultured in the presence of dimethyl sulfoxide. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 4136–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, A.; Mills, K.; Weiss, T.S.; Urban, S. Hepatocyte polarization is essential for the productive entry of the hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 2012, 55, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gripon, P.; Diot, C.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C. Reproducible high level infection of cultured adult human hepatocytes by hepatitis B virus: Effect of polyethylene glycol on adsorption and penetration. Virology 1993, 192, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, J.R.; Eichberg, J.W.; Lanford, R.E. In vitro replication and expression of hepatitis B virus from chronically infected primary chimpanzee hepatocytes. Hepatology 1989, 10, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. eLife 2012, 1, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moolla, N.; Kew, M.; Arbuthnot, P. Regulatory elements of hepatitis B virus transcription. J. Viral Hepat. 2002, 9, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Zhao, F.; Li, J.; Cheng, Z.; Tian, X.; Zhi, X.; Huang, Y.; Hu, K. Long-term maintenance of human fetal hepatocytes and prolonged susceptibility to HBV infection by co-culture with non-parenchymal cells. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 195, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winer, B.Y.; Gaska, J.M.; Lipkowitz, G.; Bram, Y.; Parekh, A.; Parsons, L.; Leach, R.; Jindal, R.; Cho, C.H.; Shrirao, A.; et al. Analysis of Host Responses to Hepatitis B and Delta Viral Infections in a Micro-scalable Hepatic Co-culture System. Hepatology 2020, 71, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakabayashi, H.; Taketa, K.; Miyano, K.; Yamane, T.; Sato, J. Growth of human hepatoma cells lines with differentiated functions in chemically defined medium. Cancer Res. 1982, 42, 3858–3863. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aden, D.P.; Fogel, A.; Plotkin, S.; Damjanov, I.; Knowles, B.B. Controlled synthesis of HBsAg in a differentiated human liver carcinoma-derived cell line. Nature 1979, 282, 615–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, V.; Bartenschlager, R. On the history of hepatitis C virus cell culture systems. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 1627–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureau, C.; Romet-Lemonne, J.L.; Mullins, J.I.; Essex, M. Production of hepatitis B virus by a differentiated human hepatoma cell line after transfection with cloned circular HBV DNA. Cell 1986, 47, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sells, M.A.; Chen, M.L.; Acs, G. Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladner, S.K.; Otto, M.J.; Barker, C.S.; Zaifert, K.; Wang, G.H.; Guo, J.T.; Seeger, C.; King, R.W. Inducible expression of human hepatitis B virus (HBV) in stably transfected hepatoblastoma cells: A novel system for screening potential inhibitors of HBV replication. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Chang, J.; Rijnbrand, R.; Lam, A.M.; Sofia, M.J.; Cuconati, A.; Guo, J.-T. Pregenomic RNA Launch Hepatitis B Virus Replication System Facilitates the Mechanistic Study of Antiviral Agents and Drug-Resistant Variants on Covalently Closed Circular DNA Synthesis. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0115022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Schneider, W.M.; Kass, M.A.; Michailidis, E.; Acevedo, A.; Pamplona Mosimann, A.L.; Bordignon, J.; Koenig, A.; Livingston, C.M.; van Gijzel, H.; et al. An RNA-based system to study hepatitis B virus replication and evaluate antivirals. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.M.; Jeng, K.S.; Hu, C.P.; Lo, S.J.; Su, T.S.; Ting, L.P.; Chou, C.K.; Han, S.H.; Pfaff, E.; Salfeld, J. Production of hepatitis B virus in vitro by transient expression of cloned HBV DNA in a hepatoma cell line. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, M.Y.; Chao, M.; Taylor, J. Initiation of replication of the human hepatitis delta virus genome from cloned DNA: Role of delta antigen. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 1945–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sureau, C. The use of hepatocytes to investigate HDV infection: The HDV/HepaRG model. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 640, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Imamura, M.; Osawa, M.; Teraoka, Y.; Piotrowski, J.; Ishida, Y.; Sozzi, V.; Revill, P.A.; Saito, T.; et al. Infection Courses, Virological Features and IFN-α responses of HBV genotypes in cell culture and animal models. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 1335–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, C.; Lucifora, J.; Delphin, M.; Heydmann, L.; Heuschkel, M.J.; Pons, C.; Goto, K.; Scheers, E.; Schuster, C.; Durantel, D.; et al. A stable hepatitis D virus-producing cell line for host target and drug discovery. Antivir. Res. 2023, 209, 105477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gripon, P.; Rumin, S.; Urban, S.; Le Seyec, J.; Glaise, D.; Cannie, I.; Guyomard, C.; Lucas, J.; Trepo, C.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C. Infection of a human hepatoma cell line by hepatitis B virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15655–15660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantz, O.; Parent, R.; Durantel, D.; Gripon, P.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C.; Zoulim, F. Persistence of the hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA in HepaRG human hepatocyte-like cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpeinen, M.; Tolonen, A.; Chesne, C.; Guillouzo, A.; Uusitalo, J.; Pelkonen, O. Functional expression, inhibition and induction of CYP enzymes in HepaRG cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2009, 23, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Lempp, F.A.; Mehrle, S.; Nkongolo, S.; Kaufman, C.; Fälth, M.; Stindt, J.; Königer, C.; Nassal, M.; Kubitz, R.; et al. Hepatitis B and D viruses exploit sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide for species-specific entry into hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1070–1083.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, T.; Budzinska, M.A.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Shackel, N.A.; Urban, S. Hepatitis B Virus DNA Integration Occurs Early in the Viral Life Cycle in an In Vitro Infection Model via Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide-Dependent Uptake of Enveloped Virus Particles. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02007-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luangsay, S.; Gruffaz, M.; Isorce, N.; Testoni, B.; Michelet, M.; Faure-Dupuy, S.; Maadadi, S.; Ait-Goughoulte, M.; Parent, R.; Rivoire, M.; et al. Early inhibition of hepatocyte innate responses by hepatitis B virus. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutz, P.; Metz, P.; Lempp, F.A.; Bender, S.; Qu, B.; Schöneweis, K.; Seitz, S.; Tu, T.; Restuccia, A.; Frankish, J.; et al. HBV Bypasses the Innate Immune Response and Does Not Protect HCV From Antiviral Activity of Interferon. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1791–1804.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Filzmayer, C.; Ni, Y.; Sültmann, H.; Mutz, P.; Hiet, M.S.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Bartenschlager, R.; Urban, S. Hepatitis D virus replication is sensed by MDA5 and induces IFN-β/λ responses in hepatocytes. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucifora, J.; Michelet, M.; Salvetti, A.; Durantel, D. Fast Differentiation of HepaRG Cells Allowing Hepatitis B and Delta Virus Infections. Cells 2020, 9, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, R.; Yang, D.; Xu, B.; Deng, R.; Xue, B.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Tang, S.; et al. Establishment of cell culture model and humanized mouse model of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 12, e0274523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choijilsuren, G.; Jhou, R.-S.; Chou, S.-F.; Chang, C.-J.; Yang, H.-I.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Chuang, W.-L.; Yu, M.-L.; Shih, C. Heparin at physiological concentration can enhance PEG-free in vitro infection with human hepatitis B virus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lempp, F.A.; Schlund, F.; Rieble, L.; Nussbaum, L.; Link, C.; Zhang, Z.; Ni, Y.; Urban, S. Recapitulation of HDV infection in a fully permissive hepatoma cell line allows efficient drug evaluation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Engelskircher, L.; Verch, G.; Tu, T.; Lempp, F.A.; Urban, S. Generation and characterization of a stable cell line persistently replicating and secreting the human hepatitis delta virus. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrier, E.R.; Colpitts, C.C.; Bach, C.; Heydmann, L.; Weiss, A.; Renaud, M.; Durand, S.C.; Habersetzer, F.; Durantel, D.; Abou-Jaoudé, G.; et al. A Targeted Functional RNA interference screen uncovers glypican 5 as an entry factor for hepatitis B and D viruses. Hepatology 2016, 63, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrier, E.R.; Weiss, A.; Bach, C.; Heydmann, L.; Turon-Lagot, V.; Kopp, A.; El Saghire, H.; Crouchet, E.; Pessaux, P.; Garcia, T.; et al. Combined small molecule and loss-of-function screen uncovers estrogen receptor alpha and CAD as host factors for HDV infection and antiviral targets. Gut 2020, 69, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Mouse Embryonic and Adult Fibroblast Cultures by Defined Factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, G.J.; Hay, D.C.; Park, I.H.; Fletcher, J.; Hannoun, Z.; Payne, C.M.; Dalgetty, D.; Black, J.R.; Ross, J.A.; Samuel, K.; et al. Generation of functional human hepatic endoderm from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Hepatology 2010, 51, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si-Tayeb, K.; Noto, F.K.; Nagaoka, M.; Li, J.; Battle, M.A.; Duris, C.; North, P.E.; Dalton, S.; Duncan, S.A. Highly efficient generation of human hepatocyte-like cells from induced pluripotent stem cells. Hepatology 2010, 51, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hockemeyer, D.; Jaenisch, R. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Meet Genome Editing. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 18, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Qu, B.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, C.; Deng, W.; Thi, V.L.D.; Xia, Y. Stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells as model for viral hepatitis research. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 9605252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlomai, A.; Schwartz, R.E.; Ramanan, V.; Bhatta, A.; De Jong, Y.P.; Bhatia, S.N.; Rice, C.M. Modeling host interactions with hepatitis B virus using primary and induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocellular systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12193–12198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Carpentier, A.; Cheng, X.; Block, P.D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Protzer, U.; Liang, T.J. Human stem cell-derived hepatocytes as a model for hepatitis B virus infection, spreading and virus-host interactions. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, F.; Mitani, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Takayama, K.; Tachibana, M.; Watashi, K.; Wakita, T.; Iijima, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Mizuguchi, H. Human induced-pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells as an in vitro model of human hepatitis B virus infection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, F.; Garn, J.; Anagho, H.A.; Vondran, F.W.R.; von Hahn, T.; Pietschmann, T.; Carpentier, A. Hepatitis D Virus Infection, Innate Immune Response and antiviral treatments in stem cell-derived hepatocytes. Liver Int. 2023, 43, 2116–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, S.; Kakinuma, S.; Asahina, Y.; Kamiya, A.; Miyoshi, M.; Tsunoda, T.; Nitta, S.; Asano, Y.; Nagata, H.; Otani, S.; et al. Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Hepatic Cell Lines as a new model for host interaction with hepatitis B virus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, H.; Qu, B.; Prawira, A.; Maurer, L.; Hu, J.; Fu, R.M.; Lempp, F.A.; Zhang, Z.; Grimm, D.; Wu, X.; et al. Human pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells for hepatitis D virus studies. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, A.; Sheldon, J.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Brown, R.J.P.; Pietschmann, T. Efficient acute and chronic infection of stem cell-derived hepatocytes by hepatitis C virus. Gut 2020, 69, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Xia, Y.; Serti, E.; Block, P.D.; Chung, M.; Chayama, K.; Rehermann, B.; Liang, T.J. Hepatitis B virus evades innate immunity of hepatocytes but activates cytokine production by macrophages. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1779–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megahed, F.A.K.; Zhou, X.; Sun, P. The interactions between HBV and the innate immunity of hepatocytes. Viruses 2020, 12, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takebe, T.; Sekine, K.; Enomura, M.; Koike, H.; Kimura, M.; Ogaeri, T.; Zhang, R.R.; Ueno, Y.; Zheng, Y.W.; Koike, N.; et al. Vascularized and functional human liver from an iPSC-derived organ bud transplant. Nature 2013, 499, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.Z.; Zheng, Y.W.; Miyakawa, K.; Murata, S.; Zhang, R.R.; Sekine, K.; Ueno, Y.; Takebe, T.; Wakita, T.; Ryo, A.; et al. Recapitulation of hepatitis B virus–host interactions in liver organoids from human induced pluripotent stem cells. EBioMedicine 2018, 35, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huch, M.; Dorrell, C.; Boj, S.F.; Van Es, J.H.; Li, V.S.W.; Van De Wetering, M.; Sato, T.; Hamer, K.; Sasaki, N.; Finegold, M.J.; et al. In vitro expansion of single Lgr5 + liver stem cells induced by Wnt-driven regeneration. Nature 2013, 494, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unzu, C.; Planet, E.; Brandenberg, N.; Fusil, F.; Cassano, M.; Perez-Vargas, J.; Friedli, M.; Cosset, F.