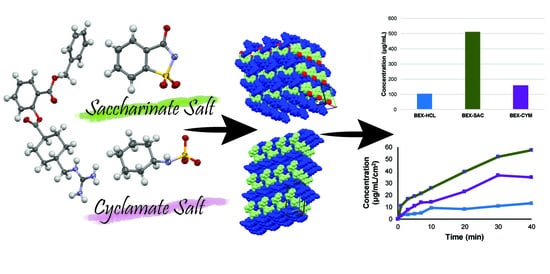
Solubility Improvement of Benexate through Salt Formation Using Artificial Sweetener
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Salts
2.2.2. Powder X-Ray Diffraction
2.2.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry and Thermogravimetry
2.2.4. Single-Crystal X-Ray Diffraction and Refinements
2.2.5. Solubility and Intrinsic Dissolution Rate
2.2.6. Dynamic Vapor Sorption
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ohara, T.; Kitamura, S.; Kitagawa, K.; Terada, K. Dissolution mechanism of poorly water-soluble drug from extended release solid dispersion system with ethylcellulose and hydroxypropylcellulose. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 302, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, S.; Hamaura, T.; Furuyama, N.; Kusai, A.; Yonemochi, E.; Terada, K. Effects of water content in physical mixture and heating temperature of troglitazone-PVP K30 solid dispersion prepared by closed meting method. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 302, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liversidge, G.G.; Cundy, K.C. Particle size reduction for improvement of oral bioavailability of hydrophobic drugs: I. Absolute oral bioavaibility of nanocrystalline danazol in beagle dogs. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 125, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, R.H.; Peters, K. Nanosuspensions for the formulation of poorly soluble drugs: I. Preparation by a size-reduction technique. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 160, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, J.; Ankola, D.D.; Beniwal, V.; Singh, D.; Kumar, M.N.V.R. Nanoparticle encapsulation improves oral bioavailability of curcumin by at least 9-fold when compared to curcumin administered with piperine as absorption enhancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 37, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, D.; Cutler, D.J.; Chan, H.K.; Yun, J.; Raper, J.A. What is a suitable dissolution method for drug nanoparticles? Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 1696–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tommasini, S.; Raneri, D.; Ficarra, R.; Calabro, M.L.; Stancanelli, R.; Ficarra, P. Improvement in solubility and dissolution rate of flavonoids by complexation with β-cyclodextrin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2004, 35, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, N.B.; Chowdary, K.P.R.; Murthy, K.V.R.; Satyanayana, V.; Haman, A.R.; Becket, G. Physicochemical characterization and dissolution properties of meloxicam-cyclodectrin binary systems. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2004, 35, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, J.L. The current status of solid dispersions. Pharm. Acta Helv. 1986, 61, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Putra, O.D.; Yonemochi, E.; Uekusa, H. Isostructural multicomponent gliclazide crystals with improved solubility. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 6568–6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Zhang, Y.S.; Pang, B.; Hyun, D.C.; Yang, M.; Xia, Y. Engineered nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12320–12354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krug, H.F. Nanosafety research-Are we on the right track? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12304–12319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyane, J.R.; Arias-Blanco, M.J.; Gines, J.M.; Rabasco, A.M.; Perez-Martinez, J.I.; Mor, M.; Giordano, F. Nuclear magnetic resonance investigations of the inclusion complexation of gliclazide with β-cyclodextrin. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desiraju, G.R. Supramolecular synthons in crystal engineering- A new organic synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1995, 34, 2311–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desiraju, G.R. Crystal engineering: A holistic view. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 8342–8356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putra, O.D.; Umeda, D.; Nugraha, Y.P.; Furuishi, T.; Nagase, H.; Fukuzawa, K.; Uekusa, H.; Yonemochi, E. Solubility improvement of epalerstat by layered structure formation via cocrystallization. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 2614–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visheshwar, P.; McMahon, J.A.; Bis, J.A.; Zawarotko, M.J. Pharmaceutical cocrystals. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 499–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeno, Y.; Fukami, T.; Kawahata, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Tagami, T.; Ozeki, T.; Suzuki, T.; Tomono, K. Novel pharmaceutical cocrystal consisting paracetamol and trimethylglycine, a new promising cocrystal former. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trask, A.V.; Motherwell, W.D.S.; Jones, W. Pharmaceutical cocrystallization: Engineering a remedy for caffeine hydration. Cryst. Growth Des. 2005, 5, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainurofiq, A.; Mauludin, R.; Mudhakir, D.; Umeda, D.; Soewandhi, S.N.; Putra, O.D.; Yonemochi, E. Improving mechanical properties of desloratadine via multicomponent crystal formation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 111, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, N.; Rodriguez-Hornedo, N. Engineering cocrsystal solubility, stability and pHmax by micellar solubilization. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 5219–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putra, O.D.; Furuishi, T.; Yonemochi, E.; Terada, K.; Uekusa, H. Drug-drug multicomponent crystals as an effective technique to overcome weaknesses in parent drugs. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 3577–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, O.D.; Umeda, D.; Nugraha, Y.P.; Nango, K.; Yonemochi, E.; Uekusa, H. Simultaneous improvement of epalerstat photostability and solubility via cocrystallization: A case study. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Karpinski, P.H.; Sutton, P.; Liu, Y.; Hook, D.F.; Hu, B.; Blacklock, T.J.; Fanwick, P.E.; Prashad, M.; Godtfredsen, S.; et al. LCZ696: A dual-acting sodium supramolecular complex. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 275–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campoli-Richards, D.M.; Sorkin, E.M.; Heel, R.C. Inosine pranobex: A preliminary review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy. Drugs 1986, 32, 383–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Umeda, D.; Putra, O.D.; Uekusa, H.; Yonemochi, E. Drug-drug multicomponent crystal of acedoben-dimepranol 2:1. X-ray Struct. Anal. Online 2016, 32, 39–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, O.D.; Yoshida, T.; Umeda, D.; Higashi, K.; Uekusa, H.; Yonemochi, E. Crystal structure determination of dimenhydrinate after more than 60 years: Solving salt-cocrystal ambiguity via solid state characterizations and solubility study. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 5223–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordignon, S.; Vioglio, P.C.; Priola, E.; Vionovich, E.; Gobetto, R.; Nishiyama, Y.; Chierotti, M.R. Engineering codrug solid forms: Mechanochemical synthesis of an indometacine-caffeine system. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 5744–5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakuria, R.; Sarma, B. Drug-drug and drug-nutraceutical cocrsytals/salts as alternative medicine for combination therapy: A crystal engineering approach. Crystals 2018, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saal, C.; Becker, A. Pharmaceutical salts: A summary on doses of salt formers from the orange book. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berge, S.M.; Bighley, L.M. Monkhouse, D.C. Introduction. In Handbook of Pharmaceutical Salts: Properties, Selection, and Use; Stahl, P.H., Wermuth, C.G., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2002; Volume 1, pp. 1–7. ISBN 3-906390-26-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bastin, R.J.; Bowker, M.J.; Slater, B.J. Salt selection and optimization procedures form pharmaceutical new chemical entities. Org. Proc. Res. Dev. 2000, 4, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, O.D.; Yoshida, T.; Umeda, D.; Gunji, M.; Uekusa, H.; Yonemochi, E. Crystallographic analysis of phase dissociation related to anomalous solubility of irsogladine maleate. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 6714–6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, T.; Matsunaga, K. Nitric oxide-associated vasorelaxing effect of an anti-ulcer agent, benexate hydrocholoride betadex. Drug. Dev. Res. 1995, 36, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muranushi, N.; Yoshida, M.; Kinoshita, H.; Hirose, F.; Fukuda, T.; Doteuchi, M.; Yamada, H. Studies of benexate CD: Effect of inclusion compound formation on the antiulcer activity of benexate, the effective ingredient of benexate CD. Folia Pharmacol. Jpn. 1988, 91, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, Y.; Odaguchi, K.; Jyoyama, H.; Yasui, K.; Mizui, T. Differential effect of benexate hydrochloride betadex on prostaglandin levels in stomach and inflammatory sites in rats. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 72, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banarjee, R.; Bhatt, P.M.; Ravindra, N.V.; Desiraju, G.R. Saccharin salts of active pharmaceutical ingredients, their crystal structure, and increased water solubilities. Cryst. Growth Des. 2005, 5, 2299–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.M.; Ravindra, N.V.; Banarjee, R.; Desiraju, G.R. Saccharin as a salt former. Enhanced solubilities of saccharinates of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Chem. Commun. 2005, 28, 1073–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashi, T. Calculated Using ABSCOR: Empirical Absorption Correction Based on Fourier Series Approximation; Rigaku: The Woodland, TX, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Burla, M.C.; Caliandro, R.; Camalli, M.; Carrozzini, B.; Cascarano, G.L.; De Caro, L.; Giacovazzo, C.; Polidori, G.; Spagna, R. SIR2004: An improved tool for crystal structure determination and refinement. J. Appl. Cryst. 2005, 38, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Cryst. 2008, A64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C.F.; Bruno, I.J.; Chisholm, J.A.; Edgington, P.R.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Rodriguez-Monge, L.; Taylor, R.; van der Streek, J.; Wood, P.A. Mercury CSD 2.0- New features for visualization and investigation of crystal structures. J. Appl. Cryst. 2008, 41, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Hu, S.; Sun, C.C. Expedited development of a highly dose orally disintegrating metformin tablet enabled by sweet salt formation with acesulfame. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Parameters | BEX–SAC | BEX–CYM |
|---|---|---|
| Moiety formula | C23H28N3O4·C7H4NO3S·H2O | C23H28N3O4·C6H12NO3S |
| Formula weight | 610.67 | 588.71 |
| Crystal system | Triclinic | Triclinic |
| Space group | P-1 | P-1 |
| a (Å) | 8.8182 (2) | 6.97200 (18) |
| b (Å) | 12.8387 (3) | 10.3577 (3) |
| c (Å) | 14.1237 (4) | 21.5218 (6) |
| α (°) | 82.167 (6) | 103.718 (7) |
| β (°) | 79.787 (6) | 91.536 (6) |
| γ (°) | 70.139 (5) | 96.783 (7) |
| V (Å3) | 1475.06 (8) | 1496.85 (9) |
| Z, Z′ | 2, 1 | 2, 1 |
| T (K) | 173 | 173 |
| Unique ref. | 5291 (Rint = 0.031) | 5377 (Rint = 0.031) |
| Refined parameters | 416 | 394 |
| Goodness-of-fit on F2 | 1.06 | 1.13 |
| Final R indices [I > 2σ (I)] | R1 = 0.0337 | R1 = 0.0418 |
| CCDC number | 1840914 | 1840913 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dwichandra Putra, O.; Umeda, D.; Fujita, E.; Haraguchi, T.; Uchida, T.; Yonemochi, E.; Uekusa, H. Solubility Improvement of Benexate through Salt Formation Using Artificial Sweetener. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10020064
Dwichandra Putra O, Umeda D, Fujita E, Haraguchi T, Uchida T, Yonemochi E, Uekusa H. Solubility Improvement of Benexate through Salt Formation Using Artificial Sweetener. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(2):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10020064
Chicago/Turabian StyleDwichandra Putra, Okky, Daiki Umeda, Eriko Fujita, Tamami Haraguchi, Takahiro Uchida, Etsuo Yonemochi, and Hidehiro Uekusa. 2018. "Solubility Improvement of Benexate through Salt Formation Using Artificial Sweetener" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 2: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10020064
APA StyleDwichandra Putra, O., Umeda, D., Fujita, E., Haraguchi, T., Uchida, T., Yonemochi, E., & Uekusa, H. (2018). Solubility Improvement of Benexate through Salt Formation Using Artificial Sweetener. Pharmaceutics, 10(2), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10020064