Biphasic Dissolution as an Exploratory Method during Early Drug Product Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Ibuprofen Immediate Release Formulations
2.2.2. Dissolution Tests
Compendial Dissolution Method
Non-Compendial Dissolution Methods—Physiologically Based Exploratory Methods
2.2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
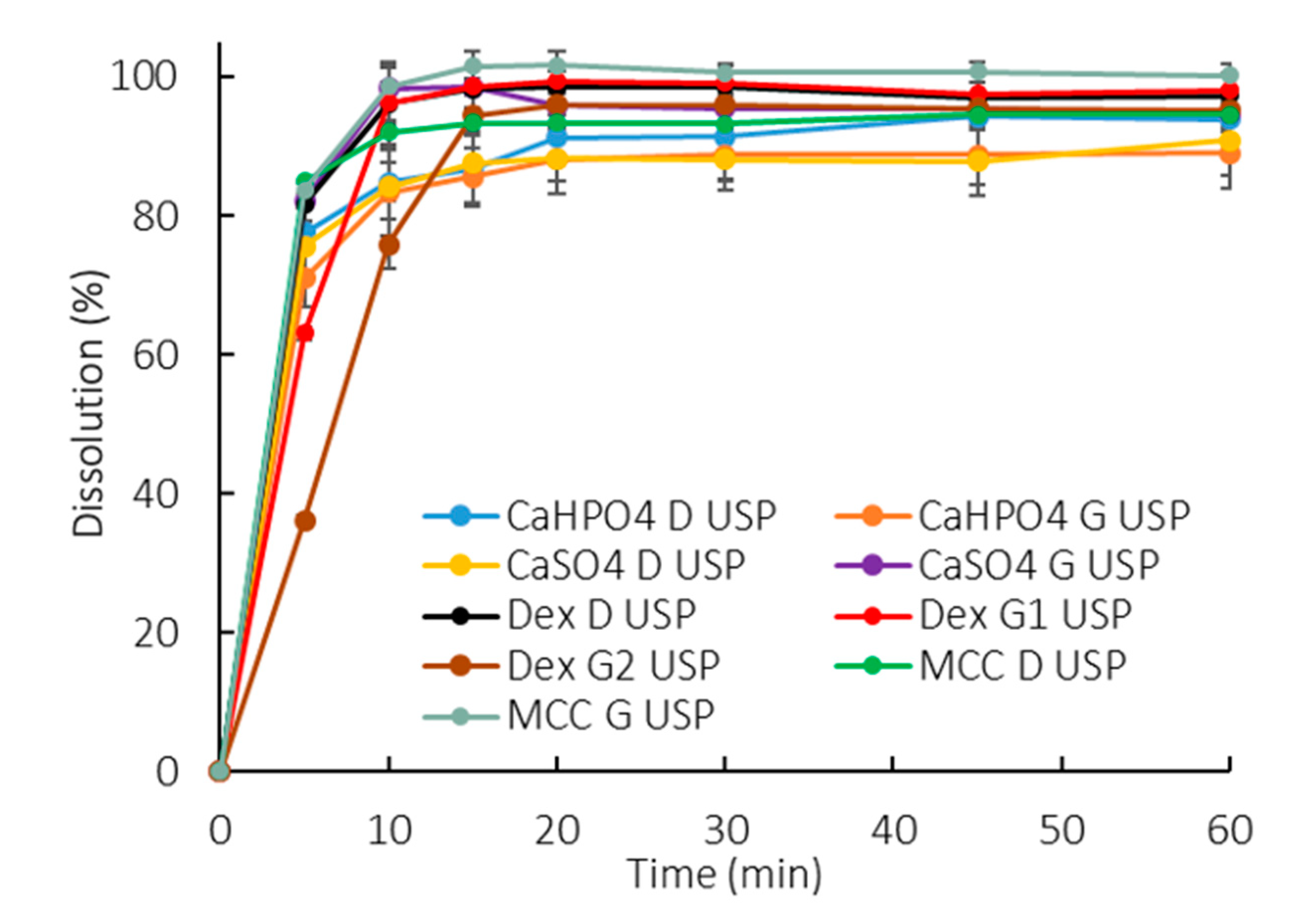
3.1. Compendial Dissolution Tests
3.2. Non-Compendial Dissolution Tests—Physiologically Based Exploratory Methods
3.2.1. Monophasic Dissolution with Low Buffer Capacity Medium
3.2.2. Biphasic Dissolution Test with Low Buffer Capacity Medium
Biphasic Dissolution with 200 mL of Aqueous Phase
Biphasic Dissolution with 900 mL of Aqueous Phase
3.2.3. Dissolution Medium pH Recovery
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations of the Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dokoumetzidis, A.; Macheras, P. A century of dissolution research: From Noyes and Whitney to the Biopharmaceutics Classification System. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 321, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abend, A.; Curran, D.; Kuiper, J.; Lu, X.; Li, H.; Hermans, A.; Kotwal, P.; Diaz, D.A.; Cohen, M.J.; Zhang, L.; et al. Dissolution Testing in Drug Product Development: Workshop Summary Report. AAPS J. 2019, 21, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, D.J.; Pygall, S.R.; Cooper, V.B.; Mann, J.C. Overcoming sink limitations in dissolution testing: A review of traditional methods and the potential utility of biphasic systems. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012, 64, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibaldi, B.M.; Feldman, S. Establishment of Sink Conditions in Dissolution Rate Determinations. J. Pharm. Sci. 1967, 56, 1238–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestieau, A.; Evrard, B. In vitro biphasic dissolution tests and their suitability for establishing in vitro-in vivo correlations: A historical review. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 102, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hens, B.; Tsume, Y.; Bermejo, M.; Paixao, P.; Koenigsknecht, M.J.; Baker, J.R.; Hasler, W.L.; Lionberger, R.; Fan, J.; Dickens, J.; et al. Low Buffer Capacity and Alternating Motility along the Human Gastrointestinal Tract: Implications for in Vivo Dissolution and Absorption of Ionizable Drugs. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 4281–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenigsknecht, M.J.; Baker, J.R.; Wen, B.; Frances, A.; Zhang, H.; Yu, A.; Zhao, T.; Tsume, Y.; Pai, M.P.; Bleske, B.E.; et al. In Vivo Dissolution and Systemic Absorption of Immediate Release Ibuprofen in Human Gastrointestinal Tract under Fed and Fasted Conditions. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 4295–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral Silva, D.; Al-Gousous, J.; Davies, N.M.; Bou Chacra, N.; Webster, G.K.; Lipka, E.; Amidon, G.; Löbenberg, R. Simulated, biorelevant, clinically relevant or physiologically relevant dissolution media: The hidden role of bicarbonate buffer. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 142, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieg, B.J.; Taghavi, S.M.; Amidon, G.L.; Amidon, G.E. In Vivo Predictive Dissolution: Comparing the Effect of Bicarbonate and Phosphate Buffer on the Dissolution of Weak Acids and Weak Bases. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 2894–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsume, Y.; Igawa, N.; Drelich, A.J.; Amidon, G.E.; Amidon, G.L. The Combination of GIS and Biphasic to Better Predict In Vivo Dissolution of BCS Class IIb Drugs, Ketoconazole and Raloxifene. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsume, Y.; Igawa, N.; Drelich, A.J.; Ruan, H.; Amidon, G.E.; Amidon, G.L. The in vivo predictive dissolution for immediate release dosage of donepezil and danazol, BCS class IIc drugs, with the GIS and the USP II with biphasic dissolution apparatus. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 100920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Shi, Y.; Vela, S.; Marroum, P.; Gao, P. Developing Quantitative In Vitro–in Vivo Correlation for Fenofibrate Immediate-Release Formulations with the Biphasic Dissolution-Partition Test Method. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Krakow, S.; Shi, Y.; Rosenberg, J.; Gao, P. In vitro characterization of ritonavir formulations and correlation to in vivo performance in dogs. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 115, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Staufenbiel, S.; Bodmeier, R. Evaluation of a biphasic in vitro dissolution test for estimating the bioavailability of carbamazepine polymorphic forms. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 105, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Staufenbiel, S.; Hao, S.; Wang, B.; Dashevskiy, A.; Bodmeier, R. Development of a discriminative biphasic in vitro dissolution test and correlation with in vivo pharmacokinetic studies for differently formulated racecadotril granules. J. Control. Release 2017, 255, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Vela, S.; Shi, Y.; Marroum, P.; Gao, P. In Vitro Characterization of Ritonavir Drug Products and Correlation to Human in Vivo Performance. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 3801–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doluisio, J.T.; Swintosky, J.V. Drug partitioning II in vitro model for drug absorption. J. Pharm. Sci. 1964, 53, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudie, D.M.; Shi, Y.; Ping, H.; Gao, P.; Amidon, G.L.; Amidon, G.E. Mechanistic analysis of solute transport in an in vitro physiological two-phase dissolution apparatus. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2012, 33, 378–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azarmi, S.; Roa, W.; Löbenberg, R. Current perspectives in dissolution testing of conventional and novel dosage forms. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 328, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalepu, S.; Nekkanti, V. Insoluble drug delivery strategies: Review of recent advances and business prospects. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- USP, United States Pharmacopeia. Rockville: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, 42nd ed.; United States Pharmacopeial Convention: Rockville, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mudie, D.M.; Murray, K.; Hoad, C.L.; Pritchard, S.E.; Garnett, M.C.; Amidon, G.L.; Gowland, P.A.; Spiller, R.C.; Amidon, G.E.; Marciani, L. Quantification of Gastrointestinal Liquid Volumes and Distribution Following a 240 mL Dose of Water in the Fasted State. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 3039–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Zou, A.; Li, W.; Yao, C.; Xie, S. DDSolver: An add-in program for modeling and comparison of drug dissolution profiles. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuo, J.; Gao, Y.; Bou-Chacra, N.; Löbenberg, R. Evaluation of the DDSolver software applications. BioMed Res. Int. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grady, H.; Elder, D.; Webster, G.K.; Mao, Y.; Lin, Y.; Flanagan, T.; Mann, J.; Blanchard, A.; Cohen, M.J.; Lin, J.; et al. Industry’s View on Using Quality Control, Biorelevant, and Clinically Relevant Dissolution Tests for Pharmaceutical Development, Registration, and Commercialization. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cristofoletti, R.; Dressman, J.B. Matching phosphate and maleate buffer systems for dissolution of weak acids: Equivalence in terms of buffer capacity of bulk solution or surface pH? Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 103, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieg, B.J. In Vivo Predictive Dissolution: Analyzing the Impact of Bicarbonate Buffer and Hydrodynamics on Dissolution. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mooney, K.G.; Mintun, M.A.; Himmelstein, K.J.; Stella, V.J. Dissolution kinetics of carboxylic acids I: Effect of pH under unbuffered conditions. J. Pharm. Sci. 1981, 70, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Gousous, J.; Sun, K.X.; McNamara, D.P.; Hens, B.; Salehi, N.; Langguth, P.; Bermejo, M.; Amidon, G.E.; Amidon, G.L. Mass Transport Analysis of the Enhanced Buffer Capacity of the Bicarbonate-CO2 Buffer in a Phase-Heterogenous System: Physiological and Pharmaceutical Significance. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 5291–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieg, B.J.; Taghavi, S.M.; Amidon, G.L.; Amidon, G.E. In vivo predictive dissolution: Transport analysis of the CO2, bicarbonate in vivo buffer system. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 3473–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Secretory Functions of the Alimentary Tract. Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology, 13th ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; Chapter 65. [Google Scholar]
- Uebbing, L.; Klumpp, L.; Webster, G.K.; Löbenberg, R. Justification of disintegration testing beyond current FDA criteria using in vitro and in silico models. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valizadeh, H.; Nokhodchi, A.; Qarakhani, N.; Zakeri-Milani, P.; Azarmi, S.; Hassanzadeh, D.; Löbenberg, R. Physicochemical Characterization of Solid Dispersions of Indomethacin with PEG 6000, Myrj 52, Lactose, Sorbitol, Dextrin, and Eudragit® E100. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2004, 30, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.A.; Webster, G.K.; Bou-chacra, N.; Löbenberg, R. The Significance of Disintegration Testing in Pharmaceutical Development. Dissolution Technol. 2018, 25, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, R.; Sheskey, P.; Owen, S. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients, 5th ed.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Baradari, H.; Damia, C.; Dutreih-colas, M.; Laborde, E.; Pécout, N.; Champion, E.; Chulia, D.; Viana, M. Calcium phosphate porous pellets as drug delivery systems: Effect of drug carrier composition on drug loading and in vitro release. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 32, 2679–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.H.; Ben-Nissan, B.; Matinlinna, J.P.; Conway, R.C. Current perspectives: Calcium phosphate nanocoatings and nanocomposite coatings in dentistry. J. Dent. Res. 2013, 92, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mccarthy, L.G.; Kosiol, C.; Healy, A.M.; Bradley, G.; Sexton, J.C.; Corrigan, I. Simulating the Hydrodynamic Conditions in the United States Pharmacopeia Paddle Dissolution Apparatus. AAPS PharmSciTech 2003, 4, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Todaro, V.; Persoons, T.; Grove, G.; Healy, A.M.; D’Arcy, D.M. Characterization and Simulation of Hydrodynamics in the Paddle, Basket and Flow-through Dissolution Testing Apparatuses—A Review. Dissolution Technol. 2017, 24, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, B. An Evaluation of the USP Dissolution Apparatus. Master’s Thesis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, M.; García, M.A.; Al-Gousous, J.; Ruiz-Picazo, A.; Thieringer, F.; Nguyen, M.A.; Månsson, W.; Galle, P.R.; Langguth, P. In vitro prediction of in vivo absorption of ibuprofen from suspensions through rational choice of dissolution conditions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 149, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjögren, E.; Abrahamsson, B.; Augustijns, P.; Becker, D.; Bolger, M.B.; Brewster, M.; Brouwers, J.; Flanagan, T.; Harwood, M.; Heinen, C.; et al. In vivo methods for drug absorption—Comparative physiologies, model selection, correlations with in vitro methods (IVIVC), and applications for formulation/API/excipient characterization including food effects. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 57, 99–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangani, S.; Li, X.; Zhou, P.; Del-Barrio, M.A.; Chiu, R.; Cauchon, N.; Gao, P.; Medina, C.; Jasti, B. Dissolution of poorly water-soluble drugs in biphasic media using USP 4 and fiber optic system. Clin. Res. Regul. Aff. 2009, 26, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Gao, P.; Gong, Y.; Ping, H. Application of a biphasic test for characterization of in vitro drug release of immediate release formulations of celecoxib and its relevance to in vivo absorption. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 1458–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestieau, A.; Lebrun, S.; Cahay, B.; Brouwers, A.; Streel, B.; Cardot, J.-M.; Evrard, B. Evaluation of different in vitro dissolution tests based on level A in vitro—In vivo correlations for fenofibrate self-emulsifying lipid-based formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 112, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Durdunji, A.; Alkhatib, H.S.; Al-Ghazawi, M. Development of a biphasic dissolution test for Deferasirox dispersible tablets and its application in establishing an in vitro-in vivo correlation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 102, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, I.; Cadwallader, D.E. Dissolution of Slightly Soluble Powders under Sink Conditions lll: Transport of Drug Solution across Screens and Membrane Barriers. J. Pharm. Sci. 1971, 60, 1496–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, I.; Cadwallader, D.E. Dissolution of Slightly Soluble Powders under Sink Conditions ll: Griseofulvin Powders. J. Pharm. Sci. 1971, 60, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Erickson, B.; Jayasankar, A.; Lu, L.; Marsh, K.; Menon, R.; Gao, P. Assessing Supersaturation and Its Impact on in Vivo Bioavailability of a Low-Solubility Compound ABT-072 wth a Dual pH, Two-Phase Dissolution Method. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2886–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| MCC D | MCC G | CaHPO4 D | CaHPO4 G | Dex D | Dex G1 | Dex G2 | CaSO4 D | CaSO4 G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avicel PH102 (800 mg) | Avicel PH102 (800 mg) | Avicel PH102 (400 mg) | Avicel PH102 (400 mg) | Avicel PH102 (400 mg) | Avicel PH102 (400 mg) | Avicel PH102 (460 mg) | Avicel PH102 (400 mg) | Avicel PH102 (400 mg) |
| Ibuprofen (400 mg) | Ibuprofen (400 mg) | Ibuprofen (400 mg) | Ibuprofen (400 mg) | Ibuprofen (400 mg) | Ibuprofen (400 mg) | Ibuprofen (400 mg) | Ibuprofen (400 mg) | Ibuprofen (400 mg) |
| CS (3%) | CS (5%) | CS (3%) | CS (5%) | CS (3%) | CS (5%) | CS (5%) | CS (3%) | CS (5%) |
| Mg Stearate (1%) | Mg Stearate (1%) | Mg Stearate (1%) | Mg Stearate (1%) | Mg Stearate (1%) | Mg Stearate (1%) | Mg Stearate (1%) | Mg Stearate (1%) | Mg Stearate (1%) |
| CaHPO4 (400 mg) | CaHPO4 (400 mg) | Dextrose (400 mg) | Dextrose (400 mg) | Dextrose (400 mg) | CaSO4 (400 mg) | CaSO4 (400 mg) | ||
| Starch 1500 (210 mg) | Starch 1500 (210 mg) | Starch 1500 (210 mg) | Starch 1500 (210 mg) | |||||
| Expected microclimate effect | ||||||||
| - | ↑ | ↓ | ↓↓ | ↑↑ | ||||
| D formulations | ||||||
| Dextrose | MCC | CaSO4 | ||||
| Org 200 | Aq 900 | Org 200 | Aq 900 | Org 200 | Aq 900 | |
| Dextrose | NA | NA | Fail | Pass | Pass | Pass |
| MCC | Fail | Pass | NA | NA | Fail | Pass |
| CaHPO4 | Fail | Fail | Fail | Fail | Fail | Fail |
| G formulations | ||||||
| CaHPO4 | MCC | CaSO4 | ||||
| Org 200 | Aq 900 | Org 200 | Aq 900 | Org 200 | Aq 900 | |
| Dex G1 | Pass | Fail | Pass | Fail | Pass | Fail |
| Dex G2 | Fail | - | Fail | - | Fail | - |
| MCC | Pass | Pass | NA | NA | Fail | Pass |
| CaHPO4 | NA | NA | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amaral Silva, D.; Al-Gousous, J.; Davies, N.M.; Bou Chacra, N.; Webster, G.K.; Lipka, E.; Amidon, G.L.; Löbenberg, R. Biphasic Dissolution as an Exploratory Method during Early Drug Product Development. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12050420
Amaral Silva D, Al-Gousous J, Davies NM, Bou Chacra N, Webster GK, Lipka E, Amidon GL, Löbenberg R. Biphasic Dissolution as an Exploratory Method during Early Drug Product Development. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(5):420. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12050420
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmaral Silva, Daniela, Jozef Al-Gousous, Neal M. Davies, Nadia Bou Chacra, Gregory K. Webster, Elke Lipka, Gordon L. Amidon, and Raimar Löbenberg. 2020. "Biphasic Dissolution as an Exploratory Method during Early Drug Product Development" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 5: 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12050420
APA StyleAmaral Silva, D., Al-Gousous, J., Davies, N. M., Bou Chacra, N., Webster, G. K., Lipka, E., Amidon, G. L., & Löbenberg, R. (2020). Biphasic Dissolution as an Exploratory Method during Early Drug Product Development. Pharmaceutics, 12(5), 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12050420










