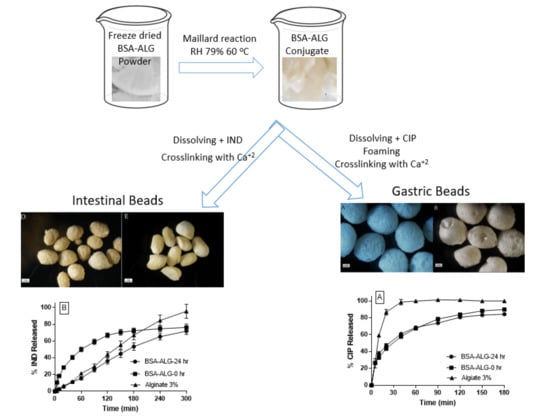
Potential Use of the Maillard Reaction for Pharmaceutical Applications: Gastric and Intestinal Controlled Release Alginate-Albumin Beads
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- -
- SGM: 0.1M hydrochloric acid (pH 1.2).
- -
- SIM: 2.4g HEPES and 8.5g NaCl were dissolved in 1 L distilled water to obtain concentrations of 9.2 mM and 150 mM respectively. The pH was then adjusted to 6.5 using diluted HCl or NaOH solutions as required.
2.2. Preparation of Bovine Serum Albumin-Alginate (BSA-ALG) Conjugates
2.3. Characterization of BSA-ALG Conjugates
2.3.1. Ultraviolet (UV) Absorbance Measurement
2.3.2. Free Amino Group Determination
2.3.3. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.3.4. Rheological Analysis
2.3.5. Foamability and Foam Stability Measurement
2.4. Beads Preparation, Characterization and Drug Release Studies
2.4.1. Floating Gastro-Retentive Beads Preparation
2.4.2. Intestinal Beads Preparation
2.4.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4.4. Drug Release Study
2.4.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterisation of ALG-BSA Conjugates
3.2. Beads Preparation, Characterization and Drug Release Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hodge, J.E. Dehydrated foods, chemistry of browning reactions in model systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1953, 1, 928–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljahdali, N.; Carbonero, F. Impact of Maillard reaction products on nutrition and health: Current knowledge and need to understand their fate in the human digestive system. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamanna, N.; Mahmood, N. Food Processing and Maillard Reaction Products: Effect on Human Health and Nutrition. Int. J. Food Sci. 2015, 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hakkak, J.; Al-Hakkak, F. Functional egg white–pectin conjugates prepared by controlled Maillard reaction. J. Food Eng. 2010, 100, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hakkak, J.; Kavale, S. Improvement of emulsification properties of sodium caseinate by conjugating to pectin through the Maillard reaction. Int. Congr. Ser. 2002, 1245, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, C.M.; Melton, L.D.; Stanley, R.A. Creating Proteins with Novel Functionality via the Maillard Reaction: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2006, 46, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, E.; Zhao, Y. Preparation, characterization and toxicology properties of α- and β-chitosan Maillard reaction products nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 89, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelman, R.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Levitzky, I.; Shahar, T.; Livney, Y.D. Hyaluronic acid-serum albumin conjugate-based nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 24337–24353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xue, J.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, M.; Chang, C.; Luo, Y. Synthetic surfactant- and cross-linker-free preparation of highly stable lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles as potential oral delivery vehicles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yao, P. Self-Assembly of Ibuprofen and Bovine Serum Albumin−Dextran Conjugates Leading to Effective Loading of the Drug. Langmuir 2009, 25, 6385–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.G. The Need for Drugs and Drug Delivery Systems. In Fundamentals and Applications of Controlled Release Drug Delivery; Siepmann, J., Siegel, R.A., Rathbone, M.J., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead, L.; Fell, J.T.; Collett, J.H.; Sharma, H.L.; Smith, A.M. Floating dosage forms: An in vivo study demonstrating prolonged gastric retention. J. Control. Release 1998, 55, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Dalaty, A.; Karam, A.; Najlah, M.; Alany, R.G.; Khoder, M. Effect of non-cross-linked calcium on characteristics, swelling behaviour, drug release and mucoadhesiveness of calcium alginate beads. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 140, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangsansarid, J.; Cheetangdee, N.; Kinoshita, N.; Fukuda, K. Bovine Serum Albumin-Sugar Conjugates through the Maillard Reaction: Effects on Interfacial Behavior and Emulsifying Ability. J. Oleo Sci. 2008, 57, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Admassu, H.; Zhao, W.; Yang, R.; Gasmalla, M.A.A.; Alsir, E.L. Stabilizing Food Emulsions By Protein—Polysaccharide Conjugates Of Maillard Reaction-A Review. Int. J. Technol. Enhanc. Emerg. Eng. Res. (IJTEEE) 2015, 3, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Pandit, J.K. Multi-Unit Floating Alginate System: Effect of Additives on Ciprofloxacin Release AU—Srinatha, A. Drug Deliv. 2008, 15, 471–476. [Google Scholar]
