Elucidation of Inverse Agonist Activity of Bilastine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Intracellular Ca2+ Measurement Ca2+ Imaging
2.3. Measurement of [3H]-Inositol Phosphates Formation
2.4. Real-Time Quantitative RT-PCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
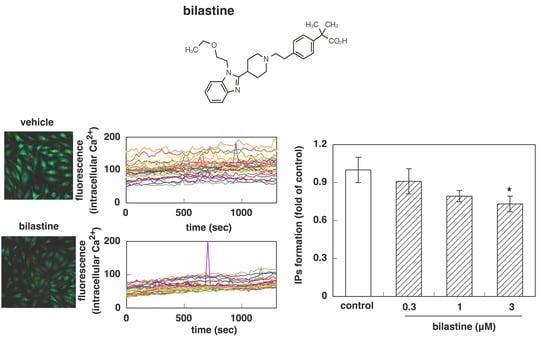
3.1. Effect of Bilastine on Intracellular Ca2+ Elevation by Constitutive and Agonist-Induced H1R Activation
3.2. Effect of Bilastine on IPs Accumulation by Constitutive and Agonist-Induced H1R Activation
3.3. Effect of Bilastine on Constitutive H1R Gene Expression
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Okubo, K.; Kurono, Y.; Ichimura, K.; Enomoto, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Kawauchi, H.; Suzaki, H.; Fujieda, S.; Masuyama, K. Japanese Society of Allergology: Japanese guidelines for allergic rhinitis. Allrgol. Int. 2017, 66, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuguchi, H.; Hatano, M.; Matsushita, C.; Umehara, H.; Kuroda, W.; Kitamura, Y.; Takeda, N.; Fukui, H. Repeated pretreatment with antihistamines suppresses transcriptional upregulations of histamine H1 receptor and interleukin-4 genes in toluene-2,4-diisocyanate-sensitized rats. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 108, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mizuguchi, H.; Kitamura, Y.; Kondo, Y.; Kuroda, W.; Yoshida, H.; Miyamoto, Y.; Hattori, M.; Fukui, H.; Takeda, N. Preseasonal prophylactic treatment with antihistamines suppresses nasal symptoms and expression of histamine H1 receptor mRNA in the nasal mucosa of patients with pollinosis. Methods Find Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2010, 32, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, Y.; Nakagawa, H.; Fujii, T.; Sakoda, T.; Enomoto, T.; Mizuguchi, H.; Fukui, H.; Takeda, N. Effects of antihistamine on up-regulation of histamine H1 receptor mRNA in the nasal mucosa of patients with pollinosis induced by controlled cedar pollen challenge in an environmental exposure unit. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 129, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mizuguchi, H.; Terao, T.; Kitai, M.; Ikeda, M.; Yoshimura, Y.; Das, A.K.; Kitamura, Y.; Takeda, N.; Fukui, H. Involvement of Protein Kinase C/Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase/Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase-1 (PARP-1) Signaling Pathway in Histamine-induced Up-regulation of Histamine H1 Receptor Gene Expression in HeLa Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 30542–30551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mizuguchi, H.; Nariai, Y.; Kato, S.; Nakano, T.; Kanayama, T.; Kashiwada, Y.; Nemoto, H.; Kawazoe, K.; Takaishi, Y.; Kitamura, Y.; et al. Maackiain is a novel antiallergic compound that suppresses transcriptional upregulation of the histamine H1 receptor and interleukin-4 genes. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e00166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nariai, Y.; Mizuguchi, H.; Ogasawara, T.; Nagai, H.; Sasaki, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Yoshimura, Y.; Kitamura, Y.; Nemoto, H.; Takeda, N.; et al. Disruption of Heat Shock Protein 90 (Hsp90)-Protein Kinase Cδ (PKCδ) Interaction by (−)-Maackiain Suppresses Histamine H1 Receptor Gene Transcription in HeLa Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 27393–27402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leurs, R.; Church, M.K.; Taglialatela, M. H1-antihistamines: Inverse agonism, anti-inflammatory actions and cardiac effects. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2002, 32, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuguchi, H.; Ono, S.; Hattori, M.; Fukui, H. Inverse agonistic activity of antihistamines and suppression of histamine H1 receptor gene expression. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 118, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mizuguchi, H.; Ono, S.; Hattori, M.; Sasaki, Y.; Fukui, H. Usefulness of HeLa cells to evaluate inverse agonistic activity of antihistamines. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 15, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadakata, H.; Mizuguchi, H.; Fukui, H. Suppressive effect of epinastine on intracellular Ca2+ elevation by histamine-independent activation of histamine H1 receptor. Allergol. Immunol. 2017, 24, 122–126. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Corcostegui, R.; Labeaga, L.; Innerarity, A.; Berisa, A.; Orjales, A. Preclinical pharmacology of bilastine, a new selective histamine H1 receptor antagonist: Receptor selectivity and in vitro antihistaminic activity. Drugs R D 2005, 6, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcostegui, R.; Labeaga, L.; Innerarity, A.; Berisa, A.; Orjales, A. In vivo pharmacological characterisation of bilastine, a potent and selective histamine H1 receptor antagonist. Drugs R D 2006, 7, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, K.; Yoshikawa, T.; Yanai, A.; Nakamura, T.; Ilda, T.; Leurs, R.; Tashiro, M. The clinical pharmacology of non-sedating antihistamines. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 178, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet, J.; Khaltaev, N.; Cruz, A.A.; Denburg, J.; Fokkens, W.J.; Togias, A.; Zuberbier, T.; Baena-Cagnani, C.E.; Canonica, G.W.; Van Weel, C.; et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) 2008. Allergy 2008, 63, 8–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Das, A.K.; Yoshimura, S.; Mishima, R.; Fujimoto, K.; Mizuguchi, H.; Dev, S.; Wakayama, Y.; Kitamura, Y.; Horio, S.; Takeda, N.; et al. Stimulation of histamine H1 receptor up-regulates histamine H1 receptor itself through activation of receptor gene transcription. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 103, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, R.L.; Anthes, J.C.; Kreutner, W.; Harris, A.G.; West, R.E., Jr. Desloratadine inhibits constitutive and histamine-stimulated nuclear factor-kB activity consistent with inverse agonism at the histamine H1 receptor. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2004, 135, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, T.; Shiroishi, M.; Weyand, S.; Tsujimoto, H.; Winter, G.; Katritch, V.; Abagyan, R.; Cherezov, V.; Liu, W.; Han, G.W.; et al. Structure of the human histamine H1 receptor complex with doxepin. Nature 2011, 475, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakker, R.A.; Jongejan, A.; Sansuk, K.; Hacksell, U.; Timmerman, H.; Brann, M.R.; Weiner, D.M.; Pardo, L.; Leurs, R. Constitutively active mutants of the histamine H1 receptor suggest a conserved hydrophobic asparagine-cage that constrains the activation of class A G protein-coupled receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 73, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakker, R.A.; Schoonus, S.B.J.; Smit, M.J.; Timmmerman, H.; Leurs, R. Histamine H1-receptor activation of nuclear factor-κB: Roles of Gβγ- and Gαq/11-subunits in constitutive and agonist-mediated signaling. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 60, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridolo, E.; Montagni, M.; Bonzano, L.; Incorvaia, C.; Canonica, G.W. Bilastine: New insight into antihistamine treatment. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2015, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fonquerna, S.; Miralpeix, M.; Pagès, L.; Puig, C.; Cardús, A.; Antón, F.; Cárdenas, Á.; Vilella, D.; Aparici, M.; Calaf, E.; et al. Synthesis and Structure-Activity Relationships of Novel Histamine H1 Antagonists: Indolylpiperidinyl Benzoic Acid Derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 6326–6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosma, R.; van den Bor, J.; Vischer, H.F.; Labeaga, L.; Leurs, R. The long duration of action of the second generation antihistamine bilastine coincides with its long residence time at the histamine H1 receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 838, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawauchi, H.; Yanai, K.; Wang, D.Y.; Itahashi, K.; Okubo, K. Antihistamines for allergic rhinitis treatment from the viewpoint of nonsedative properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mizuguchi, H.; Wakugawa, T.; Sadakata, H.; Kamimura, S.; Takemoto, M.; Nakagawa, T.; Yabumoto, M.; Kitamura, Y.; Takeda, N.; Fukui, H. Elucidation of Inverse Agonist Activity of Bilastine. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060525
Mizuguchi H, Wakugawa T, Sadakata H, Kamimura S, Takemoto M, Nakagawa T, Yabumoto M, Kitamura Y, Takeda N, Fukui H. Elucidation of Inverse Agonist Activity of Bilastine. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(6):525. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060525
Chicago/Turabian StyleMizuguchi, Hiroyuki, Tomoharu Wakugawa, Hisato Sadakata, Seiichiro Kamimura, Mai Takemoto, Tomomi Nakagawa, Masami Yabumoto, Yoshiaki Kitamura, Noriaki Takeda, and Hiroyuki Fukui. 2020. "Elucidation of Inverse Agonist Activity of Bilastine" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 6: 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060525
APA StyleMizuguchi, H., Wakugawa, T., Sadakata, H., Kamimura, S., Takemoto, M., Nakagawa, T., Yabumoto, M., Kitamura, Y., Takeda, N., & Fukui, H. (2020). Elucidation of Inverse Agonist Activity of Bilastine. Pharmaceutics, 12(6), 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060525