pH-Sensitive Folic Acid Conjugated Alginate Nanoparticle for Induction of Cancer-Specific Fluorescence Imaging
Abstract
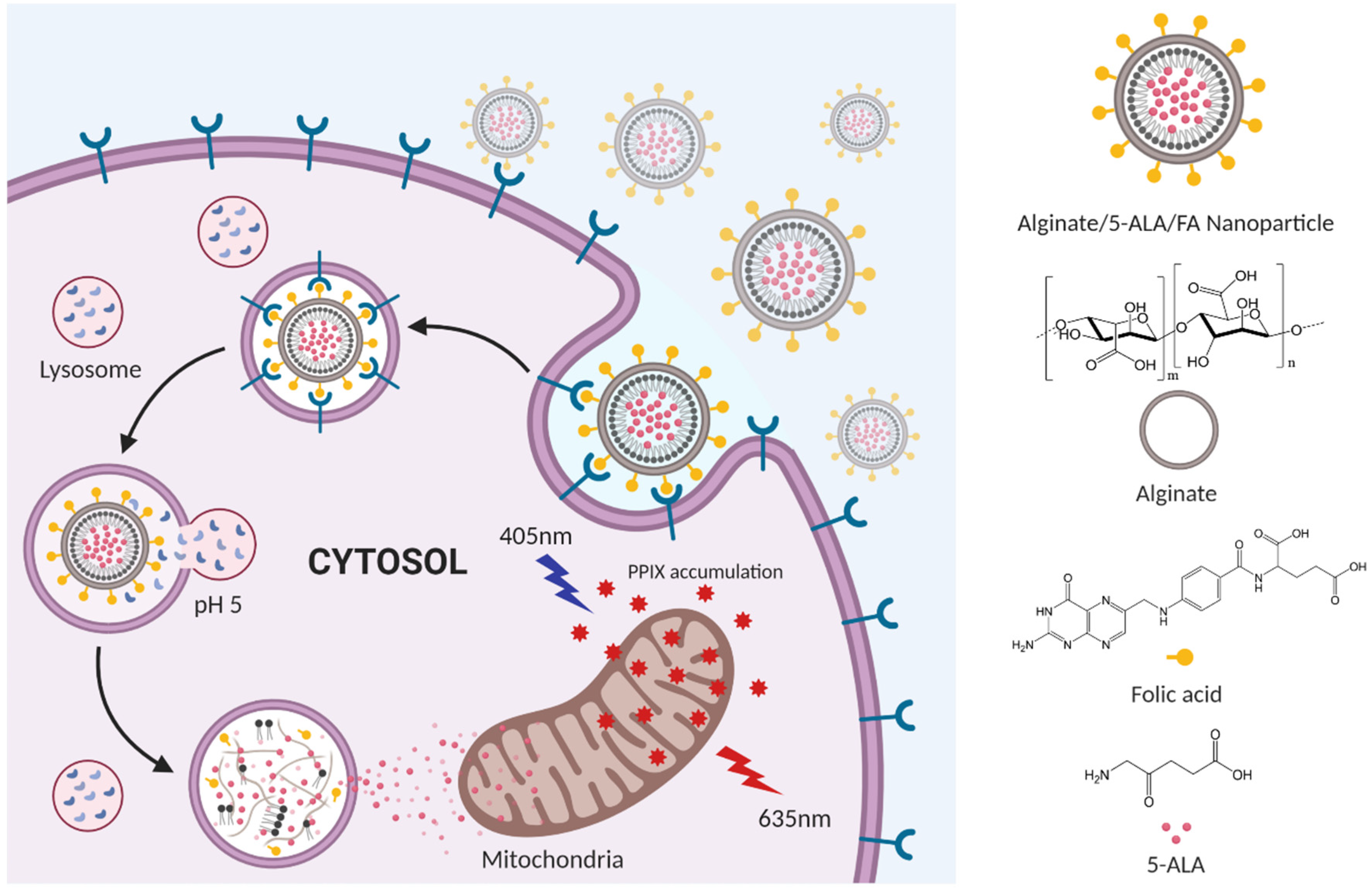
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of AF
2.3. Preparation of 5ALA Loaded NPs
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Encapsulation Efficiency and 5ALA Release Profiles
2.6. Cell Culture
2.7. Quantification of PpIX
2.8. Cytotoxicity
2.9. Cellular Internalization and Fluorescence Image of PpIX Generation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of AF
3.2. Stability and Physical Characterization of AF NPs
3.3. Release Profiles of 5ALA
3.4. Quantitative Measurement of Generated PpIX and Cytotoxicity
3.5. Cellular Internalization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, Q.; Deng, Y.; Chen, X.; Ji, J. Rational Design of Cancer Nanomedicine for Simultaneous Stealth Surface and Enhanced Cellular Uptake. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 954–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjornmalm, M.; Thurecht, K.J.; Michael, M.; Scott, A.M.; Caruso, F. Bridging Bio-Nano Science and Cancer Nanomedicine. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 9594–9613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratiwi, F.W.; Kuo, C.W.; Chen, B.C.; Chen, P.L. Recent advances in the use of fluorescent nanoparticles for bioimaging. Nanomedicine-UK 2019, 14, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Yang, M.; Duan, Y.X. Chemistry, Biology, and Medicine of Fluorescent Nanomaterials and Related Systems: New Insights into Biosensing, Bioimaging, Genomics, Diagnostics, and Therapy. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 6130–6178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostinis, P.; Berg, K.; Cengel, K.A.; Foster, T.H.; Girotti, A.W.; Gollnick, S.O.; Hahn, S.M.; Hamblin, M.R.; Juzeniene, A.; Kessel, D.; et al. Photodynamic therapy of cancer: An update. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 250–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, D.; Hervey-Jumper, S.L.; Chang, S.; Molinaro, A.M.; McDermott, M.W.; Phillips, J.J.; Berger, M.S. A prospective Phase II clinical trial of 5-aminolevulinic acid to assess the correlation of intraoperative fluorescence intensity and degree of histologic cellularity during resection of high-grade gliomas. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 124, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, D.; Zhang, J.; Bu, W.; Xing, H.; Han, F.; Xiao, Q.; Yao, Z.; Chen, F.; He, Q.; Liu, J.; et al. Dual-targeting upconversion nanoprobes across the blood-brain barrier for magnetic resonance/fluorescence imaging of intracranial glioblastoma. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.R.; Schroeder, A.B.; Grudzinski, J.J.; Rosenthal, E.L.; Warram, J.M.; Pinchuk, A.N.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Kuo, J.S.; Weichert, J.P. Beyond the margins: Real-time detection of cancer using targeted fluorophores. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guarino, V.; Caputo, T.; Altobelli, R.; Ambrosio, L. Degradation properties and metabolic activity of alginate and chitosan polyelectrolytes for drug delivery and tissue engineering applications. AIMS Mater. Sci. 2015, 2, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miao, T.; Fenn, S.L.; Charron, P.N.; Oldinski, R.A. Self-Healing and Thermoresponsive Dual-Cross-Linked Alginate Hydrogels Based on Supramolecular Inclusion Complexes. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 3740–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pawar, S.N.; Edgar, K.J. Alginate derivatization: A review of chemistry, properties and applications. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3279–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haug, A.; Myklestad, S.; Larsen, B.; Smidsrod, O. Correlation between Chemical Structure and Physical Properties of Alginates. Acta Chem. Scand. 