Availability of Authorizations from EMA and FDA for Age-Appropriate Medicines Contained in the WHO Essential Medicines List for Children 2019
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
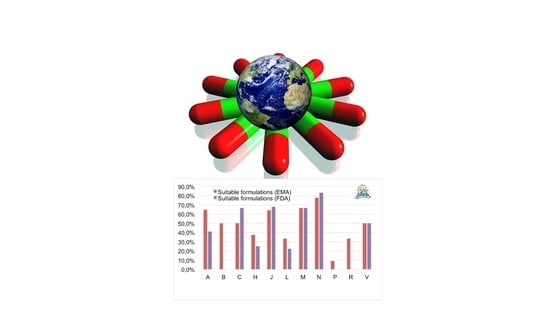
3.1. Availability and Suitability of Oral Formulations
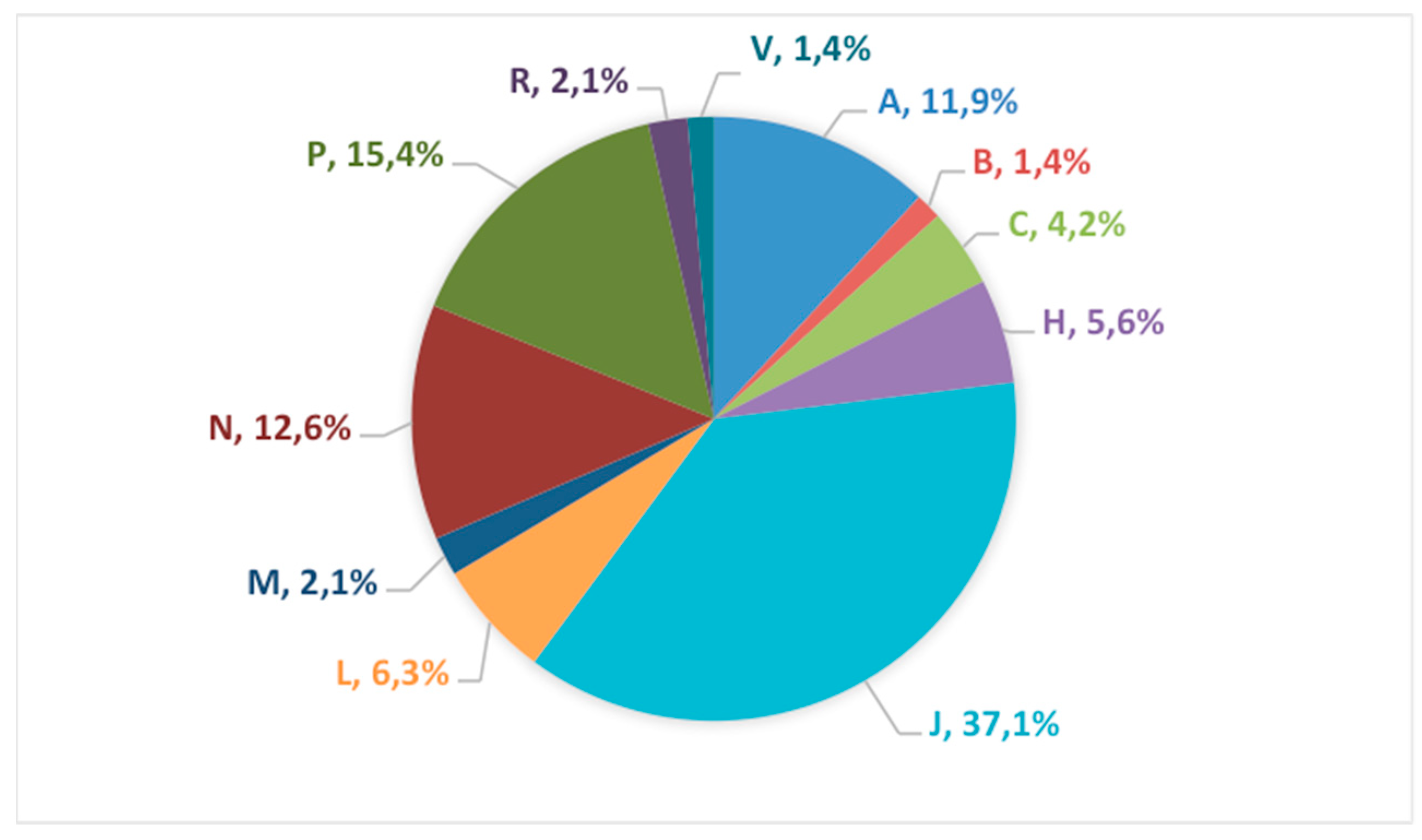
3.2. Therapeutic Class Distribution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Drug | European Medicines Agency | Food and Drug Administration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral Availability | Age-appr | Formulation | Oral Availability | Age-appr | Formulation | |
| Abacavir | yes | yes | oral solution 20 mg/mL (1999) | yes | yes | oral solution 20 mg/mL (1998) |
| Acetylcysteine | yes | yes | oral solution 20 mg/mL (2000) powder for oral suspension 100, 200 mg (2000) effervescent tablet 600 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 10% and 20% (1989) effervescent tablet 500 mg and 2500 mg |
| Acetylsalicylic acid | yes | no | tablet 100, 150, 300, 500 mg | yes | no | tablet 500 mg capsule 162.5, 325 mg |
| Acyclovir | yes | yes | oral suspension 80 mg/mL (1992) tablet 200–800 mg | yes | yes | oral suspension 200 mg/5 mL (1989) tablet 50–800 mg |
| Albendazole | yes | no | tablet 400 mg | yes | no | tablet 200 mg |
| Allopurinol | yes | no | tablet 100, 300 mg | yes | no | tablet 100, 300 mg |
| Amitriptyline | yes | yes | oral solution 50 mg/mL, 10 mg/mL (2010) tablet 25–150 mg | yes | no | tablet 25–150 mg |
| Amodiaquine | no | no | - | no | no | - |
| Amoxicillin (*in association with clavulanic acid see clavulanic acid) | yes | yes | oral suspension 250 mg/5 mL (1974) powder for oral suspension 500 mg (1990) tablet 500 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 250 mg/mL and 400 mg/mL (1982) chewable tablet 125, 250 mg (1992) tablet 250, 500 mg |
| Artesunate | no | no | - | no | no | Artemether is available |
| Ascorbic acid | yes | no | tablet 50, 100, 200 mg | no | no | - |
| Atazanavir | yes | yes | powder for oral suspension 50 mg (2016) capsule 150, 200, 300 mg | yes | yes | powder for oral suspension 50 mg (2014) capsule 150, 200, 300 mg |
| Azathioprine | yes | no | tablet 50 mg | yes | no | tablet 50 mg |
| Azithromycin | yes | yes | oral suspension 200 mg/5 mL (1992) powder for oral suspension 500 mg (1992) tablet 500 mg | yes | yes | oral suspension 200 mg/5 mL (2006) tablet 500 mg |
| Benznidazole | no | no | - | no | no | - |
| Caffeine citrate | yes | yes | oral solution 10 mg/mL (2018) | yes | yes | oral solution 10 mg/mL (2000) |
| Calcium folinate | yes | yes | oral suspension 1 mg/12 mL (1966) | no | no | - |
| Calcium gluconate | yes | no | effervescent tablet 1000 mg | no | no | - |
| Carbamazepine | yes | no | tablet 200, 400 mg | yes | yes | oral suspension 100 mg/5 mL (1987) capsule 200 mg |
| Cefixime | yes | yes | oral suspension 100 mg/5 mL (1993) capsule 200, 400 mg | yes | yes | oral suspension 100 mg/5 mL, 200 mg/5 mL (2007) chewable tablet 100,150, 200 mg |
| Cephalexin | yes | yes | oral suspension 250 mg/5 mL, 125 mg/5 mL (1996) capsule 500 mg | yes | yes | oral suspension 125 mg/5 mL, 250 mg/5 mL (1987) capsule 750 mg |
