Effect of Cationic Lipid Type in Folate-PEG-Modified Cationic Liposomes on Folate Receptor-Mediated siRNA Transfection in Tumor Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Small Interfering RNAs
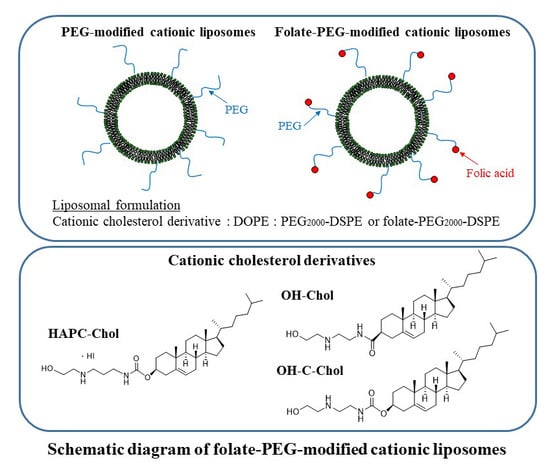
2.3. Preparation of Cationic Liposomes and siRNA Lipoplexes
2.4. Size and ζ-Potential of Cationic Liposomes and siRNA Lipoplexes
2.5. Cell Culture
2.6. Gene Silencing Effect by FA-PEG-Modified siRNA Lipoplexes in KB-Luc Cells
2.7. Gene Silencing Effect by FA-PEG-Modified siRNA Lipoplexes in KB-EGFP Cells
2.8. Cytotoxicity by FA-PEG-Modified siRNA Lipoplexes
2.9. Cellular Association with FA-PEG-Modified siRNA Lipoplexes
2.10. Gel Retardation Assay
2.11. Accessibility of siRNA in siRNA Lipoplexes
2.12. Antiproliferative Activity
2.13. Measurement of Expression Level of PLK1 mRNA
2.14. In Vivo Anti-Tumor Effect
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of FA-PEG-Modified Cationic Liposomes and siRNA Lipoplexes
3.2. Effect of Cationic Lipid of FA-PEG-Modified Cationic Liposomes on In Vitro Gene Knockdown Efficacy
3.3. Cytotoxicity by FA-PEG-Modified siRNA Lipoplexes
3.4. Association of FA-PEG-Modified siRNA Lipoplexes with Cells
3.5. Association of FA-PEG-Modified Cationic Liposomes with siRNA
3.6. Suppression of EGFP Expression by FA-PEG-Modified siRNA Lipoplexes
3.7. Antiproliferative Activity
3.8. In Vivo Gene Therapy in KB Tumor Xenografts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, R.C.; Doudna, J.A. Molecular mechanisms of RNA interference. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2013, 42, 217–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Trivedi, P.; Jain, N.K. Advances in siRNA delivery in cancer therapy. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, N.; Hamanaka, R.; Yoshimatsu, J.; Miyakawa, I. Polo-like kinases (PLKS) and cancer. Oncogene 2005, 24, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Sano, B.; Nagata, T.; Kato, H.; Sugiyama, Y.; Kunieda, K.; Kimura, M.; Okano, Y.; Saji, S. Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) is overexpressed in primary colorectal cancers. Cancer Sci. 2003, 94, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, Q.; Wang, X. PLK1, a potential target for cancer therapy. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 10, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mangala, L.S.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; Kong, X.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K. RNA interference-based therapy and its delivery systems. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, Z.; Wientjes, M.G.; Au, J.L. Delivery of siRNA therapeutics: Barriers and carriers. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhi, D.; Huang, L. Lipid-based vectors for siRNA delivery. J. Drug Target. 2012, 20, 724–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, B.; Sainlos, M.; Aissaoui, A.; Oudrhiri, N.; Hauchecorne, M.; Vigneron, J.P.; Lehn, J.M.; Lehn, P. The design of cationic lipids for gene delivery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 375–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.Y.; Guo, P.; Wen, W.C.; Wong, H.L. Lipid-based nanocarriers for RNA delivery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 3140–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariatti, M. Liposomal formulation of monovalent cholesteryl cytofectins with acyclic head groups and gene delivery: A systematic review. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2015, 16, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, Y.; Takeuchi, N.; Nakamura, M.; Yoshiike, Y.; Taguchi, M.; Ohno, H.; Ozaki, K.; Onishi, H. Effect of cationic lipid type in cationic liposomes for siRNA delivery into the liver by sequential injection of chondroitin sulfate and cationic lipoplex. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 48, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Takeuchi, N.; Tamaki, K.; Shimizu, S.; Yoshiike, Y.; Taguchi, M.; Ohno, H.; Ozaki, K.; Onishi, H. Effect of cationic lipid in cationic liposomes on siRNA delivery into the lung by intravenous injection of cationic lipoplex. J. Drug Target. 2019, 27, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, Y.; Hara, E.; Shingu, Y.; Minamiguchi, D.; Nakamura, A.; Arai, S.; Ohno, H.; Kawano, K.; Fujii, N.; Yonemochi, E. SiRNA delivery into tumor cells by cationic cholesterol derivative-based nanoparticles and liposomes. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasungu, L.; Hoekstra, D. Cationic lipids, lipoplexes and intracellular delivery of genes. J. Control. Release 2006, 116, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Huang, L. Development of non-viral vectors for systemic gene delivery. J. Control. Release 2002, 78, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, N.; Turk, M.J.; Westrick, E.; Lewis, J.D.; Low, P.S.; Leamon, C.P. Folate receptor expression in carcinomas and normal tissues determined by a quantitative radioligand binding assay. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 338, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, P.S.; Kularatne, S.A. Folate-targeted therapeutic and imaging agents for cancer. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2009, 13, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Low, P.S. Folate-targeted therapies for cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 6811–6824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, I.; Oliveira, C.N.; Sárria, M.P.; Neves Silva, J.P.; Goncalves, O.; Gomes, A.C.; Real Oliveira, M.E. Monoolein-based nanocarriers for enhanced folate receptor-mediated RNA delivery to cancer cells. J. Liposome Res. 2016, 26, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Wang, T.; Tang, R.; Wang, J.; Long, H.; Gao, X.; Tang, S. Silencing of the MYCN gene by siRNA delivered by folate receptor-targeted liposomes in LA-N-5 cells. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2010, 26, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, B.; Dong, D.W.; Shi, N.Q.; Gao, W.; Yang, Z.Z.; Cui, Y.; Cao, D.Y.; Qi, X.R. PSA-responsive and PSMA-mediated multifunctional liposomes for targeted therapy of prostate cancer. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 6976–6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Li, B.; Qi, S.; Liu, Y.; Gai, Y.; Ye, P.; Yang, G.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, P.; He, X.; et al. Co-delivery of doxorubicin and bmi1 siRNA by folate receptor targeted liposomes exhibits enhanced anti-tumor effects in vitro and in vivo. Theranostics 2014, 4, 1096–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, Y.; Kubo, H.; Higashiyama, K.; Maitani, Y. Folate-linked nanoparticles formed with DNA complexes in sodium chloride solution enhance transfection efficiency. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2005, 1, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.; Ishihara, M.; Kawaura, C.; Noji, M.; Furuno, T.; Nakanishi, M. Effect of zeta potential of cationic liposomes containing cationic cholesterol derivatives on gene transfection. FEBS Lett. 1996, 397, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, W.; Hattori, Y.; Higashiyama, K.; Maitani, Y. Hydroxyethylated cationic cholesterol derivatives in liposome vectors promote gene expression in the lung. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 354, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, Y.; Kikuchi, T.; Ozaki, K.; Onishi, H. Evaluation of in vitro and in vivo therapeutic antitumor efficacy of transduction of polo-like kinase 1 and heat shock transcription factor 1 small interfering RNA. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 4300–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hattori, Y.; Arai, S.; Kikuchi, T.; Ozaki, K.; Kawano, K.; Yonemochi, E. Therapeutic effect for liver-metastasized tumor by sequential intravenous injection of anionic polymer and cationic lipoplex of siRNA. J. Drug Target. 2016, 24, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiokawa, T.; Hattori, Y.; Kawano, K.; Ohguchi, Y.; Kawakami, H.; Toma, K.; Maitani, Y. Effect of polyethylene glycol linker chain length of folate-linked microemulsions loading aclacinomycin a on targeting ability and antitumor effect in vitro and in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 2018–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshizawa, T.; Hattori, Y.; Hakoshima, M.; Koga, K.; Maitani, Y. Folate-linked lipid-based nanoparticles for synthetic siRNA delivery in KB tumor xenografts. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, Y.; Yamashita, J.; Sakaida, C.; Kawano, K.; Yonemochi, E. Evaluation of antitumor effect of zoledronic acid entrapped in folate-linked liposome for targeting to tumor-associated macrophages. J. Liposome Res. 2015, 25, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignowski, J.M.; Schaffer, D.V. Kinetic analysis and modeling of firefly luciferase as a quantitative reporter gene in live mammalian cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 86, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronstein, I.; Fortin, J.; Stanley, P.E.; Stewart, G.S.; Kricka, L.J. Chemiluminescent and bioluminescent reporter gene assays. Anal. Biochem. 1994, 219, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corish, P.; Tyler-Smith, C. Attenuation of green fluorescent protein half-life in mammalian cells. Protein Eng. 1999, 12, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hattori, Y.; Maitani, Y. Folate-linked lipid-based nanoparticle for targeted gene delivery. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2005, 2, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhury, A.; Das, S. Folate receptor targeted liposomes encapsulating anti-cancer drugs. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2015, 16, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, M.; Sen, J.; Srujan, M.; Mukherjee, K.; Sreedhar, B.; Chaudhuri, A. Dramatic influence of the orientation of linker between hydrophilic and hydrophobic lipid moiety in liposomal gene delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 11408–11420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okayama, R.; Noji, M.; Nakanishi, M. Cationic cholesterol with a hydroxyethylamino head group promotes significantly liposome-mediated gene transfection. FEBS Lett. 1997, 408, 232–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Percot, A.; Briane, D.; Coudert, R.; Reynier, P.; Bouchemal, N.; Lievre, N.; Hantz, E.; Salzmann, J.L.; Cao, A. A hydroxyethylated cholesterol-based cationic lipid for DNA delivery: Effect of conditioning. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 278, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, J.; Mishra, S.K.; Kondaiah, P.; Bhattacharya, S. Syntheses, transfection efficacy and cell toxicity properties of novel cholesterol-based gemini lipids having hydroxyethyl head group. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 4600–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, Y.; Hagiwara, A.; Ding, W.; Maitani, Y. Nacl improves sirna delivery mediated by nanoparticles of hydroxyethylated cationic cholesterol with amido-linker. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 5228–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Liposomes | Formulation (mol%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAPC-Chol | OH-Chol | OH-C-Chol | DOPE | PEG2000-DSPE | FA-PEG2000-DSPE | PEG5000-DSPE | FA-PEG5000-DSPE | |
| LP-HAPC | 60 | - | - | 40 | - | - | - | - |
| LP-HAPC-1mol%PEG2000 | 59.4 | - | - | 39.6 | 1 | - | - | - |
| LP-HAPC-1mol%PEG5000 | 59.4 | - | - | 39.6 | - | - | 1 | - |
| LP-HAPC-2mol%PEG2000 | 58.8 | - | - | 39.2 | 2 | - | - | - |
| LP-HAPC-3mol%PEG2000 | 58.2 | - | - | 38.8 | 3 | - | - | - |
| LP-HAPC-1mol%FA-PEG2000 | 59.4 | - | - | 39.6 | - | 1 | - | - |
| LP-HAPC-1mol%FA-PEG5000 | 59.4 | - | - | 39.6 | - | - | - | 1 |
| LP-HAPC-2mol%FA-PEG2000 | 58.8 | - | - | 39.2 | - | 2 | - | - |
| LP-HAPC-3mol%FA-PEG2000 | 58.2 | - | - | 38.8 | - | 3 | - | - |
| LP-OH | - | 60 | - | 40 | - | - | - | - |
| LP-OH-1mol%PEG2000 | - | 59.4 | - | 39.6 | 1 | - | - | - |
| LP-OH-2mol%PEG2000 | - | 58.8 | - | 39.2 | 2 | - | - | - |
| LP-OH-3mol%PEG2000 | - | 58.2 | - | 38.8 | 3 | - | - | - |
| LP-OH-1mol%FA-PEG2000 | - | 59.4 | - | 39.6 | - | 1 | - | - |
| LP-OH-2mol%FA-PEG2000 | - | 58.8 | - | 39.2 | - | 2 | - | - |
| LP-OH-3mol%FA-PEG2000 | - | 58.2 | - | 38.8 | - | 3 | - | - |
| LP-OH-C | - | - | 60 | 40 | - | - | - | - |
| LP-OH-C-1mol%PEG2000 | - | - | 59.4 | 39.6 | 1 | - | - | - |
| LP-OH-C-2mol%PEG2000 | - | - | 58.8 | 39.2 | 2 | - | - | - |
| LP-OH-C-3mol%PEG2000 | - | - | 58.2 | 38.8 | 3 | - | - | - |
| LP-OH-C-1mol%FA-PEG2000 | - | - | 59.4 | 39.6 | - | 1 | - | - |
| LP-OH-C-2mol%FA-PEG2000 | - | - | 58.8 | 39.2 | - | 2 | - | - |
| LP-OH-C-3mol%FA-PEG2000 | - | - | 58.2 | 38.8 | - | 3 | - | - |
| Liposome | Liposomes | Lipoplexes (b) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (a) (nm) | PDI | ζ-Potential (a) (mV) | Size (a) (nm) | PDI | ζ-Potential (a) (mV) | |
| LP-HAPC | 103.3 ± 0.3 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 45.4 ± 2.2 | 183.6 ± 0.2 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 39.5 ± 0.8 |
| LP-HAPC-1mol%PEG2000 | 98.2 ± 2.5 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | 46.8 ± 1.0 | 185.4 ± 3.0 | 0.28 ± 0.00 | 31.5 ± 0.1 |
| LP-HAPC-1mol%PEG5000 | 103.1 ± 1.0 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 39.1 ± 0.5 | 168.8 ± 1.2 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 23.8 ± 0.8 |
| LP-HAPC-2mol%PEG2000 | 101.3 ± 2.5 | 0.26 ± 0.00 | 40.7 ± 1.5 | 179.4 ± 4.1 | 0.27 ± 0.00 | 28.3 ± 0.5 |
| LP-HAPC-3mol%PEG2000 | 97.9 ± 2.5 | 0.22 ± 0.03 | 37.6 ± 1.1 | 172.9 ± 1.2 | 0.27 ± 0.02 | 31.0 ± 1.3 |
| LP-HAPC-1mol%FA-PEG2000 | 105.3 ± 0.8 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 45.2 ± 0.5 | 208.1 ± 5.6 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 32.9 ± 1.2 |
| LP-HAPC-1mol%FA-PEG5000 | 101.6 ± 0.7 | 0.22 ± 0.00 | 37.6 ± 1.0 | 204.5 ± 1.8 | 0.28 ± 0.01 | 21.4 ± 1.3 |
