Regional Intestinal Drug Permeability and Effects of Permeation Enhancers in Rat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Pharmaceutical Excipients and Other Chemicals
2.2. Study Formulations
2.3. Animals and Study Design
2.4. Determination of Blood-to-Lumen Jejunal 51Cr-EDTA Clearance (CLCr-EDTA)
2.5. Bioanalysis
2.6. Intestinal Effective Permeability (Peff) Calculation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
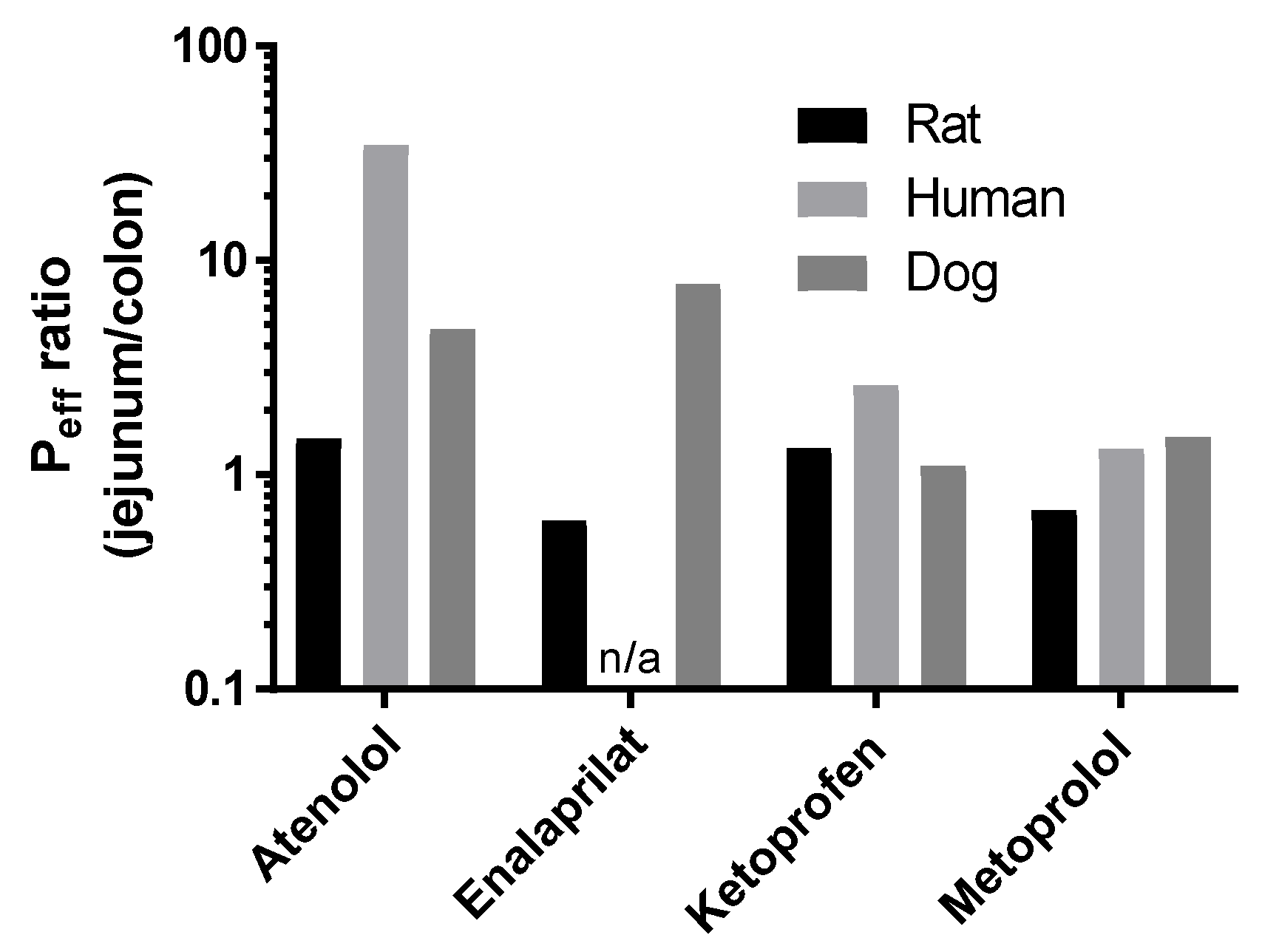
3. Results
3.1. Plasma Profiles
3.2. Lumen-to-Blood Effective Permeability (Peff) of Model Drugs
3.3. Blood-to-Lumen CLCr-EDTA Ratio
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Amidon, G.L.; Sinko, P.J.; Fleisher, D. Estimating human oral fraction dose absorbed: A correlation using rat intestinal membrane permeability for passive and carrier-mediated compounds. Pharm. Res. 1988, 5, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Gibbs, S.T.; Fang, L.; Miller, H.A.; Landowski, C.P.; Shin, H.-C.; Lennernas, H.; Zhong, Y.; Amidon, G.L.; Lawrence, X.Y. Why is it challenging to predict intestinal drug absorption and oral bioavailability in human using rat model. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 1675–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubbelboer, I.; Dahlgren, D.; Sjögren, E.; Lennernäs, H. Rat intestinal drug permeability: A status report and summary of repeated determinations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 142, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlgren, D.; Roos, C.; Lundqvist, A.; Abrahamsson, B.; Tannergren, C.; Hellström, P.M.; Sjögren, E.; Lennernäs, H. Regional intestinal permeability of three model drugs in human. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 3013–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlgren, D.; Roos, C.; Peters, K.; Lundqvist, A.; Tannergren, C.; Sjögren, E.; Sjöblom, M.; Lennernäs, H. Evaluation of drug permeability calculation based on luminal disappearance and plasma appearance in the rat single-pass intestinal perfusion model. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 142, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, S.T.; Bækdal, T.A.; Vegge, A.; Maarbjerg, S.J.; Pyke, C.; Ahnfelt-Rønne, J.; Madsen, K.G.; Schéele, S.G.; Alanentalo, T.; Kirk, R.K. Transcellular stomach absorption of a derivatized glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaar7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, P.; Pechenov, S.; Subramony, J.A. Oral peptide delivery: Translational challenges due to physiological effects. J. Control. Release 2018, 287, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, S.B.; Nielsen, L.G.; Rahbek, U.L.; Guldbrandt, M.; Brayden, D.J. Colonic absorption of salmon calcitonin using tetradecyl maltoside (TDM) as a permeation enhancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinstein, A.; Tirosh, B.; Baluom, M.; Nassar, T.; David, A.; Radai, R.; Gliko-Kabir, I.; Friedman, M. The rationale for peptide drug delivery to the colon and the potential of polymeric carriers as effective tools. J. Control. Release 1997, 46, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlgren, D.; Sjöblom, M.; Lennernäs, H. Intestinal absorption-modifying excipients: A current update on preclinical in vivo evaluations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 142, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlgren, D.; Sjöblom, M.; Hedeland, M.; Lennernäs, H. The in vivo effect of transcellular permeation enhancers on the intestinal permeability of two peptide drugs enalaprilat and hexarelin. Pharmaceutics 2020, 2, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlgren, D.; Roos, C.; Lundqvist, A.; Langguth, P.; Tannergren, C.; Sjöblom, M.; Sjögren, E.; Lennernas, H. Preclinical effect of absorption modifying excipients on rat intestinal transport of five model compounds and the intestinal barrier marker 51Cr-EDTA. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 4243–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nylander, O.; Sababi, M.; Bark, J. Characterization of 51Cr-EDTA as a marker of duodenal mucosal permeability. Acta Physiologica 1991, 143, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winiwarter, S.; Bonham, N.M.; Ax, F.; Hallberg, A.; Lennernäs, H.; Karlén, A. Correlation of human jejunal permeability (in vivo) of drugs with experimentally and theoretically derived parameters. A multivariate data analysis approach. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 4939–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennernäs, H.; Gjellan, K.; Hällgren, R.; Graffner, C. The influence of caprate on rectal absorption of phenoxymethylpenicillin: Experience from an in-vivo perfusion in humans. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2002, 54, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylander, O.; Kvietys, P.; Granger, D.N. Effects of hydrochloric acid on duodenal and jejunal mucosal permeability in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 1989, 257, G653–G660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, C.; Dahlgren, D.; Sjögren, E.; Sjöblom, M.; Hedeland, M.; Lennernäs, H. Effects of absorption-modifying excipients on jejunal drug absorption in simulated fasted and fed luminal conditions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 142, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjögren, E.; Dahlgren, D.; Roos, C.; Lennernas, H. Human in vivo regional intestinal permeability: Quantitation using site-specific drug absorption data. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 2026–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlgren, D.; Roos, C.; Johansson, P.; Lundqvist, A.; Tannergren, C.; Abrahamsson, B.; Sjögren, E.; Lennernäs, H. Regional intestinal permeability in dogs: Biopharmaceutical aspects for development of oral modified-release dosage forms. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 3022–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, C.; Dahlgren, D.; Tannergren, C.; Abrahamsson, B.; Sjögren, E.; Lennernas, H. Regional intestinal permeability in rats: A comparison of methods. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 4252–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, C.; Dahlgren, D.; Berg, S.; Westergren, J.; Abrahamsson, B.; Tannergren, C.; Sjögren, E.; Lennernäs, H. In Vivo Mechanisms of Intestinal Drug Absorption from Aprepitant Nanoformulations. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 4233–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, B.; Morris, T. Physiological parameters in laboratory animals and humans. Pharm. Res. 1993, 10, 1093–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lannoy, I.A.; Barker III, F.; Pang, K.S. Formed and preformed metabolite excretion clearances in liver, a metabolite formation organ: Studies on enalapril and enalaprilat in the single-pass and recirculating perfused rat liver. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1993, 21, 395–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roumi, M.; Marleau, S.; du Souich, P.; Maggi, T.; Deghenghi, R.; Ong, H. Kinetics and disposition of hexarelin, a peptidic growth hormone secretagogue, in rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2000, 28, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlgren, D.; Roos, C.; Lundqvist, A.; Tannergren, C.; Sjöblom, M.; Sjögren, E.; Lennernas, H. Effect of absorption-modifying excipients, hypotonicity, and enteric neural activity in an in vivo model for small intestinal transport. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 549, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlgren, D.; Roos, C.; Johansson, P.; Tannergren, C.; Lundqvist, A.; Langguth, P.; Sjöblom, M.; Sjögren, E.; Lennernas, H. The effects of three absorption-modifying critical excipients on the in vivo intestinal absorption of six model compounds in rats and dogs. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 547, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlgren, D.; Roos, C.; Lundqvist, A.; Tannergren, C.; Sjöblom, M.; Sjögren, E.; Lennernäs, H. Time-dependent effects on small intestinal transport by absorption-modifying excipients. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 132, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradissis, G.N.; Garegnani, J.A.; Whaley, R.S. Extended Release Pharmaceutical Formulations. U.S. Patent 5,133,974, 28 July 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.T.; Mohammed, S.D.; Farmer, A.D.; Wang, D.; Zarate, N.; Hobson, A.R.; Hellström, P.M.; Semler, J.R.; Kuo, B.; Rao, S.S. Regional gastrointestinal transit and pH studied in 215 healthy volunteers using the wireless motility capsule: Influence of age, gender, study country and testing protocol. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 42, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlgren, D.; Roos, C.; Sjögren, E.; Lennernäs, H. Direct In Vivo Human Intestinal Permeability (Peff) Determined with Different Clinical Perfusion and Intubation Methods. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 104, 2702–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerholm, U.; Lindahl, A.; Lennernäs, H. Regional intestinal permeability in rats of compounds with different physicochemical properties and transport mechanisms. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1997, 49, 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, S.C.; Evans, L.A.; Fortner, J.H.; McCarthy, J.M.; Sweeney, K. Dog colonoscopy model for predicting human colon absorption. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 1554–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozoya-Agullo, I.; González-Álvarez, I.; González-Álvarez, M.; Merino-Sanjuán, M.; Bermejo, M. In situ perfusion model in rat colon for drug absorption studies: Comparison with small intestine and Caco-2 cell model. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 3136–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bransford, P.; Cook, J.; Gupta, M.; Haertter, S.; He, H.; Ju, R.; Kanodia, J.; Lennernäs, H.; Lindley, D.; Polli, J.E. ICH M9 Guideline in development on Biopharmaceutics Classification System-based biowaivers: An Industrial Perspective from the IQ Consortium. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 17, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomae, A.V.; Wunderli-Allenspach, H.; Krämer, S.D. Permeation of aromatic carboxylic acids across lipid bilayers: The pH-partition hypothesis revisited. Biophys. J. 2005, 89, 1802–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlgren, D.; Lennernäs, H. Intestinal Permeability and Drug Absorption: Predictive Experimental, Computational and In Vivo Approaches. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, A.; Taniguchi, T.; Rikyuu, K.; Tsuji, T.; Fujita, T.; Murakami, M.; Muranishi, S. Effects of various protease inhibitors on the intestinal absorption and degradation of insulin in rats. Pharm. Res. 1994, 11, 1496–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, G.; Lu, Q.; Sun, Q.; Wang, M.; Li, N.; Gao, Z.; Sun, Y.; Li, T.; Han, D. Evaluation of salmon calcitonin (sCT) enteric-coated capsule for enhanced absorption and GI tolerability in rats. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2010, 36, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 23, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetih, G.; Lindberg, S.; Itoh, K.; Okada, N.; Fujita, T.; Habib, F.; Artersson, P.; Attia, M.; Yamamoto, A. Improvement of absorption enhancing effects of n-dodecyl-β-D-maltopyranoside by its colon-specific delivery using chitosan capsules. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 293, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizawa, T.; Hayashi, M.; Awazu, S. Enhancement of jejunal and colonic absorption of fosfomycin by promoters in the rat. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1987, 39, 892–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, S.; Wang, X.; Bzik, V.; McClean, S.; Brayden, D.J. Evaluation of intestinal absorption and mucosal toxicity using two promoters. II. Rat instillation and perfusion studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 38, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M.; Kusanoi, Y.; Takada, K.; Muranishi, S. Assessment of enhancing ability of medium-chain alkyl saccharides as new absorption enhancers in rat rectum. Int. J. Pharm 1992, 79, 159–169. [Google Scholar]
- Muranushi, N.; Mack, E.; Kim, S. The effects of fatty acids and their derivatives on the intestinal absorption of insulin in rat. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1993, 19, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, S.; Mrsny, R.J.; Brayden, D.J. Intestinal permeation enhancers for oral peptide delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 106, 277–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Compounds (BCS Class) | MM (g/mol) | pKa | PSA | HBA/HBD | Log P | Log D7.4 | Log D6.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atenolol (III) | 266 | 9.6 b | 88.1 | 4/4 | 0.18 | −2.0 | <−2.0 |
| Enalaprilat (III) | 348 | 3.17 b/7.84 a | 102.1 | 6/3 | −0.13 | −1.0 | −1.0 |
| Metoprolol (I) | 267 | 9.6 b | 57.8 | 4/2 | 2.07 | 0.0 | −0.5 |
| Ketoprofen (II) | 254 | 3.89 a | 54.2 | 3/1 | 3.37 | 0.1 | 0.8 |
| Conditions | Plasma Appearance Peff (×10–4 cm/s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atenolol | Enalaprilat | Ketoprofen | Metoprolol | |
| Jejunum pH 6.5 | 0.022 ± 0.01 | 0.005 ± 0.004 | 1.5 ± 1.1 | 0.28 ± 0.24 |
| Jejunum pH 7.4 | 0.016 ± 0.005 | 0.004 ± 0.001 | 0.64 ± 0.15 | 0.17 ± 0.095 |
| Colon pH 6.5 | 0.015 ± 0.007 | 0.009 ± 0.007 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 0.41 ± 0.19 |
| Colon pH 7.4 | 0.011 ± 0.005 | 0.006 ± 0.004 | 0.73 ± 0.14 | 0.38 ± 0.15 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dahlgren, D.; Cano-Cebrián, M.-J.; Olander, T.; Hedeland, M.; Sjöblom, M.; Lennernäs, H. Regional Intestinal Drug Permeability and Effects of Permeation Enhancers in Rat. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030242
Dahlgren D, Cano-Cebrián M-J, Olander T, Hedeland M, Sjöblom M, Lennernäs H. Regional Intestinal Drug Permeability and Effects of Permeation Enhancers in Rat. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(3):242. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030242
Chicago/Turabian StyleDahlgren, David, Maria-Jose Cano-Cebrián, Tobias Olander, Mikael Hedeland, Markus Sjöblom, and Hans Lennernäs. 2020. "Regional Intestinal Drug Permeability and Effects of Permeation Enhancers in Rat" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 3: 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030242
APA StyleDahlgren, D., Cano-Cebrián, M.-J., Olander, T., Hedeland, M., Sjöblom, M., & Lennernäs, H. (2020). Regional Intestinal Drug Permeability and Effects of Permeation Enhancers in Rat. Pharmaceutics, 12(3), 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030242