| Chloramphenicol | no | no | - | no | no | - |
| Chloroquine | yes | no | tablet 250 mg | yes | no | tablet 150, 300 mg |
| Chlorpromazine | yes | yes | oral solution 40 mg/mL (1955) tablet 25, 100 mg | yes | no | tablet 10–200 mg |
| Cholecalciferol | yes | yes | oral solution 2000 UI/mL (1955) | no | no | - |
| Ciprofloxacin | yes | yes | oral suspension 100 mg/mL (1999) tablet 250–750 mg | yes | yes | oral suspension 250 mg/5 mL, 500 mg/5 mL (1997) tablet 100–750 mg |
| Clarithromycin | yes | yes | oral suspension 125 mg/5 mL, 200 mg/5 mL (2004) tablet 250, 500 mg | yes | yes | oral suspension 125 mg/5 mL, 200 mg/5 mL (2002) tablet 250, 500 mg |
| Clavulanic acid | yes | yes | oral suspension 100/12.5 mg/mL (1991) powder for oral suspension 500/125 mg and 875/125 mg (1982) tablet 500/125 mg and 875/125 mg | yes | yes | oral suspension (multiple doses) (1984) chewable tablet 200/28.5 mg, 400/57 mg (2005) tablet (250–875 mg/125 mg/mL) |
| Clindamycin | yes | no | capsule 150, 300 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 75 mg/5 mL (1986) capsule 150, 300 mg |
| Clofazimine | yes | no | capsule 50 mg | yes | no | capsule 50 mg |
| Cloxacillin | yes | yes | oral suspension 125 mg/5 mL (1965) capsule 500 mg | yes | no | capsule 125, 250, 500 mg |
| Cyclizine | yes | no | tablet 50 mg | no | no | - |
| Cyclophosphamide | yes | no | dragee 50 mg | yes | no | capsule 25, 50 mg tablet 25, 50 mg |
| Cycloserine | yes | no | capsule 250 mg | yes | no | capsule 250 mg |
| Cyclosporin A | yes | yes | oral solution 100 mg/mL (1983) capsule 25–100 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 100 mg/mL (1983) capsule 25–100 mg |
| Dapsone | yes | no | tablet 50, 100 mg | yes | no | tablet 25, 100 mg |
| Darunavir | yes | yes | oral suspension 100 mg/mL (2007) tablet 75–800 mg | yes | yes | oral suspension 100 mg/mL (2011) tablet 75–800 mg |
| Dasatinib | yes | yes | powder for oral suspension 10 mg/mL (2006) tablet 20–140 mg | yes | no | tablet 20–70 mg |
| Delamanid | yes | no | tablet 50 mg | no | no | - |
| Dexamethasone | yes | yes | oral solution 10 mg/5 mL, 20 mg/5 mL (2013) tablet 1, 4, 8 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 1 mg/mL, 0.5 mg/5 mL (1983) tablet 0.5–6 mg |
| Diazepam | yes | yes | oral solution 2 mg/mL (1965) tablet 2–25 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 1 mg/mL, 5 mg/mL (1987) tablet 2, 5, 10 mg |
| Diethylcarbamazine | no | no | tablet 100 mg | no | no | - |
| Digoxin | yes | yes | oral solution 0.05 mg/mL (1960) tablet 0.25 mg | yes | yes | oral elixir 0.05 mg/mL (2004) tablet 0.0625–0.25 mg |
| Diloxamide | no | no | - | no | no | - |
| Docusate sodium | yes | no | capsule 100 mg | no | no | - |
| Dolutegravir | no | no | tablet 10–50 mg | no | no | tablet 10–50 mg |
| Doxycycline | yes | yes | oral suspension 50 mg/5 mL (1968) tablet 100 mg capsule 100, 200 mg | yes | yes | oral suspension 25 mg/5 mL (before 1982) tablet 50–150 mg, capsule 50–100 mg |
| Efavirenz | yes | no | tablet 600 mg capsule 50–200 mg | yes | no | tablet 600 mg capsule 50–200 mg |
