Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Review on Synthesis and Recent Advances
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Origin of Mesoporous Silica Materials
3. Synthesis of MSNs
3.1. Mechanism of Formation of MSNs
3.2. Approaches for the Synthesis of MSNs

3.3. Raw Materials Used and Factors Affecting the Characteristics of MSNs
3.3.1. Control of Particle Size
3.3.2. Control of Pore Size, Pore Volume and Mesostructural Ordering
3.3.3. Control of Shape
4. Drug Loading and Release of Drugs from MSNs
4.1. Drug Loading
4.2. Release of Drugs from MSNs
5. Applications of MSNs in Drug Delivery
5.1. Targeted Antitumor Therapy Using MSNs
5.2. MSNs for Anti-Inflammatory Activities
5.3. Gated Drug Release/Controlled Drug Delivery
5.3.1. pH-Responsive Drug Release
5.3.2. Redox Responsive Drug Release
5.3.3. Temperature Responsive Drug Release
5.3.4. Chemical and Enzyme Responsive Drug Release
5.3.5. External Stimuli for Drug Release
5.4. MSNs for Improvement of Solubility of Drugs
5.5. MSNs in Biomedical Imaging and Theranostic Purpose
5.6. MSNs for Bone Tissue Engineering and Repair
6. Biodistribution and Biocompatibility of MSNs
6.1. Effect of Surface Chemistry, Shape, and Size of MSNs
6.2. In Vivo Safety and Toxicity of MSNs
6.3. MSNs v/s Silica Nanoparticles
6.4. Biocompatibility of MSNs in Humans
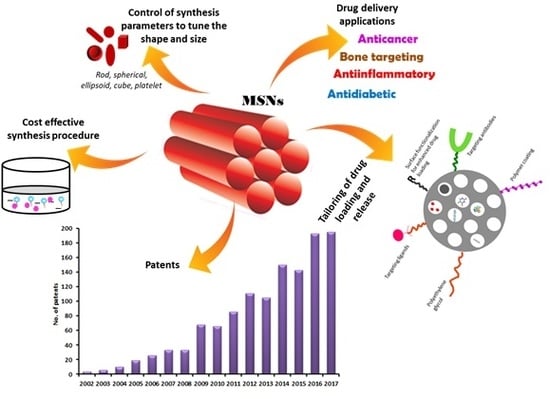
7. Recent Patents Filed in the Field of MSNs for Biomedical Applications
8. Conclusions
9. Current and Future Perspectives
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krukemeyer, M.G.; Krenn, V.; Huebner, F.; Wagner, W.; Resch, R. History and Possible Uses of Nanomedicine Based on Nanoparticles and Nanotechnological Progress. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudshinge, S.R.; Deore, A.B.; Patil, S.; Bhalgat, C.M. Nanoparticles: Emerging carriers for drug delivery. Saudi Pharm. J. 2011, 19, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankala, R.K.; Zhang, Y.S.; Wang, S.-B.; Lee, C.-H.; Chen, A.-Z. Supercritical Fluid Technology: An Emphasis on Drug Delivery and Related Biomedical Applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankala, R.K.; Zhu, K.; Sun, X.-N.; Liu, C.-G.; Wang, S.-B.; Chen, A.-Z. Cardiac Tissue Engineering on the Nanoscale. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 800–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, T.; Xie, J.; Liao, J.; Zhang, T.; Lin, S.; Lin, Y. Nanomaterials and bone regeneration. Bone Res. 2015, 3, 15029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhariri, M.; Azghani, A.; Omri, A. Liposomal antibiotics for the treatment of infectious diseases. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 1515–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, P.P.; Biswas, S.; Torchilin, V.P. Current trends in the use of liposomes for tumor targeting. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 1509–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, A.; Loomis, K.; Smith, B.; Lee, J.-H.; Yavlovich, A.; Heldman, E.; Blumenthal, R. Lipid-based nanoparticles as pharmaceutical drug carriers: From concepts to clinic. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2009, 26, 523–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, A.; Kydd, J.; Piel, B.; Rai, P. Targeting Cancer using Polymeric Nanoparticle mediated Combination Chemotherapy. Int. J. Nanomed. Nanosurg. 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.J.; Tietjen, G.T.; Saucier-Sawyer, J.K.; Saltzman, W.M. A holistic approach to targeting disease with polymeric nanoparticles. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.-H.; Kankala, R.; Wang, S.-B.; Chen, A.-Z. Leveraging Engineering of Indocyanine Green-Encapsulated Polymeric Nanocomposites for Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandita, D.; Poonia, N.; Kumar, S.; Lather, V.; Madaan, K. Dendrimers in drug delivery and targeting: Drug-dendrimer interactions and toxicity issues. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2014, 6, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiemenz, J.W.; Walsh, T.J. Lipid formulations of amphotericin B: Recent progress and future directions. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996, 22 (Suppl. 2), S133–S144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaposi’s sarcoma: DaunoXome approved. AIDS Treat. News 1996, 3–4.
- Barenholz, Y. (Chezy) Doxil®—The first FDA-approved nano-drug: Lessons learned. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batist, G.; Barton, J.; Chaikin, P.; Swenson, C.; Welles, L. Myocet (liposome-encapsulated doxorubicin citrate): A new approach in breast cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Pharm. 2002, 3, 1739–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junghanns, J.-U.A.H.; Müller, R.H. Nanocrystal technology, drug delivery and clinical applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008, 3, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giner-Casares, J.J.; Henriksen-Lacey, M.; Coronado-Puchau, M.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Inorganic nanoparticles for biomedicine: Where materials scientists meet medical research. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankala, R.K.; Tsai, P.-Y.; Kuthati, Y.; Wei, P.-R.; Liu, C.-L.; Lee, C.-H. Overcoming multidrug resistance through co-delivery of ROS-generating nano-machinery in cancer therapeutics. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuthati, Y.; Kankala, R.K.; Lee, C.-H. Layered double hydroxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications: Current status and recent prospects. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 112–113, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Burns, A.A.; Williams, R.M.; Zhou, Z.; Flesken-Nikitin, A.; Zipfel, W.R.; Wiesner, U.; Nikitin, A.Y. Core-shell silica nanoparticles as fluorescent labels for nanomedicine. J. Biomed. Opt. 2007, 12, 64007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, A.A.; Vider, J.; Ow, H.; Herz, E.; Penate-Medina, O.; Baumgart, M.; Larson, S.M.; Wiesner, U.; Bradbury, M. Fluorescent Silica Nanoparticles with Efficient Urinary Excretion for Nanomedicine. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slowing, I.I.; Trewyn, B.G.; Lin, V.S.-Y. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Intracellular Delivery of Membrane-Impermeable Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 8845–8849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deodhar, G.V.; Adams, M.L.; Trewyn, B.G. Controlled release and intracellular protein delivery from mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Biotechnol. J. 2017, 12, 1600408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, W.; Fan, R.; Miao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, C.; Shan, X.; Wan, X.; Li, J. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Carriers for Intracellular Delivery of Nucleic Acids and Subsequent Therapeutic Applications. Molecules 2017, 22, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Morita, H.; Hanagata, N. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for enhancing the delivery efficiency of immunostimulatory DNA drugs. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 5142–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möller, K.; Müller, K.; Engelke, H.; Bräuchle, C.; Wagner, E.; Bein, T. Highly efficient siRNA delivery from core–shell mesoporous silica nanoparticles with multifunctional polymer caps. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 4007–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanafi-Bojd, M.Y.; Ansari, L.; Malaekeh-Nikouei, B. Codelivery of anticancer drugs and siRNA by mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Ther. Deliv. 2016, 7, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riikonen, J.; Xu, W.; Lehto, V.-P. Mesoporous systems for poorly soluble drugs—Recent trends. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 536, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, A.; Kettiger, H.; Schoubben, A.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Ambrogi, V.; Hamidi, M. Mesoporous silica materials: From physico-chemical properties to enhanced dissolution of poorly water-soluble drugs. J. Control. Release 2017, 262, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Han, N.; Bai, L.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Che, E.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, T.; et al. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in drug delivery and biomedical applications. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamaeva, V.; Sahlgren, C.; Lindén, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in medicine—Recent advances. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Z. Mesoporous silica-based nanodevices for biological applications. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 18961–18980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Q.; Margolese, D.I.; Stucky, G.D. Stucky Surfactant Control of Phases in the Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica-Based Materials. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.S.; Vartuli, J.C.; Roth, W.J.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Kresge, C.T.; Schmitt, K.D.; Chu, C.T.W.; Olson, D.H.; Sheppard, E.W.; McCullen, S.B.; et al. A new family of mesoporous molecular sieves prepared with liquid crystal templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10834–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trewyn, B.G.; Slowing, I.I.; Giri, S.; Chen, H.-T.; Lin, V.S.-Y. Synthesis and Functionalization of a Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Based on the Sol–Gel Process and Applications in Controlled Release. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oye, G.; Sjöblom, J.; Stöcker, M. Synthesis, characterization and potential applications of new materials in the mesoporous range. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 89–90, 439–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Huo, Q.; Feng, J.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D. Nonionic Triblock and Star Diblock Copolymer and Oligomeric Surfactant Syntheses of Highly Ordered, Hydrothermally Stable, Mesoporous Silica Structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 6024–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozuka, Y.; Wongmekiat, A.; Kimura, K.; Moribe, K.; Yamamura, S.; Yamamoto, K. Effect of Pore Size of FSM-16 on the Entrapment of Flurbiprofen in Mesoporous Structures. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 53, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Kim, S.-G.; Iskandar, F.; Okuyama, K. Synthesis of spherical mesoporous silica nanoparticles with nanometer-size controllable pores and outer diameters. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 120, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkilä, T.; Salonen, J.; Tuura, J.; Hamdy, M.S.; Mul, G.; Kumar, N.; Salmi, T.; Murzin, D.Y.; Laitinen, L.; Kaukonen, A.M.; et al. Mesoporous silica material TUD-1 as a drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 331, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Schumacher, K.; von Hohenesche, C.D.F.; Grun, M.; Unger, K.K. MCM-41, MCM-48 and related mesoporous adsorbents: Their synthesis and characterisation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 187–188, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Ordered mesoporous materials for drug delivery. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 117, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, H. Structure directed reversible adsorption of organic dye on mesoporous silica in aqueous solution. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 97, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukmar, T.; Planinsek, O. Ordered mesoporous silicates as matrices for controlled release of drugs. Acta Pharm. 2010, 60, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Zhou, W.; Wan, Y. Ordered Mesoporous Materials; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2013; ISBN 3527647899. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.S.; Park, M.; Kim, T.W.; Kim, J.