Nano-Vesicle Based Anti-Fungal Formulation Shows Higher Stability, Skin Diffusion, Biosafety and Anti-Fungal Efficacy In Vitro
Abstract
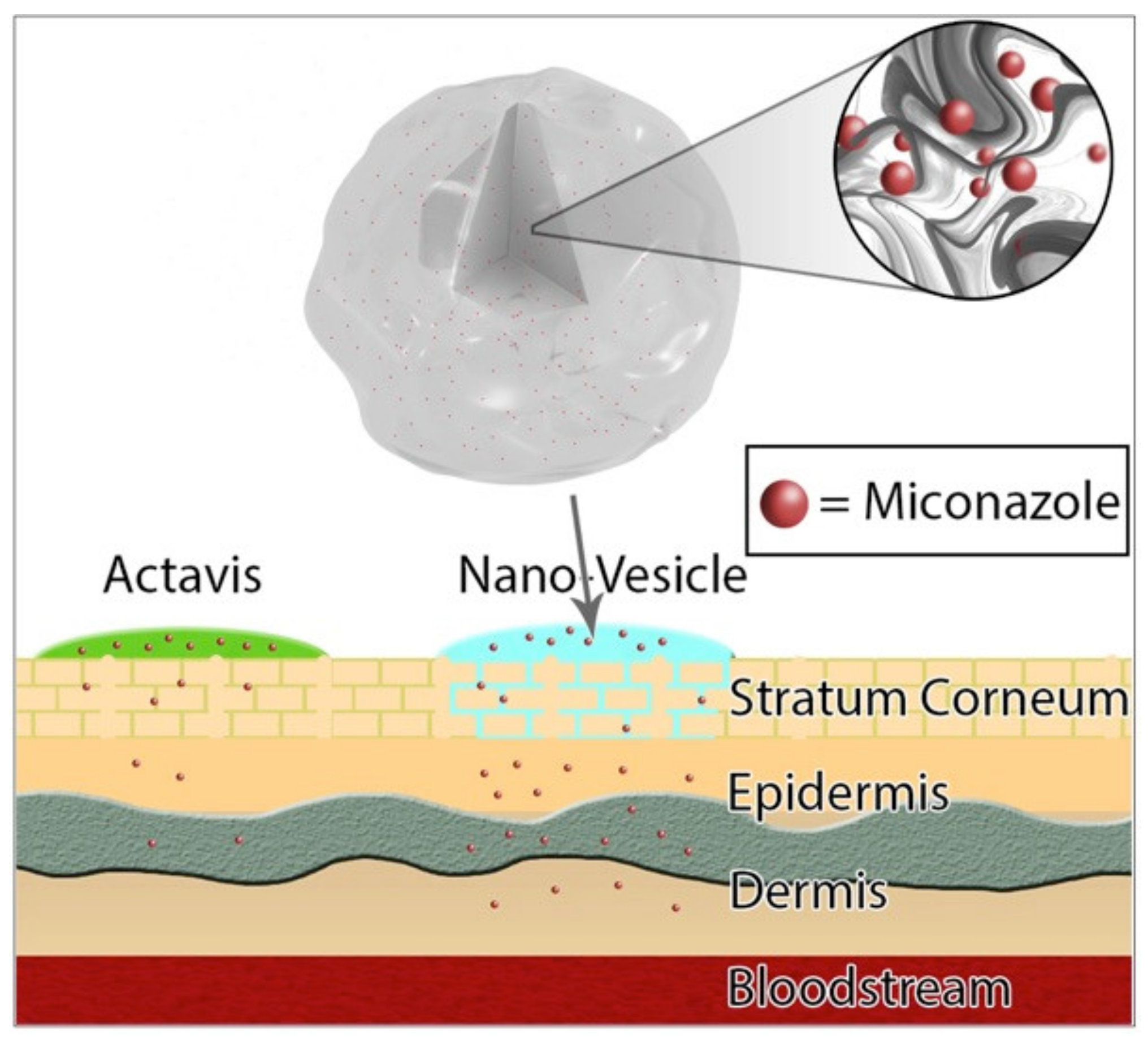
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Nano-Vesicles
2.3. Determination of Vesicle Size, Polydispersity Index, and Zeta Potential
2.4. Determination of Entrapment Efficiency
2.5. Determination of Viscosity
2.6. In Vitro Permeation Study
2.7. Separation of the SC Layer
2.8. Fungal Assay
2.9. In Vitro Cytotoxicity/Biosafety
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization
3.2. In Vitro Diffusion
3.3. Anti-Fungal Study
3.4. Cytotoxicity Biosafety Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bongomin, F.; Gago, S.; Oladele, R.O.; Denning, D.W. Global and multi-national prevalence of fungal diseases—estimate precision. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.N.; de Mello, T.P.; de Souza Ramos, L.; Branquinha, M.H.; dos Santos, A.L.S. Current Challenges and Updates on the Therapy of Fungal Infections. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nenoff, P.; Krüger, C.; Ginter-Hanselmayer, G.; Tietz, H.-J. Mycology—An update. Part 1: Dermatomycoses: Causative agents, epidemiology and pathogenesis. Jddg J. Der Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2014, 12, 188–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tainwala, R.; Sharma, Y. Pathogenesis of dermatophytoses. Indian J. Dermatol. 2011, 56, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.; Carvey, M.; Beiu, C.; Hage, R. Atypical Tinea Corporis Revealing a Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection. Cureus 2020, 12, e6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bondaryk, M.; Kurzątkowski, W.; Staniszewska, M. Antifungal agents commonly used in the superficial and mucosal candidiasis treatment: Mode of action and resistance development. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2013, 5, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Wang, C.; Zhao, R.; Du, L.; Fang, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhao, Z. Review of Stratum Corneum Impedance Measurement in Non-Invasive Penetration Application. Biosensors 2018, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Byrd, A.L.; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J.A. The human skin microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, P.R.; Brogden, R.N.; Pinder, R.M.; Speight, T.M.; Avery, G.S. Miconazole. Drugs 1975, 9, 406–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; Pradhan, H.; Mohanta, G. Concept of essential medicines and rational use in public health. Indian J. Community Med. 2010, 35, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roemer, T.; Krysan, D.J. Antifungal Drug Development: Challenges, Unmet Clinical Needs, and New Approaches. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a019703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firooz, A.; Namdar, R.; Nafisi, S.I.; Maibach, H. Nano-Sized Technologies for Miconazole Skin Delivery. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2016, 17, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenechukwu, F.C.; Attama, A.A.; Ibezim, E.C.; Nnamani, P.O.; Umeyor, C.E.; Uronnachi, E.M.; Momoh, M.A.; Akpa, P.A.; Ozioko, A.C. Novel Intravaginal Drug Delivery System Based on Molecularly PEGylated Lipid Matrices for Improved Antifungal Activity of Miconazole Nitrate. Biomed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bellmann, R.; Smuszkiewicz, P. Pharmacokinetics of antifungal drugs: Practical implications for optimized treatment of patients. Infection 2017, 45, 737–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolla, P.K.; Meraz, C.A.; Rodriguez, V.A.; Deaguero, I.; Singh, M.; Yellepeddi, V.K.; Renukuntla, J. Clotrimazole Loaded Ufosomes for Topical Delivery: Formulation Development and In-Vitro Studies. Molecules 2019, 24, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boer, M.; Duchnik, E.; Maleszka, R.; Marchlewicz, M. Structural and biophysical characteristics of human skin in maintaining proper epidermal barrier function. Postep. Dermatol. I Alergol. 