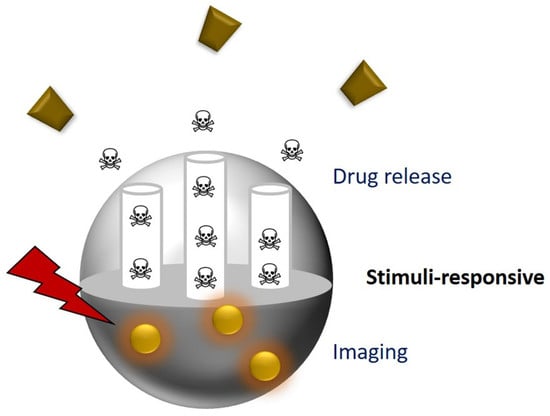
Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Theranostic Antitumoral Nanomedicines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Optical Theranostics
3. Photoacustic Theranostics
4. Ultrasound Theranostics
5. Magnetic Resonance Theranostics
6. Radionuclide-Based Theranostics
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations List
| CD | carbon dots |
| CPT | camptothecin |
| DBCO | dibenzocyclooctyne |
| Dox | doxorubicin |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| EPR | enhanced permeation and retention effect |
| FDA | food and drug administration |
| HER2 | human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| ICG | indocyanine green |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| MSN | mesoporous silica nanoparticles |
| MTX | mitoxantrone |
| NIR | near infrared radiation |
| PA | photoacoustic imaging |
| PDT | photodynamic therapy (PDT) |
| PEG | polyethyleneglycol |
| PET | positron emission tomography |
| PFP | perfluoropentane |
| PTT | photothermal therapy |
| RF | radiofrequencies |
| SPION | superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles |
| THPMA | 2-tetrahydropyranyl methacrylate |
| US | ultrasounds |
| UV | ultraviolet light |
| VIS | visible light |
References
- Tibbitt, M.W.; Dahlman, J.E.; Langer, R. Emerging frontiers in drug delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 704–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arranja, A.G.; Pathak, V.; Lammers, T.; Shi, Y. Tumor-targeted nanomedicines for cancer theranostics. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 115, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Kantoff, P.W.; Wooster, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Cancer nanomedicine: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 17, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, Y.; Maeda, H. A new concept for macromolecular therapeutics in cancer chemotherapy: Mechanism of tumoritropic accumulation of proteins and the antitumor agent smancs. Cancer Res. 1986, 46, 6387–6392. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, R.K.; Stylianopoulos, T. Delivering nanomedicine to solid tumors. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 7, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maeda, H. Toward a full understanding of the EPR effect in primary and metastatic tumors as well as issues related to its heterogeneity. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 91, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danhier, F.; Ansorena, E.; Silva, J.M.; Coco, R.; Le Breton, A.; Préat, V. PLGA-based nanoparticles: An overview of biomedical applications. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Rezaei-Sadabady, R.; Davaran, S.; Joo, S.; Zarghami, N.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Samiei, M.; Kouhi, M.; Nejati-Koshki, K. Liposome: Classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duncan, R.; Izzo, L. Dendrimer biocompatibility and toxicity. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 2215–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, Y.M.; Kang, Y.; Kim, W.J. Tumor-homing, size-tunable clustered nanoparticles for anticancer therapeutics. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 9358–9367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, A. Ceramic nanoparticles for cancer treatment. In Bio-Ceramics with Clinical Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 421–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Robinson, J.T.; Sun, X.; Dai, H. PEGylated nanographene oxide for delivery of water-insoluble cancer drugs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10876–10877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bazak, R.; Houri, M.; El Achy, S.; Kamel, S.; Refaat, T. Cancer active targeting by nanoparticles: A comprehensive review of literature. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 141, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hui, Y.; Shan, L.; Lin-Fu, Z.; Zhu, J. Selection of DNA aptamers against DC-SIGN protein. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 306, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Carmona, M.; Baeza, A.; Rodriguez-Milla, M.A.; García-Castro, J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles grafted with a light-responsive protein shell for highly cytotoxic antitumoral therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 5746–5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Field, L.D.; Delehanty, J.B.; Chen, Y.; Medintz, I.L. Peptides for specifically targeting nanoparticles to cellular organelles: Quo vadis? Accounts Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1380–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaverde, G.; Baeza, A.; Melen, G.; Alfranca, A.; Orellana, M.R.; Vallet-Regí, M. A new targeting agent for the selective drug delivery of nanocarriers for treating neuroblastoma. