Gastrointestinal Tracking and Gastric Emptying of Coated Capsules in Rats with or without Sedation Using CT imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Capsule Filing
2.2.2. Capsule Coating
2.2.3. In Vivo Study Design
2.2.4. CT Acquisition
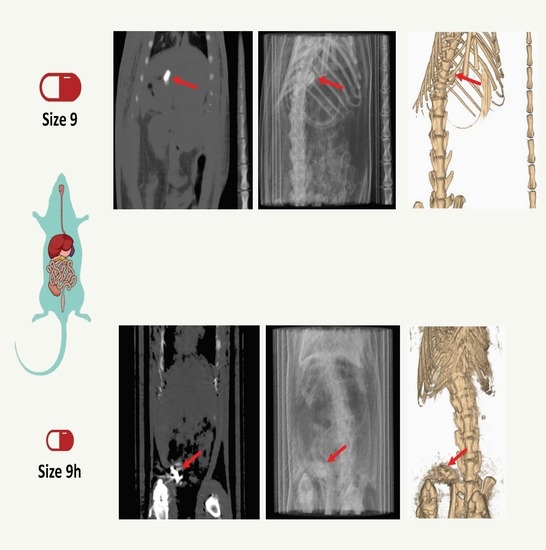
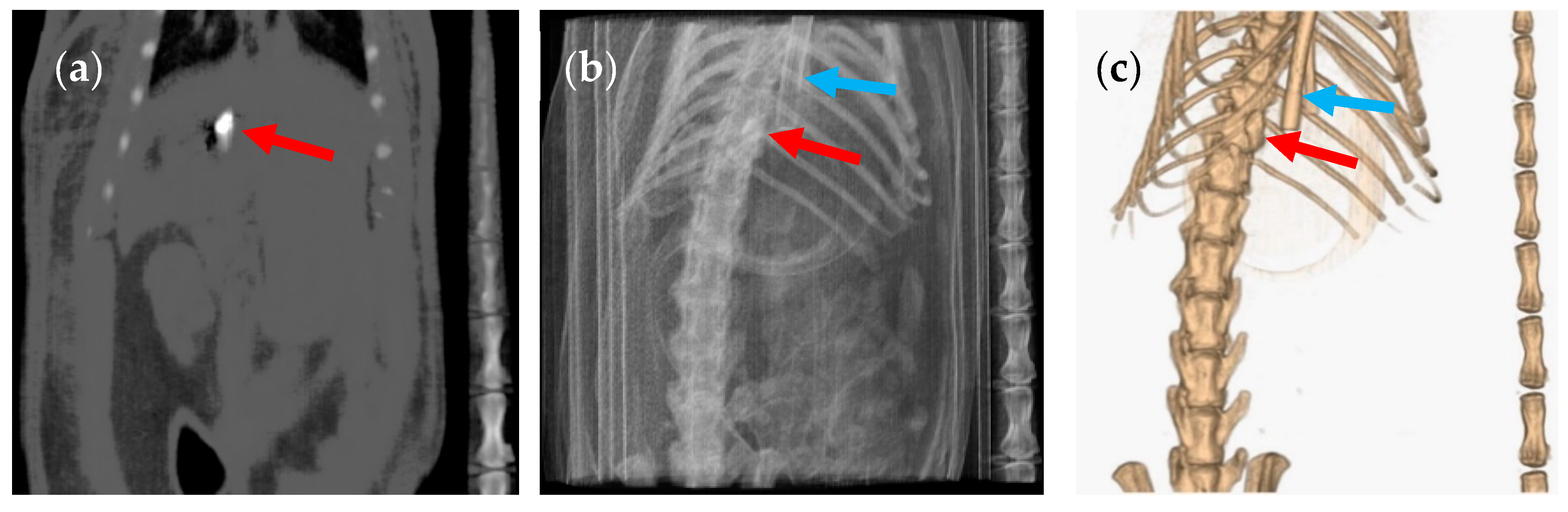
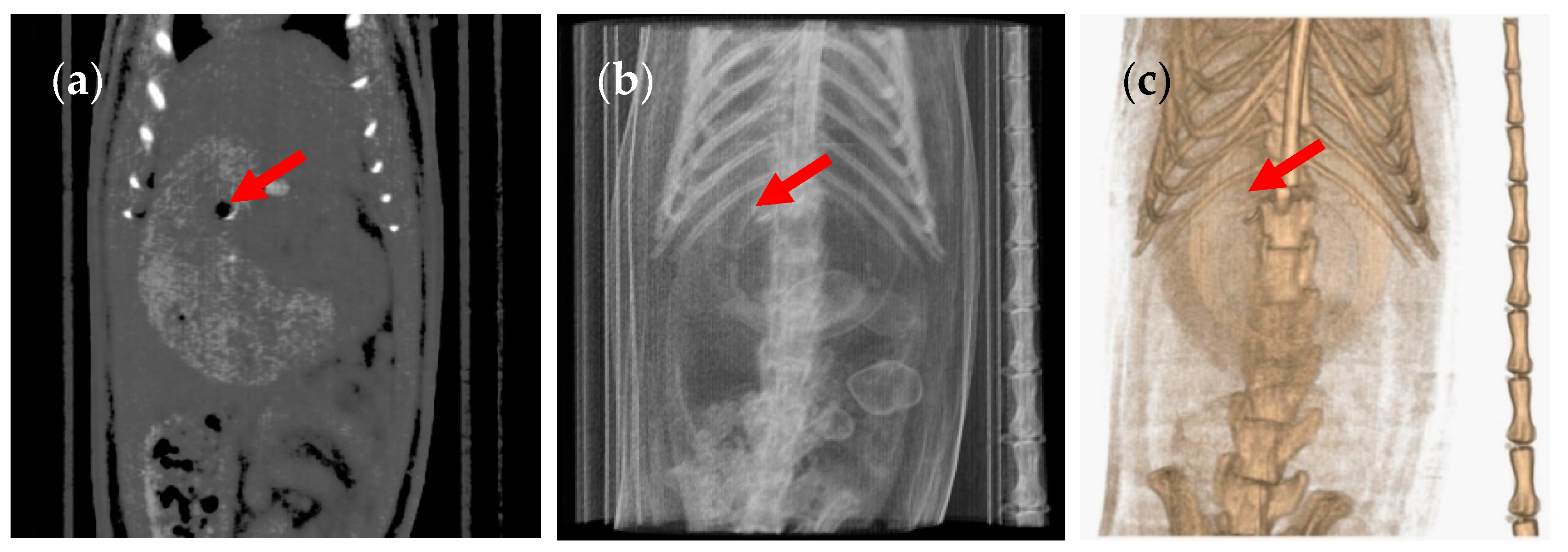
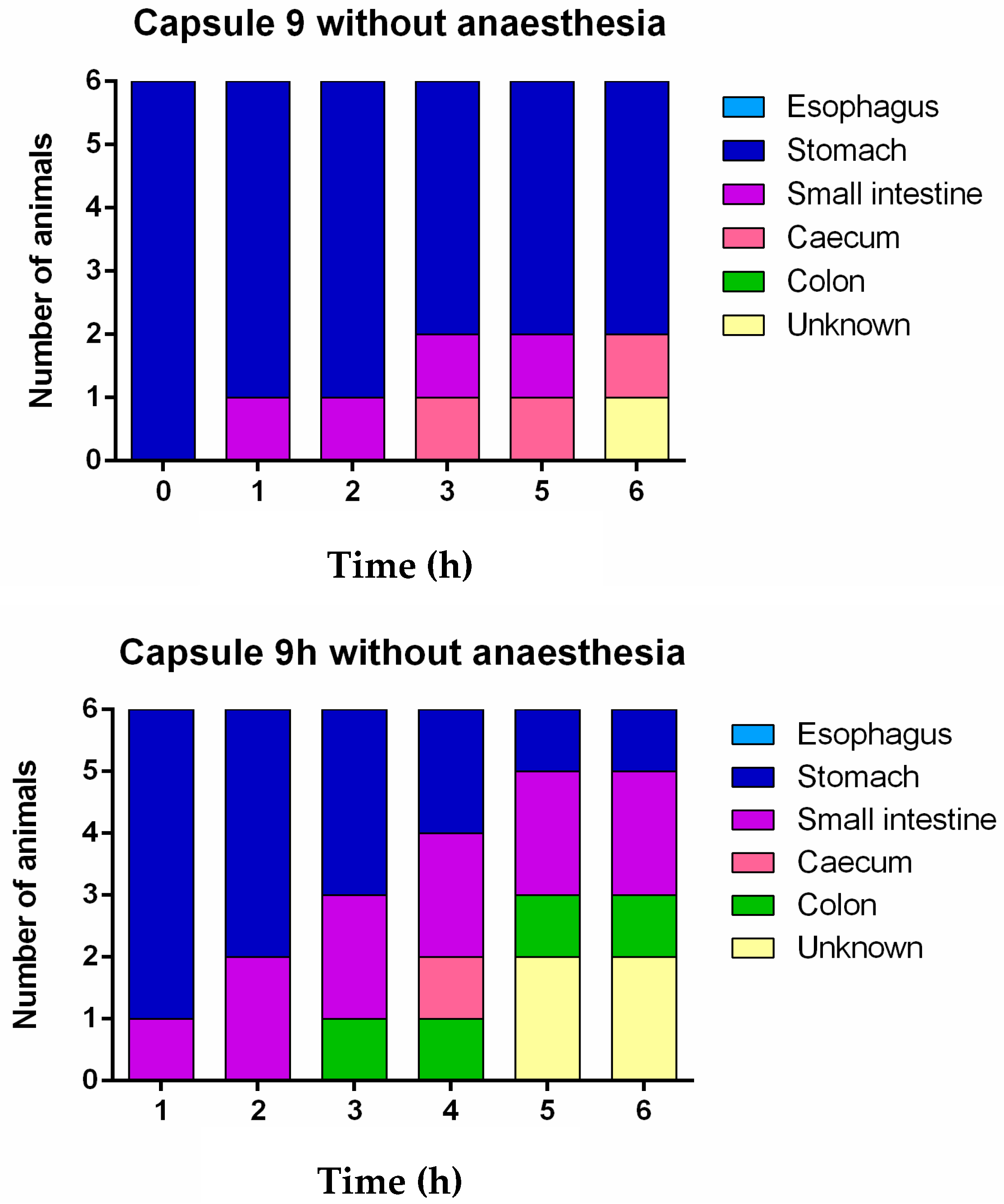
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Everitt, J.I. The future of preclinical animal models in pharmaceutical discovery and development: A need to bring in cerebro to the in vivo discussions. Toxicol. Pathol. 2015, 43, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatton, G.B.; Yadav, V.; Basit, A.W.; Merchant, H.A. Animal farm: Considerations in animal gastrointestinal physiology and relevance to drug delivery in humans. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 2747–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso-Pereira, F.; Dou, L.; Trenfield, S.J.; Madla, C.M.; Murdan, S.; Basit, A.W. Sex differences in the gastrointestinal tract of rats and the implications for oral drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 155, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, Y.; Dou, L.; Madla, C.M.; Murdan, S.; Basit, A.W. Sex-dependence in the effect of pharmaceutical excipients: Polyoxyethylated solubilising excipients increase oral drug bioavailability in male but not female rats. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mazzoni, C.; Tentor, F.; Strindberg, S.A.; Nielsen, L.H.; Keller, S.S.; Alstrøm, T.S.; Gundlach, C.; Müllertz, A.; Marizza, P.; Boisen, A. From concept to in vivo testing: Microcontainers for oral drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2017, 268, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rubbens, J.; Mols, R.; Brouwers, J.; Augustijns, P. Exploring gastric drug absorption in fasted and fed state rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 548, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seoane-Viaño, I.; Gómez-Lado, N.; Lázare-Iglesias, H.; Rey-Bretal, D.; Lamela-Gómez, I.; Otero-Espinar, F.; Blanco-Méndez, J.; Antúnez-López, J.R.; Pombo-Pasín, M.; Aguiar, P.; et al. Evaluation of the therapeutic activity of melatonin and resveratrol in inflammatory bowel disease: A longitudinal PET/CT study in an animal model. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 572, 118713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherali, F.; Varum, F.; Basit, A.W. A slippery slope: On the origin, role and physiology of mucus. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 124, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varum, F.J.O.; Veiga, F.; Sousa, J.S.; Basit, A.W. Mucus thickness in the gastrointestinal tract of laboratory animals. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 64, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayun, B.; Lin, X.; Choi, H.J. Challenges and recent progress in oral drug delivery systems for biopharmaceuticals. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chuang, E.-Y.; Lin, K.-J.; Lin, P.-Y.; Chen, H.-L.; Wey, S.-P.; Mi, F.-L.; Hsiao, H.-C.; Chen, C.-T.; Sung, H.-W. Self-assembling bubble carriers for oral protein delivery. Biomaterials 2015, 64, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghimipour, E.; Rezaei, M.; Kouchak, M.; Fatahiasl, J.; Angali, K.A.; Ramezani, Z.; Amini, M.; Dorkoosh, F.A.; Handali, S. Effects of coating layer and release medium on release profile from coated capsules with Eudragit FS 30D: An in vitro and in vivo study. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonaje, K.; Chen, Y.