Delivery of Poorly Soluble Drugs via Mesoporous Silica: Impact of Drug Overloading on Release and Thermal Profiles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Drug-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Particles
2.2.2. Drug Loading Quantification
2.2.3. In Vitro Drug Release Studies
2.2.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermal Profiles and Morphology of Drug-Loaded Mesoporous Silica
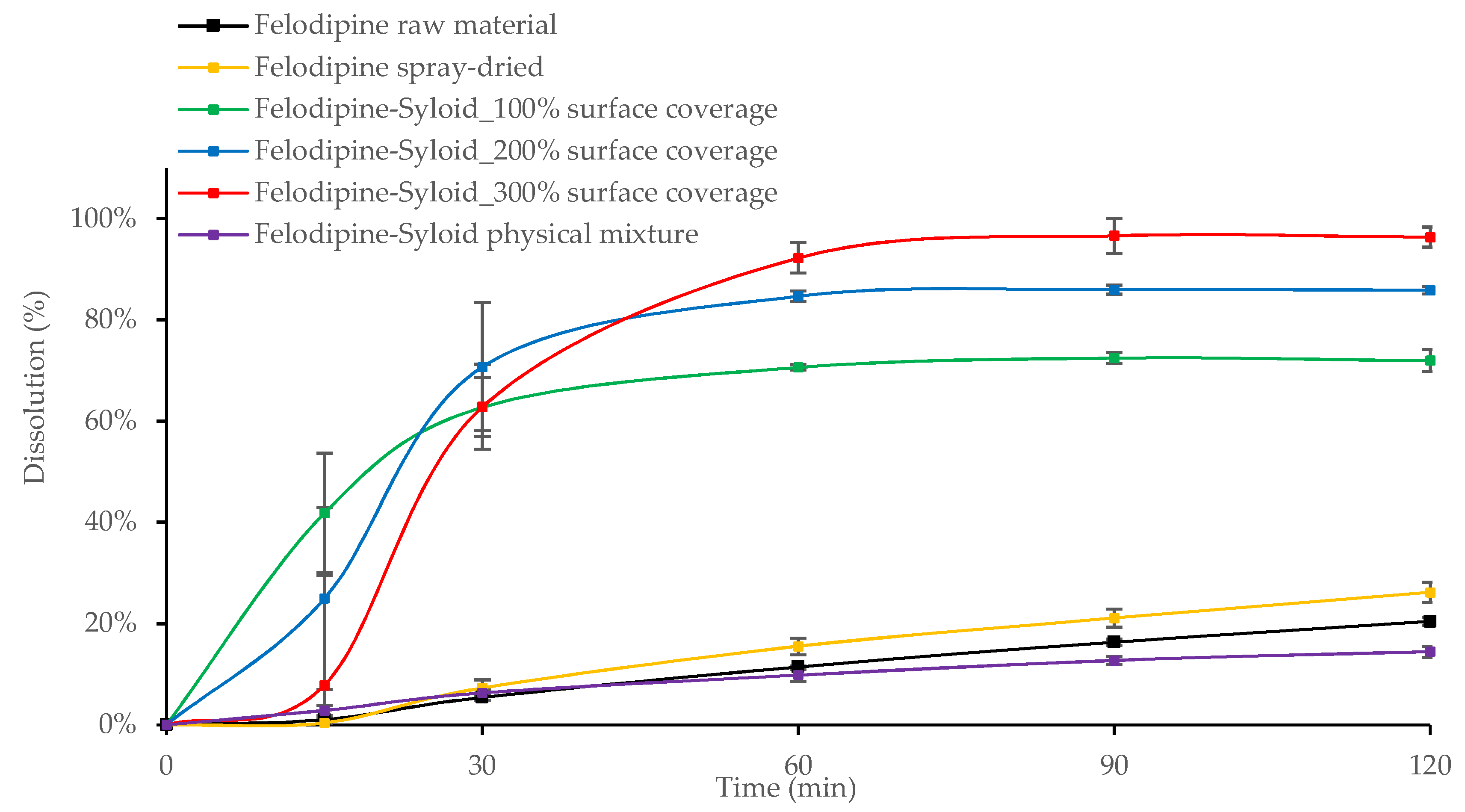
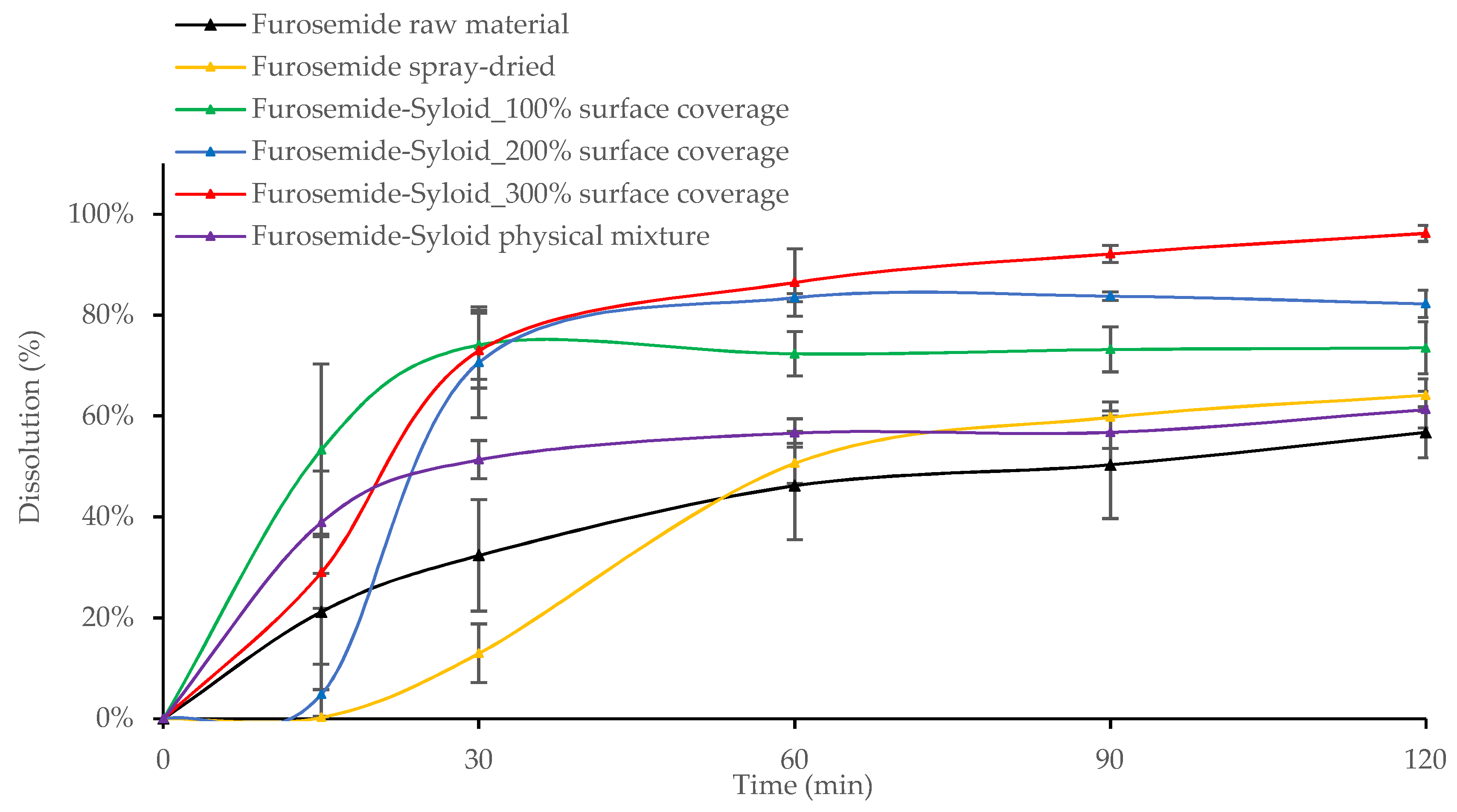
3.2. In Vitro Drug Release from Mesoporous Silica
3.3. Influence of the Addition of HPMCAS to Mesoporous Silica on Drug Loading and Dissolution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ting, J.M.; Porter, W.W.; Mecca, J.M.; Bates, F.S.; Reineke, T.M. Advances in Polymer Design for Enhancing Oral Drug Solubility and Delivery. Bioconj. Chem. 2018, 29, 939–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosselmann, S.; Williams, R.O. Route-Specific Challenges in the Delivery of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. In Formulating Poorly Soluble Drugs; Williams, R.O., Watts, A.B., Miller, D.A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zografi, G.; Newman, A. Introduction to amorphous solid dispersions. In Pharmaceutical Amorphous Solid Dispersions; Newman, A., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Bennett, A.; Feiler, A. Mesoporous ASD: Fundamentals. In Amorphous Solid Dispersions—Theory and Practice; Shah, N., Sandhu, H., Choi, D.S., Chokshi, H., Malick, A.W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 637–663. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, S.C.; Dong, Y.C.; Letchmanan, K.; Ng, W.K. Mesoporous materials and technologies for development of oral medicine. In Nanostructures for Oral Medicine; Andronescu, E., Grumezescu, A.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 699–749. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhari, Y.; Hoefer, H.; Libanati, C.; Monsuur, F.; McCarthy, W. Mesoporous Silica Drug Delivery Systems. In Amorphous Solid Dispersions—Theory and Practice; Shah, N., Sandhu, H., Choi, D.S., Chokshi, H., Malick, A.W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 665–693. [Google Scholar]
- Riikonen, J.; Xu, W.; Lehto, V.P. Mesoporous systems for poorly soluble drugs—Recent trends. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 536, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Riikonen, J.; Lehto, V.P. Mesoporous systems for poorly soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dening, T.J.; Taylor, L.S. Supersaturation Potential of Ordered Mesoporous Silica Delivery Systems. Part 1: Dissolution Performance and Drug Membrane Transport Rates. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 3489–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lainé, A.-L.; Price, D.; Davis, J.; Roberts, D.; Hudson, R.; Back, K.; Bungay, P.; Flanagan, N. Enhanced Oral Delivery of Celecoxib via the Development of a Supersaturable Amorphous Formulation Utilising Mesoporous Silica and Co-Loaded HPMCAS. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 512, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, B.; Lundborg, P.; Regårdh, C.G. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Felodipine: A Summary. Drugs 1987, 34, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chungi, V.S.; Dittert, L.W.; Smith, R.B. Gastrointestinal Sites of Furosemide Absorption in Rats. Int. J. Pharm. 1979, 4, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felodipine–PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/3333 (accessed on 20 March 2019).
- Furosemide–PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/3440 (accessed on 20 March 2019).
- Shen, S.; Ng, W.; Chia, L.; Hu, J.; Tan, R. Physical state and dissolution of ibuprofen formulated by co-spray drying with mesoporous silica: Effect of pore and particle size. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 410, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrogi, V.; Perioli, L.; Pagano, C.; Latterini, L.; Marmottini, F.; Ricci, M.; Rossi, C. MCM-41 for Furosemide Dissolution Improvement. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 147, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrogi, V.; Perioli, L.; Pagano, C.; Marmottini, F.; Ricci, M.; Sagnella, A.; Rossi, C. Use of SBA-15 for Furosemide Oral Delivery Enhancement. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 46, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The United States Pharmacopoeia (USP 36). United States Pharmacopoeia Convention; United States Pharmacopoeia: Rockville, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- HPLC Analysis of Furosemide (Lasix) in Horse Serum on Discovery® C18 after SPE Using Discovery® DSC-18. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/technical-documents/articles/analytical-applications/hplc/hplc-analysis-of-furosemide-lasix-in-horse-serum-g003764.html (accessed on 20 March 2019).
