Co-Loading of Ascorbic Acid and Tocopherol in Eudragit-Nutriosomes to Counteract Intestinal Oxidative Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Vesicle Characterization
2.4. Stability of Vesicle Dispersions
2.5. Vesicle Behaviour in Gastrointestinal Fluids
2.6. Biocompatibility of the Vesicles in Caco-2 Cells
2.7. Antioxidant Activity of the Vesicles
2.8. Intestinal Wound Healing Activity of the Vesicles
2.9. Statistical Analysis of Data
3. Results
3.1. Vesicle Preparation and Characterization
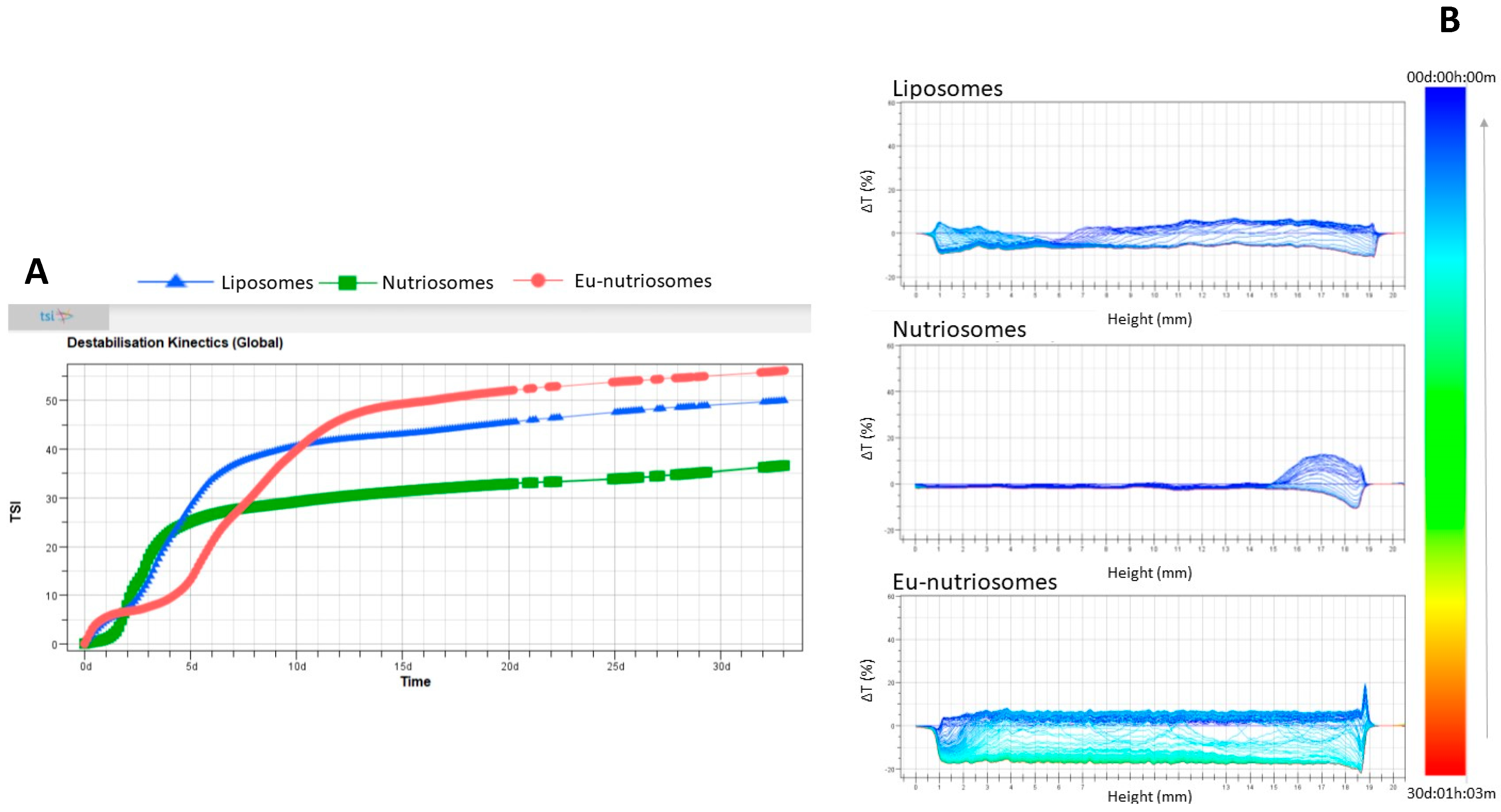
3.2. Vesicle Stability
3.3. Vesicle Behaviour in Gastrointestinal Fluids
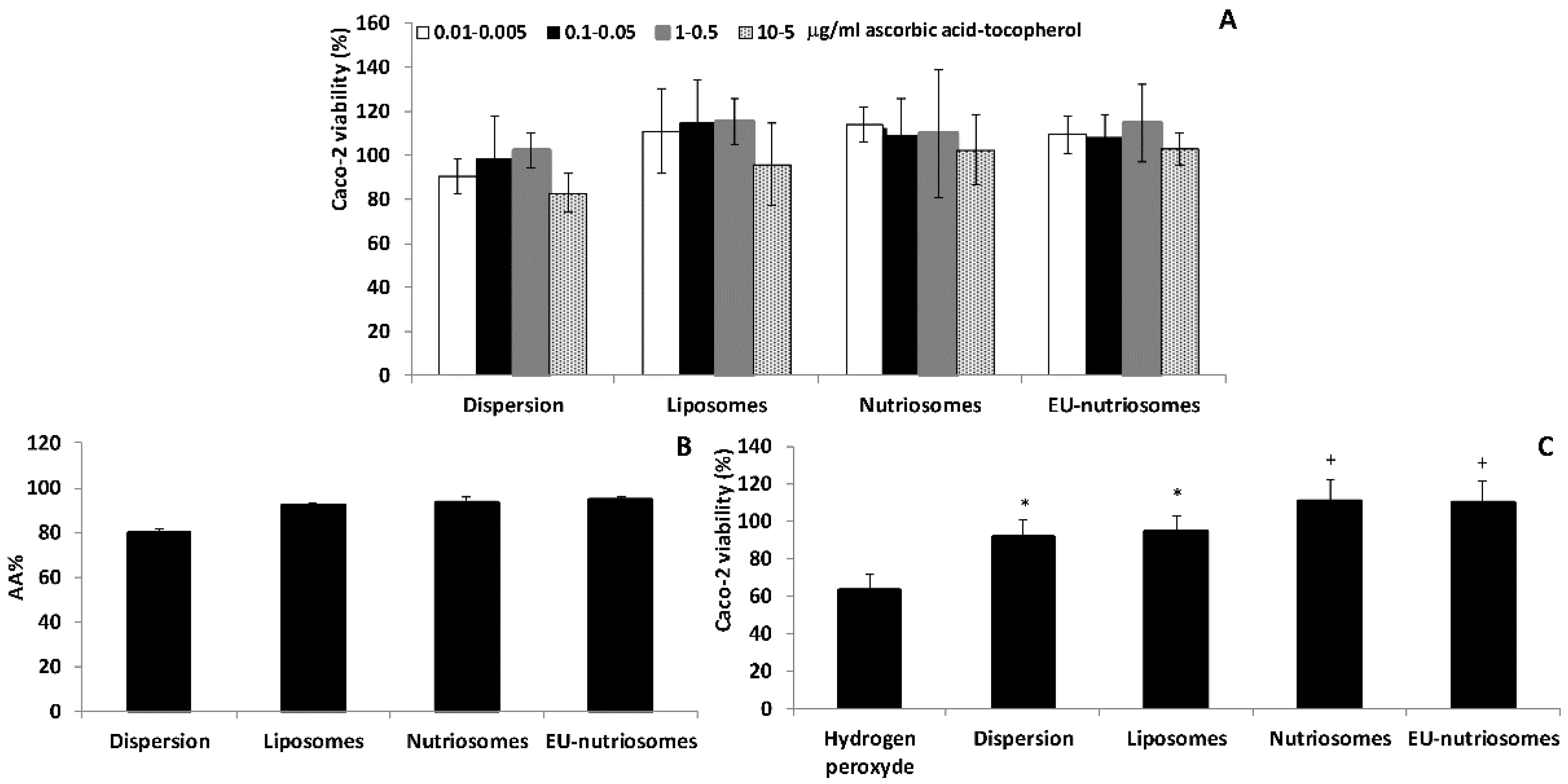
3.4. Vesicle Biocompatibility In Vitro
3.5. Antioxidant Activity of the Vesicles
3.6. Intestinal Wound Healing Activity of the Vesicles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carr, A.C.; Vissers, M.C.M. Synthetic or food-derived vitamin C-Are they equally bioavailable? Nutrients 2013, 5, 4284–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waniek, S.; Di Giuseppe, R.; Esatbeyoglu, T.; Plachta-Danielzik, S.; Ratjen, I.; Jacobs, G.; Nöthlings, U.; Koch, M.; Schlesinger, S.; Rimbach, G.; et al. Vitamin E (α-and γ-tocopherol) levels in the community: Distribution, clinical and biochemical correlates, and association with dietary patterns. Nutrients 2018, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatariah, Z.; Tengku Zulkhairuazha, T.Y.; Wan Rosli, W.I. Ascorbic acid quantification in Benincasa hispida fruit extracted using different solvents. Int. Food Res. J. 2015, 22, 208–212. [Google Scholar]
- Majagi, S.I.; Bhosle, T.N.; Patil, P.A. Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic activity of Dl-Alpha-Tocopheryl Acetate and its interaction with aspirin in Wistar rats. Int. J. Drug Dev. Res. 2011, 3, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Masri, O.A.; Chalhoub, J.M.; Sharara, A.I. Role of vitamins in gastrointestinal diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 5191–5209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, P.; Gu, Y.; Gu, J.