Docetaxel-Loaded Disulfide Cross-Linked Nanoparticles Derived from Thiolated Sodium Alginate for Colon Cancer Drug Delivery
Abstract
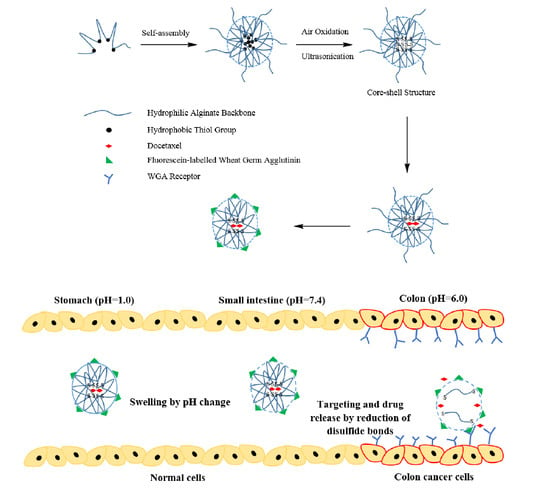
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis and Characterisation of Thiolated Sodium Alginate
2.3. Preparation and Characterisation of Blank Disulfide Cross-Linked Nanoparticles
2.3.1. Stability Studies of Nanoparticles
2.3.2. pH Sensitivity Studies of Nanoparticles
2.3.3. Reduction Response Studies of Nanoparticles
2.4. Preparation, Characterisation and In Vitro Drug Release Studies of Drug-Loaded Nanoparticles
2.5. Preparation and Characterisation of fWGA-Conjugated Blank Nanoparticles
2.6. Preparation and Characterisation of fWGA-Conjugated Drug-Loaded Nanoparticles
2.7. Cytocompatibility Studies—MTT Assay
2.8. Cellular Uptake Studies
2.8.1. Cellular Uptake Efficiency
2.8.2. Fluorescent Imaging
2.8.3. Confocal Laser Imaging
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterisation of MPA1–MPA5
3.2. Characterisation of MP1–MP5
3.3. Characterisation of DMP1–DMP5
3.4. Characterisation of fMP2 and fDMP2
3.5. DLS Analysis
3.6. Surface Morphology
3.7. Stability Study
3.8. pH Sensitivity Studies
3.9. Reduction Response Studies
3.10. In Vitro Drug Release Studies
3.11. Cytocompatibility Studies—MTT
3.12. Cellular Uptake of fDMP2
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Azizah, A.M.; Nor Saleha, I.T.; Noor Hashimah, A.; Asmah, Z.A.; Mastulu, W. Malaysian National Cancer Registry Report 2007-2011; MOH/P/IKN/01.16 (AR); National Cancer Institute, Ministry of Health: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2016; pp. 29–38.
- QUASAR Collaborative Group. Adjuvant chemotherapy versus observation in patients with colorectal cancer: A randomised study. Lancet 2007, 370, 2020–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, P.P.; Date, A.A.; Patravale, V.B. Overcoming poor oral bioavailability using nanoparticle formulations—opportunities and limitations. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2012, 9, e87–e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde, J.; Oliva, N.; Zhang, Y.; Artzi, N. Local triple-combination therapy results in tumour regression and prevents recurrence in a colon cancer model. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, A.K.; Philip, B. Colon targeted drug delivery systems: A review on primary and novel approaches. Oman Med. J. 2010, 25, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Qiao, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Huang, L.; Ji, D.; Guan, Q. Interactions of self-assembled Bletilla Striata polysaccharide nanoparticles with bovine serum albumin and biodistribution of its docetaxel-loaded nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verweij, J.; Clavel, M.; Chevalier, B. Paclitaxel (Taxol) and docetaxel (Taxotere): Not simply two of a kind. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 1994, 5, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowinsky, E.K. The development and clinical utility of the taxane class of antimicrotubule chemotherapy agents. Annu. Rev. Med. 1997, 48, 353–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.D.; Sparreboom, A.; Verweij, J. Clinical pharmacokinetics of docetaxel: Recent developments. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2006, 45, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engels, F.K.; Mathot, R.A.A.; Verweij, J. Alternative drug formulations of docetaxel: A review. Anticancer Drugs 2007, 18, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.R.; Muralidharan, S.; Dhanaraj, S.A.; Umadevi, S.K. A novel drug delivery systems of colon targeted: A review. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2013, 5, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Rangari, N.T.; Prashant, P. Review on recent and novel approaches to colon targeted drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Res. 2015, 3, 167–186. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, P.; Water, J.J.; Bohr, A.; Rantanen, J. Chitosan-based nano-embedded microparticles: Impact of nanogel composition on physicochemical properties. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wahlgren, M.; Axenstrand, M.; Håkansson, Å.; Marefati, A.; Pedersen, B.L. In vitro methods to study colon release: State of the art and an outlook on new strategies for better in-vitro biorelevant release media. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chowdhury, A.; Singh, H. A review: Different approaches of colon targeted drug delivery system. Am. J. PharmTech Res. 2014, 4, 104–117. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, V.; Khiang Peh, K.; Sahudin, S. Synthesis, characterisation, and evaluation of a cross-linked disulphide amide-anhydride-containing polymer based on cysteine for colonic drug delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 24670–24691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Q.; Tao, C.; Li, W.; Wang, J.X.; Le, Y.; Zhang, J.J. Preparation of reduction-responsive camptothecin nanocapsules by combining nanoprecipitation and in situ polymerization for anticancer therapy. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Yin, X.; Yin, X.; Chen, A.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, G.; Liao, W.; Huang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.Y. Dual pH/redox-responsive mixed polymeric micelles for anticancer drug delivery and controlled release. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, X.; Luo, Y.; Chen, J.; Yuan, W.E. Advances in redox-responsive drug delivery systems of tumor microenvironment. J. Nanobiotechnology 2018, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, D.; Lei, J.; Cui, H.; Lu, N.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gao, C.; Zheng, H.; Yin, Y. Disulfide cross-linked nanospheres from sodium alginate derivative for inflammatory bowel disease: Preparation, characterization, and in vitro drug release behavior. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, E.T.L.; Johnson, S.K.; Williams, B.A.; Mikkelsen, D.; McCourt, E.; Stanley, R.A.; Mereddy, R.; Halley, P.J.; Steadman, K.J. Optimizing prednisolone loading into distiller’s dried grain kafirin microparticles, and in vitro release for oral delivery. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teranishi, R.; Matsuki, R.; Yuba, E.; Harada, A.; Kono, K. Doxorubicin delivery using pH and redox dual-responsive hollow nanocapsules with a cationic electrostatic barrier. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savin, C.-L.; Tiron, C.; Carasevici, E.; Stan, C.S.; Ibanescu, S.A.; Simionescu, B.C.; Peptu, C.A. Entrapment of N-hydroxyphthalimide carbon dots in different topical gel formulations: New composites with anticancer activity. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aderibigbe, B.A.; Buyana, B. Alginate in wound dressings. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davidovich-Pinhas, M.; Bianco-Peled, H. Alginate-PEGAc: A new mucoadhesive polymer. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittaya-Areekul, S.; Kruenate, J.; Prahsarn, C. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of mucoadhesive properties of alginate/chitosan microparticles containing prednisolone. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 312, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Cho, Y.W.; Park, K. Nanoparticles for oral delivery: Targeted nanoparticles with peptidic ligands for oral protein delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Yao, W.D.; Rao, Y.F.; Lu, X.Y.; Gao, J.Q. pH-responsive carriers for oral drug delivery: Challenges and opportunities of current platforms. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau, Y.K.; Lim, V. Colon targeted drug delivery of branch-chained disulphide cross-linked polymers: Design, synthesis, and characterisation studies. Chem. Cent. J. 2016, 10, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mat Yusuf, S.N.A.; Ng, Y.M.; Ayub, A.D.; Ngalim, S.H.; Lim, V. Characterisation and evaluation of trimesic acid derivatives as disulphide cross-linked polymers for potential colon targeted drug delivery. Polymers 2017, 9, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Mukherjee, D.; Mishra, R.; Kundu, P.P. Development of pH sensitive polyurethane–alginate nanoparticles for safe and efficient oral insulin delivery in animal models. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 41835–41846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, C.; Podczeck, F.; Veiga, F.; Sousa, J. Influence of the coating formulation on enzymatic digestibility and drug release from 5-aminosalicylic acid pellets coated with mixtures of high-amylose starch and Surelease® intended for colon-specific drug delivery. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2010, 36, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glavas-Dodov, M.; Calis, S.; Crcarevska, M.S.; Geskovski, N.; Petrovska, V.; Goracinova, K. Wheat germ agglutinin-conjugated chitosan-Ca-alginate microparticles for local colon delivery of 5-FU: Development and in vitro characterization. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 381, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Ho, P.C.; Lim, L.Y. Wheat germ agglutinin-conjugated PLGA nanoparticles for enhanced intracellular delivery of paclitaxel to colon cancer cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 400, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabor, F.; Bogner, E.; Weissenboeck, A.; Wirth, M. The lectin-cell interaction and its implications to intestinal lectin-mediated drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 459–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Ahuja, M.; Kumar, A.; Kaur, H. Gellan-thioglycolic acid conjugate: Synthesis, characterization and evaluation as mucoadhesive polymer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, S.; Kwok, K.C.; Wang, Y.; Bao, H. An improved method to determine SH and -S-S- group content in soymilk protein. Food Chem. 2004, 88, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Hornof, M.; Zoidl, T. Thiolated polymers-thiomers: Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of chitosan-2-iminothiolane conjugates. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 260, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Tang, F.; Zhang, J.; Lee, S.M.Y.; Wang, R. Glutathione-responsive nanoparticles based on a sodium alginate derivative for selective release of doxorubicin in tumor cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 2337–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Liu, T.; Dang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wang, W.; Guo, J.; Zhang, X.; He, G.; Zheng, H.; Yin, Y.; et al. pH/redox responsive core cross-linked nanoparticles from thiolated carboxymethyl chitosan for in vitro release study of methotrexate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammadi, N.I.; Abba, Y.; Hezmee, M.N.M.; Razak, I.S.A.; Jaji, A.Z.; Isa, T.; Mahmood, S.K.; Zakaria, M.Z.A.B. Formulation of a sustained release docetaxel loaded cockle shell-derived calcium carbonate nanoparticles against breast cancer. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanan, N.A.; Chiu, H.I.; Ramachandran, M.R.; Tung, W.H.; Mohamad Zain, N.N.; Yahaya, N.; Lim, V. Cytotoxicity of plant-mediated synthesis of metallic nanoparticles: A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yakop, F.; Abd Ghafar, S.A.; Yong, Y.K.; Saiful Yazan, L.; Mohamad Hanafiah, R.; Lim, V.; Eshak, Z. Silver nanoparticles Clinacanthus nutans leaves extract induced apoptosis towards oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Artif. Cells Nanomedicine Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayub, A.D.; Chiu, H.I.; Mat Yusuf, S.N.A.; Abd Kadir, E.; Ngalim, S.H.; Lim, V. Biocompatible disulphide cross-linked sodium alginate derivative nanoparticles for oral colon- targeted drug delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomedicine Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, L.L.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Hao, N.J.; Chen, D.; Tang, F.Q. Fabrication of PLGA coated silica nanorattle for controlling the drug release behavior. Chinese Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 3631–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weissenboeck, A.; Bogner, E.; Wirth, M.; Gabor, F. Binding and uptake of wheat germ agglutinin-grafted PLGA-nanospheres by Caco-2 monolayers. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 1917–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Lim, L.Y. Preparation and in vitro anticancer activity of wheat germ agglutinin (WGA)-conjugated PLGA nanoparticles loaded with paclitaxel and isopropyl myristate. J. Control. Release 2005, 107, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smitha, K.T.; Anitha, A.; Furuike, T.; Tamura, H.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. In vitro evaluation of paclitaxel loaded amorphous chitin nanoparticles for colon cancer drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 104, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, T.; Liang, X.; Li, J.; Shen, Q. Folate and borneol modified bifunctional nanoparticles for enhanced oral absorption. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Xie, J.; Tong, Y.W.; Wang, C.H. Effect of PEG conformation and particle size on the cellular uptake efficiency of nanoparticles with the HepG2 cells. J. Control. Release 2007, 118, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, F.; Chen, L.; Peng, Z.; Kong, L.X. Synthesis and characterization of folate conjugated chitosan and cellular uptake of its nanoparticles in HT-29 cells. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Gao, N.; Zhou, Y.; Nie, J.; Cheng, W.; Luo, M. Polydopamine-Based “Four-in-One” Versatile nanoplatforms for targeted dual chemo and photothermal synergistic cancer therapy. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pizarro, J.; Guerrero, E.; Galindo, P.L. Multiple comparison procedures applied to model selection. Neurocomputing 2002, 48, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dicharry, R.M.; Ye, P.; Saha, G.; Waxman, E.; Asandei, A.D.; Parnas, R.S. Wheat gluten-thiolated poly(vinyl alcohol) blends with improved mechanical properties. Biomacrom 2006, 7, 2837–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.W. Alginate graft copolymers and alginate-co-excipient physical mixture in oral drug delivery. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 1497–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassem, A.A.; Farid, R.M.; Issa, D.A.E.; Khalil, D.S.; Abd-El-Razzak, M.Y.; Saudi, H.I.; Eltokhey, H.M.; El-Zamarany, E.A. Development of mucoadhesive microbeads using thiolated sodium alginate for intrapocket delivery of resveratrol. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 487, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepúlveda-Rivas, S.; Fritz, H.F.; Valenzuela, C.; Santiviago, C.A.; Morales, J.O. Development of novel EE/Alginate polyelectrolyte complex nanoparticles for lysozyme delivery: Physicochemical properties and in vitro safety. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhatia, M.; Ahuja, M.; Mehta, H. Thiol derivatization of Xanthan gum and its evaluation as a mucoadhesive polymer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 131, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Xie, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Tian, N.; Zhu, W.; Yan, G.; Wu, C.; Hu, H. Development of high drug-loading nanomicelles targeting steroids to the brain. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2013, 9, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Narkar, M.; Sher, P.; Pawar, A. Stomach-specific controlled release gellan beads of acid-soluble drug prepared by ionotropic gelation method. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck-Broichsitter, M.; Rytting, E.; Lebhardt, T.; Wang, X.; Kissel, T. Preparation of nanoparticles by solvent displacement for drug delivery: A shift in the “ouzo region” upon drug loading. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 41, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, S.C.; Reis, D.P.; Pereira, M.C.; Coelho, M.A.N. Gold nanoparticles for targeting varlitinib to human pancreatic cancer cells. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, T.; Long, M.; Huo, B. Competitive binding to cuprous ions of protein and BCA in the bicinchoninic acid protein assay. Open Biomed. Eng. J. 2010, 4, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, Y.; Lim, L.Y. Mechanistic study of the uptake of wheat germ agglutinin-conjugated PLGA nanoparticles by A549 cells. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hans, M.L.; Lowman, A.M. Biodegradable nanoparticles for drug delivery and targeting. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2002, 6, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, A.; Olmo, R.; Iglesias, I.; Teijón, J.M.; Blanco, M.D. Folate-targeted nanoparticles based on albumin and albumin/alginate mixtures as controlled release systems of tamoxifen: Synthesis and in vitro characterization. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Nie, S.; Xiong, D.; Guo, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L. pH-responsive micelles based on (PCL)2(PDEA-b-PPEGMA)2 miktoarm polymer: Controlled synthesis, characterization, and application as anticancer drug carrier. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez, A.; Iglesias, I.; Lozano, R.; Teijón, J.M.; Blanco, M.D. Synthesis and characterization of thiolated alginate-albumin nanoparticles stabilized by disulfide bonds. Evaluation as drug delivery systems. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, Y. Study of nanoparticles aggregation/agglomeration in polymer particulate nanocomposites by mechanical properties. Compos. Part. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 84, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Kast, C.E.; Richter, M.F. Improvement in the mucoadhesive properties of alginate by the covalent attachment of cysteine. J. Control. Release 2001, 71, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Sadeghi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Modified carrageenan. 5. Preparation, swelling behavior, salt- and pH-sensitivity of partially hydrolyzed crosslinked carrageenan-graft-polymethacrylamide superabsorbent hydrogel. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2004, 15, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S.; Wang, A. Synthesis, characterization and swelling behaviors of sodium alginate-g-poly(acrylic acid)/sodium humate superabsorbent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 75, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Yuk, D.Y.; Moon, D.C.; Choi, S.S.; Kim, Y.; Han, S.B.; Oh, K.W.; Hong, J.T. Inhibition of NF-κB by ginsenoside Rg3 enhances the susceptibility of colon cancer cells to docetaxel. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2009, 32, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Lillard, J.W., Jr. Nanoparticle-based targeted drug delivery. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 86, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, X.; Huo, P.; Ding, Z.; Kumar, P.; Liu, B. Preparation of lutein-loaded PVA/sodium alginate nanofibers and investigation of its release behavior. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Dong, W.F.; Zhou, J.Y.; Xu, X.M.; Li, F.Q. Triggering effect of N-acetylglucosamine on retarded drug release from a lectin-anchored chitosan nanoparticles-in-microparticles system. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 449, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoder, M.; Gbormoi, H.K.; Ryan, A.; Karam, A.; Alany, R.G. Potential use of the maillard reaction for pharmaceutical applications: Gastric and intestinal controlled release alginate-albumin beads. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aslund, F.; Berndt, K.D.; Holmgren, A. Redox potentials of glutaredoxins and other thiol-disulfide oxidoreductases of the thioredoxin superfamily determined by direct protein-protein redox equilibria. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 30780–30786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, H.; Wang, L.; Zhao, K.; Li, N.; Shi, Z.; Ge, Z.; Jin, Z. Fabrication, mechanical properties, and biocompatibility of graphene-reinforced chitosan composites. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 2345–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Kunimoto, S.; Kawashima, H.; Takeuchi, T.; Ohno, T. Inhibitory effect of laidlomysin on human immunodeficiency virus replication. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 2000, 53, 975–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mo, Y.; Lim, L.Y. Paclitaxel-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: Potentiation of anticancer activity by surface conjugation with wheat germ agglutinin. J. Control. Release 2005, 108, 244–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Sun, C.; Feng, N.; Zhou, W.; Yang, Y.; Tan, R.; Chen, Z.; Wu, S.; Zhao, J. Wheat germ agglutinin-grafted lipid nanoparticles: Preparation and in vitro evaluation of the association with Caco-2 monolayers. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 397, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Sample | MD (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MP1 | 195 ± 7 | 0.46 ± 0.02 | −2.1 ± 6.7 |
