How Do Orodispersible Tablets Behave in an In Vitro Oral Cavity Model: A Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
Materials
3. Disintegration Testing Using the Oral Cavity Model
4. Disintegration Testing Using the European Pharmacopoeia Methodology
5. Results and Discussion
6. Disintegration Testing Using the European Pharmacopoeia Methodology
7. Disintegration Testing Using the Oral Cavity Model
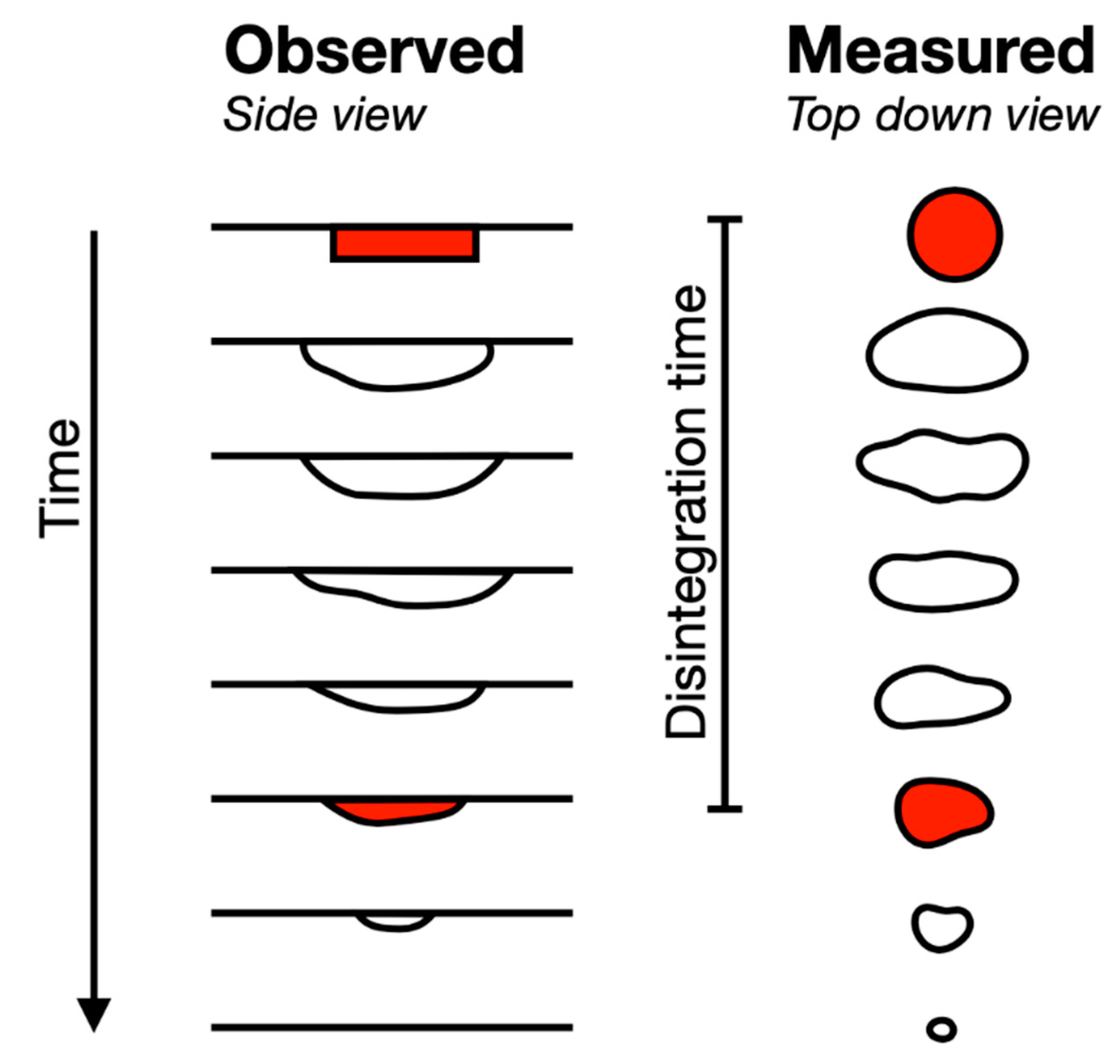
- The later time is assumed to correspond to ODT thin film formation and contact with the palate—as per the observation made during the experimental procedure (Figure 3, left).