-E.; Papoulis, D.; Komarneni, S.; Choi, J. Adsorbate-dependent uptake behavior of topographically bi-functionalized ordered mesoporous silica materials. J. Porous Mater. 2015, 22, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.Q.; Zhao, X.S. Nanoporous Materials: Science and Engineering; Series on Chemical Engineering; Imperial College Press: London, UK; World Scientific Publishing Co.: Singapore, 2004; Volume 4, ISBN 978-1-86094-210-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, S.; Geng, W.; He, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, B.; Duan, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q. Effect of framework structure, pore size and surface modification on the adsorption performance of methylene blue and Cu2+ in mesoporous silica. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 539, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayoral, A.; Blanco, R.M.; Diaz, I. Location of enzyme in lipase-SBA-12 hybrid biocatalyst. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2013, 90, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarneau, A.; Cambon, H.; Di Renzo, F.; Ryoo, R.; Choi, M.; Fajula, F. Microporosity and connections between pores in SBA-15 mesostructured silicas as a function of the temperature of synthesis. New J. Chem. 2003, 27, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lercher, J.A.; Kaliaguine, S.; Gobin, O.C. SBA-16 Materials Synthesis, Diffusion and Sorption Properties; Technical University of Munich: Munich, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kleitz, F.; Liu, D.; Gopinathan, M.A.; Park, I.-S.; Solovyov, L.A.; Shmakov, A.N.; Ryoo, R. Large Cage Face-Centered-Cubic Fm3m Mesoporous Silica: Synthesis and Structure. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 14296–14300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbasi, J.R.; Zirakbash, A. Synthesis, characterization and drug release studies of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)/KIT-5 nanocomposite as an innovative organic–inorganic hybrid carrier system. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 12463–12471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jammaer, J.; Aerts, A.; D’Haen, J.; Seo, J.W.; Martens, J.A. Convenient synthesis of ordered mesoporous silica at room temperature and quasi-neutral pH. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 8290–8293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vialpando, M.; Aerts, A.; Persoons, J.; Martens, J.; Van Den Mooter, G. Evaluation of ordered mesoporous silica as a carrier for poorly soluble drugs: Influence of pressure on the structure and drug release. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 3411–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stober, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grün, M.; Lauer, I.; Unger, K.K. The synthesis of micrometer- and submicrometer-size spheres of ordered mesoporous oxide MCM-41. Adv. Mater. 1997, 9, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, J.L.; Impéror-Clerc, M. Mechanism of self-assembly in the synthesis of silica mesoporous materials: In situ studies by X-ray and neutron scattering. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 4071–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Qiu, H.; Zeng, W.; Sakamoto, Y.; Terasaki, O.; Sakamoto, K.; Chen, Q.; Che, S. Formation Mechanism of Anionic Surfactant-Templated Mesoporous Silica. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 3904–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flodström, K.; Wennerström, H.; Alfredsson, V. Mechanism of Mesoporous Silica Formation. A Time-Resolved NMR and TEM Study of Silica−Block Copolymer Aggregation. Langmuir 2004, 20, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attard, G.S.; Glyde, J.C.; Göltner, C.G. Liquid-crystalline phases as templates for the synthesis of mesoporous silica. Nature 1995, 378, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundblom, A.; Oliveira, C.L.P.; Palmqvist, A.E.C.; Pedersen, J.S. Modeling In Situ Small-Angle X-ray Scattering Measurements Following the Formation of Mesostructured Silica. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 7706–7713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollamby, M.J.; Borisova, D.; Brown, P.; Eastoe, J.; Grillo, I.; Shchukin, D. Growth of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Monitored by Time-Resolved Small-Angle Neutron Scattering. Langmuir 2012, 28, 4425–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edler, K.J. Current Understanding of Formation Mechanisms in Surfactant-Templated Materials. Aust. J. Chem. 2005, 58, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Dumée, L.F.; Garvey, C.J.; Feng, C.; She, F.; Rookes, J.E.; Mudie, S.; Cahill, D.M.; Kong, L. A New Insight into Growth Mechanism and Kinetics of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles by In Situ Small Angle X-ray Scattering. Langmuir 2015, 31, 8478–8487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danks, A.E.; Hall, S.R.; Schnepp, Z. The evolution of “sol–gel” chemistry as a technique for materials synthesis. Mater. Horiz. 2016, 3, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, C.E.; Khushalani, D.; Lebeau, B.; Mann, S. Nanoscale Materials with Mesostructured Interiors. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadasivan, S.; Fowler, C.E.; Khushalani, D.; Mann, S. Nucleation of MCM-41 Nanoparticles by Internal Reorganization of Disordered and Nematic-Like Silica–Surfactant Clusters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 2151–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K.; Kobler, J.; Bein, T. Colloidal suspensions of mercapto-functionalized nanosized mesoporous silica. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, C.J.; Lu, Y.; Sellinger, A.; Fan, H. Evaporation-Induced Self-Assembly: Nanostructures Made Easy. Adv. Mater. 1999, 11, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontecave, T.; Boissiere, C.; Baccile, N.; Plou, F.J.; Sanchez, C. Using Evaporation-Induced Self-Assembly for the Direct Drug Templating of Therapeutic Vectors with High Loading Fractions, Tunable Drug Release, and Controlled Degradation. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 4671–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Chen, F.; Cai, W. Biomedical applications of functionalized hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Focusing on molecular imaging. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Hong, H.; Shi, S.; Goel, S.; Valdovinos, H.F.; Hernandez, R.; Theuer, C.P.; Barnhart, T.E.; Cai, W. Engineering of Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Remarkably Enhanced Tumor Active Targeting Efficacy. Sci. Rep. 2015, 4, 5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Shi, J.; Chen, H.; Shen, W.; Dong, X. A facile method to synthesize novel hollow mesoporous silica spheres and advanced storage property. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 84, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, J.; Hua, Z.; Chen, H.; Ruan, M.; Yan, D. Hollow Spheres of Mesoporous Aluminosilicate with a Three-Dimensional Pore Network and Extraordinarily High Hydrothermal Stability. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 609–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.W.; Archer, L.A.; Yang, Z. Hollow Micro-/Nanostructures: Synthesis and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 3987–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, X.; Chen, L.; Li, C.; He, C.; He, L.; Kong, L. Functionalization of Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Improved 5-FU Loading. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Luo, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, X.; Cai, K. Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles facilitated drug delivery via cascade pH stimuli in tumor microenvironment for tumor therapy. Biomaterials 2016, 83, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, S.; Farsangi, Z.J.; Beitollahi, A.; Mirkazemi, M.; Rezayat, S.M.; Sarkar, S. Synthesis of hollow mesoporous silica (HMS) nanoparticles as a candidate for sulfasalazine drug loading. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 11225–11232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, M.; Zenibana, H.; Nandi, M.; Bhaumik, A.; Nakashima, K. Synthesis of mesoporous hollow silica nanospheres using polymeric micelles as template and their application as a drug-delivery carrier. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 13381–13389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Cheng, X.; Feng, W.; Qiu, K.; Chen, L.; Nie, W.; Yin, Z.; Mo, X.; Wang, H.; He, C. Synthesis of hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles with tunable shell thickness and pore size using amphiphilic block copolymers as core templates. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 11834–11842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, N.; Pan, W.; Yu, Z.; Yang, L.; Tang, B. Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Tunable Structures for Controlled Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 2123–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, Y. Synthesis, Properties, and Applications of Hollow Micro-/Nanostructures. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10983–11060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, M.; Tang, J.; Qiao, Q.; Wu, T.; Qi, Y.; Tan, S.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Z. Biodegradable Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Regulating Tumor Microenvironment and Enhancing Antitumor Efficiency. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3276–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-S.; Wu, S.-H.; Tseng, C.-T.; Hung, Y.; Chang, C.; Mou, C.-Y. Synthesis of hollow silica nanospheres with a microemulsion as the template. Chem. Commun. 2009, 0, 3542–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Su, B. An electrochemistry assisted approach for fast, low-cost and gram-scale synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 65922–65926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, S.; Gao, K.; Shen, H.; Jiang, X.; Long, Y.; Chen, Y. Organic/inorganic hybrid mesoporous silica membrane rapidly synthesized by a microwave-assisted method and its application in enzyme adsorption and electrocatalysis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3267–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-G.; Bein, T. Microwave synthesis of molecular sieve MCM-41. Chem. Commun. 1996, 925–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrivel, S.; Chen, C.-T.; Kao, H.-M. The ultrafast sonochemical synthesis of mesoporous silica MCM-41. New J. Chem. 2010, 34, 2109–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoussi, Y.; Bastide, S.; Abderrabba, M.; Chehimi, M.M. Sonochemical synthesis of Fe3O4@NH2-mesoporous silica@Polypyrrole/Pd: A core/double shell nanocomposite for catalytic applications. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 41, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourhly, A.; Khachani, M.; Hamidi, A.E.; Kacimi, M.; Halim, M.; Arsalane, S. The Synthesis and Characterization of Low-cost Mesoporous Silica SiO2 from Local Pumice Rock Regular Paper. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinjokun, A.I.; Ojumu, T.V.; Ogunfowokan, A.O. Biomass, Abundant Resources for Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica Material. In Microporous and Mesoporous Materials; InTech: Vienna, Austria, 2016; pp. 105–117. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.-S.; Haynes, C.L. Impacts of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Size, Pore Ordering, and Pore Integrity on Hemolytic Activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 4834–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.; Neumann, A.; Bremer, I.; Su, Y.; Dräger, G.; Kasper, C.; Behrens, P. Nanoporous silica nanoparticles as biomaterials: Evaluation of different strategies for the functionalization with polysialic acid by step-by-step cytocompatibility testing. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2015, 26, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Z.