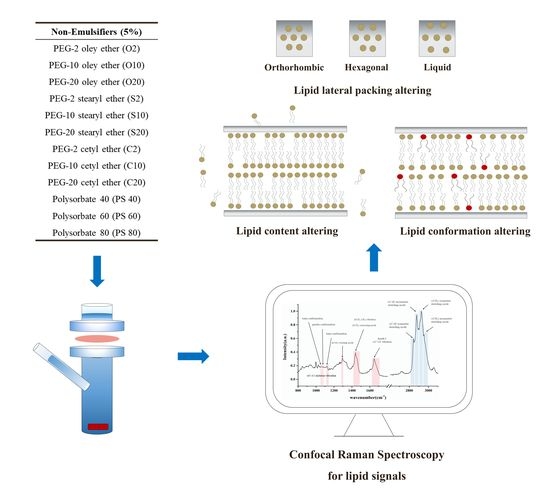
Systematic Investigation of the Effect of Non-Ionic Emulsifiers on Skin by Confocal Raman Spectroscopy—A Comprehensive Lipid Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Dermatomed Porcine Ear Skin
2.3. Incubation of Porcine Ear Skin in Franz Diffusion Cells
2.4. Isolation of Stratum Corneum
2.5. Confocal Raman Spectroscopy (CRS)
2.6. Determination of Skin Surface and Thickness
2.7. Lipid Signals in Fingerprint Region
2.7.1. C–C Skeleton Vibration Mode
2.7.2. CH2 Twisting and Scissoring Mode
2.7.3. CH2 and CH3 Stretching and C=O Vibration Mode
2.8. Lipid Signals in High Wavenumber Region
2.8.1. Gaussian Deconvolution Process
2.8.2. ν (C–H) Symmetric and Asymmetric Stretching
2.8.3. ν (CH3) Symmetric and Asymmetric Stretching
2.9. Data Analysis
2.9.1. Raman Spectra Pre-Processing
2.9.2. Principle Component Analysis
2.9.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Lipid Content Analysis with Normalized Lipid Signal
3.2. CH2 Twisting and Scissoring Mode Analysis
3.3. C–C Skeleton Conformation Analysis
3.4. Lateral Packing Analysis in HWN Region
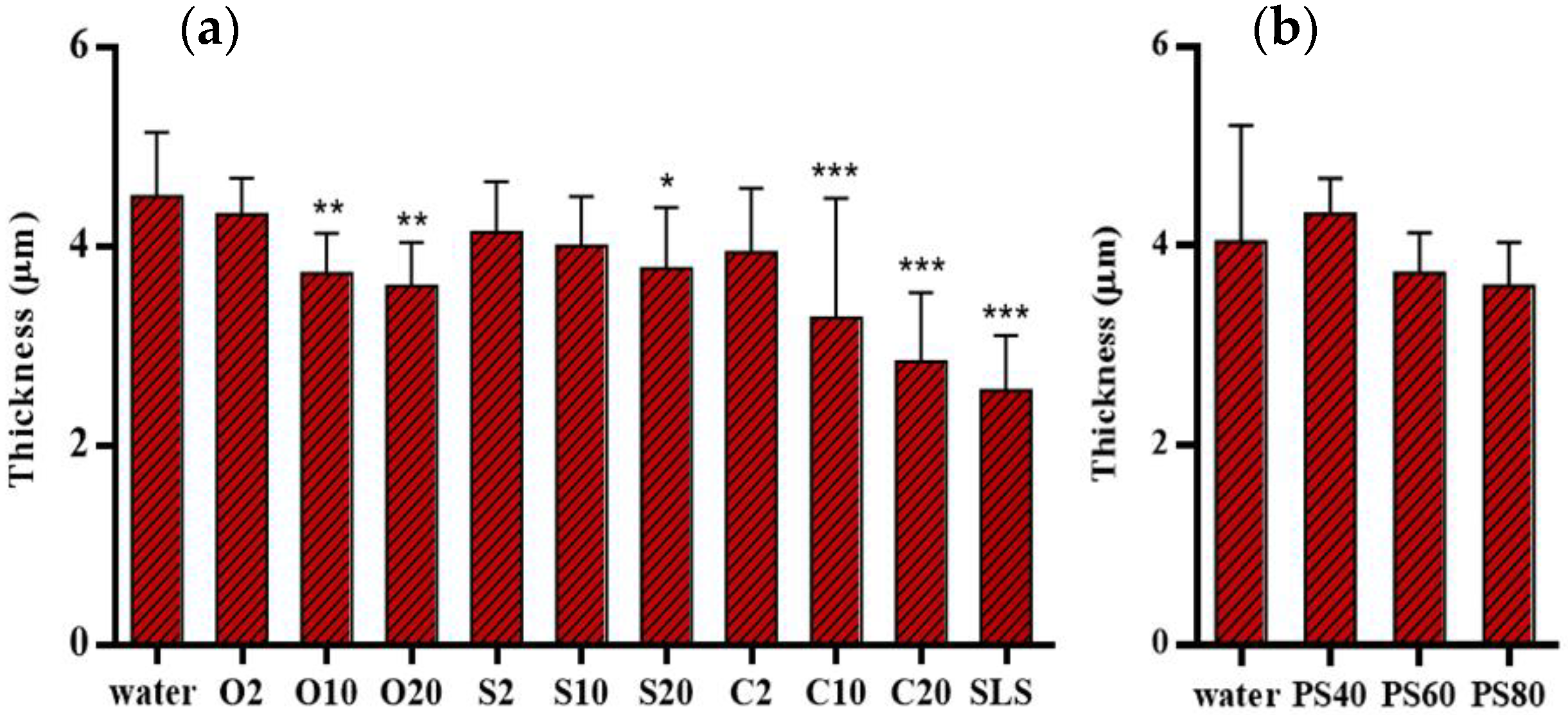
3.5. Skin Thickness Measurement
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Gooris, G.S. The Lipid Organisation in Human Stratum Corneum and Model Systems. Open Dermatol. J. 2014, 4, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwstra, J.A. The skin barrier in healthy and diseased state. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2006, 1758, 2080–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weerheim, A.; Ponec, M. Determination of stratum corneum lipid profile by tape stripping in combination with high-performance thin-layer chromatography. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2001, 293, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caussin, J.; Gooris, G.S.; Janssens, M.; Bouwstra, J.A. Lipid organization in human and porcine stratum corneum differs widely, while lipid mixtures with porcine ceramides model human stratum corneum lipid organization very closely. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2008, 1778, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warner, R.R.; Boissy, Y.L.; Lilly, N.A.; Spears, M.J.; McKillop, K.; Marshall, J.L.; Stone, K.J. Water disrupts stratum corneum lipid lamellae: Damage is similar to surfactants. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 113, 960–966. [Google Scholar]
- Van Smeden, J.; Janssens, M.; Boiten, W.A.; Van Drongelen, V.; Furio, L.; Vreeken, R.J.; Hovnanian, A.; Bouwstra, J.A. Intercellular Skin Barrier Lipid Composition and Organization in Netherton Syndrome Patients. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broere, F.; Gooris, G.; Schlotter, Y.M.; Rutten, V.P.M.G.; Bouwstra, J.A. Altered lipid properties of the stratum corneum in Canine Atopic Dermatitis. Bba-Biomembr. 2018, 1860, 526–533. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, G.P.; Rajeshwarrao, P. Nonionic surfactant vesicular systems for effective drug delivery—An overview. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2011, 1, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghanbarzadeh, S.; Khorrami, A.; Arami, S. Nonionic surfactant-based vesicular system for transdermal drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, E.S.; Chang, S.Y.; Hahn, M.; Chi, S.C. Enhancing effect of polyoxyethylene alkyl ethers on the skin permeation of ibuprofen. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 209, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárány, E.; Lindberg, M.; Lodén, M. Unexpected skin barrier influence from nonionic emulsifiers. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 195, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.M.C.; Hu, L.; Sousa, J.J.S.; Pais, A.A.C.C.; Michniak-Kohn, B.B. A combination of nonionic surfactants and iontophoresis to enhance the transdermal drug delivery of ondansetron HCl and diltiazem HCl. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 80, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Lunter, D.J. Confocal Raman microspectroscopy as an alternative method to investigate the extraction of lipids from stratum corneum by emulsifiers and formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Lunter, D.J. Confocal Raman microspectroscopy as an alternative to differential scanning calorimetry to detect the impact of emulsifiers and formulations on stratum corneum lipid conformation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 121, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, K.A.; Walker, M.; Olejnik, O. Non-ionic Surfactant Effects on Hairless Mouse Skin Permeability Characteristics. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1988, 40, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiume, M.M.; Heldreth, B.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.; Marks, J.G.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; et al. Safety Assessment of Alkyl PEG Ethers as Used in Cosmetics. Int. J. Toxicol. 2012, 31, 169S–244S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruijtier-Pölloth, C. Safety assessment on polyethylene glycols (PEGs) and their derivatives as used in cosmetic products. Toxicology 2005, 214, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappisi, L. Polyoxyethylene alkyl ether carboxylic acids: An overview of a neglected class of surfactants with multiresponsive properties. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 250, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czamara, K.; Majzner, K.; Pacia, M.Z.; Kochan, K.; Kaczor, A.; Baranska, M. Raman spectroscopy of lipids: A review. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2015, 46, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.M.; Bonnier, F.; Ptasinski, K.; Lambkin, H.; Flynn, K.; Lyng, F.M.; Byrne, H.J. Raman spectroscopic mapping for the analysis of solar radiation induced skin damage. Analyst 2013, 138, 3946–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stamatas, G.N.; de Sterke, J.; Hauser, M.; von Stetten, O.; van der Pol, A. Lipid uptake and skin occlusion following topical application of oils on adult and infant skin. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2008, 50, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Smeden, J.; Janssens, M.; Kaye, E.C.J.; Caspers, P.J.; Lavrijsen, A.P.; Vreeken, R.J.; Bouwstra, J.A. The importance of free fatty acid chain length for the skin barrier function in atopic eczema patients. Exp. Dermatol. 2014, 23, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.A.; Li, S.K. Chemical enhancer solubility in human stratum corneum lipids and enhancer mechanism of action on stratum corneum lipid domain. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 383, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lunter, D.; Daniels, R. Confocal Raman microscopic investigation of the effectiveness of penetration enhancers for procaine delivery to the skin. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 126015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunter, D.; Daniels, R. Measuring skin penetration by confocal Raman microscopy (CRM): Correlation to results from conventional experiments. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2016: Biomedical Applications in Molecular, Structural, and Functional Imaging, San Diego, CA, USA, 1–3 March 2016; Volume 9788, p. 978829. [Google Scholar]
- Choe, C.S.; Schleusener, J.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. Age related depth profiles of human Stratum Corneum barrier-related molecular parameters by confocal Raman microscopy in vivo. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2018, 172, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pany, A.; Klang, V.; Peinhopf, C.; Zecevic, A.; Ruthofer, J.; Valenta, C. Hair removal and bioavailability of chemicals: Effect of physicochemical properties of drugs and surfactants on skin permeation ex vivo. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 567, 118477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyumvuhore, R.; Tfayli, A.; Duplan, H.; Delalleau, A.; Manfait, M.; Baiilet-Guffroy, A. Effects of atmospheric relative humidity on Stratum Corneum structure at the molecular level: Ex vivo Raman spectroscopy analysis. Analyst 2013, 138, 4103–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyumvuhore, R.; Tfayli, A.; Duplan, H.; Delalleau, A.; Manfait, M.; Baillet-Guffroy, A. Raman spectroscopy: A tool for biomechanical characterization of Stratum Corneum. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2013, 44, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tfayli, A.; Guillard, E.; Manfait, M.; Baillet-Guffroy, A. Raman spectroscopy: Feasibility of in vivo survey of stratum corneum lipids, effect of natural aging. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2012, 22, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rygula, A.; Majzner, K.; Marzec, K.M.; Kaczor, A.; Pilarczyk, M.; Baranska, M. Raman spectroscopy of proteins: A review. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2013, 44, 1061–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, C.S.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. Gaussian-function-based deconvolution method to determine the penetration ability of petrolatum oil into in vivo human skin using confocal Raman microscopy. Laser Phys. 2014, 24, 105601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savić, S.; Weber, C.; Savić, M.M.; Müller-Goymann, C. Natural surfactant-based topical vehicles for two model drugs: Influence of different lipophilic excipients on in vitro/in vivo skin performance. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 381, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobi, U.; Kaiser, M.; Toll, R.; Mangelsdorf, S.; Audring, H.; Otberg, N.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Porcine ear skin: An in vitro model for human skin. Ski. Res. Technol. 2007, 13, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tfaili, S.; Gobinet, C.; Josse, G.; Angiboust, J.F.; Manfait, M.; Piot, O. Confocal Raman microspectroscopy for skin characterization: A comparative study between human skin and pig skin. Analyst 2012, 137, 3673–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kligman, A.M. Preparation of Isolated Sheets of Human Stratum Corneum. Arch. Dermatol. 2011, 88, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Smeden, J.; Janssens, M.; Gooris, G.S.; Bouwstra, J.A. The important role of stratum corneum lipids for the cutaneous barrier function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2014, 1841, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, T.E.; Houlne, M.P.; Harris, J.M. Spatially Resolved Analysis of Small Particles by Confocal Raman Microscopy: Depth Profiling and Optical Trapping. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathout, R.M.; Mansour, S.; Mortada, N.D.; Geneidi, A.S.; Guy, R.H. Uptake of microemulsion components into the stratum corneum and their molecular effects on skin barrier function. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppel, M.; Baurecht, D.; Holper, E.; Mahrhauser, D.; Valenta, C. Validation of the combined ATR-FTIR/tape stripping technique for monitoring the distribution of surfactants in the stratum corneum. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 472, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, C.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. A depth-dependent profile of the lipid conformation and lateral packing order of the stratum corneum in vivo measured using Raman microscopy. Analyst 2016, 141, 1981–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.C.; Edwards, H.G.M.; Barry, B.W. Raman spectra of human keratotic biopolymers: Skin, callus, hair and nail. J. Raman Spectrosc. 1994, 25, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, R.G.; Hsu, S.L.; Krimm, S. Vibrational spectra in the CH stretching region and the structure of the polymethylene chain. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Spectrosc. 1978, 34, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tfayli, A.; Guillard, E.; Manfait, M.; Baillet-Guffroy, A. Thermal dependence of Raman descriptors of ceramides. Part I: Effect of double bonds in hydrocarbon chains. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1281–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, J.C.; Klang, V.; Hoppel, M.; Mahrhauser, D.; Valenta, C. Natural microemulsions: Formulation design and skin interaction. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallach, D.F.H.; Verma, S.P.; Jeffrey, F. Application of laser Raman and infrared spectroscopy to the analysis of membrane structure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Rev. Biomembr. 1978, 559, 153–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, C.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. Analysis of Human and Porcine Skin in vivo/ex vivo for Penetration of Selected Oils by Confocal Raman Microscopy. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2015, 28, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, C.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. Confocal Raman microscopy for investigating the penetration of various oils into the human skin in vivo. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 79, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vater, C.; Adamovic, A.; Ruttensteiner, L.; Steiner, K.; Tajpara, P.; Klang, V.; Elbe-Bürger, A.; Wirth, M.; Valenta, C. Cytotoxicity of lecithin-based nanoemulsions on human skin cells and ex vivo skin permeation: Comparison to conventional surfactant types. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 566, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Non-Ionic Emulsifiers | Alkyl Chain | Alkyl Chain LENGTH and Saturation | Number of Oxyethylene Group | Abbreviations | HLB Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEG-2 oleyl ether | Oleyl alcohol | C18, C9–C10 unsaturated | 2 | O2 | 5.0 |
| PEG-10 oleyl ether | Oleyl alcohol | C18, C9–C10 unsaturated | 10 | O10 | 12.4 |
| PEG-20 oleyl ether | Oleyl alcohol | C18, C9–C10 unsaturated | 20 | O20 | 15.3 |
| PEG-2 stearyl ether | Stearyl alcohol | C18 | 2 | S2 | 4.9 |
| PEG-10 stearyl ether | Stearyl alcohol | C18 | 10 | S10 | 12.4 |
| PEG-20 stearyl ether | Stearyl alcohol | C18 | 20 | S20 | 15.3 |
| PEG-2 cetyl ether | Cetyl alcohol | C16 | 2 | C2 | 5.3 |
| PEG-10 cetyl ether | Cetyl alcohol | C16 | 10 | C10 | 12.9 |
| PEG-20 cetyl ether | Cetyl alcohol | C16 | 20 | C20 | 15.7 |
| PEG-20 sorbitan monopalmitate | Palmitic acid | C16 | 20 | PS40 | 15.6 |
| PEG-20 sorbitan monostearate | Stearic acid | C18 | 20 | PS60 | 14.9 |
| PEG-20 sorbitan monooleate | Oleic acid | C18, C9–C10 unsaturated | 20 | PS80 | 15 |
| PEG Alkyl Ethers | Chemical Structures | PEG Sorbitan Fatty Acid Esters | Chemical Structures |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEG-n oleyl ether |  | PEG-20 sorbitan monopalmitate (Polysorbate 40) |  |
| PEG-n stearyl ether |  | PEG-20 sorbitan monostearate (Polysorbate 60) | 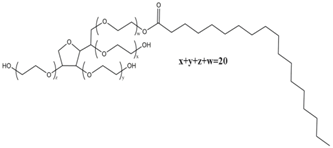 |
| PEG-n cetyl ether | 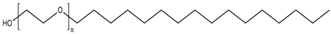 | PEG-20 sorbitan monooleate (Polysorbate 80) |  |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Lunter, D.J. Systematic Investigation of the Effect of Non-Ionic Emulsifiers on Skin by Confocal Raman Spectroscopy—A Comprehensive Lipid Analysis. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030223
Liu Y, Lunter DJ. Systematic Investigation of the Effect of Non-Ionic Emulsifiers on Skin by Confocal Raman Spectroscopy—A Comprehensive Lipid Analysis. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(3):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030223
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yali, and Dominique Jasmin Lunter. 2020. "Systematic Investigation of the Effect of Non-Ionic Emulsifiers on Skin by Confocal Raman Spectroscopy—A Comprehensive Lipid Analysis" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 3: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030223
APA StyleLiu, Y., & Lunter, D. J. (2020). Systematic Investigation of the Effect of Non-Ionic Emulsifiers on Skin by Confocal Raman Spectroscopy—A Comprehensive Lipid Analysis. Pharmaceutics, 12(3), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030223