- The very small areas became erratic and deviations became larger, particularly on thin layer formation, as this would break up, becoming difficult to determine/measure using edge detection.
- Provision of a consistent measure for a trend seen for all three ODTs.
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neos Therapeutics Brands. Highlights of Prescribing Information Cotempla XR-ODT. FDA Food Drug Administration 2017. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/205489s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2020).
- Arbor Pharmaceuticals. Highlights of Prescribing Information Evekeo ODT. FDA Food Drug Administration 2019. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/209905s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2020).
- GlaxoSmithKline. Highlights of Prescribing Information Lamictal ODT. FDA Food Drug Administration 2018. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/020241s060,020764s053,022251s024lbl.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2020).
- TerSera Therapeutics. Highlights of Prescribing Information QMIZ ODT. FDA Food Drug Administration 2018. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/211210s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2020).
- Llorca, P.M. Discussion of prevalence and management of discomfort when swallowing pills: Orodispersible tablets expand treatment options in patients with depression. Ther. Deliv. 2011, 2, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, F.; Ernest, T.B.; Tuleu, C.; Gul, M.O. Formulation approaches to pediatric oral drug delivery: Benefits and limitations of current platforms. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 1727–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orubu, E.S.; Tuleu, C. Medicines for children: Flexible solid oral formulations. Bull. World Health Organ. 2017, 95, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelbary, G.; Eouani, C.; Prinderre, P.; Joachim, J.; Reynier, J.; Piccerelle, P. Determination of the in vitro disintegration profile of rapidly disintegrating tablets and correlation with oral disintegration. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 292, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danileviciūte, V.; Sveikata, A.; Adomaitiene, V.; Gumbrevicius, G.; Fokas, V.; Sveikatiene, R. Efficacy, tolerability, and preference of mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets in depressed patients: A 17-week naturalistic study in Lithuania. Medicina 2009, 45, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wade, A.G.; Crawford, G.M.; Young, D. A survey of patient preferences for a placebo orodispersible tablet. Patient Prefer. Adher. 2012, 6, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conseil de L’Europe. European Pharmacopoeia, 10th Ed. Eur Pharm. 2020, 10, 323–324. [Google Scholar]
- Gohel, M.; Patel, M.; Amin, A.; Agrawal, R.; Dave, R.; Bariya, N. Formulation design and optimization of mouth dissolve tablets of nimesulide using vacuum drying technique. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2004, 5, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dor, P.J.M.; Fix, J.A. In vitro determination of disintegration time of quick-dissolve tablets using a new method. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2000, 5, 575–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narazaki, R.; Harada, T.; Takami, N.; Kato, Y.; Ohwaki, T. A new method for disintegration studies of rapid disintegrating tablet. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 704–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redfearn, A.G.; Hanson, B. A mechanical simulator of tongue–palate compression to investigate the oral flow of non-Newtonian fluids. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 2018, 23, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfearn, A.; Scarpa, M.; Orlu, M.; Hanson, B. In vitro oral cavity model for screening the disintegration behavior of orodispersible films: A bespoke design. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1831–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, E.M.; Green, J.R. Coordinative organization of lingual propulsion during the normal adult swallow. Dysphagia 2007, 21, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- SPI Pharma. Pharmaburst® 500 n.d. Available online: https://www.spipharma.com/en/products/drug-delivery-systems/pharmaburst-500/ (accessed on 17 February 2020).
