Preparation, Characterization, and In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study of the Supercritical Fluid-Processed Liposomal Amphotericin B
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography of AmB
2.3. Solubility and Stability of AmB in Organic Solvents
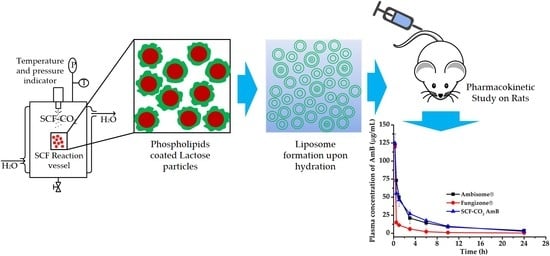
2.4. Preparation of Liposomal AmB by the SCF-CO2 Method
2.5. Preparation of Liposomal AmB by the Conventional Method
2.6. Lyophilization of Liposomal AmB
2.7. Characterization of Liposomal AmB
2.7.1. Determination of Particle Size, PDI, and Zeta Potential of Liposomal AmB
2.7.2. Encapsulation Efficiency Measurement
2.7.3. Small X-ray Scattering
2.7.4. Freeze-Fracture Electron Microscopy
2.7.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.8. Stability Study
2.9. Hemolysis Test from Rat Erythrocytes (RBCs)
2.10. In Vivo Study
2.10.1. Pharmacokinetic Study in Sprague-Dawley Rats
2.10.2. Determination of Plasma AmB
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Screening of Organic Solvent Systems
3.2. Optimization of the Preparation Process for Liposomal AmB
3.2.1. Effect of Organic Solvents on the Preparation of Liposomal AmB
3.2.2. Effect of Temperature and Pressure on the SCF-CO2 Process
3.2.3. Effect of Lipid Concentration on the EE of Liposomes
3.3. Lamellarity of Liposomes
3.4. Morphology of Liposomes
3.4.1. Freeze-Fracture Electron Microscopy
3.4.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy
3.5. Effect of Lyophilization on Liposomal AmB
3.6. Stability of Liposomal AmB
3.7. Hemolysis Properties
3.8. In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study
4. Discussion
4.1. Screening of Organic Solvent Systems
4.2. Optimization of the Preparation Process for Liposomal AmB
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Serrano, D.R.; Hernandez, L.; Fleire, L.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, I.; Montoya, A.; Ballesteros, M.P.; Dea-Ayuela, M.A.; Miro, G.; Bolas-Fernandez, F.; Torrado, J.J. Hemolytic and pharmacokinetic studies of liposomal and particulate amphotericin B formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 447, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Garcia, R.; de Pablo, E.; Ballesteros, M.P.; Serrano, D.R. Unmet clinical needs in the treatment of systemic fungal infections: The role of amphotericin B and drug targeting. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 525, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilley, J.C. Clinical efficacy of amphotericin B lotion in the treatment of various cutaneous monilial infections. J. La. State Med. Soc. Off. Organ La. State Med. Soc. 1962, 114, 433–435. [Google Scholar]
- Eldem, T.; Arican-Cellat, N.; Agabeyoglu, I.; Akova, M.; Kansu, E. Pharmacokinetics of liposomal amphotericin B in neutropenic cancer patients. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 213, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iman, M.; Huang, Z.; Szoka, F.C., Jr.; Jaafari, M.R. Characterization of the colloidal properties, in vitro antifungal activity, antileishmanial activity and toxicity in mice of a distigmasterylhemisuccinoyl-glycero-phosphocholine liposome-intercalated amphotericin B. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 408, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mehenni, L.; Lahiani-Skiba, M.; Ladam, G.; Hallouard, F.; Skiba, M. Preparation and Characterization of Spherical Amorphous Solid Dispersion with Amphotericin B. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrado, J.J.; Espada, R.; Ballesteros, M.P.; Torrado-Santiago, S. Amphotericin B Formulations and Drug Targeting. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2405–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italia, J.; Yahya, M.; Singh, D.; Kumar, M.R. Biodegradable nanoparticles improve oral bioavailability of amphotericin B and show reduced nephrotoxicity compared to intravenous Fungizone®. Pharma. Res. 2009, 26, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debouzy, J.C.; Mehenni, L.; Crouzier, D.; Lahiani-Skiba, M.; Nugue, G.; Skiba, M. NMR and ESR study of amphotericin B interactions with various binary phosphatidylcholine/phosphatidylglycerol membranes. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 521, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Berestein, G.; Hopfer, R.L.; Mehta, R.; Mehta, K.; Hersh, E.M.; Juliano, R.L. Liposome-encapsulated amphotericin B for treatment of disseminated candidiasis in neutropenic mice. J. Infect. Dis. 1984, 150, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Jiang, W.; Lionberger, R.; Lawrence, X.Y. Bioequivalence for Liposomal Drug Products. In FDA Bioequivalence Standards; Yu, L.X., Li, B., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 13, pp. 275–296. [Google Scholar]
