Carbamazepine Gel Formulation as a Sustained Release Epilepsy Medication for Pediatric Use
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
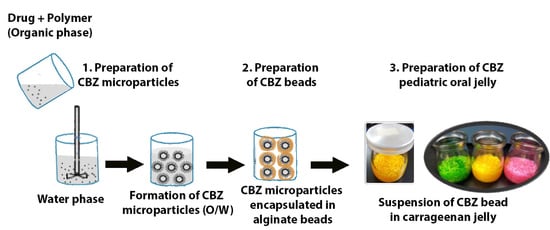
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of CBZ-Loaded Microparticles
2.3. Encapsulation of CBZ-Loaded Microparticles in Alginate Beads
2.4. Loading of CBZ Alginate Beads in a Gel Vehicle
2.5. Characterization of CBZ Oral Gel
2.5.1. Physical Appearance and Syneresis
2.5.2. Homogeneity
2.5.3. Rheology
2.6. In Vitro Drug Release
2.7. Stability Study
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. CBZ-Loaded Microparticles
3.2. CBZ-Loaded Microparticles in Alginate Beads
3.3. CBZ Oral Gel
3.3.1. Physical Appearance and Syneresis
3.3.2. Homogeneity
3.3.3. Rheology
3.4. In Vitro Drug Release
3.5. Stability Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zajicek, A.; Fossler, M.J.; Barrett, J.S.; Worthington, J.H.; Ternik, R.; Charkoftaki, G.; Lum, S.; Breitkreutz, J.; Baltezor, M.; Macheras, P. A report from the pediatric formulations task force: Perspectives on the state of child-friendly oral dosage forms. AAPS J. 2013, 15, 1072–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standing, J.F.; Tuleu, C. Paediatric formulations—Getting to the heart of the problem. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 300, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiele, J.T.; Quinzler, R.; Klimm, H.-D.; Pruszydlo, M.G.; Haefeli, W.E. Difficulties swallowing solid oral dosage forms in a general practice population: Prevalence, causes, and relationship to dosage forms. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 69, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. ICH E11 (R1) Guideline on Clinical Investigation of Medicinal Products in the Pediatric Population; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nunn, T. Age Appropriate Formulations—Paediatric Needs; National Institute for Health Research: Southampton, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nunn, T.; Williams, J. Formulation of medicines for children. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 59, 674–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolters Kluwer Health, A.S.O. H.-S.P. Cerner Multum and Micromedex from Truven Health Carbamazepine. Available online: https://www.drugs.com/cdi/carbamazepine.html (accessed on 8 September 2018).
- Yuan, H.G.; Kalfas, G.; Ray, W.H. Suspension polymerization. J. Macromol. Sci. Part C Polym. Rev. 1991, 31, 215–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costenbader, V.; Markson, S. School suspension: A study with secondary school students. J. Sch. Psychol. 1998, 36, 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomer, D.; Dupuis, L.; MacGregor, D.; Soldin, S. Palatability and relative bioavailability of an extemporaneous carbamazepine oral suspension. Clin. Pharm. 1987, 6, 646–649. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, D.; Mycek, J.; Harvey, R.; Champe, P. Lippincott’s illustrated reviews: Pharmacology. Philadelphia 2006, 3, 413–415. [Google Scholar]
- Magalhães, J.; Rodrigues, A.T.; Roque, F.; Figueiras, A.; Falcão, A.; Herdeiro, M.T. Use of off-label and unlicenced drugs in hospitalised paediatric patients: A systematic review. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernest, T.B.; Elder, D.P.; Martini, L.G.; Roberts, M.; Ford, J.L. Developing paediatric medicines: Identifying the needs and recognizing the challenges. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, V.; Xu, X.; Barwe, S.P.; Yang, X.; Czymmek, K.; Waldman, S.A.; Mason, R.W.; Jia, X.; Rajasekaran, A.K. Dexamethasone-loaded block copolymer nanoparticles induce leukemia cell death and enhance therapeutic efficacy: A novel application in pediatric nanomedicine. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 10, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, M.F.; Yadavilli, S.; Sze, R.W.; Nazarian, J.; Fernandes, R. Manganese-containing Prussian blue nanoparticles for imaging of pediatric brain tumors. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 2581. [Google Scholar]
- Basha, R.; Sabnis, N.; Heym, K.; Bowman, W.P.; Lacko, A.G. Targeted nanoparticles for pediatric leukemia therapy. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, M.C.; Cheng, D.; Tarquinio, K.M.; Webster, T.J. Nanotechnology: Pediatric applications. Pediatr. Res. 2010, 67, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutschmann, A.; Schlagenhauf, A.; Leschnik, B.; Hoffmann, K.M.; Hauer, A.; Muntean, W. Increased procoagulant function of microparticles in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease: Role in increased thrombin generation. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 56, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chicella, M.; Branim, B.; Lee, K.R.; Phelps, S.J. Comparison of microparticle enzyme and fluorescence polarization immunoassays in pediatric patients not receiving digoxin. Ther. Drug Monit. 