1967, 21, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pizzuti, V.J.; Misra, R.; Lee, J.; Torregrosa-Allen, S.E.; Currie, M.P.; Clark, S.R.; Patel, A.P.; Schorr, C.R.; Jones-Hall, Y.; Childress, M.O.; et al. Folic Acid-Conjugated Radioluminescent Calcium Tungstate Nanoparticles as Radio-Sensitizers for Cancer Radiotherapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 4776–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leamon, C.P.; Reddy, J.A. Folate-targeted chemotherapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1127–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.K.; Park, J.; Jon, S. Targeting Strategies for Multifunctional Nanoparticles in Cancer Imaging and Therapy. Theranostics 2012, 2, 3–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gazzali, A.M.; Lobry, M.; Colombeau, L.; Acherar, S.; Azais, H.; Mordon, S.; Arnoux, P.; Baros, F.; Vanderesse, R.; Frochot, C. Stability of folic acid under several parameters. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 93, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.J.; Ahamed, M.; Alhadlaq, H.A.; Alrokayan, S.A.; Kumar, S. Targeted anticancer therapy: Overexpressed receptors and nanotechnology. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 436, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, P.S.; Antony, A.C. Folate receptor-targeted drugs for cancer and inflammatory diseases—Preface. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2004, 56, 1055–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kohler, N.; Zhang, M.Q. Surface modification of superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles and their intracellular uptake. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.K.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, Y.M. Preparation and characterization of methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)/poly(epsilon-caprolactone) amphiphilic block copolymeric nanospheres for tumor-specific folate-mediated targeting of anticancer drugs. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, S.; Knap, B.; Przystupski, D.; Saczko, J.; Kedzierska, E.; Knap-Czop, K.; Kotlinska, J.; Michel, O.; Kotowski, K.; Kulbacka, J. Photodynamic therapy–mechanisms, photosensitizers and combinations. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.J.; Jin, Q.; Wang, H.B.; Teng, W.Z.; Wu, J.; Tong, H.X.; Chen, T.T.; Ji, J. Intracellular Dual Fluorescent Lightup Bioprobes for Image-Guided Photodynamic Cancer Therapy. Small 2016, 12, 3870–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachar, M.; Anderson, K.E.; Ma, X. Protoporphyrin IX: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 356, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.N.; Han, H.J.; Jin, Q.; Li, Z.H.; Li, H.; Ji, J. Design and Proof of Programmed 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Prodrug Nanocarriers for Targeted Photodynamic Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 14596–14605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.J.; Lin, F.H.; Tsai, H.M.; Lin, C.F.; Chin, H.C.; Wong, J.M.; Shieh, M.J. Alginate-folic acid-modified chitosan nanoparticles for photodynamic detection of intestinal neoplasms. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2174–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.; Kim, G.; Jeong, S.; Lee, B.; Kim, S.; Koh, W.G.; Lee, K. Cancer Selective Turn-On Fluorescence Imaging Using a Biopolymeric Nanocarrier. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.N.; Edgar, K.J. Chemical modification of alginates in organic solvent systems. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 4095–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapishon, V.; Whitney, R.A.; Champagne, P.; Cunningham, M.F.; Neufeld, R.J. Polymerization Induced Self-Assembly of Alginate Based Amphiphilic Graft Copolymers Synthesized by Single Electron Transfer Living Radical Polymerization. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 2040–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, K.L.; Jagadeeshan, S.; Nair, S.A.; Kumar, G.S.V. Folic Acid Conjugated delta-Valerolactone-Poly(ethylene glycol) Based Triblock Copolymer as a Promising Carrier for Targeted Doxorubicin Delivery. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu-Quang, H.; Vinding, M.S.; Nielsen, T.; Ullisch, M.G.; Nielsen, N.C.; Nguyen, D.T.; Kjems, J. Pluronic F127-Folate Coated Super Paramagenic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Contrast Agent for Cancer Diagnosis in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Polymers 2019, 11, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Rana, S.; Srivastava, R.S.; Misra, R.D. On the chemical synthesis and drug delivery response of folate receptor-activated, polyethylene glycol-functionalized magnetite nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmento, B.; Ferreira, D.; Veiga, F.; Ribeiro, A. Characterization of insulin-loaded alginate nanoparticles produced by ionotropic pre-gelation through DSC and FTIR studies. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 66, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Z.F.; Wang, Q.; Du, Y.M. Alginate/gelatin blend films and their properties for drug controlled release. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 280, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, G.T.; Morris, E.R.; Rees, D.A.; Smith, P.J.C.; Thom, D. Biological Interactions between Polysaccharides and Divalent Cations: Egg-Box Model. FEBS Lett. 1973, 32, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, W.; Kim, B.Y.S.; Rutka, J.T.; Chan, W.C.W. Nanoparticle-mediated cellular response is size-dependent. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chithrani, B.D.; Ghazani, A.A.; Chan, W.C.W. Determining the size and shape dependence of gold nanoparticle uptake into mammalian cells. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, A.; Pavelkova, A.; Postnikov, P.S.; Sedlarik, V. Enhancement of 5-aminolevulinic acid phototoxicity by encapsulation in polysaccharides based nanocomplexes for photodynamic therapy application. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2017, 175, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Kaul, S.C.; Wadhwa, R.; Miyako, E. Folic Acid Receptor-Mediated Targeting Enhances the Cytotoxicity, Efficacy, and Selectivity of Withania somnifera Leaf Extract: In vitro and in vivo Evidence. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Qu, Q.; Zhao, Y. Targeted delivery of 5-aminolevulinic acid by multifunctional hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for photodynamic skin cancer therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 10671–10676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.W.; Zhang, J.L.; Shi, L.H.; Xian, M.; Dong, C.; Shuang, S.M. Folic acid-conjugated carbon dots as green fluorescent probes based on cellular targeting imaging for recognizing cancer cells. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 42159–42167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Lee, K. pH-Sensitive Folic Acid Conjugated Alginate Nanoparticle for Induction of Cancer-Specific Fluorescence Imaging. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060537
Lee S, Lee K. pH-Sensitive Folic Acid Conjugated Alginate Nanoparticle for Induction of Cancer-Specific Fluorescence Imaging. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(6):537. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060537
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sara, and Kangwon Lee. 2020. "pH-Sensitive Folic Acid Conjugated Alginate Nanoparticle for Induction of Cancer-Specific Fluorescence Imaging" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 6: 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060537
APA StyleLee, S., & Lee, K. (2020). pH-Sensitive Folic Acid Conjugated Alginate Nanoparticle for Induction of Cancer-Specific Fluorescence Imaging. Pharmaceutics, 12(6), 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060537