-A.; Zhang, L.; Guo, M.; Liu, Y.; Huo, Q. Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles via Controlled Hydrolysis and Condensation of Silicon Alkoxide. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 3823–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K.; Kobler, J.; Bein, T. Colloidal Suspensions of Nanometer-Sized Mesoporous Silica. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Bu, X.; Pine, D.J. Control of Pore Sizes in Mesoporous Silica Templated by Liquid Crystals in Block Copolymer−Cosurfactant−Water Systems. Langmuir 2000, 16, 5304–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Safty, S.A.; Evans, J. Formation of highly ordered mesoporous silica materials adopting lyotropic liquid crystal mesophases. J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayari, A.; Yang, Y. Nonionic oligomeric polymer directed synthesis of highly ordered large pore periodic mesoporous organosilica. Chem. Commun. 2002, 0, 2582–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, M.; Lee, S.G. Synthesis, Characterization and Drug Release Capability of New Cost Effective Mesoporous Silica Nano Particle for Ibuprofen Drug Delivery. Int. J. Control Autom. 2013, 6, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richer, R. Direct synthesis of functionalized mesoporous silica by non-ionic alkylpolyethyleneoxide surfactant assembly. Chem. Commun. 1998, 0, 1775–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prouzet, E.; Cot, F.; Nabias, G.; Larbot, A.; Kooyman, P.; Pinnavaia, T.J. Assembly of Mesoporous Silica Molecular Sieves Based on Nonionic Ethoxylated Sorbitan Esters as Structure Directors. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 1498–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, J.L.; Michaux, F.; Stébé, M.J. Nanostuctured mesoporous materials from different silica sources using fluorinated surfactants as templates. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 510, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevet, D.; Jouannin, C.; Tourné-Péteilh, C.; Devoisselle, J.-M.; Vioux, A.; Viau, L. Self-encapsulation of a drug-containing ionic liquid into mesoporous silica monoliths or nanoparticles by a sol–gel process. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 82916–82923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Singh, R.K.; Perez, R.A.; Abou Neel, E.A.; Kim, H.-W.; Chrzanowski, W. Silica-based mesoporous nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery. J. Tissue Eng. 2013, 4, 2041731413503357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zainal, N.A.; Rizal, S.; Shukor, A.; Azwana, H.; Wab, A.; Razak, K.A. Study on the Effect of Synthesis Parameters of Silica Nanoparticles Entrapped with Rifampicin. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2013, 32, 2245–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Synthesis and formation of hierarchical mesoporous silica network in acidic aqueous solutions of sodium silicate and cationic surfactant. Colloid J. 2010, 72, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Yang, Y.; O’Brien, J.S.; Breznan, D.; Nimesh, S.; Bernatchez, S.; Hill, M.; Sayari, A.; Vincent, R.; Kumarathasan, P. Synthesis and Physicochemical Characterization of Mesoporous SiO2 Nanoparticles. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Kruk, M. Pluronic-P123-Templated Synthesis of Silica with Cubic Ia3d Structure in the Presence of Micelle Swelling Agent. Langmuir 2015, 31, 7623–7632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, E.; Mori, S.; Shimojima, A.; Wada, H.; Kuroda, K. Fabrication of colloidal crystals composed of pore-expanded mesoporous silica nanoparticles prepared by a controlled growth method. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 2464–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunphy, D.R.; Sheth, P.H.; Garcia, F.L.; Brinker, C.J. Enlarged Pore Size in Mesoporous Silica Films Templated by Pluronic F127: Use of Poloxamer Mixtures and Increased Template/SiO2 Ratios in Materials Synthesized by Evaporation-Induced Self-Assembly. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Toni, A.; Ibrahim, M.; Labis, J.; Khan, A.; Alhoshan, M. Optimization of Synthesis Parameters for Mesoporous Shell Formation on Magnetic Nanocores and Their Application as Nanocarriers for Docetaxel Cancer Drug. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 11496–11509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchoucha, M.; Côté, M.-F.; Caudreault, R.C.; Fortin, M.-A.; Kleitz, F. Size-Controlled Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Tunable Drug Release and Enhanced Anti-Tumoral Activity. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 4243–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Werner-Zwanziger, U.; Zwanziger, J.; Wiesner, U. Controlling Growth of Ultrasmall Sub-10 nm Fluorescent Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, L.U.; Kim, C.K. Size Control of Silica Nanoparticles and Their Surface Treatment for Fabrication of Dental Nanocomposites. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, Y.-D.; Lian, H.-Y.; Leo, S.-Y.; Wang, S.-G.; Yamauchi, Y.; Wu, K.C.-W. Controlling Particle Size and Structural Properties of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Using the Taguchi Method. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 13158–13165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Urata, C.; Ujiie, H.; Yamauchi, Y.; Kuroda, K. Preparation of aqueous colloidal mesostructured and mesoporous silica nanoparticles with controlled particle size in a very wide range from 20 nm to 700 nm. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 6145–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez, N.I.; Gonzalez, Z.; Ferrari, B.; Castro, Y. Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles by sol–gel as nanocontainer for future drug delivery applications. Bol. Soc. Esp. Cerám. Vidr. 2017, 56, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanyika, H.; Gatebe, E.; Kioni, P.; Tang, Z.; Gao, Y. Synthesis and characterization of ordered mesoporous silica nanoparticles with tunable physical properties by varying molar composition of reagents. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 5, 2402–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, K.; Fukushima, Y. Synthesis of mono-dispersed mesoporous silica spheres with highly ordered hexagonal regularity using conventional alkyltrimethylammonium halide as a surfactant. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 1579–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regi, M.; Rámila, A.; del Real, R.P.; Pérez-Pariente, J. A New Property of MCM-41: Drug Delivery System. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, S.M.; Hurley, K.R.; Datt, A.; Swindlehurst, G.; Haynes, C.L. Ultraporous Mesostructured Silica Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 3193–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, A.; Ahmad, T.; Ganguli, A.K. Silica Mesostructures: Control of Pore Size and Surface Area Using a Surfactant-Templated Hydrothermal Process. Langmuir 2010, 26, 14901–14908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmqvist, A.E.C. Synthesis of ordered mesoporous materials using surfactant liquid crystals or micellar solutions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 8, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Huang, K.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhao, W.; Liu, C.; Shi, J. Sub-150 nm mesoporous silica nanoparticles with tunable pore sizes and well-ordered mesostructure for protein encapsulation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 407, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, B.; Rámila, A.; Pérez-Pariente, J.; Díaz, I.; Vallet-Regí, M. MCM-41 Organic Modification as Drug Delivery Rate Regulator. Chem. Mater. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Martinez, Á.; Doadrio, A.L.; Pérez-Pariente, J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Release evaluation of drugs from ordered three-dimensional silica structures. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 26, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möller, K.; Bein, T. Talented Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Zhu, H.; Wu, D.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, S. Dendritic Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres Synthesized by a Novel Dual-Templating Micelle System for the Preparation of Functional Nanomaterials. Langmuir 2017, 33, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.-J.; Xing, J.-L.; Pang, J.-L.; Jiang, S.-H.; Lam, K.-F.; Yang, T.-Q.; Xue, Q.-S.; Zhang, K.; Wu, P. Facile Synthesis of Size Controllable Dendritic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 22655–22665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Li, L.; Liu, T.; Hao, N.; Liu, H.; Chen, D.; Tang, F. The Shape Effect of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles on Biodistribution, Clearance, and Biocompatibility In Vivo. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5390–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Teng, X.; Chen, D.; Tang, F.; He, J. The effect of the shape of mesoporous silica nanoparticles on cellular uptake and cell function. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.; Luo, Z.-S.; Pang, W.-Q.; Fan, Y.-W.; Chen, X.-H.; Cui, F.-Z. Dilute Solution Routes to Various Controllable Morphologies of MCM-41 Silica with a Basic Medium. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhou, Y.; He, T.; Song, G.; Wu, F.; Jiang, F.; Hu, J. One-pot morphology-controlled synthesis of various shaped mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 5718–5726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Gao, J.; Tang, F. Controlled preparation of rod- and top-like MCM-41 mesoporous silica through one-step route. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2005, 351, 1705–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björk, E.M.; Söderlind, F.; Odén, M. Tuning the Shape of Mesoporous Silica Particles by Alterations in Parameter Space: From Rods to Platelets. Langmuir 2013, 29, 13551–13561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, N.; Li, L.; Tang, F. Facile preparation of ellipsoid-like MCM-41 with parallel channels along the short axis for drug delivery and assembly of Ag nanoparticles for catalysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 11565–11568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Gu, T.; Mao, D.; Xiao, X.; Yuan, P.; Yu, M.; Xia, L.; Ji, Q.; Meng, L.; Song, W.; et al. Synthesis of Nonspherical Mesoporous Silica Ellipsoids with Tunable Aspect Ratios for Magnetic Assisted Assembly and Gene Delivery. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Moon, S.-W.; Zin, W.-C. High-yield synthesis of monodispersed SBA-15 equilateral hexagonal platelet with thick wall. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 3857–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-C.; Lin, H.-P.; Chao, M.-C.; Mou, C.-Y.; Tang, C.-Y. Mesoporous Silica Platelets with Perpendicular Nanochannels via a Ternary Surfactant System. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1657–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, S.; Wiench, J.W.; Yoo, J.-C.; Pruski, M.; Lin, V.S.-Y. Organic Functionalization and Morphology Control of Mesoporous Silicas via a Co-Condensation Synthesis Method. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 4247–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, C. Charge-Reversal APTES-Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with High Drug Loading and Release Controllability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 17166–17175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchoucha, M.; Gaudreault, R.C.; Fortin, M.-A.; Kleitz, F. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: Selective Surface Functionalization for Optimal Relaxometric and Drug Loading Performances. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 5911–5923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Shi, J.; Shen, W.; Chen, H.; Dong, X.; Ruan, M. Preparation of novel hollow mesoporous silica spheres and their sustained-release property. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2633–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanikumar, L.; Kim, H.Y.; Oh, J.Y.; Thomas, A.P.; Choi, E.S.; Jeena, M.T.; Joo, S.H.; Ryu, J.-H. Noncovalent Surface Locking of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Exceptionally High Hydrophobic Drug Loading and Enhanced Colloidal Stability. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 2701–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Balas, F.; Arcos, D. Mesoporous Materials for Drug Delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7548–7558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanikumar, L.; Jeena, M.T.; Kim, K.; Yong Oh, J.; Kim, C.; Park, M.-H.; Ryu, J.-H. Spatiotemporally and Sequentially-Controlled Drug Release from Polymer Gatekeeper–Hollow Silica Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, K.-C.; Mou, C.-Y. Pore-expanded mesoporous silica nanoparticles with alkanes/ethanol as pore expanding agent. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 169, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-H.; Na, H.-K.; Kim, Y.-K.; Ryoo, S.-R.; Cho, H.S.; Lee, K.E.; Jeon, H.; Ryoo, R.; Min, D.-H. Facile Synthesis of Monodispersed Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Ultralarge Pores and Their Application in Gene Delivery. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 3568–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, F.; Zhu, G.; Huang, S.; Li, S.; Sun, J.; Zhang, D.; Qiu, S. Controlled release of Captopril by regulating the pore size and morphology of ordered mesoporous silica. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 92, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doadrio, J.C.; Sousa, E.M.B.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Doadrio, A.L.; Perez-Pariente, J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Functionalization of mesoporous materials with long alkyl chains as a strategy for controlling drug delivery pattern. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balas, F.; Manzano, M.; Horcajada, P.; Vallet-Regí, M. Confinement and Controlled Release of Bisphosphonates on Ordered Mesoporous Silica-Based Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8116–8117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, A.; Colilla, M.; Balas, F.; Vallet-Regí, M. Surface Electrochemistry of Mesoporous Silicas as a Key Factor in the Design of Tailored Delivery Devices. Langmuir 2010, 26, 5038–5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datt, A.; El-Maazawi, I.; Larsen, S.C. Aspirin Loading and Release from MCM-41 Functionalized with Aminopropyl Groups via Co-condensation or Postsynthesis Modification Methods. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 18358–18366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.-W.; Hidajat, K.; Kawi, S. Functionalized SBA-15 Materials as Carriers for Controlled Drug Delivery: Influence of Surface Properties on Matrix−Drug Interactions. Langmuir 2005, 21, 9568–9575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.K.; Pandey, H.; Agarwal, V.; Ramteke, P.W.; Pandey, A.C. Nanoengineered mesoporous silica nanoparticles for smart delivery of doxorubicin. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Wang, Y.; Bai, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, T.; Kang, W.; Wang, S. Facile synthesis of the lipid bilayer coated mesoporous silica nanocomposites and their application in drug delivery. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 219, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, C.; Rayappan, K.; Thangam, R.; Bhanumathi, R.; Shanthi, K.; Vivek, R.; Thirumurugan, R.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Sivasubramanian, S.; Gunasekaran, P.; et al. Combinatorial nanocarrier based drug delivery approach for amalgamation of anti-tumor agents in breast cancer cells: An improved nanomedicine strategy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Diab, R.; Joubert, O.; Canilho, N.; Pasc, A. Core–shell microcapsules of solid lipid nanoparticles and mesoporous silica for enhanced oral delivery of curcumin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 140, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Hargrove, D.; Lu, X. Improving paclitaxel pharmacokinetics by using tumor-specific mesoporous silica nanoparticles with intraperitoneal delivery. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 1951–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.; Kulanthaivel, S.; Mondal, A.; Mishra, S.; Banerjee, B.; Bhaumik, A.; Banerjee, I.; Giri, S. Mesoporous silica nanoparticle based enzyme responsive system for colon specific drug delivery through guar gum capping. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 150, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saroj, S.; Rajput, S.J. Tailor-made pH-sensitive polyacrylic acid functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for efficient and controlled delivery of anti-cancer drug Etoposide. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 1198–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiyagarajan, V.; Lin, S.-X.; Lee, C.-H.; Weng, C.-F. A focal adhesion kinase inhibitor 16-hydroxy-cleroda-3,13-dien-16,15-olide incorporated into enteric-coated nanoparticles for controlled anti-glioma drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 141, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, M.; Ubaidulla, U.; Hemalatha, P.; Peng, M.M.; Jang, H.T. Development of Duloxetine Hydrochloride Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: Characterizations and In Vitro Evaluation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohseni, M.; Gilani, K.; Mortazavi, S.A. Preparation and characterization of rifampin loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a potential system for pulmonary drug delivery. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 14, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El Nabarawi, M.A.; Hassen, D.H.; Taha, A.A. Inclusion and characterization of ketoprofen into different mesoporous silica nanoparticles using three loading methods. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar]
- Yoncheva, K.; Popova, M.; Szegedi, A.; Mihaly, J.; Tzankov, B.; Lambov, N.; Konstantinov, S.; Tzankova, V.; Pessina, F.; Valoti, M. Functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for oral delivery of budesonide. J. Solid State Chem. 2014, 211, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudakavi, R.J.; Raichur, A.M.; Chakravortty, D. Lipid coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles as an oral delivery system for targeting and treatment of intravacuolar Salmonella infections. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 61160–61166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudakavi, R.J.; Vanamali, S.; Chakravortty, D.; Raichur, A.M. Development of arginine based nanocarriers for targeting and treatment of intracellular Salmonella. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 7022–7032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koneru, B.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Chavala, S.; Miller, M.; Holbert, B.; Conson, M.; Ni, A.; Di Pasqua, A. Tetracycline-Containing MCM-41 Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Escherichia coli. Molecules 2015, 20, 19690–19698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexa, I.F.; Ignat, M.; Popovici, R.F.; Timpu, D.; Popovici, E. In vitro controlled release of antihypertensive drugs intercalated into unmodified SBA-15 and MgO modified SBA-15 matrices. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 436, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doadrio, A.L.; Sánchez-Montero, J.M.; Doadrio, J.C.; Salinas, A.J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a new carrier methodology in the controlled release of the active components in a polypill. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 97, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; He, D.; Cai, L.; He, X.; Wang, K.; Yang, X.; Li, L.; Li, S.; Su, X. Alizarin Complexone Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Smart System Integrating Glucose-Responsive Double-Drugs Release and Real-Time Monitoring Capabilities. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8358–8366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.-K.; Lin, S.-X.; Tsai, M.-J.; Leong, M.; Lin, S.-R.; Kankala, R.; Lee, C.-H.; Weng, C.-F. Encapsulation of 16-Hydroxycleroda-3,13-Dine-16,15-Olide in Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as a Natural Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Potentiated Hypoglycemia in Diabetic Mice. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Varshney, R.R.; Ren, L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, D.-A. In-vitro osteogenesis of synovium stem cells induced by controlled release of bisphosphate additives from microspherical mesoporous silica composite. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3996–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Feng, W.; Qiu, K.; Chen, L.; Wang, W.; Nie, W.; Mo, X.; He, C. BMP-2 Derived Peptide and Dexamethasone Incorporated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Enhanced Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 15777–15789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriagada, F.; Correa, O.; Günther, G.; Nonell, S.; Mura, F.; Olea-Azar, C.; Morales, J. Morin Flavonoid Adsorbed on Mesoporous Silica, a Novel Antioxidant Nanomaterial. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.; Xue, M.; Xia, T.; Ji, Z.; Tarn, D.Y.; Zink, J.I.; Nel, A.E. Use of Size and a Copolymer Design Feature To Improve the Biodistribution and the Enhanced Permeability and Retention Effect of Doxorubicin-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in a Murine Xenograft Tumor Model. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 4131–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Qu, Q.; Zhao, Y. Targeted Delivery of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid by Multifunctional Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Photodynamic Skin Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 10671–10676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravian, P.; Shafiee Ardestani, M.; Khoobi, M.; Ostad, S.N.; Dorkoosh, F.A.; Akbari Javar, H.; Amanlou, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles functionalized with folic acid/methionine for active targeted delivery of docetaxel. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 7315–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Xu, C.; Wen, L.; Han, M.K.; Xiao, B.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Viennois, E.; Merlin, D. A Hyaluronidase-Responsive Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery System for Targeting Colon Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 7208–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gary-Bobo, M.; Brevet, D.; Benkirane-Jessel, N.; Raehm, L.; Maillard, P.; Garcia, M.; Durand, J.-O. Hyaluronic acid-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for efficient photodynamic therapy of cancer cells. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2012, 9, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, G.; Pan, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Li, G.; Dian, L.; Chen, B.; Wu, C. Lactosaminated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for asialoglycoprotein receptor targeted anticancer drug delivery. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaillant, O.; El Cheikh, K.; Warther, D.; Brevet, D.; Maynadier, M.; Bouffard, E.; Salgues, F.; Jeanjean, A.; Puche, P.; Mazerolles, C.; et al. Mannose-6-Phosphate Receptor: A Target for Theranostics of Prostate Cancer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 5952–5956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gary-Bobo, M.; Mir, Y.; Rouxel, C.; Brevet, D.; Basile, I.; Maynadier, M.; Vaillant, O.; Mongin, O.; Blanchard-Desce, M.; Morère, A.; et al. Mannose-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Efficient Two-Photon Photodynamic Therapy of Solid Tumors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11425–11429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Liao, Y.