- Barratt, G.; Bretagne, S. Optimizing efficacy of Amphotericin B through nanomodification. Int. J. Nanomed. 2007, 2, 301. [Google Scholar]
- Karn, P.R.; Cho, W.; Hwang, S.J. Liposomal drug products and recent advances in the synthesis of supercritical fluid-mediated liposomes. Nanomedicine (London) 2013, 8, 1529–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler-Moore, J.; Proffitt, R.T. AmBisome: Lipsomal formulation, structure, mechanism of action and pre-clinical experience. J. Antimicrob. Ther. 2002, 49, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.S. Amphotericin B colloidal dispersion: An improved antifungal therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 47, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.F.; Nahata, M.C. A comparative review of conventional and lipid formulations of amphotericin B. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 1999, 24, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamill, R.J. Amphotericin B formulations: A comparative review of efficacy and toxicity. Drugs 2013, 73, 919–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moen, M.D.; Lyseng-Williamson, K.A.; Scott, L.J. Liposomal amphotericin B: A review of its use as empirical therapy in febrile neutropenia and in the treatment of invasive fungal infections. Drugs 2009, 69, 361–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivnay, B.; Wakim, J.; Avery, K.; Petrochenko, P.; Myung, J.H.; Kozak, D.; Yoon, S.; Landrau, N.; Nivorozhkin, A. Critical process parameters in manufacturing of liposomal formulations of amphotericin B. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 565, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzar, S.M.; Hyun, S.M.; Kim, J.H.; Park, H.J.; Kim, M.S.; Park, J.S.; Hwang, S.J. Enhancing the solubility and bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs using supercritical antisolvent (SAS) process. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 538, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karn, P.R.; Kim, H.D.; Kang, H.; Sun, B.K.; Jin, S.E.; Hwang, S.J. Supercritical fluid-mediated liposomes containing cyclosporin A for the treatment of dry eye syndrome in a rabbit model: Comparative study with the conventional cyclosporin A emulsion. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 3791–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karn, P.R.; Cho, W.; Park, H.-J.; Park, J.-S.; Hwang, S.-J. Characterization and stability studies of a novel liposomal cyclosporin A prepared using the supercritical fluid method: Comparison with the modified conventional Bangham method. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 365. [Google Scholar]
- Karn, P.R.; Jin, S.E.; Lee, B.J.; Sun, B.K.; Kim, M.S.; Sung, J.H.; Hwang, S.J. Preparation and evaluation of cyclosporin A-containing proliposomes: A comparison of the supercritical antisolvent process with the conventional film method. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 5079–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadimi, U.S.; Balasubramanian, D.R.; Ganni, U.R.; Balaraman, M.; Govindarajulu, V. In vitro studies on liposomal amphotericin B obtained by supercritical carbon dioxide–mediated process. Nanomedicine 2007, 3, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Srinivasan, S.; Yuan, W.M.; Ming, R.; Liu, Y.Y.; Dai, Z.P.; Noble, C.O.; Hayes, M.E.; Zheng, N.; Jiang, W.L.; et al. Development of a flow-through USP 4 apparatus drug release assay for the evaluation of amphotericin B liposome. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 134, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.