| Enalapril | no | no | tablet 2.5–20 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 1 mg/mL (2013) tablet 2.5–20 mg |
| Entecavir | yes | yes | oral solution 0.05 mg/mL (2006) tablet 0.5, 1 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 0.05 mg/mL (2005) tablet 0.5, 1 mg |
| Ethambutol | yes | no | dragee 400 mg | yes | no | tablet 100, 400 mg |
| Ethionamide | no | no | - | yes | no | tablet 250 mg |
| Ethosuximide | yes | yes | syrup 250 mg/5 mL (2007) capsule 250 mg | yes | yes | syrup 250 mg/5 mL (2003) capsule 250 mg |
| Etoposide | yes | no | capsule 50 mg | yes | no | capsule 50 mg |
| Fexinidazole | no | no | - | no | no | - |
| Fluconazole | yes | yes | oral suspension 200 mg/5 mL and 40 mg/5 mL, 2 mg/mL (1991) capsule 50–200 mg | yes | yes | oral suspension 200 mg/5 mL, 50 mg/5 mL (1993) tablet 50–200 mg |
| Flucytosine | no | no | - | yes | no | capsule 250, 500 mg |
| Fludrocortisone | yes | no | tablet 0.1mg | yes | no | tablet 0.1 mg |
| Fluoxetine | yes | yes | oral solution 20 mg/5 mL (2002) tablet 20 mg capsule 20, 60 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 20 mg/5 mL (1991) tablet 10–60 mg capsule 10–40 mg |
| Folic acid | yes | yes | oral solution 2.5 mg/mL (2010) tablet 0.4, 5 mg | yes | no | tablet 1 mg |
| Furosemide | yes | yes | oral solution 20 mg/5 mL and 40 mg/5 mL (1998) tablet 20, 40 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 10 mg/mL, 40 mg/5 mL (1987) tablet 20–80 mg |
| Griseofulvine | yes | no | tablet 125, 250, 500 mg | yes | yes | oral suspension 125 mg/5 mL (2005) tablet 250, 500 mg |
| Haloperidol | yes | yes | oral solution 2 mg/mL, 1 mg/mL (1994)tablet 10 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 2 mg/mL (1993)tablet 0.5–10 mg |
| Hydrochlorothiazide | yes | no | tablet 25, 50 mg | yes | no | tablet 12.5–50 mg capsule 12.5 mg |
| Hydrocortisone | yes | yes | granule formulation 0.5, 1, 2, 5 mg (2018) tablet 5–20 mg | yes | no | tablet 2.5–20 mg |
| Hydroxicarbamide | yes | no | capsule 200–500 mg | yes | no | capsule 100–1000 mg |
| Hydroxychloroquine | yes | no | tablet 200 mg | yes | no | tablet 200 mg |
| Ibuprofen | yes | yes | oral suspension 20 mg/mL, 40 mg/mL (2004) powder for oral suspension 200–600 mg (2000) tablet 200–600 mg | yes | yes | oral suspension 100 mg/5 mL (1995) chewable tablet 50, 100 mg (1998) tablet 400-800 mg |
| Imatinib | yes | no | tablet 50, 100, 400 mg capsule 100, 400 mg | yes | no | tablet 100, 400 mg |
| Isoniazid | yes | no | tablet 50, 100 mg | yes | yes | syrup 50 mg/5 mL (1983) tablet 100, 3000 mg |
| Itraconazole | yes | yes | oral solution 10 mg/mL (1996) capsule 100 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 10 mg/mL (1997) capsule 100 mg |
| Ivermectin | yes | no | tablet 3 mg | yes | no | tablet 3 mg |
| Lactulose | yes | yes | oral solution 10 g/15 mL (1992) | yes | yes | oral solution 10g/15 mL (1992) |
| Lamivudine | yes | yes | oral solution 5 mg/mL and 10 mg/mL (1996) tablet 150, 300 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 5 mg/mL and 10 mg/mL (1995) tablet 150, 300m g |