-M.; Xie, Z.-A.; Xu, J.-Q.; Zhao, X.-D.; Huang, K.-M.; Wang, J.-Y.; Jiang, X.-S.; Fan, S.-W.; et al. Ascorbic Acid Attenuates Multifidus Muscles Injury and Atrophy after Posterior Lumbar Spine Surgery by Suppressing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in a Rat Model. Spine 2018, 43, E1249–E1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Liu, Y.; Xie, T.; Liu, F. α-Tocopherol protected against cobalt nanoparticles and cocl 2 induced cytotoxicity and inflammation in Balb/3T3 cells. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2018, 40, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoi, T.; Otani, T.; Ishii, K. In vivo fluorescence bioimaging of ascorbic acid in mice: Development of an efficient probe consisting of phthalocyanine, TEMPO, and albumin. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hategekimana, J.; Masamba, K.G.; Ma, J.; Zhong, F. Encapsulation of vitamin E: Effect of physicochemical properties of wall material on retention and stability. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 124, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joanitti, G.A.; Sawant, R.S.; Torchilin, V.P.; de Freitas, S.M.; Azevedo, R.B. Optimizing liposomes for delivery of Bowman-Birk protease inhibitors—Platforms for multiple biomedical applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 167, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalán-Latorre, A.; Pleguezuelos-Villa, M.; Castangia, I.; Manca, M.L.; Caddeo, C.; Nácher, A.; Díez-Sales, O.; Peris, J.E.; Pons, R.; Escribano-Ferrer, E.; et al. Nutriosomes: Prebiotic delivery systems combining phospholipids, a soluble dextrin and curcumin to counteract intestinal oxidative stress and inflammation. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 1957–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A. Colon Targeting Using pH Sensitive Materials. Adv. Res. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 8, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, M.L.; Peris, J.E.; Melis, V.; Valenti, D.; Cardia, M.C.; Lattuada, D.; Escribano-Ferrer, E.; Fadda, A.M.; Manconi, M. Nanoincorporation of curcumin in polymer-glycerosomes and evaluation of their in vitro-in vivo suitability as pulmonary delivery systems. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 105149–105159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, M.L.; Valenti, D.; Sales, O.D.; Nacher, A.; Fadda, A.M.; Manconi, M. Fabrication of polyelectrolyte multilayered vesicles as inhalable dry powder for lung administration of rifampicin. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 472, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Chattopadhyay, R.; Mitra, S.; Crowe, S.E. Oxidative Stress: An Essential Factor in the Pathogenesis of Gastrointestinal Mucosal Diseases. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 329–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inokuma, T.; Haraguchi, M.; Fujita, F.; Tajima, Y.; Kanematsu, T. Oxidative stress and tumor progression in colorectal cancer. Hepatogastroenterology 2009, 56, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tian, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Pathomechanisms of Oxidative Stress in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Potential Antioxidant Therapies. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caddeo, C.; Manca, M.L.; Matos, M.; Gutierrez, G.; Díez-Sales, O.; Peris, J.E.; Usach, I.; Fernàndez-Busquets, X.; Fadda, A.M.; Manconi, M. Functional response of novel bioprotective poloxamer-structured vesicles on inflamed skin. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample | Size (nm) | PI | ZP (mV) | EE Ascorbic Acid (%) | EE Tocopherol (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liposomes | 100 ± 11 | 0.16 | −44 ± 3 | 82 ± 9 | 10 ± 8 |
| Nutriosomes | 111 ± 8 | 0.07 | −42 ± 3 | 74 ± 5 | 12 ± 6 |
