Alterations in Expression and Function of ABC Family Transporters at Blood-Brain Barrier under Liver Failure and Their Clinical Significances
Abstract
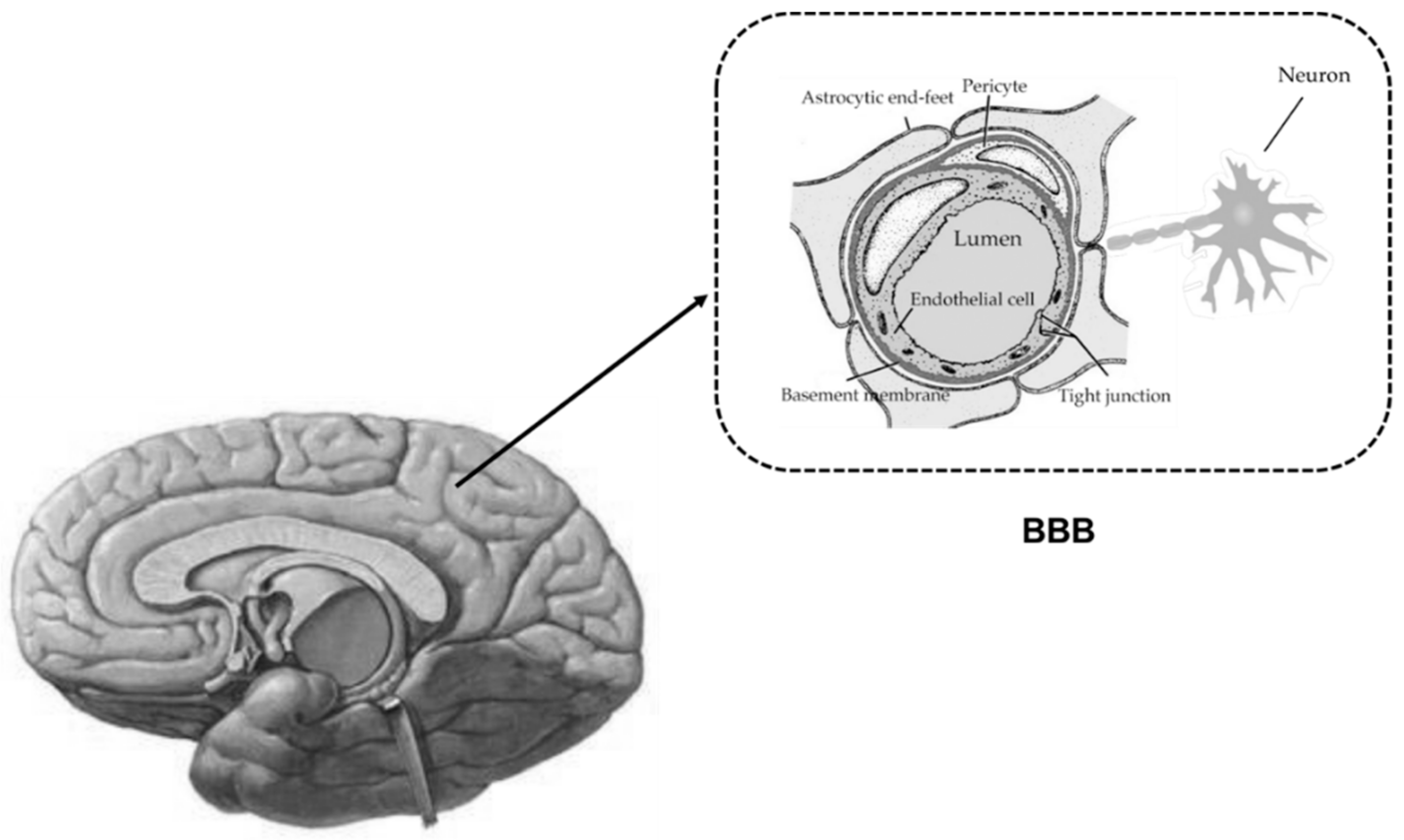
:1. Introduction
2. ABC Drug Transporters Expressed at BBB and Their Functions
3. Alterations in BBB Permeability under Liver Failure
4. Alterations in Expression and Function of ABC Transporters at BBB by Liver Failure
5. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Redzic, Z. Molecular biology of the blood-brain and the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barriers: Similarities and differences. Fluids Barriers CNS 2011, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Covarrubias, L.; Slosky, L.M.; Thompson, B.J.; Davis, T.P.; Ronaldson, P.T. Transporters at CNS barrier sites: Obstacles or opportunities for drug delivery? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 1422–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strazielle, N.; Ghersi-Egea, J.F. Physiology of blood-brain interfaces in relation to brain disposition of small compounds and macromolecules. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 1473–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Ahmad, A.; Taboada, C.B.; Gassmann, M.; Ogunshola, O.O. Astrocytes and pericytes differentially modulate blood-brain barrier characteristics during development and hypoxic insult. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2011, 31, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daneman, R.; Zhou, L.; Kebede, A.A.; Barres, B.A. Pericytes are required for blood-brain barrier integrity during embryogenesis. Nature 2010, 468, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Menachem, E.; Johansson, B.B.; Svensson, T.H. Increased vulnerability of the blood-brain barrier to acute hypertension following depletion of brain noradrenaline. J. Neural Transm. 1982, 53, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarnitsky, D.; Gross, Y.; Lorian, A.; Shalev, A.; Lamensdorf, I.; Bornstein, R.; Shorer, S.; Mayevsky, A.; Patel, K.P.; Abbott, N.J.; et al. Blood-brain barrier opened by stimulation of the parasympathetic sphenopalatine ganglion: A new method for macromolecule delivery to the brain. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 101, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterworth, R.F. The liver-brain axis in liver failure: Neuroinflammation and encephalopathy. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudsen, G.M.; Schmidt, J.; Almdal, T.; Paulson, O.B.; Vilstrup, H. Passage of amino acids and glucose across the blood-brain barrier in patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 1993, 17, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile, A.S.; Saito, K.; al-Mardini, H.; Record, C.O.; Hughes, R.D.; Harrison, P.; Williams, R.; Li, Y.; Heyes, M.P. The relationship between plasma and brain quinolinic acid levels and the severity of hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology 1995, 108, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, A.S.; Saito, K.; Li, Y.; Heyes, M.P. The relationship between plasma and brain quinolinic acid levels and the severity of hepatic encephalopathy in animal models of fulminant hepatic failure. J. Neurochem. 1995, 64, 2607–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullahi, W.; Davis, T.P.; Ronaldson, P.T. Functional expression of P-glycoprotein and organic anion transporting polypeptides at the blood-brain barrier: Understanding transport mechanisms for improved CNS drug delivery? AAPS J. 2017, 19, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinkel, A.H.; Jonker, J.W. Mammalian drug efflux transporters of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) family: An overview. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, A.; Obach, R.S.; Smith, B.J.; Hosea, N.A.; Becker, S.; Callegari, E.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Choo, E.; Cianfrogna, J.; et al. The impact of P-glycoprotein on the disposition of drugs targeted for indications of the central nervous system: Evaluation using the mdr1a/1b knockout mouse model. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2005, 33, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonker, J.W.; Wagenaar, E.; van Deemter, L.; Gottschlich, R.; Bender, H.M.; Dasenbrock, J.; Schinkel, A.H. Role of blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein in limiting brain accumulation and sedative side-effects of asimadoline, a peripherally acting analgaesic drug. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 127, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mayer, U.; Wagenaar, E.; Dorobek, B.; Beijnen, J.H.; Borst, P.; Schinkel, A.H. Full blockade of intestinal P-glycoprotein and extensive inhibition of blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein by oral treatment of mice with PSC833. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 2430–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinkel, A.H.; Smit, J.J.; van Tellingen, O.; Beijnen, J.H.; Wagenaar, E.; van Deemter, L.; Mol, C.A.; van der Valk, M.A.; Robanus-Maandag, E.C.; te Riele, H.P.; et al. Disruption of the mouse mdr1a P-glycoprotein gene leads to a deficiency in the blood-brain barrier and to increased sensitivity to drugs. Cell 1994, 77, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shityakov, S.; Forster, C. Multidrug resistance protein P-gp interaction with nanoparticles (fullerenes and carbon nanotube) to assess their drug delivery potential: A theoretical molecular docking study. Int. J. Comput. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 6, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.; Miller, M.C.; Monahan, R.; Osgood, D.P.; Stopa, E.G.; Silverberg, G.D. P-glycoprotein expression and amyloid accumulation in human aging and alzheimer’s disease: Preliminary observations. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 2475–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesuriya, H.C.; Bullock, J.Y.; Faull, R.L.; Hladky, S.B.; Barrand, M.A. ABC efflux transporters in brain vasculature of alzheimer’s subjects. Brain Res. 2010, 1358, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deo, A.K.; Borson, S.; Link, J.M.; Domino, K.; Eary, J.F.; Ke, B.; Richards, T.L.; Mankoff, D.A.; Minoshima, S.; O’Sullivan, F.; et al. Activity of P-glycoprotein, a beta-amyloid transporter at the blood-brain barrier, is compromised in patients with mild alzheimer disease. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartz, A.M.; Miller, D.S.; Bauer, B. Restoring blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein reduces brain amyloid-beta in a mouse model of alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 77, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Xu, X.; Yang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Liu, X.; Xie, L. Impaired function and expression of P-glycoprotein in blood-brain barrier of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Brain Res. 2006, 1123, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Jia, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, G.; Xie, L. Insulin therapy restores impaired function and expression of P-glycoprotein in blood-brain barrier of experimental diabetes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, D.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Xie, L.; Pang, X.; Liu, L. Attenuated function and expression of P-glycoprotein at blood-brain barrier and increased brain distribution of phenobarbital in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 561, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Wang, X.T.; Liu, L.; Yao, D.; Liu, C.; Zhang, M.; Guo, H.F.; Liu, X.D. P-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 are oppositely altered in brain of rats with thioacetamide-induced acute liver failure. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.Y.D.