-T.; Liu, C.-H.; Yu, J. Liver cancer cells: Targeting and prolonged-release drug carriers consisting of mesoporous silica nanoparticles and alginate microspheres. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 2767–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarty, R.; Goel, S.; Hong, H.; Chen, F.; Valdovinos, H.F.; Hernandez, R.; Barnhart, T.E.; Cai, W. Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for tumor vasculature targeting and PET image-guided drug delivery. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, P.; Qin, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, X.-C.; Huo, Z.-J. Hyaluronic acid-tagged silica nanoparticles in colon cancer therapy: Therapeutic efficacy evaluation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 6445–6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; She, X.; Wang, T.; He, L.; Shigdar, S.; Duan, W.; Kong, L. Overcoming acquired drug resistance in colorectal cancer cells by targeted delivery of 5-FU with EGF grafted hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 14080–14092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, K.; Tripathy, J.; Datey, A.; Chakravortty, D.; Raichur, A.M. Mesoporous silica–chondroitin sulphate hybrid nanoparticles for targeted and bio-responsive drug delivery. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, H.; Hu, J.; Han, X.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y. Transferrin gated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for redox-responsive and targeted drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 152, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.; Lian, S.; Lin, H.; Gao, Y.; Jia, L. EpCAM aptamer-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for efficient colon cancer cell-targeted drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 83, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brevet, D.; Gary-Bobo, M.; Raehm, L.; Richeter, S.; Hocine, O.; Amro, K.; Loock, B.; Couleaud, P.; Frochot, C.; Morère, A.; et al. Mannose-targeted mesoporous silica nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy. Chem. Commun. 2009, 1475–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.; Ghosh, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Pandey, B.; Sil, P.C. Targeted delivery of quercetin loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles to the breast cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2016, 1860, 2065–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, S.; Chen, F.; Hong, H.; Valdovinos, H.F.; Hernandez, R.; Shi, S.; Barnhart, T.E.; Cai, W. VEGF121-Conjugated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle: A Tumor Targeted Drug Delivery System. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 21677–21685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Wu, F.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Lu, B.; et al. Preparation and characterization of a dual-receptor mesoporous silica nanoparticle–hyaluronic acid–RGD peptide targeting drug delivery system. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 40427–40435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankala, R.K.; Kuthati, Y.; Liu, C.-L.; Mou, C.-Y.; Lee, C.-H. Killing cancer cells by delivering a nanoreactor for inhibition of catalase and catalytically enhancing intracellular levels of ROS. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 86072–86081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankala, R.K.; Liu, C.-G.; Chen, A.-Z.; Wang, S.-B.; Xu, P.-Y.; Mende, L.K.; Liu, C.-L.; Lee, C.-H.; Hu, Y.-F. Overcoming Multidrug Resistance through the Synergistic Effects of Hierarchical pH-Sensitive, ROS-Generating Nanoreactors. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 2431–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, S.A.; Brunella, V.; Berlier, G.; Ugazio, E.; Scalarone, D. Effect of Multimodal Pore Channels on Cargo Release from Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarudin, N.H.N.; Jalil, A.A.; Triwahyono, S.; Salleh, N.F.M.; Karim, A.H.; Mukti, R.R.; Hameed, B.H.; Ahmad, A. Role of 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane in the preparation of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for ibuprofen delivery: Effect on physicochemical properties. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 180, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, E.; Dehghannejad, N.; Hashemikia, S.; Ghasemnejad, M.; Tabebordbar, H. Synthesis and surface modification of mesoporous silica nanoparticles and its application as carriers for sustained drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2014, 21, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braz, W.R.; Rocha, N.L.; de Faria, E.H.; Silva, M.L.; Ciuffi, K.J.; Tavares, D.C.; Furtado, R.A.; Rocha, L.A.; Nassar, E.J. Incorporation of anti-inflammatory agent into mesoporous silica. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 385103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Z. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for stimuli-responsive controlled drug delivery: Advances, challenges, and outlook. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.T.H.; Webb, R.I.; Lambert, L.K.; Strounina, E.; Lee, E.C.; Parat, M.-O.; McGuckin, M.A.; Popat, A.; Cabot, P.J.; Ross, B.P. Bifunctional Succinylated ε-Polylysine-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for pH-Responsive and Intracellular Drug Delivery Targeting the Colon. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 9470–9483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi Nasab, N.; Hassani Kumleh, H.; Beygzadeh, M.; Teimourian, S.; Kazemzad, M. Delivery of curcumin by a pH-responsive chitosan mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cancer treatment. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Peng, B. Chitosan-Capped Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as pH-Responsive Nanocarriers for Controlled Drug Release. Chem. Asian J. 2014, 9, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Tang, Q.; Yang, D.; Zhang, J.Z.; Zhang, F.; Hu, J. Preparation of pH-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles and Their Application in Controlled Drug Delivery. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 9926–9932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Nie, J.; Xu, L.; Liang, C.; Peng, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, T.; Mei, L.; Huang, L.; Zeng, X. pH-Sensitive Delivery Vehicle Based on Folic Acid-Conjugated Polydopamine-Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Targeted Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 18462–18473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Tian, X.; Sun, Y.; Lu, D.; Yang, W. pH-sensitive poly(glutamic acid) grafted mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 450, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Yu, L.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Tong, G.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X. Tannin as a gatekeeper of pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 85436–85441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Oh, K.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, C. Controlled Release of Guest Molecules from Mesoporous Silica Particles Based on a pH-Responsive Polypseudorotaxane Motif. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1455–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Sha, Z.; Di, D.; Han, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S. Mechanism study on pH-responsive cyclodextrin capped mesoporous silica: Effect of different stalk densities and the type of cyclodextrin. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 165704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuthati, Y.; Kankala, R.K.; Lin, S.-X.; Weng, C.-F.; Lee, C.-H. pH-Triggered Controllable Release of Silver–Indole-3 Acetic Acid Complexes from Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (IBN-4) for Effectively Killing Malignant Bacteria. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 2289–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Han, N.; Zhao, Q.; Bai, L.; Li, J.; Jiang, T.; Wang, S. Redox-responsive mesoporous silica as carriers for controlled drug delivery: A comparative study based on silica and PEG gatekeepers. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 72, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, C.-Q. pH and redox-operated nanovalve for size-selective cargo delivery on hollow mesoporous silica spheres. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 480, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bathfield, M.; Reboul, J.; Cacciaguerra, T.; Lacroix-Desmazes, P.; Gérardin, C. Thermosensitive and Drug-Loaded Ordered Mesoporous Silica: A Direct and Effective Synthesis Using PEO-b-PNIPAM Block Copolymers. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 3374–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Trewyn, B.G.; Slowing, I.I.; Lin, V.S.-Y. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle-Based Double Drug Delivery System for Glucose-Responsive Controlled Release of Insulin and Cyclic AMP. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8398–8400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Yang, M.-Y.; Wu, H.-X.; Tang, Z.-W.; Xiao, J.-Y.; Liu, C.-J.; Zhuo, R.-X. Glucose- and pH-Responsive Nanogated Ensemble Based on Polymeric Network Capped Mesoporous Silica. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 6310–6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, R.; Ribes, À.; Mas, N.; Aznar, E.; Sancenón, F.; Marcos, M.D.; Murguía, J.R.; Venkataraman, A.; Martínez-Máñez, R. Thrombin-Responsive Gated Silica Mesoporous Nanoparticles as Coagulation Regulators. Langmuir 2016, 32, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayam, S.R.; Venkatesan, P.; Sung, Y.-M.; Sung, S.-Y.; Hu, S.-H.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Wu, S.-P. An NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) enzyme responsive nanocarrier based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles for tumor targeted drug delivery in vitro and in vivo. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 12307–12317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, B.; Luo, Z.; Ding, X.; Li, J.; Dai, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, X.; Ye, J.; Cai, K. Enzyme responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted tumor therapy in vitro and in vivo. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 3614–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, K.; Gupta, S.; Gnanadhas, D.P.; Ramamurthy, P.C.; Chakravortty, D.; Raichur, A.M. Protamine-Capped Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Biologically Triggered Drug Release. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2014, 31, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, T.; Cao, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huo, Q. Enzyme and voltage stimuli-responsive controlled release system based on β-cyclodextrin-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 4355–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Febvay, S.; Marini, D.M.; Belcher, A.M.; Clapham, D.E. Targeted Cytosolic Delivery of Cell-Impermeable Compounds by Nanoparticle-Mediated, Light-Triggered Endosome Disruption. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2211–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Detrembleur, C.; De Pauw-Gillet, M.-C.; Mornet, S.; Jérôme, C.; Duguet, E. Gold Nanorods Coated with Mesoporous Silica Shell as Drug Delivery System for Remote Near Infrared Light-Activated Release and Potential Phototherapy. Small 2015, 11, 2323–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.-P.; Liao, P.-Y.; Su, C.-H.; Yeh, C.-S. Formation of Oligonucleotide-Gated Silica Shell-Coated Fe3O4-Au Core–Shell Nanotrisoctahedra for Magnetically Targeted and Near-Infrared Light-Responsive Theranostic Platform. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 10062–10075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeza, A.; Guisasola, E.; Ruiz-Hernández, E.; Vallet-Regí, M. Magnetically Triggered Multidrug Release by Hybrid Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.L.; Cabañas, M.V.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Polymer-Grafted Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Ultrasound-Responsive Drug Carriers. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11023–11033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-J.; Matsuda, H.; Zhou, H.; Honma, I. Ultrasound-Triggered Smart Drug Release from a Poly(dimethylsiloxane)– Mesoporous Silica Composite. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 3083–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.L.; Villaverde, G.; Cabañas, M.V.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. From proof-of-concept material to PEGylated and modularly targeted ultrasound-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 2785–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Sun, G.; Wang, M.; Zhou, B.; Fu, J. Voltage/pH-Driven Mechanized Silica Nanoparticles for the Multimodal Controlled Release of Drugs. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 21295–21304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuthati, Y.; Kankala, R.K.; Busa, P.; Lin, S.-X.; Deng, J.-P.; Mou, C.-Y.; Lee, C.-H. Phototherapeutic spectrum expansion through synergistic effect of mesoporous silica trio-nanohybrids against antibiotic-resistant gram-negative bacterium. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 169, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, C.A.; Ahern, R.J.; Dontireddy, R.; Ryan, K.B.; Crean, A.M. Mesoporous silica formulation strategies for drug dissolution enhancement: A review. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukara, K.; Schueller, L.; Rosier, J.; Martens, M.A.; Daems, T.; Verheyden, L.; Eelen, S.; Speybroeck, M.V.; Libanati, C.; Martens, J.A.; et al. Ordered mesoporous silica to enhance the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs: Proof of concept in man. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 108, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, X.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Increasing the Oral Bioavailability and Permeation of Poorly Water Soluble Drugs. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.J.K.; Slipper, I.; Walunj, A.; Jain, A.; Favretto, M.E.; Kallinteri, P.; Douroumis, D. Inclusion of poorly soluble drugs in highly ordered mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 387, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreejith, S.; Ma, X.; Zhao, Y. Graphene Oxide Wrapping on Squaraine-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Bioimaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 17346–17349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Sugihara, F.; Matsushita, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Mizukami, S.; Kikuchi, K. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for 19F magnetic resonance imaging, fluorescence imaging, and drug delivery. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 1986–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, B.-H.; Hwang, D.W.; Jung, H.S.; Jang, J.; Kim, H.; Kang, H.; Kang, T.; Kyeong, S.; Lee, H.; Jeong, D.H.; et al. Ultrasensitive, Biocompatible, Quantum-Dot-Embedded Silica Nanoparticles for Bioimaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helle, M.; Rampazzo, E.; Monchanin, M.; Marchal, F.; Guillemin, F.; Bonacchi, S.; Salis, F.; Prodi, L.; Bezdetnaya, L. Surface Chemistry Architecture of Silica Nanoparticles Determine the Efficiency of in Vivo Fluorescence Lymph Node Mapping. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 8645–8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Regí, M. Ordered Mesoporous Materials in the Context of Drug Delivery Systems and Bone Tissue Engineering. Chem. Eur. J. 2006, 12, 5934–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Ruiz-González, L.; Doadrio, J.C.; González-Calbet, J.M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Tissue regeneration: A new property of mesoporous materials. Solid State Sci. 2005, 7, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, M.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Lyu, Y.; Wei, J.; Wei, S. Peptide-laden mesoporous silica nanoparticles with promoted bioactivity and osteo-differentiation ability for bone tissue engineering. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 131, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Chang, J. Mesoporous bioactive glasses: Structure characteristics, drug/growth factor delivery and bone regeneration application. Interface Focus 2012, 2, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Noriega, A.; Arcos, D.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Sakamoto, Y.; Terasaki, O.; Vallet-Regí, M. Ordered Mesoporous Bioactive Glasses for Bone Tissue Regeneration. Chem. Mater 2006, 18, 3137–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzuto, G.; Molinari, A. Liposomes as nanomedical devices. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 975–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.E.; Chen, Z.; Shin, D.M. Nanoparticle therapeutics: An emerging treatment modality for cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palazzolo, S.; Bayda, S.; Hadla, M.; Caligiuri, I.; Corona, G.; Toffoli, G.; Rizzolio, F. The Clinical translation of Organic Nanomaterials for Cancer Therapy: A Focus on Polymeric Nanoparticles, Micelles, Liposomes and Exosomes. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaly, N.; Xiao, Z.; Valencia, P.M.; Radovic-Moreno, A.F.; Farokhzad, O.C. Targeted polymeric therapeutic nanoparticles: Design, development and clinical translation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2971–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slowing, I.I.; Wu, C.-W.; Vivero-Escoto, J.L.; Lin, V.S.-Y. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Reducing Hemolytic Activity towards Mammalian Red Blood Cells. Small 2009, 5, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nash, T.; Allison, A.C.; Harington, J.S. Physico-Chemical Properties of Silica in Relation to its Toxicity. Nature 1966, 210, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, F.; Li, Y.; Shi, J. In vivo Biodistribution and Urinary Excretion of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: Effects of Particle Size and PEGylation. Small 2011, 7, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Malugin, A.; Ghandehari, H. Impact of Silica Nanoparticle Design on Cellular Toxicity and Hemolytic Activity. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5717–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townson, J.L.; Lin, Y.-S.; Agola, J.O.; Carnes, E.C.; Leong, H.S.; Lewis, J.D.; Haynes, C.L.; Brinker, C.J. Re-examining the Size/Charge Paradigm: Differing in Vivo Characteristics of Size- and Charge-Matched Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16030–16033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, T.; Fu, C.; Tan, L.; Meng, X.; Liu, H. Biodistribution, excretion, and toxicity of mesoporous silica nanoparticles after oral administration depend on their shape. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ran, F.; Cui, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Q.; Gao, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, S. A comparison between sphere and rod nanoparticles regarding their in vivo biological behavior and pharmacokinetics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, S.P.; Padera, R.F.; Langer, R.; Kohane, D.S. The biocompatibility of mesoporous silicates. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4045–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Liong, M.; Li, Z.; Zink, J.I.; Tamanoi, F. Biocompatibility, biodistribution, and drug-delivery efficiency of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cancer therapy in animals. Small 2010, 6, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Li, L.; Chen, D. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Biocompatibility and Drug Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1504–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, P.-Z.; Nguyen, K.T.; Wang, X.-J.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, H.; Tan, N.S.; Zhao, Y. Biocompatible, Uniform, and Redispersible Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Cancer-Targeted Drug Delivery In Vivo. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2450–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, R.; Li, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, D. Biphase Stratification Approach to Three-Dimensional Dendritic Biodegradable Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Zeng, B.; Liang, S.; Long, M.; Xu, H. Synthesis of pH-Responsive Biodegradable Mesoporous Silica–Calcium Phosphate Hybrid Nanoparticles as a High Potential Drug Carrier. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 44402–44409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Li, L.; Teng, X.; Huang, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, D.; Ren, J.; He, J.; Tang, F. Single and repeated dose toxicity of mesoporous hollow silica nanoparticles in intravenously exposed mice. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 1657–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.; Liu, T.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Chen, D.; Tang, F. The absorption, distribution, excretion and toxicity of mesoporous silica nanoparticles in mice following different exposure routes. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2565–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Shi, J. In Vivo Bio-Safety Evaluations and Diagnostic/Therapeutic Applications of Chemically Designed Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3144–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asefa, T.; Tao, Z. Biocompatibility of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 2265–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napierska, D.; Thomassen, L.C.; Lison, D.; Martens, J.A.; Hoet, P.H. The nanosilica hazard: Another variable entity. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2010, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, K.R. The chemistry of silica and its potential health benefits. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2007, 11, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Croissant, J.G.; Fatieiev, Y.; Khashab, N.M. Degradability and Clearance of Silicon, Organosilica, Silsesquioxane, Silica Mixed Oxide, and Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-H.; Lee, M.-S.; Kim, D.; Lee, T.K.; Kwon, T.K.; Yun, H.; Khang, S.-H. The comparative immunotoxicity of mesoporous silica nanoparticles and colloidal silica nanoparticles in mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, E.; Penate-Medina, O.; Zanzonico, P.B.; Carvajal, R.D.; Mohan, P.; Ye, Y.; Humm, J.; Gonen, M.; Kalaigian, H.; Schoder, H.; et al. Clinical translation of an ultrasmall inorganic optical-PET imaging nanoparticle probe. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 260ra149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benezra, M.; Penate-Medina, O.; Zanzonico, P.B.; Schaer, D.; Ow, H.; Burns, A.; DeStanchina, E.; Longo, V.; Herz, E.; Iyer, S.; et al. Multimodal silica nanoparticles are effective cancer-targeted probes in a model of human melanoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2768–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukara, K.; Schueller, L.; Rosier, J.; Daems, T.; Verheyden, L.; Eelen, S.; Martens, J.A.; Van den Mooter, G.; Bugarski, B.; Kiekens, F. In Vivo Performance of Fenofibrate Formulated With Ordered Mesoporous Silica Versus 2-Marketed Formulations: A Comparative Bioavailability Study in Beagle Dogs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2381–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley, C.E.; Carnes, E.C.; Wu, T.; Felton, L.A.; Sasaki, D.Y. Antibiotic Protocells and Related Pharmaceutical Formulations and Methods of Treatment. U.S. Patent 20170165375A1, 15 June 2017. Available online: https://www.google.com/patents/US20170165375 (accessed on 7 November 2017).