| LP-HAPC-2mol%FA-PEG2000 | 97.3 ± 0.1 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 41.5 ± 1.1 | 172.9 ± 1.2 | 0.27 ± 0.02 | 28.3 ± 0.9 |
| LP-HAPC-3mol%FA-PEG2000 | 88.3 ± 0.6 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 35.2 ± 0.4 | 175.7 ± 1.2 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | 29.0 ± 1.4 |
| LP-OH | 108.9 ± 1.2 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 46.7 ± 1.7 | 173.5 ± 3.7 | 0.22 ± 0.02 | 45.3 ± 0.5 |
| LP-OH-1mol%PEG2000 | 104.1 ± 8.0 | 0.31 ± 0.02 | 39.9 ± 1.6 | 187.9 ± 0.6 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | 38.0 ± 2.2 |
| LP-OH-2mol%PEG2000 | 110.5 ± 4.7 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | 46.4 ± 3.2 | 292.1 ± 1.8 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | 29.0 ± 1.0 |
| LP-OH-3mol%PEG2000 | 104.4 ± 3.0 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 44.1 ± 1.0 | 205.8 ± 5.6 | 0.28 ± 0.01 | 24.2 ± 0.8 |
| LP-OH-1mol%FA-PEG2000 | 92.6 ± 1.4 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 46.4 ± 1.7 | 180.1 ± 2.8 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 35.2 ± 1.4 |
| LP-OH-2mol%FA-PEG2000 | 106.4 ± 1.4 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 39.5 ± 0.2 | 202.3 ± 9.7 | 0.24 ± 0.03 | 20.8 ± 0.3 |
| LP-OH-3mol%FA-PEG2000 | 83.5 ± 1.7 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 34.2 ± 1.7 | 197.7 ± 1.5 | 0.28 ± 0.01 | 28.5 ± 0.6 |
| LP-OH-C | 91.4 ± 1.4 | 0.12 ± 0.02 | 49.1 ± 2.2 | 172.4 ± 1.9 | 0.24 ± 0.00 | 41.4 ± 2.9 |
| LP-OH-C-1mol%PEG2000 | 100.0 ± 0.6 | 0.24 ± 0.00 | 43.5 ± 0.7 | 220.8 ± 5.4 | 0.26 ± 0.01 | 38.9 ± 5.7 |
| LP-OH-C-2mol%PEG2000 | 108.5 ± 2.1 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 47.1 ± 1.9 | 258.2 ± 9.3 | 0.26 ± 0.01 | 38.5 ± 1.0 |
| LP-OH-C-3mol%PEG2000 | 110.9 ± 0.9 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | 48.8 ± 0.7 | 201.5 ± 1.9 | 0.26 ± 0.00 | 29.8 ± 1.3 |
| LP-OH-C-1mol%FA-PEG2000 | 103.8 ± 2.4 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 51.5 ± 1.6 | 245.5 ± 1.2 | 0.12 ± 0.00 | 31.6 ± 0.7 |
| LP-OH-C-2mol%FA-PEG2000 | 105.8 ± 2.7 | 0.22 ± 0.01 | 43.3 ± 1.6 | 188.8 ± 1.2 | 0.26 ± 0.01 | 29.1 ± 1.1 |
| LP-OH-C-3mol%FA-PEG2000 | 104.7 ± 1.9 | 0.26 ± 0.01 | 46.6 ± 1.8 | 415.4 ± 70.0 | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 22.0 ± 0.4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hattori, Y.; Shimizu, S.; Ozaki, K.-i.; Onishi, H. Effect of Cationic Lipid Type in Folate-PEG-Modified Cationic Liposomes on Folate Receptor-Mediated siRNA Transfection in Tumor Cells. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11040181
Hattori Y, Shimizu S, Ozaki K-i, Onishi H. Effect of Cationic Lipid Type in Folate-PEG-Modified Cationic Liposomes on Folate Receptor-Mediated siRNA Transfection in Tumor Cells. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(4):181. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11040181
Chicago/Turabian StyleHattori, Yoshiyuki, Satono Shimizu, Kei-ichi Ozaki, and Hiraku Onishi. 2019. "Effect of Cationic Lipid Type in Folate-PEG-Modified Cationic Liposomes on Folate Receptor-Mediated siRNA Transfection in Tumor Cells" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 4: 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11040181
APA StyleHattori, Y., Shimizu, S., Ozaki, K.-i., & Onishi, H. (2019). Effect of Cationic Lipid Type in Folate-PEG-Modified Cationic Liposomes on Folate Receptor-Mediated siRNA Transfection in Tumor Cells. Pharmaceutics, 11(4), 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11040181