- Gittings, S.; Turnbull, N.; Roberts, C.J.; Gershkovich, P. Dissolution methodology for taste masked oral dosage forms. J. Control. Release 2014, 173, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawker, T.H.; Sonies, B.; Stone, M.; Baum, B.J. Real-time ultrasound visualization of tongue movement during swallowing. J. Clin. Ultrasound 1983, 11, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamori, M.; Hosomi, N.; Takaki, S.; Oda, M.; Hiraoka, A.; Yoshikawa, M.; Matsushima, H.; Ochi, K.; Tsuga, K.; Maruyama, H.; et al. Tongue thickness evaluation using ultrasonography can predict swallowing function in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. Clin. Neurophysiol 2016, 127, 1669–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijailovich, S.M.; Stojanovic, B.; Kojic, M.; Liang, A.; Wedeen, V.J.; Gilbert, R.J. Derivation of a finite-element model of lingual deformation during swallowing from the mechanics of mesoscale myofiber tracts obtained by MRI. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 109, 1500–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stone, M. A three-dimensional model of tongue movement based on ultrasound and X-ray microbeam data. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1990, 87, 2207–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasko, S.M.; Kent, R.D.; Westbury, J.R. Variability in tongue movement kinematics during normal liquid swallowing. Dysphagia 2002, 17, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, S.; Nakao, S.; Nakauma, M.; Funami, T.; Hori, K.; Ono, T.; Kohyama, K.; Nishinari, K. Compression test of food gels on artificial tongue and its comparison with human test. J. Texture Stud. 2012, 44, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payan, Y.; Perrier, P. Synthesis of V-V sequences with a 2D biomechanical tongue model controlled by the equilibrium point hypothesis. Speech Commun. 1997, 22, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.; Kieser, J.; Bolter, C.; Swain, M.V.; Singh, B.; Waddell, J.N. tongue pressure patterns during water swallowing. Dysphagia 2009, 25, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittings, S.; Turnbull, N.; Henry, B.; Roberts, C.J.; Gershkovich, P. Characterisation of human saliva as a platform for oral dissolution medium development. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 91, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The United States Pharmacopeial Convention. Disintegration 2020. Available online: https://www.usp.org/sites/default/files/usp/document/harmonization/gen-chapter/april-2019-m99460.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2020).
- Kamba, M.; Seta, Y.; Takeda, N.; Hamaura, T.; Kusai, A.; Nakane, H.; Nishimura, K. Measurement of agitation force in dissolution test and mechanical destructive force in disintegration test. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 250, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornhorst, G.M.; Singh, R. Bolus Formation and disintegration during digestion of food carbohydrates. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2012, 11, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner-Hattler, L.; Wyss, K.; Schoelkopf, J.; Huwyler, J.; Puchkov, M. In vitro characterization and mouthfeel study of functionalized calcium carbonate in orally disintegrating tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 534, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, S.I.; Uchida, S.; Kanada, K.; Namiki, N. Effect of granule properties on rough mouth feel and palatability of orally disintegrating tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 484, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, B.J.; Dziemidowicz, K.; Lopez, F.; Orlu, M.; Tuleu, C.; Edwards, A.J.; Ernest, T.B. Co-processed excipients for dispersible tablets–part 1: Manufacturability. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 2598–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brniak, W.; Jachowicz, R.; Krupa, A.; Skórka, T.; Niwinski, K. Evaluation of co-processed excipients used for direct compression of orally disintegrating tablets (ODT) using novel disintegration apparatus. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2012, 18, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| ODT Hardness (kp) | OCM Disintegration Time (s) | EuPh Disintegration Time (s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| 1.9 | 112 | 10.4 | 11 | 0.7 |
| 8.1 | 119 | 10.6 | 25 | 1.6 |
| 13.3 | 153 | 10.8 | 34 | 2.7 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Desai, N.; Redfearn, A.; MacLeod, G.; Tuleu, C.; Hanson, B.; Orlu, M. How Do Orodispersible Tablets Behave in an In Vitro Oral Cavity Model: A Pilot Study. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070651
Desai N, Redfearn A, MacLeod G, Tuleu C, Hanson B, Orlu M. How Do Orodispersible Tablets Behave in an In Vitro Oral Cavity Model: A Pilot Study. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(7):651. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070651
Chicago/Turabian StyleDesai, Neel, Andrew Redfearn, Graeme MacLeod, Catherine Tuleu, Ben Hanson, and Mine Orlu. 2020. "How Do Orodispersible Tablets Behave in an In Vitro Oral Cavity Model: A Pilot Study" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 7: 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070651
APA StyleDesai, N., Redfearn, A., MacLeod, G., Tuleu, C., Hanson, B., & Orlu, M. (2020). How Do Orodispersible Tablets Behave in an In Vitro Oral Cavity Model: A Pilot Study. Pharmaceutics, 12(7), 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12070651