1998, 20, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayh, K.I.; Zahran, A.M.; El-Abaseri, T.B.; Mohamed, A.O.; El-Metwally, T.H. Hypoxia biomarkers, oxidative stress, and circulating microparticles in pediatric patients with thalassemia in Upper Egypt. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2014, 20, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertini, B.; Di Sabatino, M.; Melegari, C.; Passerini, N. Formulating SLMs as oral pulsatile system for potential delivery of melatonin to pediatric population. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 469, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, D.; Semsarilar, M.; Guthrie, J.T.; Perrier, S. Cellulose modification by polymer grafting: A review. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2046–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakemore, W.R.; Harpell, A.R. Carrageenan. In Food Stabilisers, Thickeners and Gelling Agents; Blackwell Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 73–94. [Google Scholar]
- Sosnik, A. Alginate Particles as Platform for Drug Delivery by the Oral Route: State-of-the-Art. ISRN Pharm. 2014, 2014, 926157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, K.; Satyanarayana, V.; Nagiat, H.; Fathi, A.; Shanta, A.; Prameela, A. Formulation development and evaluation of novel oral jellies of carbamazepine using pectin, guar gum, and gellan gum. Asian J. Pharm. 2014, 8, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, K. Alendronate sodium hydrate (oral jelly) for the treatment of osteoporosis: Review of a novel, easy to swallow formulation. Clin. Interv. Aging 2013, 8, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, S.; Takahashi, A.; Itoh, K.; Ishitani, M.; Dairaku, M.; Togashi, M.; Mikami, R.; Attwood, D. Preparation and evaluation of gel formulations for oral sustained delivery to dysphagic patients. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2009, 35, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satyanarayana, A.D.; Kulkarni, K.P.; Shivakumar, G.H. Gels and jellies as a dosage form for dysphagia patients: A review. Curr. Drug Ther. 2011, 6, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosca, I.D.; Watari, F.; Uo, M. Microparticle formation and its mechanism in single and double emulsion solvent evaporation. J. Control. Release 2004, 99, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Young, T.J.; Sarkari, M.; Williams, R.O., III; Johnston, K.P. Preparation of cyclosporine A nanoparticles by evaporative precipitation into aqueous solution. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 242, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, D.; Barker, S.; Banning, D.; Booth, S. An investigation into the mechanisms of self-emulsification using particle size analysis and low frequency dielectric spectroscopy. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 114, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, N.; Shinzato, R.; Kiyokawa, M.; Kaneuchi, M.; Sugawara, M.; Kohri, N. Development of acetylcysteine jelly for the prevention of radiocontrast-induced reductions in renal function and its evaluation. Jpn. J. Pharm. Health Care Sci. 2005, 31, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, B.E. Alginates as biomaterials in tissue engineering. In Carbohydrate Chemistry: Chemical and Biological Approaches; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2011; Volume 37, pp. 227–258. [Google Scholar]
- Brinker, C.J.; Scherer, G.W. Sol-Gel Science: The Physics and Chemistry of Sol-Gel Processing; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Garud, N.; Garud, A. Preparation and in-vitro evaluation of metformin microspheres using non-aqueous solvent evaporation technique. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2012, 11, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, A.; Hanawa, T.; Sugihara, M. Application of glycerogelatin as oral dosage form for the elderly. J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Jpn. 1994, 54, 77. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, V.P.; Tsong, Y.; Sathe, P.; Liu, J.-P. In vitro dissolution profile comparison—Statistics and analysis of the similarity factor, f2. Pharm. Res. 1998, 15, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-P.; Ma, M.-C.; Chow, S.-C. Statistical evaluation of similarity factor f2 as a criterion for assessment of similarity between dissolution profiles. Drug Inf. J. 1997, 31, 1255–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocaña, J.; Frutos, G.; Sánchez, P. Using the similarity factor f2 in practice: A critical revision and suggestions for its standard error estimation. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2009, 99, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawazi, S.M.; Hadi, H.A.B.; Al-Mahmood, S.M.A.; Doolaanea, A. Development and Validation of UV-VIS Spectroscopic Method of Assay of Carbamazepine in Microparticles. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2019, 11, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.