| Lamotrigine | yes | yes | chewable tablet 2, 5, 25 mg (1994) tablet 200 mg | yes | yes | chewable tablet 2, 5, 25 mg (1998) tablet 200 mg |
| Levamisole | yes | no | tablet 50 mg | no | no | - |
| Levofloxacine | yes | no | tablet 250, 500 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 250 mg/10 mL (2011) tablet 250, 500 mg |
| Levothyroxin | yes | yes | oral solution 25 mcg/5 mL (2012) tablet 25-200 mcg | yes | no | capsule 13–200 mcg |
| Linezolid | yes | yes | oral solution 100 mg/5 mL (2001) tablet 600 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 100 mg/5 mL (2000) tablet 600 mg |
| Lopinavir | yes | yes | oral solution 80 mg/5 mL (2001) tablet 100, 200 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 80 mg/5 mL (2000) tablet 100, 200 mg |
| Loratadine | yes | yes | syrup 1 mg/mL (2001) tablet 10 mg | no | no | - |
| Mebendazole | yes | yes | oral suspension 20 mg/mL (1976) tablet 100 mg | yes | no | tablet 100 mg |
| Mefloquine | yes | no | tablet 250 mg | yes | no | tablet 250 mg |
| Mercaptopurine | yes | yes | oral suspension 20 mg/mL (2012) tablet 50 mg | yes | yes | oral suspension 50 mg/mL (2014) tablet 50 mg |
| Mesna | yes | no | tablet 200, 400 mg | yes | no | tablet 400 mg |
| Metformin | yes | yes | oral solution 500 mg/5 mL (2013) powder for oral suspension 850 mg (2013) tablet 500–1000 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 500 mg/5 mL (2003) tablet 500–1000 mg |
| Methadone | yes | yes | oral solution 1 mg/mL, 5 mg/mL (2002) oral concentrate 20 mg/mL (1996) tablet 5–40mg | yes | yes | oral solution 5 mg/5 mL, 10 mg/5 mL (1982) oral concentrate 20 mg/mL (1994) tablet 5–40 mg |
| Methotrexate | yes | yes | oral solution 2 mg/mL (2017) tablet 2.5–10 mg | yes | no | tablet 2.5–15 mg |
| Methylprednisolone | yes | no | tablet 2–40 mg | yes | no | tablet 2–32 mg |
| Metoclopramide | yes | yes | oral solution 1 mg/mL (1964) tablet 5, 10 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 1 mg/mL (1993) tablet 5, 10 mg |
| Metronidazole | yes | yes | oral suspension 125 mg/5 mL, 200 mg/5 mL (1969) tablet 20–500 mg | yes | no | tablet 250, 500, 750 mg capsule 375 mg |
| Midazolam | yes | yes | oromucosal solution in syringe 5 mg/mL (2012) | yes | yes | syrup 2 mg/mL (2002) |
| Miltefosine | no | no | - | yes | no | capsule 50 mg |
| Morphine | yes | yes | oral solution (multiple doses) (2003) tablet (multiple doses) tablet extended release 5–200 mg | yes | yes | oral solution (multiple doses) (2008) tablet (multiple doses) tablet extended release 15–200 mg |
| Moxifloxacin | yes | no | tablet 400 mg | yes | no | tablet 400 mg |
| Neostigmine | yes | no | tablet 15 mg | no | no | - |
| Nevirapine | yes | yes | oral suspension 50 mg/5 mL (2000) tablet 200 mg | yes | yes | oral suspension 50 mg/5 mL (1998) tablet 200 mg |
| Niclosamide | yes | no | chewable tablet 500 mg | no | no | - |
| Nifurtimox | no | no | - | no | no | - |
| Nilotinib | yes | no | capsule 50, 150, 200 mg | yes | no | capsule 50, 150, 200 mg |
| Nitrofurantoin | yes | yes | oral suspension 25 mg/5 mL (1960) tablet 50–150 mg capsule 50–100 mg | yes | yes | oral suspension 25 mg/5 mL (before 1982) tablet 50–150 mg capsule 25–100 mg |