| EU-nutriosomes | 114 ± 14 | 0.10 | −46 ± 4 | 76 ± 6 | 13 ± 9 |
| Sample | Time | pH 1.2 | pH 7.0 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (nm ± SD) | PI | ZP (mV ± SD) | Size (nm ± SD) | PI | ZP (mV ± SD) | ||
| Liposomes | t0 | 210 ± 22 | 0.37 | +11 ± 2 | 123 ± 16 | 0.17 | +6 ± 2 |
| t2/6h | 265 ± 24 | 0.50 | +12 ± 2 | 141 ± 16 | 0.23 | +7 ± 2 | |
| Nutriosomes | t0 | 206 ± 40 | 0.22 | +11 ± 3 | 106 ± 8 | 0.11 | +8 ± 3 |
| t2/6h | 363 ± 38 | 0.55 | +12 ± 3 | 112 ± 7 | 0.09 | +7 ± 3 | |
| EU-nutriosomes | t0 | 153 ± 13 | 0.17 | +6 ± 1 | 109 ± 9 | 0.10 | +7 ± 2 |
| t2/6h | 141 ± 16 | 0.23 | +7 ± 1 | 116 ± 11 | 0.11 | +6 ± 2 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rezvani, M.; Manca, M.L.; Caddeo, C.; Escribano-Ferrer, E.; Carbone, C.; Peris, J.E.; Usach, I.; Diez-Sales, O.; Fadda, A.M.; Manconi, M. Co-Loading of Ascorbic Acid and Tocopherol in Eudragit-Nutriosomes to Counteract Intestinal Oxidative Stress. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11010013
Rezvani M, Manca ML, Caddeo C, Escribano-Ferrer E, Carbone C, Peris JE, Usach I, Diez-Sales O, Fadda AM, Manconi M. Co-Loading of Ascorbic Acid and Tocopherol in Eudragit-Nutriosomes to Counteract Intestinal Oxidative Stress. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleRezvani, Maryam, Maria Letizia Manca, Carla Caddeo, Elvira Escribano-Ferrer, Claudia Carbone, José Esteban Peris, Iris Usach, Octavio Diez-Sales, Anna Maria Fadda, and Maria Manconi. 2019. "Co-Loading of Ascorbic Acid and Tocopherol in Eudragit-Nutriosomes to Counteract Intestinal Oxidative Stress" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11010013
APA StyleRezvani, M., Manca, M. L., Caddeo, C., Escribano-Ferrer, E., Carbone, C., Peris, J. E., Usach, I., Diez-Sales, O., Fadda, A. M., & Manconi, M. (2019). Co-Loading of Ascorbic Acid and Tocopherol in Eudragit-Nutriosomes to Counteract Intestinal Oxidative Stress. Pharmaceutics, 11(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11010013