-J.; Chen, H.-L.; Wey, S.-P.; Juang, J.-H.; Nguyen, H.-N.; Hsu, C.-W.; Lin, K.-J.; Sung, H.-W. Enteric-coated capsules filled with freeze-dried chitosan/poly(γ-glutamic acid) nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3384–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.P.; Boyd, K.L.; Wallace, J.M. Evaluation of mice undergoing serial oral gavage while awake or anesthetized. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2016, 55, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.W.; Healy, T.E.; Balfour, T.W.; Hardcastle, J.D. Effects of inhalation anaesthetic agents on the electrical and mechanical activity of the rat duodenum. Br. J. Anaesth. 1982, 54, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hall, J.A.; Dunlop, C.I.; Solie, T.N.; Hodgson, D.S.; Twedt, D.C. Gastric myoelectric and motor activity in dogs after isoflurane anesthesia. Vet. Surg. 1995, 24, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torjman, M.C.; Joseph, J.I.; Munsick, C.; Morishita, M.; Grunwald, Z. Effects of isoflurane on gastrointestinal motility after brief exposure in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 294, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyanes, A.; Fernandez-Ferreiro, A.; Majeed, A.; Gomez-Lado, N.; Awad, A.; Luaces-Rodriguez, A.; Gaisford, S.; Aguiar, P.; Basit, A.W. PET/CT imaging of 3D printed devices in the gastrointestinal tract of rodents. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 536, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reix, N.; Guhmann, P.; Bietiger, W.; Pinget, M.; Jeandidier, N.; Sigrist, S. Duodenum-specific drug delivery: In vivo assessment of a pharmaceutically developed enteric-coated capsule for a broad applicability in rat studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 422, 338–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, K.; Greindl, M.; Kremser, C.; Wolf, C.; Debbage, P.