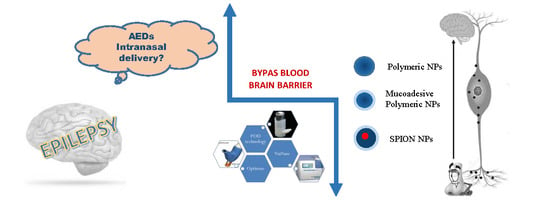
Epilepsy Disease and Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Polymeric Nanoparticles: An Overview
Abstract
Share and Cite
Musumeci, T.; Bonaccorso, A.; Puglisi, G. Epilepsy Disease and Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Polymeric Nanoparticles: An Overview. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11030118
Musumeci T, Bonaccorso A, Puglisi G. Epilepsy Disease and Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Polymeric Nanoparticles: An Overview. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(3):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11030118
Chicago/Turabian StyleMusumeci, Teresa, Angela Bonaccorso, and Giovanni Puglisi. 2019. "Epilepsy Disease and Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Polymeric Nanoparticles: An Overview" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 3: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11030118
APA StyleMusumeci, T., Bonaccorso, A., & Puglisi, G. (2019). Epilepsy Disease and Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Polymeric Nanoparticles: An Overview. Pharmaceutics, 11(3), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11030118