- Brinker, C.J.; Townson, J.; Lin, Y.-S.; Durfee, P.N. Core and Surface Modification of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles to Achieve Cell Specific Targeting In Vivo. U.S. Patent 20160287717A1, 6 October 2016. Available online: https://www.google.com/patents/US20160287717 (accessed on 7 November 2017).
- Brinker, C.J.; Ashley, C.E.; Jiang, X.; Liu, J.; Peabody, D.S.; Wharton, W.R.; Carnes, E.; Chackerian, B.; Willman, C.L. Protocells and Their Use for Targeted Delivery of Multicomponent Cargos to Cancer Cells. U.S. Patent 8992984B1, 31 March 2015. Available online: https://www.google.com/patents/US8992984 (accessed on 7 November 2017).
- Brinker, J.C.; Lin, Y. Torroidal Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (TMSNPS) and Related Protocells. U.S. Patent 20160338954A1, 24 November 2016. Available online: http://www.freepatentsonline.com/y2016/0338954.html (accessed on 7 November 2017).
- Ashley, C.E.; Brinker, C.J.; Carnes, E.C.; Fekrazad, M.H.; Felton, L.A.; Negrete, O.; Padilla, D.P.; Wilkinson, B.S.; Wilkinson, D.C.; Willman, C.L. Porous Nanoparticle-Supported Lipid Bilayers (Protocells) for Targeted Delivery Including Transdermal Delivery of Cargo and Methods Thereof. U.S. Patent EP2765997A4, 24 June 2015. Available online: https://www.google.co.in/patents/EP2765997A4?cl=esCached (accessed on 7 November 2017).
- Nel, A.E.; Zink, J.I.; Meng, H. Lipid Bilayer Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with a High Loading Capacity for One or More Anticancer Agents. U.S. Patent 20160008283A1, 14 January 2016. Available online: https://www.google.com/patents/US20160008283?cl=en (accessed on 7 November 2017).
- Oktem, H.A.; Ozalp, V.C.; Hernandez, F.J.; Hernandez, L.I. Applications and Tools Based on Silica Particles Coated with Biological or Synthetic Molecules. U.S. Patent 20170172935A1, 22 June 2017. Available online: https://www.google.com/patents/US20170172935 (accessed on 7 November 2017).
- Won, C. Composition for Delivering Bioactive Material or Protein, and Use Thereof. U.S. Patent 20170172923A1, 22 June 2017. Available online: https://www.google.com/patents/US20170172923 (accessed on 7 November 2017).
- Weng, C.-F.; Chia, Y.-C.; Lee, C.-H.; Varadharajan, T. HCD Formulation for Cancer Treatment. U.S. Patent 20160243236A1, 25 August 2016. Available online: https://www.google.com/patents/US20160243236 (accessed on 7 November 2017).
- Lee, K.; Lai, J.; Shah, B. FRET-Based Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Real-Time Monitoring of Drug Release. U.S. Patent 9408918B1, 9 August 2016. Available online: http://www.freepatentsonline.com/9408918.html (accessed on 7 November 2017).
- Shou-Cang, S.; Kiong, N.W.; Chia, L.; Tan, R. Nanostructured Material Formulated with Bone Cement for Effective Antibiotic Delivery. U.S. Patent 9155814B2, 13 October 2015. Available online: https://www.google.com/patents/US9155814 (accessed on 7 November 2017).
- Liu, Y.; Lay, C.L. Stimuli-Responsive Interpolymer Complex Coated Hollow Silica Vesicles. U.S. Patent 20150182468A1, 2 July 2015. Available online: https://www.google.com/patents/US20150182468 (accessed on 7 November 2017).
- Zink, J.I.; Nel, A.E.; Xia, T.; Ji, Z.; Meng, H.; Li, Z.; Liong, M.; Xue, M.; Tarn, D.Y. Cationic Polymer Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles and Uses Thereof. U.S. Patent 20120207795A1, 16 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liong, M.; Lu, J.; Tamanoi, F.; Zink, J.I.; Nel, A. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. U.S. Patent 20100255103A1, 7 October 2010. Available online: https://www.google.ch/patents/US20100255103 (accessed on 7 November 2017).
- Lee, C.-H.; Lo, L.-W.; Yang, C.-S.; Mou, C.-Y. Charged Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery System for Controlled Release and Enhanced Bioavailability. U.S. Patent 20100104650A1, 29 April 2010. Available online: https://www.google.com/patents/US20100104650 (accessed on 7 November 2017).
- Lin, V.; Trewyn, B.; Huh, S.; Whitman, C. Antimicrobial Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. U.S. Patent 20060018966A1, 26 January 2006. Available online: https://www.google.com/patents/US20060018966 (accessed on 7 November 2017).