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Comparative in vivo mucoadhesion studies of thiomer formulations using magnetic resonance imaging and fluorescence detection. J. Control. Release 2006, 115, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalziel, J.E.; Young, W.; Bercik, P.; Spencer, N.J.; Ryan, L.J.; Dunstan, K.E.; Lloyd-West, C.M.; Gopal, P.K.; Haggarty, N.W.; Roy, N.C. Tracking gastrointestinal transit of solids in aged rats as pharmacological models of chronic dysmotility. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 28, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, L.; Szigeti, K.; Mathe, D.; Metello, L.F. The role of molecular imaging in modern drug development. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 936–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tuleu, C.; Basit, A.W.; Waddington, W.A.; Ell, P.J.; Newton, J.M. Colonic delivery of 4-aminosalicylic acid using amylose-ethylcellulose-coated hydroxypropylmethylcellulose capsules. Aliment. Pharmacol. 2002, 16, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuleu, C.; Khela, M.K.; Evans, D.F.; Jones, B.E.; Nagata, S.; Basit, A.W. A scintigraphic investigation of the disintegration behaviour of capsules in fasting subjects: A comparison of hypromellose capsules containing carrageenan as a gelling agent and standard gelatin capsules. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 30, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christmann, V.; Rosenberg, J.; Seega, J.; Lehr, C.M. Simultaneous in vivo visualization and localization of solid oral dosage forms in the rat gastrointestinal tract by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Pharm. Res. 