| Nystatin | yes | yes | oral suspension 100,000 UI/mL (1957) | yes | yes | oral suspension 100,000 UI/mL (1983) tablet 500,000 UI |
| Omeprazole | yes | no | capsule 10, 20, 40 mg | yes | yes | powder for oral suspension 2.5, 10 mg (2008) capsule 10, 20, 40 mg |
| Ondansetron | yes | yes | oral solution 4 mg/5 mL (2014) syrup 4 mg/5 mL (2011) oral soluble film 4, 8 mg (2010) tablet 4, 8 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 4 mg/5 mL (1997) oral soluble film 4, 8 mg (1999) tablet 4–24 mg |
| Oseltamivir | yes | yes | oral suspension 6 mg/mL (2012) capsule 30–75 mg | yes | yes | oral suspension 6 mg/mL (2011) capsule 30–75 mg |
| Oxamniquine | no | no | - | yes | no | capsule 250 mg |
| P-aminosalicylic acid | no | no | - | yes | yes | powder for oral suspension 4 g (1982) tablet 500, 1000 mg |
| Paracetamol (acetaminophen) | yes | yes | oral solution 100 mg/mL (1971) tablet 325–1000 mg | yes | yes | tablet 250, 650 mg |
| Phenobarbital | yes | no | tablet 15–100 mg | no | no | - |
| Phenoxymethylpenicillin potassium | yes | yes | oral solution 250 mg/5 mL, 125 mg/5 mL (2012) powder for oral solution 250 mg (1987) capsule 400 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 250 mg/5 mL, 125 mg/5 mL (before 1982) tablet 250, 500 mg |
| Phenytoin sodium | yes | yes | oral suspension 125 mg/5 mL (1992) tablet 100 mg | yes | yes | oral suspension 125 mg/5 mL (before 1982) chewable tablet 50 mg |
| Phytomenadione | yes | yes | oral solution 2 mg/0.2 mL, 10 mg/1 mL (drinkable ampoule) (1957) | yes | yes | oral solution 10 mg/1 mL (drinkable ampoule) (1983) |
| Potassium iodide | yes | no | tablet 100–300 μg | no | no | - |
| Praziquantel | no | no | - | yes | no | tablet 600 mg |
| Prednisolone | yes | yes | oral suspension 10 mg/mL, 13.33 mg/mL (1969) tablet 5–15 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 5–20 mg/5 mL (1986) tablet 10–30 mg |
| Primaquine | no | no | - | yes | no | tablet 15 mg |
| Proguanil | yes | no | tablet 100 mg (in association with atovacuone) | yes | no | tablet 100 mg (in association with atovacuone) |
| Propranolol | yes | yes | oral solution 10 mg/5 mL, 40 mg/5 mL (2000) oral solution 3.75 mg/mL (2014) tablet 10–80 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 20 mg/5 mL, 40 mg/5 mL (1987) oral solution 4 mg/mL (2014) tablet 10–80 mg |
| Propylthiouracil | yes | no | tablet 50 mg | yes | no | tablet 50 mg |
| Pyrantel | yes | yes | oral suspension 250 mg/5 mL (1972) chewable tablet 250 mg | no | no | - |
| Pyrazinamide | yes | no | tablet 250, 500 mg | yes | no | tablet 500 mg |
| Pyridostigmine | yes | yes | syrup 12 mg/mL (1982) tablet 60 mg | yes | yes | syrup 60 mg/5 mL (before 1982) tablet 60 mg |
| Pyridoxine | yes | yes | oral solution 30.7 mg/mL (1969) tablet 50, 300 mg | no | no | - |
| Pyrimethamine | yes | no | tablet 25 mg | yes | no | tablet 25 mg |
| Pyronaridine tetraphosphate | no | no | - | no | no | - |
| Quinine | yes | no | tablet 200 mg | yes | no | capsule 324 mg |
| Raltegravir | yes | yes | powder for oral suspension 100 mg (2007) chewable tablet 25, 100 mg (2013) tablet 400, 600 mg | yes | yes | powder for oral suspension 100 mg (2013) chewable tablet 25, 100 mg (2011) tablet 400, 600 mg |