-J.; Park, H.J.; et al. Methods and apparatus for preparing novel liposome. European Patent Office EP2538921A2, 24 February 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.M.; Costa, A.; Burgess, D.J. Protein Encapsulation in Unilamellar Liposomes: High Encapsulation Efficiency and A Novel Technique to Assess Lipid-Protein Interaction. Pharm. Res. Dordr. 2012, 29, 1919–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarfraz, M.; Afzal, A.; Yang, T.; Gai, Y.K.; Raza, S.M.; Khan, M.W.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, X.; Xiang, G.Y. Development of Dual Drug Loaded Nanosized Liposomal Formulation by A Reengineered Ethanolic Injection Method and Its Pre-Clinical Pharmacokinetic Studies. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otake, K.; Imura, T.; Sakai, H.; Abe, M. Development of a new preparation method of liposomes using supercritical carbon dioxide. Langmuir 2001, 17, 3898–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otake, K.; Shimomura, T.; Goto, T.; Imura, T.; Furuya, T.; Yoda, S.; Takebayashi, Y.; Sakai, H.; Abe, M. Preparation of liposomes using an improved supercritical reverse phase evaporation method. Langmuir 2006, 22, 2543–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Tian, Z.F.; Zhao, X.T.; Li, N.; Garamus, V.M.; Yin, P.H.; Zou, A.H. Dual-modified bufalin loaded liposomes for enhanced tumor targeting. Colloid Surf. A 2019, 571, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Minh, L.V.; Liu, J.W.; Angelov, B.; Drechsler, M.; Garamus, V.M.; Willumeit-Roemer, R.; Zou, A.H. Baicalin loaded in folate-PEG modified liposomes for enhanced stability and tumor targeting. Colloid Surf. B 2016, 140, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Peng, L.; Liao, G.; Chen, Z.; Li, C. Noncovalent Complexation of Amphotericin B with Poly(beta-Amino Ester) Derivates for Treatment of C. Neoformans Infection. Polymers (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, A.; Fiorello, C.V.; Baden, R.M.; Liu, J.H.; Burmas, N.C.; Ruvalcaba, C.A.; Monroy, R.; Mohr, F.C.; Gehring, R.; Delplanque, J.P.; et al. Amphotericin B concentrations in healthy mallard ducks (Anas platyrhynchos) following a single intratracheal dose of liposomal amphotericin B using an atomizer. Med. Mycol. 2018, 56, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, F.A.; Beggs, W.H.; Sarosi, G.A. Influence of antioxidants on the bioactivity of amphotericin B. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1977, 11, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espuelas, M.; Legrand, P.; Irache, J.; Gamazo, C.; Orecchioni, A.; Devissaguet, J.-P.; Ygartua, P. Poly (ε-caprolacton) nanospheres as an alternative way to reduce amphotericin B toxicity. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 158, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverchon, E.; De Marco, I.; Torino, E. Nanoparticles production by supercritical antisolvent precipitation: A general interpretation. J. Supercrit. Flu. 2007, 43, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, W. Adsorption and diffusion of supercritical carbon dioxide in slit pores. Langmuir 2000, 16, 8063–8070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, T.T.H.; Dan, L.; Duc, L.; Tung, B.T.; Hue, P.T.M. Preparation and Characterization of Freeze-dried Liposomes Loaded with Amphotericin B. Curr. Drug Ther. 2019, 14, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleman, A.; Marin, D.; Taladrid, D.; Montero, P.; Gomez-Guillen, M.C. Encapsulation of antioxidant sea fennel (Crithmum maritimum) aqueous and ethanolic extracts in freeze-dried soy phosphatidylcholine liposomes. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bothun, G.D.; Knutson, B.L.; Strobel, H.J.; Nokes, S.E. Liposome fluidization and melting point depression by pressurized CO2 determined by fluorescence anisotropy. Langmuir 2005, 21, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Grainger, D.W. Lyophilized liposome-based parenteral drug development: Reviewing complex product design strategies and current regulatory environments. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moribe, K.; Maruyama, K.; Iwatsuru, M. Molecular localization and state of amphotericin B in PEG liposomes. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 193, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, H.; Koike, T.; Saheki, A.; Sonoke, S.; Tomii, Y.; Seki, J. Evaluation of the efficacy and toxicity of amphotericin B incorporated in lipid nano-sphere (LNS®). Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 263, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Organic Solvent Systems | kobs (hr−1) | t1/2 (h) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| DMSO | 0.1244 | 5.57 | 0.888 |
