Re-Epithelialization Appraisal of Skin Wound in a Porcine Model Using a Salmon-Gelatin Based Biomaterial as Wound Dressing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Salmon-Gelatin Biomaterial
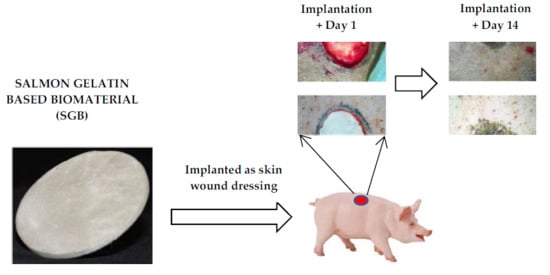
2.3. Animal Procedures
2.4. Histological Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Microstructure of Salmon-Gelatin Biomaterial
3.2. In Vivo Assessment of Salmon-Gelatin Biomaterial
3.3. Histological Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vig, K.; Chaudhari, A.; Tripathi, S.; Dixit, S.; Sahu, R.; Pillai, S.; Dennis, V.A.; Singh, S.R. Advances in skin regeneration using tissue engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priya, S.G.; Jungvid, H.; Kumar, A. Skin tissue engineering for tissue repair and regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part B 2008, 14, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, R.F.; Barrias, C.C.; Granja, P.L.; Bartolo, P.J. Advanced biofabrication strategies for skin regeneration and repair. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 603–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimnejad, M.; Derakhshanfar, S.; Zhong, W. Biomaterials and tissue engineering for scar management in wound care. Burns Trauma 2017, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacNeil, S. Biomaterials for tissue engineering of skin. Mater. Today 2008, 11, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echave, M.C.; Saenz del Burgo, L.; Pedraz, J.L.; Orive, G. Gelatin as biomaterial for tissue engineering. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 3567–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, S.; Rodrigues, G.; Martins, G.; Henriques, C.; Silva, J.C. Evaluation of nanofibrous scaffolds obtained from blends of chitosan, gelatin and polycaprolactone for skin tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 1174–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, S.R.; Rodrigues, G.; Martins, G.G.; Henriques, C.M.; Silva, J.C. In vitro evaluation of crosslinked electrospun fish gelatin scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Ikeda, T.; Yanagiguchi, K.; Hayashi, Y. Potency of fish collagen as a scaffold for regenerative medicine. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 302932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enrione, J.; Pino, K.; Pepczynska, M.; Brown, D.; Ortiz, R.; Sánchez, E.; Acevedo, C. A novel biomaterial based on salmon-gelatin and it’s in vivo evaluation as sterile wound-dressing. Mater. Lett. 2018, 212, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.; Martin, J.R.; Sarett, S.M.; Pollins, A.C.; Cardwell, N.L.; Davidson, J.M.; Guelcher, S.A.; Nanney, L.B.; Duvall, C.L. Porcine ischemic wound-healing model for preclinical testing of degradable biomaterials. Tissue Eng. Part C 2017, 23, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seaton, M.; Hocking, A.; Gibran, N.S. Porcine models of cutaneous wound healing. ILAR J. 2015, 56, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Har-el, y.; Gerstenhaber, J.; Brodsky, R.; Huneke, R.; Lelkes, P. Electrospun soy protein scaffolds as wound dressings: Enhanced reepithelialization in a porcine model of wound healing. Wound Med. 2014, 5, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobson, C. A novel anaesthetic regimen for surgical procedures in guineapigs. Lab. Anim. 2001, 35, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.S.; Rhim, K.J.; Jang, W.S.; Lee, S.J.; Son, Y.; Lee, S.S.; Park, S.; Lim, S.M. Beta-irradiation ((1)(6)(6)ho patch)-induced skin injury in mini-pigs: Effects on nf-kappab and cox-2 expression in the skin. J. Vet. Sci. 2015, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.Y.; Huang, T.T.; Chen, C.H.; Cheng, B.; Hwang, S.M.; Hsieh, P.C. Injection of human cord blood cells with hyaluronan improves postinfarction cardiac repair in pigs. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, L.E.; Dearth, C.L.; Johnson, S.A.; Londono, R.; Medberry, C.J.; Daly, K.A.; Badylak, S.F. In vivo degradation of 14c-labeled porcine dermis biologic scaffold. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 8297–8304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enrione, J.; Diaz-Calderon, P.; Weinstein-Oppenheimer, C.R.; Sanchez, E.; Fuentes, M.A.; Brown, D.I.; Herrera, H.; Acevedo, C.A. Designing a gelatin/chitosan/hyaluronic acid biopolymer using a thermophysical approach for use in tissue engineering. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 36, 1947–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, T.P.; Eaglstein, W.H.; Davis, S.C.; Mertz, P. The pig as a model for human wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2001, 9, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, G.; Li, X.; Cao, H.; Zhou, R.; Li, L. Variations of melanocortin receptor 1 (MC1R) gene in three pig breeds. J. Genet. Genomics 2007, 34, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuggle, C.K.; Wang, Y.; Couture, O. Advances in swine transcriptomics. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2007, 3, 132–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Engrav, L.H.; Muangman, P.; Muffley, L.A.; Zhu, K.Q.; Carrougher, G.J.; Underwood, R.A.; Gibran, N.S. Nerve quantification in female red duroc pig (frdp) scar compared to human hypertrophic scar. Burns 2004, 30, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernatchez, S.F.; Parks, P.J.; Grussing, D.M.; Matalas, S.L.; Nelson, G.S. Histological characterization of a delayed wound healing model in pig. Wound Repair Regen. 