| Ranitidine | yes | yes | oral solution 150mg/10mL (2007) tablet 150, 300 mg | yes | yes | syrup 15 mg/mL (2007) tablet 150, 300 mg capsule 150, 300 mg |
| Retinol | no (available in association) | no | - | no | no | - |
| Ribavirin | yes | yes | oral solution 40 mg/mL (2005) capsule 200 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 40 mg/mL (2003) tablet 200-600 mg capsule 200 mg |
| Riboflavin | no (available in association) | no | - | no (available in association) | no | - |
| Rifampicin | yes | yes | oral suspension 100 mg/mL (1968) syrup 100 mg/5 mL capsule 300 mg | yes | no | capsule 150, 300 mg |
| Rifapentine | no | no | - | yes | no | tablet 150 mg |
| Ritonavir | yes | yes | oral solution 100 mg/mL (1996) tablet 100 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 100 mg/mL (1996) tablet 100 mg |
| Spironolactone | yes | no | tablet 25, 50, 100 mg | yes | no | tablet 25, 50, 100 mg |
| Stavudine | no | no | - | yes | yes | oral solution 1 mg/mL (1996) capsule 15–40 mg |
| Succimer | no | no | - | yes | no | capsule 100 mg |
| Sulfadiazine | yes | no | tablet 500 mg | yes | no | tablet 500 mg |
| Sulfametoxazole | yes | yes | oral suspension 40 mg/mL (1968) tablet 100 mg | yes | yes | oral suspension 200 mg/5 mL (1983) tablet 400, 800 mg |
| Thiamine | yes | no | tablet 50, 100, 300 mg | no | no | - |
| Tioguanine | yes | no | tablet 40 mg | yes | no | tablet 40 mg |
| Triclabendazole | no | no | - | no | no | - |
| Trimethoprim | yes | yes | oral suspension 8 mg/mL (1974) tablet 20 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 40 mg/5 mL (2000) tablet 80, 160 mg |
| Valganciclovir | yes | yes | oral solution 50 mg/mL (2008) tablet 450 mg | yes | yes | oral solution 50 mg/mL (2009) tablet 450 mg |
| Valproic acid | yes | yes | prolonged release granules 500 mg (2006) oral solution 200 mg/mL (1970) tablet 500 mg | yes | yes | syrup 250 mg/5 mL (before 1982) capsule 250 mg |
| Voriconazole | yes | yes | oral suspension 200 mg/5 mL (2004) tablet 50, 200 mg | yes | yes | oral suspension 200 mg/5 mL (2003) tablet 50, 200 mg |
| Warfarin | yes | yes | oral suspension 1 mg/mL (2010) tablet 1–10 mg | yes | no | tablet 1–10 mg |
| Zidovudine | yes | yes | oral solution 50 mg/5 mL (1991) capsule 100, 250, 300 mg | yes | yes | syrup 50 mg/5 mL (1989) tablet 300 mg, capsule 100 mg |
| Zinc sulfate | yes | no | effervescent tablet 45 mg capsule 25 mg | no | no | - |
References
- Shirkey, H. Therapeutic orphans. J. Pediatr. 1968, 72, 119–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preis, M.; Breitkreutz, J. Pediatric Drug Development and Dosage Form Design. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 239–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasi, P.A.; Egger, G.F.; Pallidis, C.; Saint-Raymond, A. Enabling Development of Paediatric Medicines in Europe: 10 Years of the EU Paediatric Regulation. Paediatr. Drugs 2017, 19, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.M.; Davis, J.M. Challenges and opportunities to enhance global drug development in neonates. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2017, 29, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharaj, A.R.; Edginton, A.N.; Fotaki, N. Assessment of Age-Related Changes in Pediatric Gastrointestinal Solubility. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 52–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, H.K.; Fotaki, N.; Klein, S. Paediatric oral biopharmaceutics: Key considerations and current challenges. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 73, 102–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, J.-M.; Bouzom, F.; Hugues, C.; Ungell, A.-L. Oral drug absorption in pediatrics: The intestinal wall, its developmental changes and current tools for predictions. Biopharm Drug Dispos 2017, 38, 209–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, G.L.; Abdel-Rahman, S.M.; Alander, S.W.; Blowey, D.L.; Leeder, J.S.; Kauffman, R.E. Developmental pharmacology--drug disposition, action, and therapy in infants and children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Riet-Nales, D.A.; Kozarewicz, P.; Aylward, B.; de Vries, R.; Egberts, T.C.G.; Rademaker, C.M.A.; Schobben, A.F.A.M. Paediatric Drug Development and Formulation Design-a European Perspective. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daousani, C.; Karalis, V.D. Paediatric Medicines: Regulatory and Scientific Issues. Drug Res. (Stuttg) 2017, 67, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP); Paediatric Committee (PDCO). Guideline on Pharmaceutical Development of Medicines for Paediatric Use. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-pharmaceutical-development-medicines-paediatric-use_en.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2019).
- Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP); Anonymous. Formulations of choice for the paediatric population. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/formulations-choice-paediatric-population (accessed on 18 October 2019).
- Thabet, Y.; Klingmann, V.; Breitkreutz, J. Drug Formulations: Standards and Novel Strategies for Drug Administration in Pediatrics. J Clin Pharmacol 2018, 58 (Suppl. S10), S26–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickley, R.G. Pediatric Oral Formulations: An Updated Review of Commercially Available Pediatric Oral Formulations Since 2007. J Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1335–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization WHO. WHO Model Lists of Essential Medicines. Available online: http://www.who.int/medicines/publications/essentialmedicines/en/ (accessed on 16 March 2019).
- Food and Drug Administration. Orange Book: Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/ob/index.cfm (accessed on 1 July 2019).
- Agencia Española del Medicamento y Productos Sanitarios. CIMA-Centro de información de medicamentos. Available online: https://cima.aemps.es/cima/publico/home.html (accessed on 1 July 2019).
- Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency of United Kingdom Electronic Medicines Compendium (eMC). Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/ (accessed on 1 July 2019).