| DMSO-vit C | 0.0594 | 11.66 | 0.746 |
| DMSO-HCl | 5.5074 | 0.13 | 0.874 |
| DMA-vit C | 0.2808 | 2.47 | 0.986 |
| DMA-HCl | 2.4844 | 0.28 | 0.97 |
| DMF-vit C | 0.2949 | 2.35 | 0.891 |
| DMF-HCl | 15.5025 | 0.04 | 0.981 |
| MeOH + CHCl3-vit C | Not Done | Not Done | Not Done |
| MeOH + CHCl3-HCl | 2.2989 | 0.30 | 0.953 |
| Organic Solvents | Size (nm) | PDI | EE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DMSO | 771 ± 89 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | 81.2 ± 2.2 |
| DMSO-vit C | 833 ± 78 | 0.22 ± 0.02 | 82.0 ± 1.9 |
| DMA-vit C | 849 ± 108 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | 91.5 ± 2.3 |
| DMF-vit C | 1109 ± 112 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 90.2 ± 3.0 |
| MeOH + CHCl3-HCl | 692 ± 62 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 35.8 ± 5.2 |
| Temp. (°C) | Pressure (MPa) | Mean Diameter (nm) | PDI a | EE (%) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35 | 20 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 45 | 10 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 45 | 15 | 761.0 ± 56.5 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 91.7 ± 4.2 |
| 45 | 20 | 949.3 ± 84.4 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 90.5 ± 5.7 |
| 45 | 25 | 855.7 ± 76.2 | 0.25 ± 0.02 | 84.2 ± 2.9 |
| 45 | 30 | 821.3 ± 69.2 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | 79.7 ± 5.5 |
| 55 | 20 | 801.6 ± 74.9 | 0.20 ± 0.02 | 86.3 ± 4.5 |
| 65 | 20 | 839.1 ± 81.7 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 77.1 ± 4.2 |
| Condition | Size (nm) | ZP (mV) | Yield (%) | EE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before LP | 137.3 ± 7.3 | −42.5 ± 1.0 | 91.6 ± 1.2 | 89.2 ± 1.8 |
| After LP | 146.8 ± 2.2 | −43.6 ± 1.7 | 90.2 ± 1.0 | 88.9 ± 2.2 |
| Parameters | Groups | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| AmBisome® | SCF-CO2 Liposomal AmB | Fungizone® | |
| C(0.25 h) (µg/mL) | 122.28 ± 15.60 | 124.83 ± 12.41 | 119.61 ± 0.76 |
| AUC(0–24 h) (µg·h/mL) | 316.79 ± 60.46 | 325.64 ± 32.76 | 76.10 ± 1.56 |
| AUC(0–∞) (µg·h/mL) | 369.45 ± 60.06 | 349.81 ± 28.50 | 79.66 ± 2.74 |
| t1/2 (h) | 9.76 ± 1.74 | 6.25 ± 0.50 | 6.98 ± 1.50 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, C.-b.; Abuzar, S.M.; Karn, P.R.; Cho, W.; Park, H.J.; Cho, C.-W.; Hwang, S.-J. Preparation, Characterization, and In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study of the Supercritical Fluid-Processed Liposomal Amphotericin B. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110589
Lim C-b, Abuzar SM, Karn PR, Cho W, Park HJ, Cho C-W, Hwang S-J. Preparation, Characterization, and In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study of the Supercritical Fluid-Processed Liposomal Amphotericin B. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(11):589. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110589
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Chang-baek, Sharif Md Abuzar, Pankaj Ranjan Karn, Wonkyung Cho, Hee Jun Park, Cheong-Weon Cho, and Sung-Joo Hwang. 2019. "Preparation, Characterization, and In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study of the Supercritical Fluid-Processed Liposomal Amphotericin B" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 11: 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110589
APA StyleLim, C.-b., Abuzar, S. M., Karn, P. R., Cho, W., Park, H. J., Cho, C.-W., & Hwang, S.-J. (2019). Preparation, Characterization, and In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study of the Supercritical Fluid-Processed Liposomal Amphotericin B. Pharmaceutics, 11(11), 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110589