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 4831–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Yang, K.; Chen, M.; Tian, R.; Ma, Q.; Zhu, L. Hybrid graphene/Au activatable theranostic agent for multimodalities imaging guided enhanced photothermal therapy. Biomaterials 2016, 79, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanson, C.; Diou, O.; Thévenot, J.; Ibarboure, E.; Soum, A.; Brûlet, A.; Miraux, S.; Thiaudière, E.; Tan, S.; Brisson, A.; et al. Doxorubicin loaded magnetic polymersomes: Theranostic nanocarriers for MR imaging and magneto-chemotherapy. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1122–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, S.; Chen, F.; Cai, W. Biomedical applications of functionalized hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Focusing on molecular imaging. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jakobsson, U.; Mäkilä, E.; Airaksinen, A.J.; Alanen, O.; Etilé, A.; Köster, U.; Ranjan, S.; Salonen, J.; Santos, H.A.; Helariutta, K. Porous silicon as a platform for radiation theranostics together with a novel RIB-based radiolanthanoid. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2019, 2019, 3728563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, J.W.; Bae, Y.H. EPR: Evidence and fallacy. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, S.; Tavares, A.J.; Dai, Q.; Ohta, S.; Audet, J.; Dvorak, H.F.; Chan, W.C.W. Analysis of nanoparticle delivery to tumours. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhwani, S.; Syed, A.M.; Ngai, J.; Kingston, B.R.; Maiorino, L.; Rothschild, J.; Macmillan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Rajesh, N.U.; Hoang, T.; et al. The entry of nanoparticles into solid tumours. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, S.; Dutta, D.; Nie, S. Active transcytosis and new opportunities for cancer nanomedicine. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 478–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, B.; Poon, W.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Lin, Z.P.; Kingston, B.R.; Tavares, A.J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Valic, M.S.; Syed, A.M.; et al. The dose threshold for nanoparticle tumour delivery. Nat. Mater. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogart, L.K.; Pourroy, G.; Murphy, C.J.; Puntes, V.F.; Pellegrino, T.; Rosenblum, D.; Peer, D.; Lévy, R. Nanoparticles for imaging, sensing, and therapeutic intervention. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3107–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, D.; Joshi, N.; Tao, W.; Karp, J.M.; Peer, D. Progress and challenges towards targeted delivery of cancer therapeutics. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baeza, A.; Ruiz-Molina, D.; Vallet-Regí, M. Recent advances in porous nanoparticles for drug delivery in antitumoral applications: Inorganic nanoparticles and nanoscale metal-organic frameworks. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 14, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeza, A.; Manzano, M.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Recent advances in mesoporous silica nanoparticles for antitumor therapy: Our contribution. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vallet-Regi, M.; Rámila, A.; Del Real, R.P.; Pérez-Pariente, J. A new property of MCM-41: Drug delivery system. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, A.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Advances in mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted stimuli-responsive drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 12, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, S.K.; Selvaraj, S. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Importance of surface modifications and its role in drug delivery. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 14328–14334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, F.; Cornelius, M.; Morell, J.; Fröba, M. Silica-based mesoporous organic–inorganic hybrid materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 3216–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Tambe, P.; Paknikar, K.M.; Gajbhiye, V. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as cutting-edge theranostics: Advancement from merely a carrier to tailor-made smart delivery platform. J. Control. Release 2018, 287, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquib, M.; Farooq, M.A.; Banerjee, P.; Akhtar, F.; Filli, M.S.; Boakye-Yiadom, K.O.; Kesse, S.; Raza, F.; Maviah, M.B.J.; Mavlyanova, R.; et al. Targeted and stimuli–responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery and theranostic use. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2019, 107, 2643–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.-I.; Sahu, A.; Kim, Y.H.; Tae, G. Photothermal cancer therapy and imaging based on gold nanorods. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 40, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Choi, Y. Indocyanine green-loaded hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a novel theranostics. In Proceedings of the 2nd World Congress on New Technologies, Budapest, Hungary, 18–19 August 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.-J.; Liu, L.-H.; Li, Z.-Y.; Zhuo, R.-X.; Zhang, X.