- Vidal Vademecum International Vademecum. Available online: https://www.vademecum.es/equivalencia (accessed on 1 July 2019).
- Engel, A.; Siderius, P.; World Health Organization; Regional Office for Europe. The Consumption of Drugs; Report on a Study, 1966–1967; Engel, A., Siderius, P., Eds.; World Health Organization, Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. ATC/DDD Classification System. Available online: http://www.who.int/medicines/regulation/medicines-safety/toolkit_methodology_history/en/ (accessed on 29 October 2019).
- Minghetti, P.; Palmieri, I.; Selmin, F. When authorized medicinal products are not available: Possible alternatives to meet legitimate expectations of patients. J. Pharm. Health Serv. Res. 2010, 1, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steven Hirschfeld, A.Z. Brief Selective History of Pediatric Initiatives in the United States of America. Available online: http://archives.who.int/eml/expcom/children/Items/USinitiatives.pdf (accessed on 19 January 2020).
- Del Moral Sanchez, J.M.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, I.; Cerda-Revert, A.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, M.; Navarro-Ruiz, A.; Amidon, G.L.; Bermejo, M. Biopharmaceutical optimization in neglected diseases for paediatric patients by applying the provisional paediatric biopharmaceutical classification system. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 2231–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batchelor, H.K.; Marriott, J.F. Formulations for children: Problems and solutions. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 79, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salunke, S.; Brandys, B.; Giacoia, G.; Tuleu, C. The STEP (Safety and Toxicity of Excipients for Paediatrics) database: Part 2—The pilot version. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 457, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajicek, A.; Fossler, M.J.; Barrett, J.S.; Worthington, J.H.; Ternik, R.; Charkoftaki, G.; Lum, S.; Breitkreutz, J.; Baltezor, M.; Macheras, P.; et al. A report from the pediatric formulations task force: Perspectives on the state of child-friendly oral dosage forms. AAPS J. 2013, 15, 1072–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- delMoral-Sanchez, J.M.; Ruiz-Picazo, A.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, M.; Navarro, A.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, I.; Bermejo, M. Impact on intestinal permeability of pediatric hyperosmolar formulations after dilution: Studies with rat perfusion method. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 557, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarmpi, P.; Flanagan, T.; Meehan, E.; Mann, J.; Fotaki, N. Biopharmaceutical aspects and implications of excipient variability in drug product performance. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 111, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, S.M.; Amidon, G.L.; Kaul, A.; Lukacova, V.; Vinks, A.A.; Knipp, G.T.; Members of the BCS Task Force. Summary of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development-best pharmaceuticals for Children Act Pediatric Formulation Initiatives Workshop-Pediatric Biopharmaceutics Classification System Working Group. Clin. Ther. 2012, 34, S11–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- delMoral-Sanchez, J.-M.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, I.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, M.; Navarro, A.; Bermejo, M. Classification of WHO Essential Oral Medicines for Children Applying a Provisional Pediatric Biopharmaceutics Classification System. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
delMoral-Sanchez, J.-M.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, I.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, M.; Navarro-Ruiz, A.; Bermejo, M. Availability of Authorizations from EMA and FDA for Age-Appropriate Medicines Contained in the WHO Essential Medicines List for Children 2019. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12040316
delMoral-Sanchez J-M, Gonzalez-Alvarez I, Gonzalez-Alvarez M, Navarro-Ruiz A, Bermejo M. Availability of Authorizations from EMA and FDA for Age-Appropriate Medicines Contained in the WHO Essential Medicines List for Children 2019. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(4):316. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12040316
Chicago/Turabian StyledelMoral-Sanchez, Jose-Manuel, Isabel Gonzalez-Alvarez, Marta Gonzalez-Alvarez, Andres Navarro-Ruiz, and Marival Bermejo. 2020. "Availability of Authorizations from EMA and FDA for Age-Appropriate Medicines Contained in the WHO Essential Medicines List for Children 2019" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 4: 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12040316
APA StyledelMoral-Sanchez, J.-M., Gonzalez-Alvarez, I., Gonzalez-Alvarez, M., Navarro-Ruiz, A., & Bermejo, M. (2020). Availability of Authorizations from EMA and FDA for Age-Appropriate Medicines Contained in the WHO Essential Medicines List for Children 2019. Pharmaceutics, 12(4), 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12040316