1997, 14, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meka, L.; Kesavan, B.; Kalamata, V.N.; Eaga, C.M.; Bandari, S.; Vobalaboina, V.; Yamsani, M.R. Design and evaluation of polymeric coated minitablets as multiple unit gastroretentive floating drug delivery systems for furosemide. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 2122–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.F.; Goins, B.A.; Phillips, W.T.; Santoyo, C.; Rice-Ficht, A.; McConville, J.T. Size discrimination in rat and mouse gastric emptying. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2013, 34, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saphier, S.; Rosner, A.; Brandeis, R.; Karton, Y. Gastrointestinal tracking and gastric emptying of solid dosage forms in rats using X-ray imaging. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 388, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving bioscience research reporting: The ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torpac. Mini Capsules for Laboratory Mice, Rats, Hamsters & Guinea Pigs. Rodent Flyer 1801. New Jersey: Torpac. n.d. Available online: https://www.torpac.com/Reference/rat/Rodent%20Flyer.pdf (accessed on 16 December 2019).
- Schiller, C.; Fröhlich, C.P.; Giessmann, T.; Siegmund, W.; Mönnikes, H.; Hosten, N.; Weitschies, W. Intestinal fluid volumes and transit of dosage forms as assessed by magnetic resonance imaging. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 22, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasban, H.; El-bendary, M.; Salama, D. A comparative study of medical imaging techniques. Int. J. Inf. Sci. Intell. Syst. 2015, 4, 37–58. [Google Scholar]
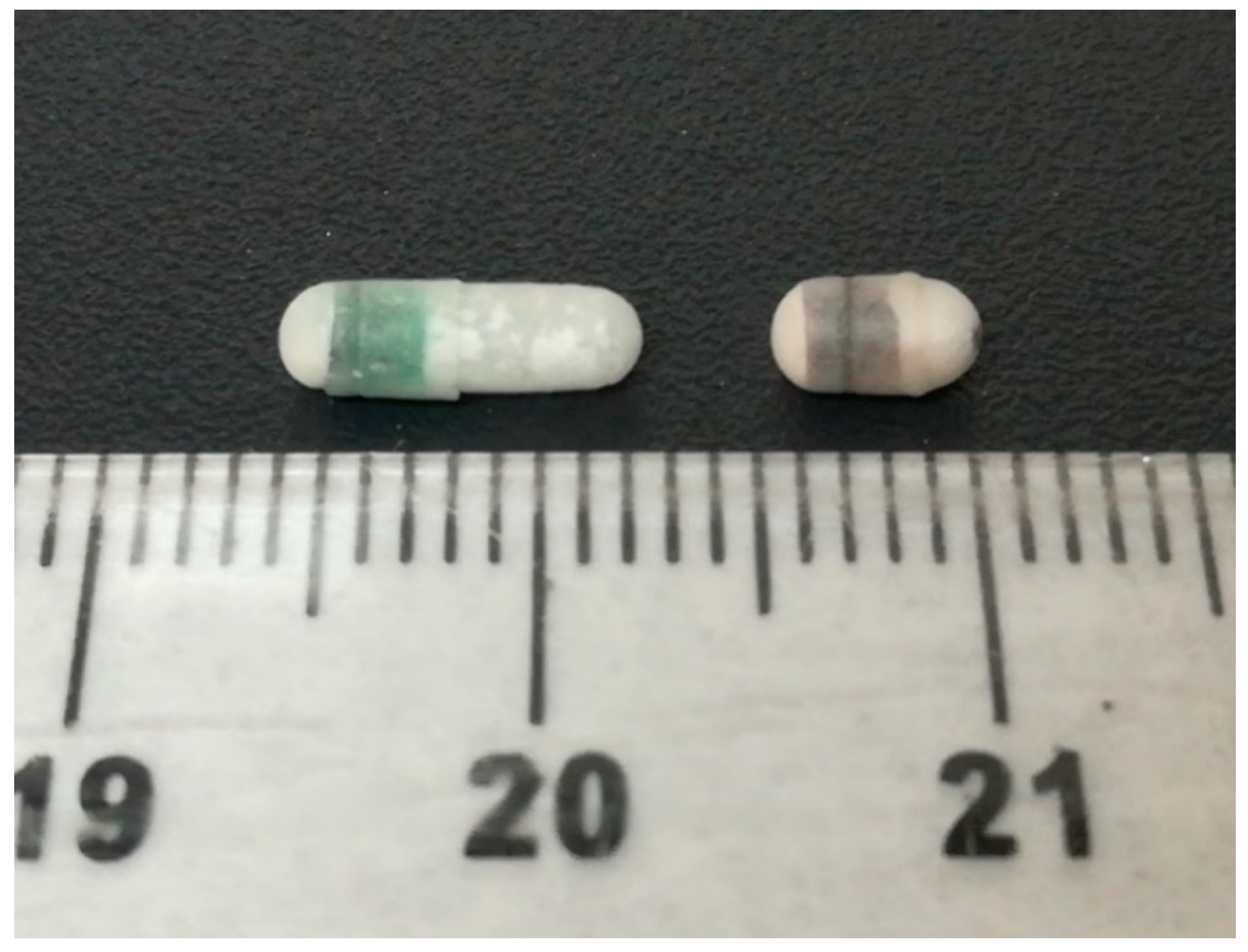





| Capsule Size | 9 | 9h |
|---|---|---|
| Desired weight of the coated formulation (mg) | 25 | 25 |
