GE11 Peptide as an Active Targeting Agent in Antitumor Therapy: A Minireview
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. EGFR and EGFR Targeting
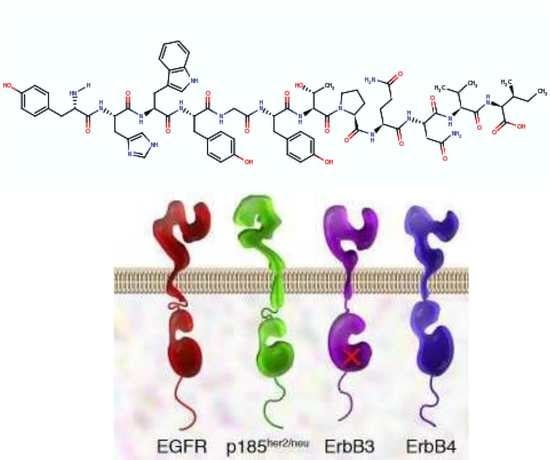
3. GE11 Structure and Biologic Activity
4. GE11 Conjugation and GE11-Conjugated Drug Delivery Systems
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Markman, M.; Gordon, A.N.; McGuire, W.P.; Muggia, F.M. Liposomal anthracycline treatment for ovarian cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2004, 31, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunjachan, S.; Blauz, A.; Mockel, D.; Theek, B.; Klessing, F.; Etrych, T.; Ulbrich, K.; VanBloois, L.; Storm, G.; Bartosz, G.; et al. Overcoming cellular multidrug resistance using classical nanomedicine formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 45, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghimi, S.M.; Hunter, A.C.; Murray, J.C. Nanomedicine: Current status and future perspectives. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 311–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghimi, S.M.; Hunter, A.C.; Andersen, T.L. Factors controlling nanoparticles pharmacokinetics: An integrated analysis and perspective. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 52, 481–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Wang, Z.; Feng, M. Nanocarriers with tunable surface properties to unblock bottlenecks in systemic drug gene delivery. J. Control. Release 2015, 214, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torchilin, V.P. Targeted pharmaceutical nanocarriers for cancer therapy and imaging. AAPS J. 2007, 9, E128–E147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, D.; Hubenak, J.R.; Mathur, A.B. Nanoparticles systems as tools to improve drug delivery and therapeutic efficacy. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2013, 101, 3646–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arpicco, S.; Lerda, C.; DallaPozza, E.; Costanzo, C.; Tsapias, N.; Stella, B.; Donadelli, M.; Dando, I.; Fattal, E.; Cattel, L.; et al. Hyaluronic acid-coated liposomes for active targeting of gemcitabine. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arpicco, S.; Milla, P.; Stella, B.; Dosio, F. Hyaluronic acid conjugates as vectors for the active targeting of drugs, genes and nanocomposites in cancer treatment. Molecules 2014, 19, 3193–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arranja, A.G.; Pathak, V.; Lammers, T.; Shi, Y. Tumor-targeted nanomedicines for cancer theranostics. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 115, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, P.P.; Biswas, S.; Torchilin, V.P. Current trends in the use of liposomes for tumor targeting. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 1509–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillone, A.; Riva, E.R.; Mondini, A.; Forte, C.; Calucci, L.; Innocenti, C.; De Julian Fernandez, C.; Cappello, V.; Gemmi, M.; Moscato, S.; et al. Active Targeting of Sorafenib: Preparation, characterization, and in vitro testing of drug-loaded magnetic solid lipid nanoparticles. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.D. Lipid-based nanoparticles in cancer diagnosis and therapy. J. Drug Deliv. 2013, 2013, 165981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, L.A.; Pereira, T.A.; Ramos, D.N.; Rezende, L.C.; Emery, F.S.; Sobral, L.M.; Leopoldino, A.M.; Lopez, R.F. Topical skin cancer therapy using doxorubicin-loaded cationic lipid nanoparticles and iontophoresis. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 11, 1975–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somani, S.; Dufès, C. Applications of dendrimers for brain delivery and cancer therapy. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 2403–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Crawford, M.; Mao, Y.; Lee, R.J.; Davis, I.C.; Elton, T.S.; Lee, L.J.; Nana-Sinkam, S.P. Therapeutic delivery of microRNA-29b by cationic lipoplexes for lung cancer. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2013, 2, E84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Crawford, M.; Yu, B.; Mao, Y.; Nana-Sinkam, S.P.; Lee, L.J. MicroRNA delivery by cationic lipoplexes for lung cancer therapy. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradishar, W.J. Albumin-bound paclitaxel: A next-generation taxane. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2006, 7, 1041–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arien, A.; Stoffels, P. History, potential, challenges and future development in nanopharmaceutical research and industry. In Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology: Innovation and Production; Cornier, J., Owen, A., Kwade, A., Vander Voorde, M.H., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, R. Polymer conjugates as anticancer nanomedicines. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 688–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, R. Polymer therapeutics at a crossroads? Finding the path for improved translation in the twenty-first century. J. Drug Target. 2017, 25, 759–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajbhiye, K.R.; Gajbhiye, J.M. EPR effect based nanocarriers targeting for treatment of cancer. Int. J. Drug Deliv. 2016, 8, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, R.; Duncan, R. Polymeric carriers: Preclinical safety and the regulatory implications for design and development of polymer therapeutics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1220–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, A.; Heller, D.A.; Winslow, M.W.; Dahlman, J.E.; Pratt, G.W.; Langer, R.; Jacks, T.; Anderson, D.G. Treating metastatic cancer with nanotechnology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, C.; Watson, A.; Kaplinsky, J.; Kamaly, N. Improved targeting of cancers with nanotherapeutics. In Cancer Nanotechnology; Zeineldin, R., Ed.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1530. [Google Scholar]
- Yarden, Y. The EGFR family and its ligands in human cancer: Signalling mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Eur. J. Cancer 2001, 37, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.T.; Berezov, A.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Debrin, J.; Murali, R.; Greene, M.I. Erb8 receptors: From oncogenes to targeted cancer therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha-Lima, C.M.; Soares, H.P.; Raez, L.E.; Singal, R. EGFR targeting of solid tumors. Cancer Control 2007, 14, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, T.M.; Iida, M.; Li, C.; Wheeler, D.L. The nuclear epidermal growth factor receptor signalling network and its role in cancer. Discov. Med. 2011, 12, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hynes, N.E.; McDonald, G. Erb receptors and signaling pathways in cancer. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Shin, D.M. Monoclonal antibodies to target epidermal growth factor receptor-positive tumors: A new paradigm for cancer therapy. Cancer 2002, 94, 1593–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Normanno, N.; De Luca, A.; Bianco, C.; Strizzi, L.; Mancino, M.; Maiello, M.R.; Carotenuto, A.; De Feo, G.; Caponigro, F.; Salomon, D.S. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signalling in cancer. Gene 2006, 366, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharkey, R.M.; Goldenberg, D.M. Targeted therapy of cancer: New prospects for antibodies and immunoconjugates. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2006, 56, 226–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, H.; Zhang, D.; Bartholomeusz, C.; Doihara, H.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Ueno, N.T. Role of epidermal growth factor receptor in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 136, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegelin, M.D.; Borczuk, A.C. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung adenocarcinoma. Lab. Investig. 2014, 94, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynch, E.; Li, J. Promising targets for modulating inflammation and mucosal healing therapy in IBD. Inflamm. Cell Signal. 2015, 2, e840. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, C.D.; Akama-Garren, E.H.; Stein, E.A.; Petralia, J.D.; Ruiz, P.J.; Edalati, A.; Lindstrom, T.M.; Robinson, W.H. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 3513–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassidy, S.; Syed, B.A. Colorectal cancer drugs market. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 525–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruoslahti, E. Peptides as targeting elements and tissue penetration devices for nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 3747–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, R.; Wu, X.; Sun, Y.; Yao, M.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Gu, J. Identification and characterization of a novel peptide ligand of epidermal growth factor receptor for targeted delivery of therapeutics. FASEB J. Res. Commun. 2005, 19, 1978–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mickeler, F.M.; Mocki, L.; Ruthardt, N.; Ogris, M.; Wagner, E.; Brauchle, C. Tuning nanoparticle uptake: Live-cell imaging reveals two distinct endocytosis mechanisms mediated by natural and artificial EGFR targeting ligand. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3417–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Liu, D.; Peng, J.; Deng, H.; Guo, Y.; Xu, L.X.; Miller, A.D.; Xu, Y. Novel peptide ligand directs liposomes towards EGF-R high-expressing cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colzani, B.; Biagiotti, M.; Speranza, G.; Dorati, R.; Modena, T.; Conti, B.; Tomasi, C.; Genta, I. Smart biodegradable nanoparticulate materials: Poly-lactide-co-glycolide functionalization with selected peptides. Curr. Nanosci. 2016, 12, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Huang, F.Z.; Cheng, L.F.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Ha, Q.; Li, I.; Wei, L.; Chen, D.W. GE11 modified liposomes for non-small lung cancer targeting preparation, ex vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 921–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abourbeh, G.; Shir, A.; Mishani, E.; Ogris, M.; Rodl, W.; Wagner, E.; Levitzki, A. PolylC GE11 polyplex inhibits EGFR-overexpressing tumours. IUBMB Life 2012, 64, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chariou, P.I.; Lee, K.L.; Wen, A.M.; Gulati, N.M.; Stewart, P.I.; Steinmetz, N.F. Detection and imaging of aggressive cancer cells using an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-targeted filamentous plant virus-based nanoparticle. Bioconjug. Chem. 2015, 26, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Master, A.M.; Rodriguez, M.E.; Kenney, M.E.; Oleinick, N.L.; Gupta, A.S. Delivery of the photosensitizer Pc4 in PEG-PCL micelles for in vitro PDT studies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 2386–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Master, A.M.; Qi, Y.; Oleinick, N.L.; Gupta, S.A. EGFR-mediated intracellular delivery of Pc4 nanoformulation for targeted photodynamic therapy of cancer: In vitro studies. Nanomedicine 2012, 8, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magadala, P.; Amiji, M. Epidermal growth factor receptor- targeted gelatin- based engineered nanocarriers for DNA delivery and transfection in human pancreatic cancer cells. AAPS J. 2008, 10, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.J.; Chien, W.H. Peptide-conjugated micelle as targeting nanocarrier for gene delivery. J. Nanopart. Res. 2008, 17, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milane, L.; Duan, Z.; Amiji, A. Development of EGFR- targeted polymer blend nanocarriers for combination Paclitaxel/Lonidamine delivery to treat multi-drug resistance in human breast and ovarian tumor cells. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Herrero, E.; Fernandez-Medarde, A. Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the future of chemotherapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 52–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.; Hunneyball, I.M. Evaluation of poly(lactic acid) as a biodegradable drug delivery system for parenteral administration. Int. J. Pharm. 1986, 30, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makadia, H.K.; Siegel, S.J. Poly Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) as Biodegradable Controlled Drug Delivery Carrier. Polymers 2011, 3, 1377–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gref, R.; Domb, A.; Quellec, P.; Blunk, T.; Muller, R.H.; Verbavatz, J.M.; Langer, R. The controlled intravenous delivery of drugs using PEG-coated sterically stabilized nanospheres. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Addio, S.M.; Saad, W.; Ansell, S.M.; Squiers, J.J.; Adamson, D.H.; Herrera-Alonso, M.; Wohl, A.R.; Hoye, T.R.; Macosko, C.W.; Mayer, L.D.; et al. Effects of block copolymer properties on nanocarrier protection from in vivo clearance. J. Control. Release 2012, 162, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentacourt, T.; Byrne, J.D.; Sunaryo, N.; Crowder, S.W.; Kadapakkam, M.; Patel, S.; Casciato, S.; Brannon-Peppas, L. PEGylation strategies for active targeting of PLA/PLGA nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2009, 91, 263–276. [Google Scholar]