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.T.; Zhang, L.L.; Liu, X.D. The effect of chronic liver failure on the function and expression of P-gp and Mrp2 in rat brain. J. China Pharm. Univ. 2012, 43, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Miao, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, B.; Liu, X. Altered function and expression of ABC transporters at the blood-brain barrier and increased brain distribution of phenobarbital in acute liver failure mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loscher, W.; Potschka, H. Role of multidrug transporters in pharmacoresistance to antiepileptic drugs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 301, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Z.; Yang, J.; Yang, H. Increased P-glycoprotein expression and decreased phenobarbital distribution in the brain of pentylenetetrazole-kindled rats. Neuropharmacology 2007, 53, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, X.; Liu, X.; Wen, T.; Xie, S.; Yao, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Xie, L. Combined effects of epileptic seizure and phenobarbital induced overexpression of P-glycoprotein in brain of chemically kindled rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 159, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kusuhara, H.; Jonker, J.W.; Schinkel, A.H.; Sugiyama, Y. Investigation of efflux transport of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate and mitoxantrone at the mouse blood-brain barrier: A minor role of breast cancer resistance protein. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 312, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Raub, T.J.; Sawada, G.A.; Kasper, S.C.; Bacon, J.A.; Bridges, A.S.; Pollack, G.M. Breast cancer resistance protein interacts with various compounds in vitro, but plays a minor role in substrate efflux at the blood-brain barrier. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittapalli, R.K.; Vaidhyanathan, S.; Sane, R.; Elmquist, W.F. Impact of P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2) on the brain distribution of a novel braf inhibitor: Vemurafenib (PLX4032). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 342, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Agarwal, S.; Shaik, N.M.; Chen, C.; Yang, Z.; Elmquist, W.F. P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein influence brain distribution of dasatinib. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 330, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sane, R.; Agarwal, S.; Mittapalli, R.K.; Elmquist, W.F. Saturable active efflux by P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein at the blood-brain barrier leads to nonlinear distribution of elacridar to the central nervous system. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 345, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, N.A.; Buckle, T.; Zhao, J.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schellens, J.H.; van Tellingen, O. Restricted brain penetration of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib due to the drug transporters P-gp and Bcrp. Investig. New Drugs 2012, 30, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Sane, R.; Gallardo, J.L.; Ohlfest, J.R.; Elmquist, W.F. Distribution of gefitinib to the brain is limited by P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2)-mediated active efflux. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 334, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durmus, S.; Sparidans, R.W.; van Esch, A.; Wagenaar, E.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schinkel, A.H. Breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) and P-glycoprotein (P-GP/ABCB1) restrict oral availability and brain accumulation of the parp inhibitor rucaparib (AG-014699). Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Sane, R.; Ohlfest, J.R.; Elmquist, W.F. The role of the breast cancer resistance protein (abcg2) in the distribution of sorafenib to the brain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 336, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, N.A.; Zhao, J.; Kroon, E.; Buckle, T.; Beijnen, J.H.; van Tellingen, O. P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein: Two dominant transporters working together in limiting the brain penetration of topotecan. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 6440–6449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nies, A.T.; Jedlitschky, G.; Konig, J.; Herold-Mende, C.; Steiner, H.H.; Schmitt, H.P.; Keppler, D. Expression and immunolocalization of the multidrug resistance proteins, Mrp1-Mrp6 (ABCC1-ABCC6), in human brain. Neuroscience 2004, 129, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, H.; Ishihara, H.; Langmann, T.; Schmitz, G.; Stieger, B.; Wieser, H.G.; Yonekawa, Y.; Frei, K. Distribution and functional activity of P-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance-associated proteins in human brain microvascular endothelial cells in hippocampal sclerosis. Epilepsy Res. 2006, 68, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, M.S.; Zerangue, N.; Woodford, K.; Roberts, L.M.; Tate, E.H.; Feng, B.; Li, C.; Feuerstein, T.J.; Gibbs, J.; Smith, B.; et al. Comparative gene expression profiles of ABC transporters in brain microvessel endothelial cells and brain in five species including human. Pharmacol. Res. 2009, 59, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soontornmalai, A.; Vlaming, M.L.; Fritschy, J.M. Differential, strain-specific cellular and subcellular distribution of multidrug transporters in murine choroid plexus and blood-brain barrier. Neuroscience 2006, 138, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcorelles, P.; Friocourt, G.; Uguen, A.; Lede, F.; Ferec, C.; Laquerriere, A. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator protein (CFTR) expression in the developing human brain: Comparative immunohistochemical study between patients with normal and mutated CFTR. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2014, 62, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Su, M.; McNutt, M.A.; Gu, J. Expression and distribution of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in neurons of the human brain. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2009, 57, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulberg, A.E.; Resta, L.P.; Wiedner, E.B.; Altschuler, S.M.; Jefferson, D.M.; Broussard, D.L. Expression and localization of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator mRNA and its protein in rat brain. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, W.; Sun, C.M.; Liu, P. Alterations of blood-brain barrier and associated factors in acute liver failure. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2013, 2013, 841707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, M.; Hughes, R.D.; Keays, R.T.; Williams, R. Electron microscopic study of brain capillaries in cerebral edema from fulminant hepatic failure. Hepatology 1992, 15, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traber, P.G.; Dal Canto, M.; Ganger, D.R.; Blei, A.T. Electron microscopic evaluation of brain edema in rabbits with galactosamine-induced fulminant hepatic failure: Ultrastructure and integrity of the blood-brain barrier. Hepatology 1987, 7, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Song, H.L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.X.; Cui, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, P. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha affects blood-brain barrier permeability and tight junction-associated occludin in acute liver failure. Liver Int. 2010, 30, 1198–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, P.; Sun, B.; Zhong, Z.; Liu, C.; Ling, Z.; Chen, Y.; Shu, N.; Zhao, K.; et al. Acute liver failure impairs function and expression of breast cancer-resistant protein (BCRP) at rat blood-brain barrier partly via ammonia-ROS-ERK1/2 activation. J. Neurochem. 2016, 138, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, V.; Singh, R.; Acharya, S.K. Predictive value of arterial ammonia for complications and outcome in acute liver failure. Gut 2006, 55, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zwirner, K.; Thiel, C.; Thiel, K.; Morgalla, M.H.; Konigsrainer, A.; Schenk, M. Extracellular brain ammonia levels in association with arterial ammonia, intracranial pressure and the use of albumin dialysis devices in pigs with acute liver failure. Metab. Brain Dis. 2010, 25, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skowronska, M.; Zielinska, M.; Wojcik-Stanaszek, L.; Ruszkiewicz, J.; Milatovic, D.; Aschner, M.; Albrecht, J. Ammonia increases paracellular permeability of rat brain endothelial cells by a mechanism encompassing oxidative/nitrosative stress and activation of matrix metalloproteinases. J. Neurochem. 