- Mahmah, O.; Tabbakh, R.; Kelly, A.; Paradkar, A. A Comparative Study of the Effect of Spray Drying and Hot-Melt Extrusion on the Properties of Amorphous Solid Dispersions Containing Felodipine. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 66, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, Y.; Tatsumi, E. Physicochemical characterization of furosemide modifications. Int. J. Pharm. 1990, 60, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cássia Da Silva, R.; Semaan, F.S.; Novák, C.; Cavalheiro, E.T.G. Thermal Behavior of Furosemide. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 111, 1933–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Guo, W.; Lin, Y.; Lin, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zeng, Y. Experimental and DFT Simulation Study of a Novel Felodipine Cocrystal: Characterization, Dissolving Properties and Thermal Decomposition Kinetics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 154, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Hao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C. Preparation of a push–pull osmotic pump of felodipine solubilized by mesoporous silica nanoparticles with a core-shell structure. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 475, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Sun, H.; Zhao, Q.; Han, N.; Bai, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Wang, S. Multilayer encapsulated mesoporous silica nanospheres as an oral sustained drug delivery system for the poorly water-soluble drug felodipine. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 47, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, H.; Nagira, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Kawashima, Y. Solid dispersion particles of tolbutamide prepared with fine silica particles by the spray-drying method. Powder Technol. 2004, 141, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Shen, S.; Tan, D.C.T.; Ng, W.K.; Liu, X.; Chia, L.S.O.; Irwan, A.W.; Tan, R.; Nowak, S.A.; Marsh, K.; et al. High Drug Load, Stable, Manufacturable and Bioavailable Fenofibrate Formulations in Mesoporous Silica: A Comparison of Spray Drying versus Solvent Impregnation Methods. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| % of Theoretical Surface Coverage | Felodipine-Syloid | Furosemide-Syloid | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretical Drug Load (%, g/g) | Actual Drug Load (%, g/g) | Normalised Actual Drug Load (×10−3 g/m2) | Loading Efficiency (%) | Theoretical Drug Load (%, g/g) | Actual Drug Load (%, g/g) | Normalised Actual Drug Load (×10−3 g/m2) | Loading Efficiency (%) | |
| 100% | 12.6 | 12.5 ± 0.3 | 0.403 ± 0.010 | 99.2 ± 2.4 | 10.8 | 11.0 ± 0.9 | 0.355 ± 0.029 | 101.9 ± 8.3 |
| 200% | 25.2 | 15.6 ± 0.2 | 0.503 ± 0.006 | 61.9 ± 0.8 | 21.6 | 16.6 ± 0.3 | 0.535 ± 0.010 * | 76.9 ± 1.4 |
| 300% | 37.8 | 21.6 ± 0.3 | 0.697 ± 0.010 * | 57.4 ± 0.8 | 32.4 | 23.9 ± 0.5 | 0.771 ± 0.016 | 73.8 ± 1.5 |
| % of Theoretical Surface Coverage | Felodipine-Syloid-HPMCAS | Furosemide-Syloid-HPMCAS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretical Drug Load (%, g/g) | Actual Drug Load (%, g/g) | Loading Efficiency (%) | Theoretical Drug Load (%, g/g) | Actual Drug Load (%, g/g) | Loading Efficiency (%) | |
| 100% | 12.6 | 13.1 ± 0.2 | 104.0 ± 1.6 | 10.8 | 10.7 ± 0.6 | 99.1 ± 5.5 |
| 200% | 25.2 | 20.3 ± 0.5 | 80.6 ± 1.9 | 21.6 | 14.7 ± 1.3 | 68.1 ± 6.0 |
| 300% | 37.8 | 30.3 ± 0.2 | 80.2 ± 0.5 | 32.4 | 23.8 ± 0.6 | 73.5 ± 1.9 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le, T.-T.; Elzhry Elyafi, A.K.; Mohammed, A.R.; Al-Khattawi, A. Delivery of Poorly Soluble Drugs via Mesoporous Silica: Impact of Drug Overloading on Release and Thermal Profiles. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11060269
Le T-T, Elzhry Elyafi AK, Mohammed AR, Al-Khattawi A. Delivery of Poorly Soluble Drugs via Mesoporous Silica: Impact of Drug Overloading on Release and Thermal Profiles. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(6):269. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11060269
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe, Tuan-Tu, Abdul Khaliq Elzhry Elyafi, Afzal R. Mohammed, and Ali Al-Khattawi. 2019. "Delivery of Poorly Soluble Drugs via Mesoporous Silica: Impact of Drug Overloading on Release and Thermal Profiles" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 6: 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11060269
APA StyleLe, T.-T., Elzhry Elyafi, A. K., Mohammed, A. R., & Al-Khattawi, A. (2019). Delivery of Poorly Soluble Drugs via Mesoporous Silica: Impact of Drug Overloading on Release and Thermal Profiles. Pharmaceutics, 11(6), 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11060269