- Chen, F.; Ma, K.; Benezra, M.; Zhang, L.; Cheal, S.M.; Phillips, E.; Yoo, B.; Pauliah, M.; Overholtzer, M.; Zanzonico, P.; et al. Cancer-Targeting Ultrasmall Silica Nanoparticles for Clinical Translation: Physicochemical Structure and Biological Property Correlations. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 8766–8779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Marketed Product | Formulation | Drug | Use | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AmBisome® | Liposome | Amphotericin B | Antifungal | [13] |
| DaunoXome® | Liposome | Daunorubicin | Kaposi’s sarcoma associated with HIV | [14] |
| Doxil® | Liposome | Doxorubicin | Kaposi’s sarcoma associated with HIV, breast cancer, ovarian cancer | [15] |
| Myocet® | Liposome | Doxorubicin | Breast cancer | [16] |
| Emend® | Nanocrystals | Aprepitant | Antiemetic | [17] |
| Megace ES® | Nanocrystals | Megestrol acetate | Anorexia | [17] |
| Tricor® | Nanocrystals | Fenofibrate | In hypercholesterolemia | [17] |
| MSN Family | MSN Type | Pore Symmetry | Pore Size (nm) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M41S | MCM-41 | 2D hexagonal P6mm | 1.5–8 | >1.0 | [42,43] |
| MCM-48 | 3D cubic Ia3d | 2–5 | >1.0 | [42,43] | |
| MCM-50 | Lamellar p2 | 2–5 | >1.0 | [44,45] | |
| SBA | SBA-11 | 3D cubic Pm3m | 2.1–3.6 | 0.68 | [45,46,47] |
| SBA-12 | 3D hexagonal P63/mmc | 3.1 | 0.83 | [48,49,50] | |
| SBA-15 | 2D hexagonal p6mm | 6–0 | 1.17 | [43,51] | |
| SBA-16 | Cubic Im3m | 5–15 | 0.91 | [43,52] | |
| KIT | KIT-5 | Cubic Fm3m | 9.3 | 0.45 | [53,54] |
| COK | COK-12 | Hexagonal P6m | 5.8 | 0.45 | [55,56] |
| Chemical Constituents | Function | References |
|---|---|---|
| Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) | Structure directing agent/template | [94,95] |
| Cetyltrimethylammonium chloride (CTAC) | Structure directing agent/template | [96,97] |
| Pluronic F123, F127 | Surfactant template | [38,98] |
| Brij-76 | Surfactant template | [99,100] |
| Triton X-100 | Surfactant | [101,102] |
| Tween 20, 40, 60, 80 | Surfactant | [103] |
| Tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) | Inorganic silica source | [94,95] |
| Tetramethoxy silane (TMOS) | Inorganic silica source | [104,105] |
| Tetrakis(2-hydroxyethyl) orthosilicate (THEOS) | Inorganic silica source | [106] |
| Trimethoxyvinylsilane (TMVS) | Inorganic silica source | [107] |
| Sodium silicate | Inorganic silica source | [108] |
| Ethanol | Cosolvent to solubilize TEOS | [97,109] |
| Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) | Base catalyst | [95] |
| Ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH) | Base catalyst | [94] |
| Triethanolamine (TEA) | Base catalyst, complexing agent and growth inhibitor | [96] |
| Diethanolamine (DEA) | Base catalyst | [96,109] |
| Disodium hydrogen phosphate-sodium dihydrogen phosphate buffer solution | Reaction medium | [109] |
| Triisopropylbenzene (TIPB) | Pore-expanding agent | [110,111] |
| Tetrapropoxysilane (TPOS) | Pore- expanding agent | [111] |
| Pluronic polymer P103 | Pore-expanding agent | [112] |
| Carrier | Drug | Loading (wt %) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCM-41 | Ibuprofen | 35.9 | [75] |
| HMSNs | 74.5 | ||
| MCM-41 | Doxorubicin | 48.16 | [74] |
| HMSNs | 112.12 | ||
| HMSNs | 5-fluorouracil | 18.54 | [78] |
| HMSNs-NH2 | 28.89 | ||
| HMSNs-COOH | 20.73 | ||
| HMSNs-CN | 22.54 | ||
| HMSNs-CH3 | 12.13 | ||
| MCM-41(C12) | Captopril | 23.6 | [151] |
| MCM-41(C16) | 34 | ||
| SBA-15 | 22.6 | ||
| MCM-41 | Erythromycin | 29 | [152] |
| SBA-15 | 34 | ||
| SBA-15 (C8) | 13 | ||
| SBA-15 (C18) | 18 | ||
| MCM-41 | Alendronate | 14 | [153] |
| MCM-41-NH2 | 37 | ||
| SBA-15 | 8 | ||
| SBA-15-NH2 | 22 | ||
| MSN-C0 | Lysozyme | 34 | [149] |
| MSN-C10 | 42 |
| Carrier | Drug | Release Rate | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCM-41 (C12) | Captopril | 45 wt % within 2 h, total drug release over 16 h | [151] |
| MCM-41 (C16) | 47.47 wt % within 2 h, total drug release >30 h | ||
| SBA-15 | 60 wt % within 0.5 h, total drug release over 16 h | ||
| SBA-15 | Erythromycin | 60% release within 5 h, total drug release within 14 h | [152] |
| SBA-15 (C8) | |||
| SBA-15 (C18) | |||
| SBA-15 unmodified (PS0) | Ibuprofen | Complete release in 10 h | [156] |
| SBA-15-NH2 by post synthesis (PS2) | Initial burst release of 50% in 10 h followed by 100% release in 3 days | ||
| SBA-15-NH2 by one pot synthesis (OPS2) | Complete release in 10 h | ||
| MSN (grafting-loading approach) | Doxorubicin | 40% in 8 h and stagnant release beyond 8 h | [143] |
| MSN (loading-grafting approach) | 10% in first 24 h, sustained beyond 160 h |
| Category | Drug | Carrier | PS, Dp (nm) | Activity Testing | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anticancer | Doxorubicin | Hollow MSNs | 120, 2.7 | HeLa cells | [157] |
| Lipid-coated MSNs | 295, 2.3 | MCF-7 human breast cancer cells | [158] | ||
| Topotecan | MCM-41 | 72.9, 2.7 | Female athymic nude mice injected with MDA-MB-231 human epithelial breast cancer cells s.c. | [159] | |
| Quercetin | MCM-41 | [159] | |||
| Curcumin | SLN-silica microcapsules | 305, 7.8 | Caco-2 cells | [160] | |
| Paclitaxel | MSNs | 100, 2.3 | PK studies in peritoneal MIA-PaCa-2 (human pancreatic cancer cell) tumour bearing nude mice | [161] | |
| 5-fluorouracil | MCM-41 | 135, 2.9 | Human colonic HT-29 cells | [162] | |
| Etoposide | MCM-41-PAA | 142.85, 3.69 | PC-3 and LNCaP human prostate cancer cells | [163] | |
| 16-hydroxy-cleroda-3,13-dien-16,15-olide (HCD) | Eudragit S100-HCD-Cu-MSN | 514, 4.3 | Athymic male nude mice injected with C6 Glioma cells s.c. | [164] | |
| Antidepressant | Duloxetine hydrochloride | MSNs | PS not reported, 2.6–7.2 | Not reported | [165] |
| Anti-tuberculosis | Rifampicin | MCM-41 | 218, 2.4 | Not reported | [166] |
| Anti-inflammatory | Ibuprofen | MSNs | PS not reported, 3.6–4.1 | Not reported | [101] |
| Ketoprofen | MCM-41 SBA-15 | 1500, 3.4 970, 6.24 | Not reported | [167] | |
| Budesonide | MCM-41 | 100, 2.7 | Coculture of HT-29 cells and PMA treated human EOL-1 (acute myeloid eosinophilic leukemia) cells | [168] | |
| Antibacterial | Ciprofloxacin | Lipid-coated MSNs | 80–100, Dp not reported | Salmonella typhimurium administered mice | [169] |
| Ciprofloxacin | Arg-MSN | 75, 7.2 | Salmonella infected BALB/c mice | [170] | |
| Tetracycline | MCM-41 | 41 and 406, Dp not reported | In vitro against Escherichia coli | [171] | |
| Antihypertensive | Captopril | SBA-15 | PS not reported, 7.15 | Not reported | [172] |
| Aliskiren | SBA-15 | [172] | |||
| Hydrochlorothiazide, Losartan potassium, Amlodipine besylate, Simvastatin | MCM-41 polypill | 150, 4.64 | Not reported | [173] | |
| Hypoglycemic drugs | Gluconated insulin Rosiglitazone maleate | Alizarin complexone-MSNs | 60–100, ~2.3 | In vitro monitoring of drug release in human serum | [174] |
| 16-hydroxycleroda-3,13-dine-16,15-olide (HCD) | MSNs | 259, 3.9 | Diet-induced ICR male diabetic mice | [175] | |
| Osteogenic | Alendronate | MCM-41 SBA-15 | PS not reported, 3.8 PS not reported, 9.0 | Not reported | [153] |
| Alendronate | HA-AL-MS-PLGA microspheres | 245–258 µm | In vitro on synovium-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) | [176] | |
| Dexamethasone | MCM-41 | 265, Dp not reported | Male Sprague−Dawley rats | [177] | |
| Antioxidant | Morin | MSNs | 150, 3 | In vitro | [178] |
| Drugs | Application | Targeting Ligand | Receptor | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-fluorouracil | Colorectal cancer | Hyaluronic acid | CD44 | [189] |
| 5-fluorouracil | Colorectal cancer | EGF | EGF | [190] |
| Curcumin | Cervical cancer | Chondroitin sulphate | CD44 | [191] |
| Docetaxel | Breast cancer | Folic acid | Folate | [181] |
| Docetaxel | Hepatoma | Lactose | Asialoglycoprotein | [184] |
| Doxorubicin | Hepatic cancer | Transferrin | Transferrin | [192] |
| Doxorubicin | Colon cancer | Aptamer | (EpCAM) | [193] |
| Photosensitizer merocyanine | Breast cancer | Mannose | Mannose | [194] |
| Quercetin | Triple negative breast cancer | cRGD peptide | Integrin receptor αvβ3 | [159] |
| Quercetin | Breast cancer | Folic acid | Folate | [195] |
| Sunitinib | Glioblastoma | VEGF121 | VEGF | [196] |
| Topotecan | Triple-negative breast cancer | cRGD peptide | Integrin receptor αvβ3 | [159] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Narayan, R.; Nayak, U.Y.; Raichur, A.M.; Garg, S. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Review on Synthesis and Recent Advances. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030118
Narayan R, Nayak UY, Raichur AM, Garg S. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Review on Synthesis and Recent Advances. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(3):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030118
Chicago/Turabian StyleNarayan, Reema, Usha Y. Nayak, Ashok M. Raichur, and Sanjay Garg. 2018. "Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Review on Synthesis and Recent Advances" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 3: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030118
APA StyleNarayan, R., Nayak, U. Y., Raichur, A. M., & Garg, S. (2018). Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Review on Synthesis and Recent Advances. Pharmaceutics, 10(3), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030118