- Farokhzad, O.C.; Jon, S.; Khademhosseini, A.; Tran, T.N.; Lavan, D.A.; Langer, R. Nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugates: A new approach for targeting prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7668–7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Master, A.M.; Gupta, S.A. EGF receptor-targeted nanocarriers for enhanced cancer treatment. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 2386–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Master, A.M.; Malamas, A.; Solanki, R.; Clausen, D.M.; Eiseman, J.L.; Gupata, S. A cell-targeted photodynamic nanomedicine strategy for head and neck cancer. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 1988–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milane, L.; Duan, Z.; Amiji, A. Pharmacokinetics and biodistributionof lonidamine/paclitaxel loaded, EGFR-targeted nanoparticles in an orthotopic animal model of multi-drug resistant breast cancer. Nanomedicine 2011, 7, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milane, L.; Duan, Z.; Amiji, A. Therapeutic efficacy and safety of paclitaxel/Lonidamine loaded EGFR-targeted nanoparticles for the treatment of multi.drug resistant cancer. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colzani, B.; Speranza, G.; Dorati, R.; Conti, B.; Modena, T.; Bruni, G.; Zagato, E.; Vermeulen, L.; Dakwar, G.R.; Braekmans, K.; et al. Design of smart GE11-PLGA/PEG-PLGA blend nanoparticulate platforms for parenteral administration of hydrophilic macromolecular drugs: Synthesis, preparation and in vitro/ex vivo characterization. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 1112–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, W. Injectable formulations of poly(lactic acid) and its copolymers in clinical use. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 213–227. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, D.R.; Webb, M.N.; Cadotte, T.H.; Gavette, M.N. Use of targeted liposome-based chemotherapeutics to treat breast cancer. Breast Cancer 2015, 9 (Suppl. 2), 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ongarora, B.G.; Fontenot, K.R.; Hu, X.; Sehgal, L.; Satyanarayana-Jois, S.D.; Vicente, M.G. Phthalocyanine-peptide conjugates for epidermal growth factor receptor targeting. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 3725–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Liu, D.; Peng, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; Gu, J.R. Peptide ligand-mediated liposome distribution and targeting to EGFR tumour in vivo. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 363, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.-W.; Liu, D.; Cao, Y.; Wang, X. GE11 peptide-conjugated nanoliposomes to enhance the combinational therapeutic efficacy of docetaxel and siRNA in laryngeal cancers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 6461–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarscheler, K.; Prapainop, K.; Mahon, E.; Rocks, L.; Bramini, M.; Kelly, P.M.; Stephan, H.; Dawson, K.A. Diagnostic nanoparticle targeting of the EGF-receptor in complex biological conditions using single-domain antibodies. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 6046–6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.; Yang, D.; Liang, X.; Ao, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Shi, B. Design and biological activity of epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted peptide doxorubicin conjugate. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 70, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Ouyang, J.; Chen, Q.; Deng, C.; Meng, F.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, R.; Lan, Q.; Zhing, Z. EGFR and CD44 dual-targeted multifunctional nanogels boost protein delivery to ovarian and breast cancers in vitro and in vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 24140–24147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeri, A.; Zalba, S.; ten Hagen, T.M.; Dadashzadeh, S.D.; Koning, G.A. EGFR targeted thermosensitive liposomes: A novel multifunctional platform for simultaneous tumor targeted and stimulus responsive drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B 2016, 146, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Genta, I.; Chiesa, E.; Colzani, B.; Modena, T.; Conti, B.; Dorati, R. GE11 Peptide as an Active Targeting Agent in Antitumor Therapy: A Minireview. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10010002
Genta I, Chiesa E, Colzani B, Modena T, Conti B, Dorati R. GE11 Peptide as an Active Targeting Agent in Antitumor Therapy: A Minireview. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleGenta, Ida, Enrica Chiesa, Barbara Colzani, Tiziana Modena, Bice Conti, and Rossella Dorati. 2018. "GE11 Peptide as an Active Targeting Agent in Antitumor Therapy: A Minireview" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10010002
APA StyleGenta, I., Chiesa, E., Colzani, B., Modena, T., Conti, B., & Dorati, R. (2018). GE11 Peptide as an Active Targeting Agent in Antitumor Therapy: A Minireview. Pharmaceutics, 10(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10010002