| MP2 | 204 ± 3 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | −49.1 ± 0.7 |
| MP3 | 211 ± 4 | 0.40 ± 0.05 | −9.7 ± 1.0 |
| MP5 | 245 ± 8 | 0.20 ± 0.02 | −54.7 ± 1.8 |
| DMP1 | 244 ± 20 | 0.35 ± 0.04 | −35.7 ± 2.7 |
| DMP2 | 219 ± 25 | 0.48 ± 0.17 | −38.6 ± 5.8 |
| DMP3 | 229 ± 14 | 0.35 ± 0.09 | −28.1 ± 2.2 |
| DMP5 | 212 ± 5 | 0.55 ± 0.09 | −17.7 ± 1.2 |
| Sample | MD (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MP2 (Before) | 204 ± 3 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | −49.1 ± 0.7 |
| fMP2 (After) | 274 ± 3 | 0.29 ± 0.02 | −15.8 ± 1.5 |
| DMP2 (Before) | 219 ± 25 | 0.48 ± 0.17 | −38.6 ± 5.8 |
| fDMP2 (After) | 289 ± 10 | 0.30 ± 0.02 | −2.2 ± 2.4 |
| (A) Sample | Before Storage | After Storage | ||
| MD (nm) | PDI | MD (nm) | PDI | |
| MP1 | 191 ± 18 | 0.62 ± 0.03 | 213 ± 80 | 0.58 ± 0.18 |
| MP2 | 226 ± 23 | 0.31 ± 0.03 | 253 ± 5 | 0.38 ± 0.12 |
| MP3 | 226 ± 32 | 0.31 ± 0.03 | 259 ± 28 | 0.48 ± 0.22 |
| MP5 | 233 ± 72 | 0.33 ± 0.02 | 257 ± 23 | 0.32 ± 0.13 |
| (B) Sample | Before Storage | After Storage | ||
| MD (nm) | PDI | MD (nm) | PDI | |
| fMP2 | 272 ± 11 | 0.29 ± 0.01 | 273 ± 8 | 0.28 ± 0.03 |
| fDMP2 | 289 ± 10 | 0.3 ± 0.02 | 303 ± 18 | 0.29 ± 0.07 |
| (A) Sample | GSH (0) | GSH (10 µM) | GSH (10 mM) | |||
| MD (nm) | PDI | MD (nm) | PDI | MD (nm) | PDI | |
| MP1 | 191 ± 18 * | 0.62 ± 0.03 | 232 ± 46 | 0.67 ± 0.04 | 289 ± 31 * | 0.67 ± 0.04 |
| MP2 | 226 ± 23 ** | 0.31 ± 0.03 | 237 ± 22 | 0.42 ± 0.01 | 393 ± 39 ** | 0.46 ± 0.01 |
| MP3 | 226 ± 32 ** | 0.31 ± 0.03 | 306 ± 17 ** | 0.36 ± 0.03 | 394 ± 12 ** | 0.43 ± 0.06 |
| MP5 | 233 ± 72 * | 0.33 ± 0.02 | 293 ± 35 | 0.32 ± 0.02 | 374 ± 12 * | 0.43 ± 0.03 |
| (B) Sample | GSH (0) | GSH (10 µM) | GSH (10 mM) | |||
| MD (nm) | PDI | MD (nm) | PDI | MD (nm) | PDI | |
| fMP2 | 274 ± 26 ** | 0.29 ± 0.02 | 299 ± 21 | 0.29 ± 0.06 | 559 ± 34 ** | 0.73 ± 0.03 |
| pH | Zero-order | First-order | Higuchi’s | Hixson-Crowell’s | Korsmeyer-Peppas’s | Kopcha’s | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | R2 | R2 | R2 | R2 | n | R2 | A/B | |
| 1.0 | 0.56 | 0.58 | 0.83 | 0.02 | 0.58 | 0.14 | 0.90 | 6.28 |
| 7.4 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.89 | 0.86 | 0.97 | −1.14 | 0.93 | 2.44 |
| 6.0 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.82 | 0.64 | 0.62 | 6.46 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiu, H.I.; Ayub, A.D.; Mat Yusuf, S.N.A.; Yahaya, N.; Abd Kadir, E.; Lim, V. Docetaxel-Loaded Disulfide Cross-Linked Nanoparticles Derived from Thiolated Sodium Alginate for Colon Cancer Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010038
Chiu HI, Ayub AD, Mat Yusuf SNA, Yahaya N, Abd Kadir E, Lim V. Docetaxel-Loaded Disulfide Cross-Linked Nanoparticles Derived from Thiolated Sodium Alginate for Colon Cancer Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(1):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010038
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiu, Hock Ing, Asila Dinie Ayub, Siti Nur Aishah Mat Yusuf, Noorfatimah Yahaya, Erazuliana Abd Kadir, and Vuanghao Lim. 2020. "Docetaxel-Loaded Disulfide Cross-Linked Nanoparticles Derived from Thiolated Sodium Alginate for Colon Cancer Drug Delivery" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 1: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010038
APA StyleChiu, H. I., Ayub, A. D., Mat Yusuf, S. N. A., Yahaya, N., Abd Kadir, E., & Lim, V. (2020). Docetaxel-Loaded Disulfide Cross-Linked Nanoparticles Derived from Thiolated Sodium Alginate for Colon Cancer Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics, 12(1), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010038