1998, 6, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Patel, D.; Khanna, S.; Gordillo, G.M.; Biswas, S.; Friedman, A.; Sen, C.K. Transcriptome-wide analysis of blood vessels laser captured from human skin and chronic wound-edge tissue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14472–14477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aukhil, I. Biology of wound healing. Periodontology 2000, 22, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Guillén, M.; Pérez-Mateos, M.; Gómez-Estaca, G.; López-Caballero, E.; Giménez, B.; Montero, P. Fish gelatin: A renewable material for developing active biodegradable films. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yao, W.; Wang, G.; LI, H. Intrinsic fluorescence investigation on the change in conformation of cross-linked gelatin gel during volume phase transition. Polymer 2000, 41, 7589–7592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avena-Bustillos, R.J.; Chiou, B.; Olsen, C.W.; Bechtel, P.J.; Olson, D.A.; McHugh, T.H. Gelation, oxygen permeability, and mechanical properties of mammalian and fish gelatin films. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, E519–E524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, K.; Liu, H.; Guo, S.; Kumar, D.N.; Wang, Q. Preparation of fish gelatin and fish gelatin/poly(l-lactide) nanofibers by electrospinning. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araghi, M.; Moslehi, Z.; Mohammadi Nafchi, A.; Mostahsan, A.; Salamat, N.; Daraei Garmakhany, A. Cold water fish gelatin modification by a natural phenolic cross-linker (ferulic acid and caffeic acid). Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 3, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.; Seo, S.; Lee, H.; Na, H.; Lee, J.; Woo, H.; Son, T. Preparation of furfuryl-fish gelatin (f-f.Gel) cured using visible-light and its application as an anti-adhesion agent. Macromol. Res. 2012, 20, 842–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, T.I.; Sakuragi, M.; Takahashi, S.; Obuse, S.; Kang, J.; Fujishiro, M.; Matsushita, H.; Gong, J.; Shimizu, S.; Tajima, Y.; et al. Visible light-induced crosslinkable gelatin. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 4005–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Shepherd, J.H.; Shepherd, D.V.; Ghose, S.; Kew, S.J.; Cameron, R.E.; Best, S.M.; Brooks, R.A.; Wardale, J.; Rushton, N. Effect of 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide and n-hydroxysuccinimide concentrations on the mechanical and biological characteristics of cross-linked collagen fibres for tendon repair. Regen. Biomater. 2015, 2, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.M.; Jackson, R.C.; Schneider, G.L.; Ghodbane, S.A.; Dunn, M.G. Carbodiimide cross-linking counteracts the detrimental effects of gamma irradiation on the physical properties of collagen-hyaluronan sponges. Journal of materials science. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasara, T.; Schumacher, S.; Stephan, R. Conventional and real-time pcr-based approaches for molecular detection and quantitation of bovine species material in edible gelatin. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 2420–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobben, A.H.; Steele, P.J.; Somerville, R.A.; Taylor, D.M.; Schreuder, B.E. Inactivation of the bse agent by the heat and pressure process for manufacturing gelatine. Vet. Rec. 2005, 157, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boran, G.; Regenstein, J.M. Fish gelatin. Adv Food Nutr Res. 2010, 60, 119–143. [Google Scholar]
- Sow, L.C.; Kong, K.; Yang, H. Structural modification of fish gelatin by the addition of gellan, kappa-carrageenan, and salts mimics the critical physicochemical properties of pork gelatin. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 1280–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Acevedo, C.A.; Sánchez, E.; Orellana, N.; Morales, P.; Olguín, Y.; Brown, D.I.; Enrione, J. Re-Epithelialization Appraisal of Skin Wound in a Porcine Model Using a Salmon-Gelatin Based Biomaterial as Wound Dressing. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11050196
Acevedo CA, Sánchez E, Orellana N, Morales P, Olguín Y, Brown DI, Enrione J. Re-Epithelialization Appraisal of Skin Wound in a Porcine Model Using a Salmon-Gelatin Based Biomaterial as Wound Dressing. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(5):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11050196
Chicago/Turabian StyleAcevedo, Cristian A., Elizabeth Sánchez, Nicole Orellana, Patricio Morales, Yusser Olguín, Donald I. Brown, and Javier Enrione. 2019. "Re-Epithelialization Appraisal of Skin Wound in a Porcine Model Using a Salmon-Gelatin Based Biomaterial as Wound Dressing" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 5: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11050196
APA StyleAcevedo, C. A., Sánchez, E., Orellana, N., Morales, P., Olguín, Y., Brown, D. I., & Enrione, J. (2019). Re-Epithelialization Appraisal of Skin Wound in a Porcine Model Using a Salmon-Gelatin Based Biomaterial as Wound Dressing. Pharmaceutics, 11(5), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11050196