Experimental and Modeling Study of Drug Release from HPMC-Based Erodible Oral Thin Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Film Production
2.3. Rheological Studies
2.4. Mechanical Strength Tests
2.5. Phase Solubility Study of Furosemide with HP--CD
2.6. Swelling-Erosion Tests
2.7. Release Studies with Vertical Franz Diffusion Cell
2.8. Release Studies with Paddle Type Dissolution Apparatus (USP II)
2.9. Release Studies with Millifluidic Flow-through Device (MFTD)
3. Transport Models
3.1. Swelling-Erosion Modeling of Thin Films
3.2. Drug Release Modeling in a Vertical Franz Diffusion Cell
- a purely diffusive transport equation in the donor compartment with drug diffusivity ,
- a purely diffusive transport equation in the membrane with drug diffusivity ,
- a purely diffusive transport equation in the cylindrical body (Domain A) with drug diffusivity ,
- a purely diffusive transport equation in the truncated cone region (Domain B) with diffusivity , Equation (22), and
- a pure diffusive transport equation in the lateral arm (Domain C) with drug diffusivity in a quiescent solvent solution.
3.3. Drug Release Modeling in the MFTD
3.4. Drug Release Modeling in the USP II Apparatus
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Film Thickness, Drug Loading, and Moisture Content
4.2. Analysis of Rheological Studies and Mechanical Strength Tests
4.3. Analysis of Phase Solubility of Furosemide with HP--CD
4.4. Analysis of Swelling-Erosion Tests
4.5. Analysis of Release Kinetics in Franz Cell
4.5.1. Analysis of Blank Solutions
4.5.2. Analysis of Release Data from Films
4.6. Analysis of Release Kinetics in USP II and MFTD Apparatuses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alsaeed, D.; Furniss, D.; Blandford, A.; Smith, F.; Orlu, M. Carers’ experiences of home enteral feeding: A survey exploring medicines administration challenges and strategies. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2018, 43, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.Y.; Choung, R.S.; Saito, Y.A.; Schleck, C.D.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Locke, G.R., III; Talley, N.J. Prevalence and risk factors for dysphagia: A U.S. community study. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 27, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, J.; Wright, D.; Wood, J. Medication errors in patients with dysphagia. Nurs. Times 2012, 108, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cilurzo, F.; Musazzi, U.M.; Franzé, S.; Selmin, F.; Minghetti, P. Orodispersible dosage forms: Biopharmaceutical improvements and regulatory requirements. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, R.P.; Puthli, S.P. Oral strip technology: Overview and future potential. J. Control Release 2009, 139, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathpalia, H.; Gupte, A. An introduction to fast dissolving oral thin film drug delivery systems: A review. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granero, G.E.; Longhi, M.R.; Mora, M.J.; Junginger, H.E.; Midha, K.K.; Shah, V.P.; Stavchansky, S.; Dressman, J.B.; Barends, D.M. Biowaiver Monographs for Immediate Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms: Furosemide. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 2544–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, Y.; Tatsumi, E. Physicochemical characterization of furosemide modifications. Int. J. Pharm. 1990, 60, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolicelli, P.; Petralito, S.; Varani, G.; Nardoni, M.; Pacelli, S.; Di Muzio, L.; Tirilló, J.; Bartuli, C.; Cesa, S.; Casadei, M.A.; et al. Effect of glycerol on the physical and mechanical properties of thin gellan gum films for oral drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 547, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnero, C.; Chattah, A.K.; Longhi, M. Improving furosemide polymorphs properties through supramolecular complexes of β-cyclodextrin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 95, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vemula, V.R.; Lagishetty, V.; Lingala, S. Solubility enhancement techniques. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2010, 5, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Ozdemir, N.; Ordu, S. Improvement of Dissolution Properties of Furosemide by Complexation with β-cyclodextrin. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1998, 24, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedacchia, A.; Adrover, A. Study of release kinetics and diffusion coefficients in swellable cellulosic thin films by means of a simple spectrophotometric technique. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2014, 92, 2550–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrover, A.; Pedacchia, A.; Petralito, S.; Spera, R. In vitro dissolution testing of oral thin films: A comparison between USP 1, USP 2 apparatuses and a new millifluidic flow-through device. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 95, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrover, A.; Nobili, M. Release kinetics from oral thin films: Theory and experiments. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 98, 188–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preis, M.; Knop, K.; Breitkreutz, J. Mechanical strength test for orodispersible and buccal films. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 461, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, T.; Connors, K.A. Phase solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum. 1965, 4, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, G.C.S.; Ramadevi, K.; Sirisha, K. Effect of β-cyclodextrin on Rheological Properties of some Viscosity Modifiers. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 76, 545–548. [Google Scholar]
- Siepmann, J.; Peppas, N.A. Modeling of drug release from delivery systems based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 48, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanu, J.S.; Soane, D.S.; Bell, A.T.; Hess, D.M. Transport Models for swelling and dissolution of thin polymer films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1989, 38, 859–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, B.; Peppas, N.A. Molecular Analysis of Drug Delivery Systems Controlled by Dissolution of the Polymer Carrier. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siepmann, J.; Gopferich, A. Mathematical modeling of bioerodible, polymeric drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 48, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambertia, G.; Galdi, I.; Barba, A.A. Controlled release from hydrogel-based solid matrices. A model accounting for water up-take, swelling and erosion. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 407, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lao, L.L.; Peppas, N.A.; Boey, F.Y.C.; Venkatraman, S.S. Modeling of drug release from bulk-degrading polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 418, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosca, I.-D.; Vergnaud, J.-M. Evaluation of the characteristics of oral dosage forms with release controlled by erosion. Comput. Biol. Med. 2008, 38, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewster, M.E.; Loftsson, T. Cyclodextrins as pharmaceutical solubilizers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 645–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayduk, W.; Laudie, H. Prediction of diffusion coefficients for non electrolytes in dilute aqueous solutions. AIChE J. 1974, 20, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
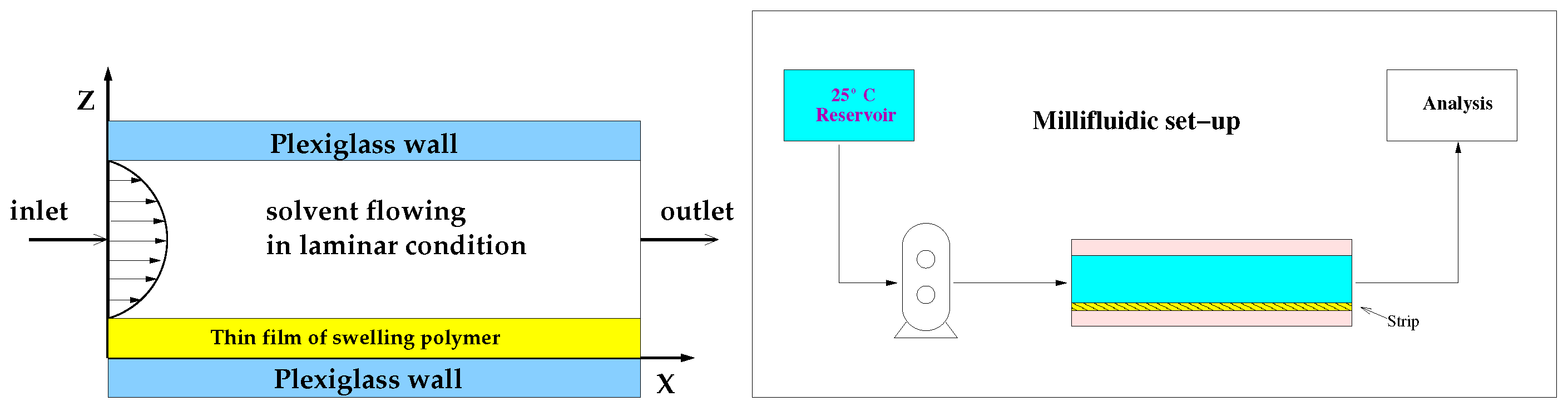










| Film | (m) | (m/s) | C (m/s) | (m/s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| without HP--CD | 87 ± 5 | 0.21 | 0.3 | 0.89 | 67.72 | 1.87 | |
| with HP--CD | 126 ± 5 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.85 | 84.37 | 3.86 |
| (m/s) | 1 (mL/min) | 2 (mL/min) | 4 (mL/min) | 5 (mL/min) | USP II |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| without HP--CD | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.41 | 0.5 | 0.64 |
| with HP--CD | 0.38 | 0.47 | 0.61 | 0.74 | 0.96 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adrover, A.; Varani, G.; Paolicelli, P.; Petralito, S.; Di Muzio, L.; Casadei, M.A.; Tho, I. Experimental and Modeling Study of Drug Release from HPMC-Based Erodible Oral Thin Films. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10040222
Adrover A, Varani G, Paolicelli P, Petralito S, Di Muzio L, Casadei MA, Tho I. Experimental and Modeling Study of Drug Release from HPMC-Based Erodible Oral Thin Films. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(4):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10040222
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdrover, Alessandra, Gabriele Varani, Patrizia Paolicelli, Stefania Petralito, Laura Di Muzio, Maria Antonietta Casadei, and Ingunn Tho. 2018. "Experimental and Modeling Study of Drug Release from HPMC-Based Erodible Oral Thin Films" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 4: 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10040222
APA StyleAdrover, A., Varani, G., Paolicelli, P., Petralito, S., Di Muzio, L., Casadei, M. A., & Tho, I. (2018). Experimental and Modeling Study of Drug Release from HPMC-Based Erodible Oral Thin Films. Pharmaceutics, 10(4), 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10040222