-Z. MMP-responsive theranostic nanoplatform based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles for tumor imaging and targeted drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 1932–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.B.; Lee, H.W.; Darmawan, B.A.; Leec, I.-K.; Cho, S.J.; Chind, J.; Kim, S.K.; Parkag, J.-O.; Soo Kim, K.; Lee, S.-W.; et al. NIR dye-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles for a multifunctional theranostic platform: Visualization of tumor and ischemic lesions, and performance of photothermal therapy. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 88, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Yang, N.; Zhong, L.; Tan, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, R.; Lai, Z.; et al. A new theranostic system based on endoglin aptamer conjugated fluorescent silica nanoparticles. Theranostics 2017, 7, 4862–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, C.; Qian, L.; Ge, J.; Fu, J.; Yuan, P.; Yao, S.C.L.; Yao, S.Q. Cell-penetrating poly(disulfide) assisted intracellular delivery of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for inhibition of miR-21 function and detection of subsequent therapeutic effects. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 9272–9276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.S.; Singh, R.; Kim, T.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Patel, K.D.; Kim, H.-W. Optical imaging and anticancer chemotherapy through carbon dot created hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2017, 55, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, R.; Aiyer, S.; Chauhan, D.S.; Srivastava, R.; Selvaraj, K. Bioresponsive carbon nano-gated multifunctional mesoporous silica for cancer theranostics. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 4537–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rampazzo, E.; Genovese, D.; Palomba, F.; Prodi, L.; Zaccheroni, N. NIR-fluorescent dye doped silica nanoparticles forin vivoimaging, sensing and theranostic. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2018, 6, 022002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, N.; Huang, P.; Fan, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Hu, J.; Liu, W.; Niu, G.; et al. Tri-stimuli-responsive biodegradable theranostics for mild hyperthermia enhanced chemotherapy. Biomaterials 2017, 126, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrauto, G.; Carniato, F.; Di Gregorio, E.; Botta, M.; Tei, L. Photoacoustic ratiometric assessment of mitoxantrone release from theranostic ICG-conjugated mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 18031–18036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, R.; Wang, D.; Xiao, L.; Chen, G.; Xia, J.; Prasad, P.N. Stable ICG-loaded upconversion nanoparticles: Silica core/shell theranostic nanoplatform for dual-modal upconversion and photoacoustic imaging together with photothermal therapy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Q.; You, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Tan, F.; Li, N. Theranostic nanoplatform: Triple-modal imaging-guided synergistic cancer therapy based on liposome-conjugated mesoporous silica nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 1963–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Mei, E.; Lin, J.; Li, F.; Chen, C.; Qing, X.; Hou, L.; Xiong, L.; et al. Light-responsive biodegradable nanorattles for cancer theranostics. Adv. Mater. 2017, 30, 1706150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Zhao, F.; Shi, M.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y. Polymeric Microbubbles for Ultrasonic Molecular Imaging and targeted therapeutics. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2011, 22, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Chen, H.; Shi, J.L. Construction of smart inorganic nanoparticle-based ultrasound contrast agents and their biomedical applications. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 1170–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, X.; Han, X.; Chen, Y. Insights into the unique functionality of inorganic micro/nanoparticles for versatile ultrasound theranostics. Biomaterials 2017, 142, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milgroom, A.; Intrator, M.; Madhavan, K.; Mazzaro, L.; Shandas, R.; Liu, B.; Park, D. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a breast-cancer targeting ultrasound contrast agent. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 116, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, H.; Guo, X.; Zhang, N.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, H.; Shi, J. Double-scattering/reflection in a single nanoparticle for intensified ultrasound imaging. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsao, N.H.; Hall, E.A.H. Enzyme-degradable hybrid polymer/silica microbubbles as ultrasound contrast agents. Langmuir 2016, 32, 6534–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, J.L.; Cabañas, M.V.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Polymer-grafted mesoporous silica nanoparticles as ultrasound-responsive drug carriers. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11023–11033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lammers, T.G.G.M.; Kiessling, F.; Hennink, W.E.; Storm, G. Drug targeting to tumors: Principles, pitfalls and (pre-) clinical progress. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florence, A.T. “Targeting” nanoparticles: The constraints of physical laws and physical barriers. J. Control. Release 2012, 164, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas, M.R.; Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Hybrid collagenase nanocapsules for enhanced nanocarrier penetration in tumoral tissues. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 24075–24081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paris, J.L.; Mannaris, C.; Cabañas, M.V.; Carlisle, R.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Coussios, C. Ultrasound-mediated cavitation-enhanced extravasation of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled-release drug delivery. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 340, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahsner, J.; Gale, E.M.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, A.; Caravan, P. Chemistry of MRI contrast agents: Current challenges and new frontiers. Chem. Rev. 2018, 119, 957–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Na, H.; Song, I.C.; Hyeon, T. Inorganic nanoparticles for MRI contrast agents. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2133–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, X.; Nie, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; He, C. Multifunctional redox-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for efficient targeting drug delivery and magnetic resonance imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 33829–33841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Lin, H.; Zhang, G.; Si, Y.; Yang, H.; Bai, G.; Yang, C.; Zhong, K.; Cai, D.; Wu, Z.; et al. Effective pH-activated theranostic platform for synchronous magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis and chemotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 31114–31123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-H.; Luo, G.-F.; Qiu, W.-X.; Lei, Q.; Liu, L.-H.; Wang, S.-B.; Zhang, X.-Z. Mesoporous silica-based versatile theranostic nanoplatform constructed by layer-by-layer assembly for excellent photodynamic/chemo therapy. Biomaterials 2017, 117, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutz, S.; Hergt, R. Magnetic nanoparticle heating and heat transfer on a microscale: Basic principles, realities and physical limitations of hyperthermia for tumour therapy. Int. J. Hyperth. 2013, 29, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, A.; Guisasola, E.; Ruiz-Hernández, E.; Vallet-Regí, M. Magnetically triggered multidrug release by hybrid mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisasola, E.; Asín, L.; Beola, L.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Beyond traditional hyperthermia: In vivo cancer treatment with magnetic-responsive mesoporous silica nanocarriers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 12518–12525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Q.; Xie, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Guo, Z.; Gao, F.; Zhao, L.; Cai, Q. A theranostic nanocomposite system based on radial mesoporous silica hybridized with Fe3O4 nanoparticles for targeted magnetic field responsive chemotherapy of breast cancer. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 4321–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Fan, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, W.; Yang, H.; Peng, C.; Shen, M.; Shi, X.; et al. Polydopamine-coated magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for multimodal cancer theranostics. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 7, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chang, Z.; Lu, M.; Shao, D.; Yue, J.; Yang, D.; Zheng, X.; Li, M.; He, K.; Zhang, M.; et al. Shape-controlled magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for magnetically-mediated suicide gene therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomaterials 2018, 154, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Manna, K.; Kayal, U.; Saha, M.; Chatterjee, S.; Chandra, D.; Hara, M.; Datta, S.; Bhaumik, A.; Das Saha, K. Folic acid-conjugated magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with quercetin: A theranostic approach for cancer management. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 23148–23164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Li, W.-P.; Huang, S.-P.; Yeh, C.-S.; Yang, C.-M. Hollow mesoporous silica nanosphere-supported FePt nanoparticles for potential theranostic applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 7598–7607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.B.; Kim, H.L.; Jeong, H.-J.; Lim, S.T.; Sohn, M.-H.; Kim, N.W. Mesoporous silica nanoparticle pretargeting for PET imaging based on a rapid bioorthogonal reaction in a living body. Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 10743–10746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Choi, J.-S.; Garcia, M.A.; Xing, Y.; Chen, K.-J.; Chen, Y.