| Average weight empty capsule (body + cap) (mg) | 10.28 | 6.38 |
| Surface area locked capsule (cm2) | 0.69 | 0.43 |
| Coating thickness (mg/cm2) | 8 | 8 |
| Coating per capsule (mg) | 5.52 | 3.44 |
| Barium sulphate (mg) | 7.5 | 7.5 |
| Required amount of lactose (mg) | 1.7 | 7.68 |
| Group Number | Capsule Size | Anaesthesia |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9 | Yes |
| 2 | 9 | No |
| 3 | 9h | Yes |
| 4 | 9h | No |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gómez-Lado, N.; Seoane-Viaño, I.; Matiz, S.; Madla, C.M.; Yadav, V.; Aguiar, P.; Basit, A.W.; Goyanes, A. Gastrointestinal Tracking and Gastric Emptying of Coated Capsules in Rats with or without Sedation Using CT imaging. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010081
Gómez-Lado N, Seoane-Viaño I, Matiz S, Madla CM, Yadav V, Aguiar P, Basit AW, Goyanes A. Gastrointestinal Tracking and Gastric Emptying of Coated Capsules in Rats with or without Sedation Using CT imaging. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(1):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010081
Chicago/Turabian StyleGómez-Lado, Noemí, Iria Seoane-Viaño, Silvia Matiz, Christine M. Madla, Vipul Yadav, Pablo Aguiar, Abdul W. Basit, and Alvaro Goyanes. 2020. "Gastrointestinal Tracking and Gastric Emptying of Coated Capsules in Rats with or without Sedation Using CT imaging" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 1: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010081
APA StyleGómez-Lado, N., Seoane-Viaño, I., Matiz, S., Madla, C. M., Yadav, V., Aguiar, P., Basit, A. W., & Goyanes, A. (2020). Gastrointestinal Tracking and Gastric Emptying of Coated Capsules in Rats with or without Sedation Using CT imaging. Pharmaceutics, 12(1), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010081