- Kamburova, K.; Mitarova, K.; Radeva, T. Polysaccharide-based nanocapsules for controlled release of indomethacin. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 519, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Tong, Z. Deposition temperature effect on release rate of indomethacin microcrystals from microcapsules of layer-by-layer assembled chitosan and alginate multilayer films. J. Control. Release 2005, 106, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hayakawa, S.; Izumori, K. Modification of Ovalbumin with a Rare Ketohexose through the Maillard Reaction: Effect on Protein Structure and Gel Properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeeb, A.F.S.A. Determination of free amino groups in proteins by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. Anal. Biochem. 1966, 14, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Yao, H.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, L. Preparation and evaluation of a novel gastric floating alginate/poloxamer inner-porous beads using foam solution. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 422, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierenga, P.A.; van Norél, L.; Basheva, E.S. Reconsidering the importance of interfacial properties in foam stability. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 344, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoder, M.; Tsapis, N.; Huguet, H.; Besnard, M.; Gueutin, C.; Fattal, E. Removal of ciprofloxacin in simulated digestive media by activated charcoal entrapped within zinc-pectinate beads. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 379, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoder, M.; Abdelkader, H.; ElShaer, A.; Karam, A.; Najlah, M.; Alany, R.G. The use of albumin solid dispersion to enhance the solubility of unionizable drugs AU—Khoder, Mouhamad. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2018, 23, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.J.; Kim, H.J.; Park, K.H.; Moon, T.W. Molecular characteristics of ovalbumin–dextran conjugates formed through the Maillard reaction. Food Chem. 2005, 92, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, C.M.; Melton, L.D.; Stanley, R.A. Functional properties of caseinate glycoconjugates prepared by controlled heating in the ‘dry’ state. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeidat, W.M.; Price, J.C. Viscosity of polymer solution phase and other factors controlling the dissolution of theophylline microspheres prepared by the emulsion solvent evaporation method. J. Microencapsul. 2003, 20, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.F.; Patel, N.M. Statistical evaluation of influence of viscosity and content of polymer on dipyridamole release from floating matrix tablets: A technical note. AAPS PharmSciTech 2007, 8, E140–E144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoder, M.; Tsapis, N.; Fattal, E. Mechanisms of antibiotic resitance and delivery strategies to prevent its emergence. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2010, 20, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoder, M.; Tsapis, N.; Domergue-Dupont, V.; Gueutin, C.; Fattal, E. Removal of residual colonic ciprofloxacin in the rat by activated charcoal entrapped within zinc-pectinate beads. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 41, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, O.N.; Burgess, D.J. Characterization of Albumin-Alginic Acid Complex Coacervation. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1989, 41, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffin, M.D.; Burke, M.D. Controlling Release by Gastroretention. In Controlled Release in Oral Drug Delivery; Wilson, C.G., Crowley, P.J., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 361–383. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.-K.; Lee, E.-J. The controlled release of blue dextran from alginate beads. Int. J. Pharm. 1992, 79, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Formulation | Floating Time in SGM |
|---|---|
| ALG 3% beads | <1 min |
| BSA-ALG-0 h beads | up to 48 h |
| BSA-ALG-24 h beads | up to 48 h |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khoder, M.; Gbormoi, H.K., Sr.; Ryan, A.; Karam, A.; Alany, R.G. Potential Use of the Maillard Reaction for Pharmaceutical Applications: Gastric and Intestinal Controlled Release Alginate-Albumin Beads. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11020083
Khoder M, Gbormoi HK Sr., Ryan A, Karam A, Alany RG. Potential Use of the Maillard Reaction for Pharmaceutical Applications: Gastric and Intestinal Controlled Release Alginate-Albumin Beads. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(2):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11020083
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhoder, Mouhamad, Henry K. Gbormoi, Sr., Ali Ryan, Ayman Karam, and Raid G. Alany. 2019. "Potential Use of the Maillard Reaction for Pharmaceutical Applications: Gastric and Intestinal Controlled Release Alginate-Albumin Beads" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 2: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11020083
APA StyleKhoder, M., Gbormoi, H. K., Sr., Ryan, A., Karam, A., & Alany, R. G. (2019). Potential Use of the Maillard Reaction for Pharmaceutical Applications: Gastric and Intestinal Controlled Release Alginate-Albumin Beads. Pharmaceutics, 11(2), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11020083