-M.; Jiang, Z.K.; Ro, T.; Wu, L.; Stout, D.B.; et al. Pretargeted positron emission tomography imaging that employs supramolecular nanoparticles with in vivo bioorthogonal chemistry. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Nam, J.; Hong, H.; Xu, Y.; Moon, J.J. Positron emission tomography-guided photodynamic therapy with biodegradable mesoporous silica nanoparticles for personalized cancer immunotherapy. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 12148–12161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, W.-Q.; Pei, Q.; Lord, M.S.; Yu, H. Engineering nanomedicines through boosting immunogenic cell death for improved cancer immunotherapy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Fan, W.; Zou, J.; Tang, W.; Li, L.; He, L.; Shen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Jacobson, O.; Aronova, M.A.; et al. Precision cancer theranostic platform by in situ polymerization in perylene diimide-hybridized hollow mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 14687–14698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Chen, F.; Valdovinos, H.F.; Jiang, D.; Goel, S.; Yu, B.; Sun, H.; Barnhart, T.E.; Moon, J.J.; Cai, W. Bacteria-like mesoporous silica-coated gold nanorods for positron emission tomography and photoacoustic imaging-guided chemo-photothermal combined therapy. Biomaterials 2018, 165, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Liu, X.; Tang, W.; Niu, D.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Gu, B.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, Y.; et al. 99mTc-conjugated manganese-based mesoporous silica nanoparticles for SPECT, pH-responsive MRI and anti-cancer drug delivery. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 19573–19580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Shi, S.; Goel, S.; Shen, X.; Xie, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Qin, X.; Yang, H.; et al. Recent advancements in mesoporous silica nanoparticles towards therapeutic applications for cancer. Acta Biomater. 2019, 89, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K.; Bein, T. Degradable drug carriers: Vanishing mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 4364–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.; Nayak, U.Y.; Raichur, A.M.; Garg, S. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: A comprehensive review on synthesis and recent advances. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohammadpour, R.; Cheney, D.L.; Grunberger, J.W.; Yazdimamaghani, M.; Jedrzkiewicz, J.; Isaacson, K.J.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; Ghandehari, H. One-year chronic toxicity evaluation of single dose intravenously administered silica nanoparticles in mice and their Ex vivo human hemocompatibility. J. Control. Release 2020, 324, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Type | Stimuli | Payload | Therapeutic Application | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optical | NIR | Indocyanine green (ICG) | PDT | [38] |
| MMP | PLGVR peptide and CPT | Chemotherapy | [39] | |
| NIR | DIR | PTT | [40] | |
| NIR | Aptamer YQ26 and Cy5.5 | Fluorescent imaging of tumoral blood vessels | [41] | |
| Gluthation/caspases | Polydisulfides, small molecule inhibitors, anti-miR-21 | Chemotherapy | [42] | |
| VIS | CD and Dox | Chemotherapy | [43] | |
| NIR | CuS | Hyperthermia | [46] | |
| Photoacustical | NIR | ICG and MTX | Chemotherapy | [47] |
| NIR | ICG and NaYF4/Yb/Er nanoparticles | Hyperthermia | [48] | |
| NIR | Gd and Dox | Hyperthermia/chemotherapy | [49] | |
| NIR | PFP and gold nanorods | Hyperthermia | [50] | |
| Ultrasound | US | p(MEO2MA)/THPMA and Dox | Chemotherapy | [57] |
| US | Co-injection with cavitation nuclei | Tumoral tissue penetration enhancers | [61] | |
| Magnetic resonance | Glutathione | Gd@BSA/Dox | Chemotherapy | [64] |
| pH | USMO/Dox | Chemotherapy | [65] | |
| Hyaluronidase/NIR | HA-CD/Gd/tirapazamide | Chemotherapy/PDT | [66] | |
| Magnetic field | PNIPAM/NHMA/SPION/Dox | Chemotherapy/hyperthermia | [69] | |
| NIR | Polydopamine/SPION | Hyperthermia | [71] | |
| Magnetic field | Polylysine/HSV-TK/GCV/SPION | Gene suicide/Hyperthermia | [72] | |
| Radionucleotide-based | NIR | neoantigen peptides/CpG/chlorin e6 | Immunotherapy/PDT | [77] |
| NIR | 64Cu/SN38 | Chemotherapy | [79] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Theranostic Antitumoral Nanomedicines. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100957
Baeza A, Vallet-Regí M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Theranostic Antitumoral Nanomedicines. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(10):957. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100957
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaeza, Alejandro, and Maria Vallet-Regí. 2020. "Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Theranostic Antitumoral Nanomedicines" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 10: 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100957
APA StyleBaeza, A., & Vallet-Regí, M. (2020). Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Theranostic Antitumoral Nanomedicines. Pharmaceutics, 12(10), 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100957