2012, 121, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wright, G.; Shawcross, D.; Olde Damink, S.W.; Jalan, R. Brain cytokine flux in acute liver failure and its relationship with intracranial hypertension. Metab. Brain Dis. 2007, 22, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Desjardins, P.; Butterworth, R.F. Direct evidence for central proinflammatory mechanisms in rats with experimental acute liver failure: Protective effect of hypothermia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2009, 29, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odeh, M.; Sabo, E.; Srugo, I.; Oliven, A. Relationship between tumor necrosis factor-alpha and ammonia in patients with hepatic encephalopathy due to chronic liver failure. Ann. Med. 2005, 37, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalan, R.; Olde Damink, S.W.; Hayes, P.C.; Deutz, N.E.; Lee, A. Pathogenesis of intracranial hypertension in acute liver failure: Inflammation, ammonia and cerebral blood flow. J. Hepatol. 2004, 41, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bemeur, C.; Qu, H.; Desjardins, P.; Butterworth, R.F. IL-1 or TNF receptor gene deletion delays onset of encephalopathy and attenuates brain edema in experimental acute liver failure. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 56, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, N.; Hsu, H.P.; Wu, C.M.; Liu, C.C.; Lei, H.Y. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha causes an increase in blood-brain barrier permeability during sepsis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 50, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Lv, S.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, J.; Li, C.; Liu, P. Tumor necrosis factor-α affects blood-brain barrier permeability in acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 23, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, J.H.; Yamamoto, S.; Steers, J.; Sevlever, D.; Lin, W.; Shimojima, N.; Castanedes-Casey, M.; Genco, P.; Golde, T.; Richelson, E.; et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 contributes to brain extravasation and edema in fulminant hepatic failure mice. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McMillin, M.A.; Frampton, G.A.; Seiwell, A.P.; Patel, N.S.; Jacobs, A.N.; DeMorrow, S. TGFβ1 exacerbates blood-brain barrier permeability in a mouse model of hepatic encephalopathy via upregulation of MMP9 and downregulation of claudin-5. Lab. Investig. 2015, 95, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Hori, T.; Ohashi, N.; Baine, A.M.; Eckman, C.B.; Nguyen, J.H. Occludin is regulated by epidermal growth factor receptor activation in brain endothelial cells and brains of mice with acute liver failure. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1294–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rigau, V.; Morin, M.; Rousset, M.C.; de Bock, F.; Lebrun, A.; Coubes, P.; Picot, M.C.; Baldy-Moulinier, M.; Bockaert, J.; Crespel, A.; et al. Angiogenesis is associated with blood-brain barrier permeability in temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 2007, 130, 1942–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, T.; Deguchi, K.; Nagotani, S.; Zhang, H.; Sehara, Y.; Tsuchiya, A.; Abe, K. Cerebral ischemia and angiogenesis. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2006, 3, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.J.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, B.; Zhe, X.; Wang, M.J.; Shi, S.T.; Bai, J.; Lin, T.; Guo, C.J.; Zhang, S.J.; et al. Disruption of the blood-brain barrier after generalized tonic-clonic seizures correlates with cerebrospinal fluid MMP-9 levels. J. Neuroinflamm. 2013, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chopp, M. Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietins in focal cerebral ischemia. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2002, 12, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspinall, R.J.; Weis, S.M.; Barnes, L.; Lutu-Fuga, K.; Bylund, D.J.; Pockros, P.J.; Cheresh, D.A. A src family kinase inhibitor improves survival in experimental acute liver failure associated with elevated cerebral and circulating vascular endothelial growth factor levels. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Ling, Z.L.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Shu, N.; Zhong, Z.Y.; Chen, Y.; Di, X.Y.; Wang, Z.J.; Liu, L.; et al. Unconjugated bilirubin elevation impairs the function and expression of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) at the blood-brain barrier in bile duct-ligated rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Sun, B.; Li, Y.; Xu, P.; Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Liu, X. Hyperammonemia enhances the function and expression of P-glycoprotein and Mrp2 at the blood-brain barrier through NF-κB. J. Neurochem. 2014, 131, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Z.H.; Murakami, T.; Okochi, A.; Yumoyo, R.; Nagai, J.; Takano, M. Expression and function of P-glycoprotein in rats with carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatic failure. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, A.; Dohgu, S.; Takata, F.; Watanabe, T.; Nishioku, T.; Matsumoto, J.; Ohkubo, Y.; Shuto, H.; Kataoka, Y. Partial hepatectomy aggravates cyclosporin A-induced neurotoxicity by lowering the function of the blood-brain barrier in mice. Life Sci. 2011, 88, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, A.J.; Wendon, J.A.; Williams, R. Subclinical seizure activity and prophylactic phenytoin infusion in acute liver failure: A controlled clinical trial. Hepatology 2000, 32, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, W.; Auzinger, G.; Dhawan, A.; Wendon, J. Acute liver failure. Lancet 2010, 376, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robey, R.W.; To, K.K.; Polgar, O.; Dohse, M.; Fetsch, P.; Dean, M.; Bates, S.E. ABCG2: A perspective. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reznicek, J.; Ceckova, M.; Ptackova, Z.; Martinec, O.; Tupova, L.; Cerveny, L.; Staud, F. MDR1 and BCRP transporter-mediated drug-drug interaction between rilpivirine and abacavir and effect on intestinal absorption. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00837-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, P.; Deng, M.; Huang, C.; Hu, T.; Jiang, L.; Li, J. Mammalian drug efflux transporters of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) family in multidrug resistance: A review of the past decade. Cancer Lett. 2016, 370, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalan, R. Acute liver failure: Current management and future prospects. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, S115–S123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mpabanzi, L.; Jalan, R. Neurological complications of acute liver failure: Pathophysiological basis of current management and emerging therapies. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 60, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romermann, K.; Helmer, R.; Loscher, W. The antiepileptic drug lamotrigine is a substrate of mouse and human breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2). Neuropharmacology 2015, 93, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lok, A.S.; McMahon, B.J.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; Wong, J.B.; Ahmed, A.T.; Farah, W.; Almasri, J.; Alahdab, F.; Benkhadra, K.; Mouchli, M.A.; et al. Antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis B viral infection in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology 2016, 63, 284–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calmet, F.H.; Yarur, A.J.; Pukazhendhi, G.; Ahmad, J.; Bhamidimarri, K.R. Endoscopic and histological features of mycophenolate mofetil colitis in patients after solid organ transplantation. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Liu, K. P-gp inhibition-based strategies for modulating pharmacokinetics of anticancer drugs: An update. Curr. Drug Metab. 