-S.; Lim, T.-K.; Voo, W.-P.; Pogaku, R.; Tey, B.T.; Zhang, Z. Effect of formulation of alginate beads on their mechanical behavior and stiffness. Particuology 2011, 9, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Pinnamaraju, P.; Ali, M.A. Water Insoluble Polymer Based Sustained Release Formulation. U.S. Patent 6251430B1, 26 June 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Follonier, N.; Doelker, E.; Cole, E.T. Evaluation of hot-melt extrusion as a new technique for the production of polymer-based pellets for sustained release capsules containing high loadings of freely soluble drugs. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1994, 20, 1323–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Zheng, Z.-B.; Yu, D.-G.; Liu, X.-K.; Qu, Y.-L.; Li, H.-L. Electrosprayed sperical ethylcellulose nanoparticles for an improved sustained-release profile of anticancer drug. Cellulose 2017, 24, 5551–5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, P.; Mishra, S.C.; Sahoo, S.; Behera, A.; Nayak, B.P. Development and characterization of ethylcellulose based microsphere for sustained release of nifedipine. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulvi, F.A.; Soni, T.G.; Shah, D.O. Extended release of timolol from ethyl cellulose microparticles laden hydrogel contact lenses. Open Pharm. Sci. J. 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoz Inc. Carbamazepine Extended-Release Tablets, USP; Sandoz Inc.: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 2917–2921. [Google Scholar]
- Gefter, J.; Zaks, B.; Kirmayer, D.; Lavy, E.; Steinberg, D.; Friedman, M. Chlorhexidine sustained-release varnishes for catheter coating–Dissolution kinetics and antibiofilm properties. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 112, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T. Mechanism of sustained-action medication. Theoretical analysis of rate of release of solid drugs dispersed in solid matrices. J. Pharm. Sci. 1963, 52, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Adibkia, K.; Valizadeh, H.; Shadbad, M.R.S.; Nokhodchi, A.; Omidi, Y.; Mohammadi, G.; Nezhadi, S.H.; Hasan, M. Kinetic analysis of drug release from nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 11, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BeMiller, J. Carrageenans, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; p. 12. [Google Scholar]




| Sample Location | Beads to Gel Ratio | CBZ Assay (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Up | (1:1) | 100.9 ± 1.3 |
| Middle | (1:1) | 99.9 ± 1.1 |
| Bottom | (1:1) | 99.2 ± 1.9 |
| Up | (1:2) | 65.4 ± 2.4 |
| Middle | (1:2) | 96.5 ± 3.3 |
| Bottom | (1:2) | 138.0 ± 4.5 |
| Model | R2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBZ Microparticles | CBZ Beads | CBZ Gel | CBZ Tablets (Tegretol®-XR) | |
| Zero Order | 0.7190 | 0.8828 | 0.8143 | 0.8601 |
| First Order | 0.8555 | 0.9968 | 0.9759 | 0.9301 |
| Higuchi | 0.9222 | 0.9842 | 0.9482 | 0.9591 |
| Korsmeyer Peppas | 0.6973 | 0.7677 | 0.8121 | 0.8457 |
| Hixson Crowell | 0.8116 | 0.9760 | 0.9527 | 0.9748 |
| Test | Initial (0) Days | 7 Days | 15 Days | 30 Days |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real Time Conditions (30 ± 2 °C/70 ± 5% RH) | ||||
| Appearance | Transparent with embedded white beads | No change | No change | No change |
| Syneresis | No | No | No | No |
| pH | 5.7 ± 0.0 | 5.4 ± 0.1 | 5.1 ± 0.0 | 4.5 ± 0.5 |
| Viscosity (mPa.s) | 644 ± 271 | 552 ± 239 | 676 ± 173 | 899 ± 208 |
| Accelerated Conditions (40 ± 2 °C/70 ± 5% RH) | ||||
| Appearance | Transparent with embedded white beads | No change | No change | No change |
| Syneresis | No | No | No | No |
| pH | 5.8 ± 0.1 | 5.4 ± 0.0 | 4.6 ± 0.1 | 5.0 ± 1.8 |
| Viscosity (mPa.s) | 357 ± 37 | 325 ± 5 | 253 ± 92 | 180 ± 22 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mawazi, S.M.; Al-Mahmood, S.M.A.; Chatterjee, B.; Hadi, H.A.; Doolaanea, A.A. Carbamazepine Gel Formulation as a Sustained Release Epilepsy Medication for Pediatric Use. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11100488
Mawazi SM, Al-Mahmood SMA, Chatterjee B, Hadi HA, Doolaanea AA. Carbamazepine Gel Formulation as a Sustained Release Epilepsy Medication for Pediatric Use. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(10):488. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11100488
Chicago/Turabian StyleMawazi, Saeid Mezail, Sinan Mohammed Abdullah Al-Mahmood, Bappaditya Chatterjee, Hazrina AB. Hadi, and Abd Almonem Doolaanea. 2019. "Carbamazepine Gel Formulation as a Sustained Release Epilepsy Medication for Pediatric Use" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 10: 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11100488
APA StyleMawazi, S. M., Al-Mahmood, S. M. A., Chatterjee, B., Hadi, H. A., & Doolaanea, A. A. (2019). Carbamazepine Gel Formulation as a Sustained Release Epilepsy Medication for Pediatric Use. Pharmaceutics, 11(10), 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11100488