-L.; Lutolf, M.P.; Wildhaber, B.E.; et al. Pharmacological Induction of a Progenitor State for the Efficient Expansion of Primary Human Hepatocytes. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2214–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Crignis, E.; Hossain, T.; Romal, S.; Carofiglio, F.; Moulos, P.; Khalid, M.M.; Rao, S.; Bazrafshan, A.; Verstegen, M.M.; Pourfarzad, F.; et al. Application of human liver organoids as a patient-derived primary model for HBV infection and related hepatocellular carcinoma. eLife 2021, 10, e60747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treyer, A.; Müsch, A. Hepatocyte polarity. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 243–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overeem, A.W.; Klappe, K.; Parisi, S.; Klöters-Planchy, P.; Mataković, L.; du Teil Espina, M.; Drouin, C.A.; Weiss, K.H.; van IJzendoorn, S.C.D. Pluripotent stem cell-derived bile canaliculi-forming hepatocytes to study genetic liver diseases involving hepatocyte polarity. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thi, V.L.; Wu, X.; Belote, R.L.; Andreo, U.; Takacs, C.N.; Fernandez, J.P.; Vale-Silva, L.A.; Prallet, S.; Decker, C.C.; Fu, R.M.; et al. Stem Cell-Derived Polarized Hepatocytes. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nell, P.; Kattler, K.; Feuerborn, D.; Hellwig, B.; Rieck, A.; Salhab, A.; Lepikhov, K.; Gasparoni, G.; Thomitzek, A.; Belgasmi, K.; et al. Identification of an FXR-Modulated Liver-Intestine Hybrid State in IPSC-Derived Hepatocyte-like Cells. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 1386–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Mitra, B.; Wang, M.; Guo, H.; Feng, Z. Elevated NTCP expression by an iPSC-derived human hepatocyte maintenance medium enhances HBV infection in NTCP-reconstituted HepG2 cells. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- March, S.; Ramanan, V.; Trehan, K.; Ng, S.; Galstian, A.; Gural, N.; Scull, M.A.; Shlomai, A.; Mota, M.M.; Fleming, H.E.; et al. Micropatterned coculture of primary human hepatocytes and supportive cells for the study of hepatotropic pathogens. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 2027–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ni, Y.; Lempp, F.A.; Walter, L.; Mutz, P.; Bartenschlager, R.; Urban, S. Hepatitis D and administered interferons control cell division-mediated virus spread. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giersch, K.; Bhadra, O.D.; Volz, T.; Allweiss, L.; Riecken, K.; Fehse, B.; Lohse, A.W.; Petersen, J.; Sureau, C.; Urban, S.; et al. Hepatitis delta virus persists during liver regeneration and is amplified through cell division both in vitro and in vivo. Gut 2019, 68, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieland, S.; Thimme, R.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. Genomic analysis of the host response to hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6669–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durantel, D.; Zoulim, F. Innate response to hepatitis B virus infection: Observations challenging the concept of a stealth virus. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1692–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucifora, J.; Durantel, D.; Testoni, B.; Hantz, O.; Levrero, M.; Zoulim, F. Control of hepatitis B virus replication by innate response of HepaRG cells. Hepatology 2010, 51, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Uchida, T.; Xia, Y.; Umarova, R.; Liu, C.J.; Chen, P.J.; Gaggar, A.; Suri, V.; Mücke, M.M.; Vermehren, J.; et al. Diminished hepatic IFN response following HCV clearance triggers HBV reactivation in coinfection. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3205–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murai, K.; Hikita, H.; Kai, Y.; Kondo, Y.; Fukuoka, M.; Fukutomi, K.; Doi, A.; Yamai, T.; Nakabori, T.; Fukuda, R.; et al. Hepatitis C Virus Infection Suppresses Hepatitis B Virus Replication via the RIG-I-like Helicase Pathway. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucifora, J.; Alfaiate, D.; Pons, C.; Michelet, M.; Ramirez, R.; Fusil, F.; Amirache, F.; Rossi, A.; Legrand, A.F.; Charles, E.; et al. Hepatitis D virus interferes with hepatitis B virus RNA production via interferon-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 958–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillich, N.; Zhang, Z.; Binder, M.; Urban, S.; Bartenschlager, R. Effect of variants in LGP2 on MDA5-mediated activation of interferon response and suppression of hepatitis D virus replication. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Nogusa, S.; Nicolas, E.; Balachandran, S.; Taylor, J. Interferon impedes an early step of hepatitis delta virus infection. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, C.Y.L.; Tham, C.Y.L.; Kah, J.; Tan, A.T.; Volz, T.; Chia, A.; Giersch, K.; Ladiges, Y.; Loglio, A.; Borghi, M.; et al. Hepatitis Delta Virus Acts as an Immunogenic Adjuvant in Hepatitis B Virus-Infected Hepatocytes. Cell Rep. Med. 2020, 1, 100060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, M.; Angelo, L.; Tétreault, Y.; Khabir, M.; Sureau, C.; Vaillant, A.; Labonté, P. HepG2BD: A novel and versatile cell line with inducible HDV replication and constitutive HBV expression. Viruses 2024, 16, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaiate, D.; Lucifora, J.; Abeywickrama-Samarakoon, N.; Michelet, M.; Testoni, B.; Cortay, J.C.; Sureau, C.; Zoulim, F.; Dény, P.; Durantel, D. HDV RNA replication is associated with HBV repression and interferon-stimulated genes induction in super-infected hepatocytes. Antiviral Res. 2016, 136, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowski, J.; Wedemeyer, H. Hepatitis delta: Immunopathogenesis and clinical challenges. Dig. Dis. 2010, 28, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Prieto, A.M.; Skelton, J.K.; Wai, S.N.; Large, E.; Lussignol, M.; Vizcay-Barrena, G.; Hughes, D.; Fleck, R.A.; Thursz, M.; Catanese, M.T.; et al. 3D microfluidic liver cultures as a physiological preclinical tool for hepatitis B virus infection. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Warner, C.; Duan, X.; Cheng, Z.; Jeyarajan, A.J.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Shao, T.; Salloum, S.; Chen, P.-J.; et al. HIV coinfection exacerbates HBV-induced liver fibrogenesis through a HIF-1α- and TGF-β1-dependent pathway. J. Hepatol. 2024; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groth, C.; Maric, J.; Garcés Lázaro, I.; Hofman, T.; Zhang, Z.; Ni, Y.; Keller, F.; Seufert, I.; Hofmann, M.; Neumann-Haefelin, C.; et al. Hepatitis D Infection Induces IFN-β-mediated NK cell activation and TRAIL-dependent cytotoxicity. Front Immunol. 2023, 14, 1287367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debelec-Butuner, B.; Quitt, O.; Schreiber, S.; Momburg, F.; Wisskirchen, K.; Protzer, U. Activation of distinct antiviral T-cell immunity: A comparison of bi- and trispecific T-cell engager antibodies with a chimeric antigen receptor targeting HBV envelope proteins. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1029214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altstetter, S.M.; Quitt, O.; Pinci, F.; Hornung, V.; Lucko, A.M.; Wisskirchen, K.; Jung, S.; Protzer, U. Hepatitis-D virus infection is not impaired by innate immunity but increases cytotoxic T-cell activity. Cells 2021, 10, 3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Model | PHHs | Huh7/HepG2 | HepaRG | dHepaRG | NTCP-Over Expressing Huh7/HepG2 | HLCs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viral entry | ++ | − | − | ++ | +++ | ++ |
| HBV replication | +++ | ++/+++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ |
| HDV replication | +++ | +++/++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | + |
| HBV Production | + | ++ | + | + | ++ | ++ |
| HDV production | + | +++ | + | + | +++ | + |
| Advantages | Gold standard | Easy to handle | Easy to handle | Mature model | Easy to handle | Mature model |
| Limitations | Limited availability | Immature model | Immature model | Heterogeneous differentiation | Immature model | Difficult differentiation |
| Model | PHHs | Huh7/HepG2 | HepaRG | dHepaRG | HLCs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stability | − | ++ | ++ | ++ | + |
| Maturity | ++ | − | − | + | + |
| Polarization | ++ | −/+ | − | ++ | ++ |
| NTCP expression | ++ | − | − | + | ++ |
| Innate immunity | ++ | −/+ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Proliferation | − | ++ | ++ | − | − |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carpentier, A. Cell Culture Models for Hepatitis B and D Viruses Infection: Old Challenges, New Developments and Future Strategies. Viruses 2024, 16, 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050716
Carpentier A. Cell Culture Models for Hepatitis B and D Viruses Infection: Old Challenges, New Developments and Future Strategies. Viruses. 2024; 16(5):716. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050716
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarpentier, Arnaud. 2024. "Cell Culture Models for Hepatitis B and D Viruses Infection: Old Challenges, New Developments and Future Strategies" Viruses 16, no. 5: 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050716
APA StyleCarpentier, A. (2024). Cell Culture Models for Hepatitis B and D Viruses Infection: Old Challenges, New Developments and Future Strategies. Viruses, 16(5), 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050716