2016, 17, 806–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzneller, P.; Kussmann, M.; Eberl, S.; Maier-Salamon, A.; Jager, W.; Bauer, M.; Langer, O.; Zeitlinger, M.; Poeppl, W. Pharmacokinetics of the P-gp inhibitor tariquidar in rats after intravenous, oral, and intraperitoneal administration. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Miao, M.X.; Sun, B.B.; Wang, Z.J.; Tang, X.G.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, K.J.; Liu, X.D.; Liu, L. Acute liver failure enhances oral plasma exposure of zidovudine in rats by downregulation of hepatic UGT2B7 and intestinal P-gp. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 1554–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, S.N.; Aleksunes, L.M.; Augustine, L.; Scheffer, G.L.; Goedken, M.J.; Jakowski, A.B.; Pruimboom-Brees, I.M.; Cherrington, N.J.; Manautou, J.E. Induction of hepatobiliary efflux transporters in acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure cases. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2007, 35, 1963–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miah, M.K.; Shaik, I.H.; Bickel, U.; Mehvar, R. Effects of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury on the P-glycoprotein activity at the liver canalicular membrane and blood-brain barrier determined by in vivo administration of rhodamine 123 in rats. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 861–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhr, M.; Holsboer, F.; Muller, M.B. Penetration of endogenous steroid hormones corticosterone, cortisol, aldosterone and progesterone into the brain is enhanced in mice deficient for both mdr1a and mdr1b P-glycoproteins. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2002, 14, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grube, M.; Hagen, P.; Jedlitschky, G. Neurosteroid transport in the brain: Role of ABC and Slc transporters. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, S.H. Endogenous steroids and pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Lancet 1990, 336, 573–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahboucha, S.; Pomier-Layrargues, G.; Mamer, O.; Butterworth, R.F. Increased levels of pregnenolone and its neuroactive metabolite allopregnanolone in autopsied brain tissue from cirrhotic patients who died in hepatic coma. Neurochem. Int. 2006, 49, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahboucha, S.; Butterworth, R.F. The neurosteroid system: Implication in the pathophysiology of hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahboucha, S.; Talani, G.; Fanutza, T.; Sanna, E.; Biggio, G.; Gamrani, H.; Butterworth, R.F. Reduced brain levels of dheas in hepatic coma patients: Significance for increased gabaergic tone in hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 61, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Species | MRP1 | MRP2 | MRP3 | MRP4 | MRP5 | MRP6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | ++ | - | ± | + | ++ | + |
| Rat | ++ | ± | ± | ++++ | ++++ | ++ |
| Mouse | ± | - | + | ++++ | + | + |
| Pig | ± | - | ++ | + | +++ | - |
| Cow | ++ | - | - | - | ++++ | - |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Y.; Liu, X. Alterations in Expression and Function of ABC Family Transporters at Blood-Brain Barrier under Liver Failure and Their Clinical Significances. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030102
Fan Y, Liu X. Alterations in Expression and Function of ABC Family Transporters at Blood-Brain Barrier under Liver Failure and Their Clinical Significances. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(3):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030102
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Yilin, and Xiaodong Liu. 2018. "Alterations in Expression and Function of ABC Family Transporters at Blood-Brain Barrier under Liver Failure and Their Clinical Significances" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 3: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030102
APA StyleFan, Y., & Liu, X. (2018). Alterations in Expression and Function of ABC Family Transporters at Blood-Brain Barrier under Liver Failure and Their Clinical Significances. Pharmaceutics, 10(3), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030102