2016, 33, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.B.; Martin, G.P.; Jones, S.A.; Akomeah, F.K. Dermal and Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems: Current and Future Prospects. Drug Deliv. 2006, 13, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lademann, J.; Richter, H.; Schanzer, S.; Knorr, F.; Meinke, M.; Sterry, W.; Patzelt, A. Penetration and storage of particles in human skin: Perspectives and safety aspects. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 77, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalekar, M.R.; Pokharkar, V.; Madgulkar, A.; Patil, N.; Patil, N. Preparation and evaluation of miconazole nitrate-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for topical delivery. Aaps Pharmscitech 2009, 10, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaszuba, M.; Corbett, J.; Watson, F.M.; Jones, A. High-concentration zeta potential measurements using light-scattering techniques. Philos. Trans. A. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2010, 368, 4439–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, P.-F.; Lu, X.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Yuan, H.-L.; Zhu, W.-F.; Zheng, Q.; Yang, M. The study on the entrapment efficiency and in vitro release of puerarin submicron emulsion. Aaps Pharmscitech 2009, 10, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.S.; Cho, K.J.; Tran, T.H.; Nurunnabi, M.; Moon, T.H.; Hong, S.M.; Lee, Y.K. In vivo NIR imaging with CdTe/CdSe quantum dots entrapped in PLGA nanospheres. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 353, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, I.S.; Cho, M.O.; Li, Z.; Nurunnabi, M.; Park, S.Y.; Kang, S.-W.W.; Huh, K.M. Synthesis and characterization of a new photo-crosslinkable glycol chitosan thermogel for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 144, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jothishankar, B.; Stein, S.L. Impact of skin color and ethnicity. Clin. Dermatol. 2019, 37, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SANYAL, D.C.; MAJI, N.K. Thermoregulation through Skin under Variable Atmospheric and Physiological Conditions. J. Theor. Biol. 2001, 208, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lademann, J.; Jacobi, U.; Surber, C.; Weigmann, H.-J.; Fluhr, J.W. The tape stripping procedure—evaluation of some critical parameters. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Lee, S.C.; Casadevall, A. Antibodies to Cryptococcus neoformans glucuronoxylomannan enhance antifungal activity of murine macrophages. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 57–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chun, C.D.; Madhani, H.D. Applying genetics and molecular biology to the study of the human pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans. Methods Enzymol. 2010, 470, 797–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cairns, T.C.; Feurstein, C.; Zheng, X.; Zheng, P.; Sun, J.; Meyer, V. A quantitative image analysis pipeline for the characterization of filamentous fungal morphologies as a tool to uncover targets for morphology engineering: A case study using aplD in Aspergillus niger. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeGraff, W.G.; Mitchell, J.B. Evaluation of a Tetrazolium-based Semiautomated Colorimetric Assay: Assessment of Chemosensitivity Testing. Cancer Res. 1987, 47, 936–942. [Google Scholar]
- Khatun, Z.; Nurunnabi, M.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Byun, Y.; Cho, K.J.; Lee, Y. kyu Optical imaging, biodistribution and toxicity of orally administered quantum dots loaded heparin-deoxycholic acid. Macromol. Res. 2015, 23, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Román, R.; Naik, A.; Kalia, Y.N.; Guy, R.H.; Fessi, H. Skin penetration and distribution of polymeric nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2004, 99, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavano, L.; Mazzotta, E.; Muzzalupo, R. Innovative topical formulations from diclofenac sodium used as surfadrug: The birth of Diclosomes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 164, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Nobes, D.S.; Vehring, R. Particle Surface Roughness Improves Colloidal Stability of Pressurized Pharmaceutical Suspensions. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljaeid, B.; Hosny, K.M. Miconazole-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: Formulation and evaluation of a novel formula with high bioavailability and antifungal activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shaker, D.S.; Ishak, R.A.H.; Ghoneim, A.; Elhuoni, M.A. Nanoemulsion: A Review on Mechanisms for the Transdermal Delivery of Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Drugs. Sci. Pharm. 2019, 87, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, M.; Stracke, F.; Hansen, S.; Schaefer, U.F. Nanoparticles and their interactions with the dermal barrier. Dermatoendocrinol. 2009, 1, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alkilani, A.Z.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Donnelly, R.F. Transdermal Drug Delivery: Innovative Pharmaceutical Developments Based on Disruption of the Barrier Properties of the stratum corneum. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 438–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, S.; Utreja, P. Vesicular nanocarrier based treatment of skin fungal infections: Potential and emerging trends in nanoscale pharmacotherapy. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 14, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Langer, R. Transdermal drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.; Rajanahalli, P.; Ahamed, M.; Rowe, J.; Hong, Y. ZnO nanoparticles induce apoptosis in human dermal fibroblasts via p53 and p38 pathways. Toxicol. Vitr. 2011, 25, 1721–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Formulations | Miconazole (mg) | Cholesterol (mg) | Sodium Oleate (mg) | Miconazole Loading Efficiency (%) | Size Distribution (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:0.5:1 | 100 | 50 | 100 | 43.9 ± 7.8 | 252 ± 62 | 76 ± 5 |
| 1:1:0.5 | 100 | 100 | 50 | 59.7 ± 3.3 | 337 ± 58 | 85 ± 3 |
| 1:1:1 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 3.1 ± 0.5 | 383 ± 103 | 88 ± 5 |
| 1:2:1 | 100 | 200 | 100 | 3.1 ± 0.6 | 269 ± 57 | 93 ± 4 |
| 1:1:2 | 100 | 100 | 200 | 3.3 ± 0.6 | 308 ±79 | 74 ± 7 |
| 1:2:2 | 100 | 200 | 200 | 3.4 ± 0.5 | 372 ± 135 | 64 ± 7 |
| Ethnicity | Gender | Age | BMI | Stretch Marks | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caucasian | Male | 24 | 29.9 | Severe | Abdomen |
| African/Black | Female | 43 | 26.9 | Severe | Abdomen |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deaguero, I.G.; Huda, M.N.; Rodriguez, V.; Zicari, J.; Al-Hilal, T.A.; Badruddoza, A.Z.M.; Nurunnabi, M. Nano-Vesicle Based Anti-Fungal Formulation Shows Higher Stability, Skin Diffusion, Biosafety and Anti-Fungal Efficacy In Vitro. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060516
Deaguero IG, Huda MN, Rodriguez V, Zicari J, Al-Hilal TA, Badruddoza AZM, Nurunnabi M. Nano-Vesicle Based Anti-Fungal Formulation Shows Higher Stability, Skin Diffusion, Biosafety and Anti-Fungal Efficacy In Vitro. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(6):516. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060516
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeaguero, Isaac G., Md Nurul Huda, Victor Rodriguez, Jade Zicari, Taslim A. Al-Hilal, Abu Zayed Md Badruddoza, and Md Nurunnabi. 2020. "Nano-Vesicle Based Anti-Fungal Formulation Shows Higher Stability, Skin Diffusion, Biosafety and Anti-Fungal Efficacy In Vitro" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 6: 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060516
APA StyleDeaguero, I. G., Huda, M. N., Rodriguez, V., Zicari, J., Al-Hilal, T. A., Badruddoza, A. Z. M., & Nurunnabi, M. (2020). Nano-Vesicle Based Anti-Fungal Formulation Shows Higher Stability, Skin Diffusion, Biosafety and Anti-Fungal Efficacy In Vitro. Pharmaceutics, 12(6), 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060516






