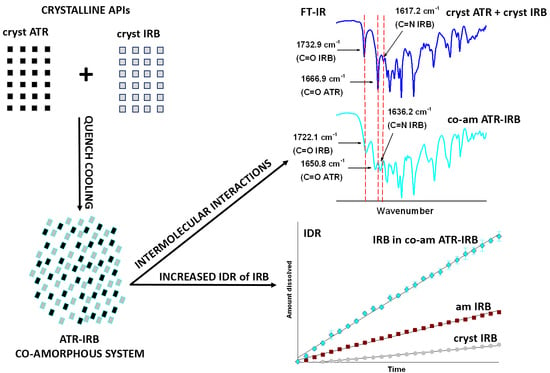
Physicochemical Characterization of a Co-Amorphous Atorvastatin-Irbesartan System with a Potential Application in Fixed-Dose Combination Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
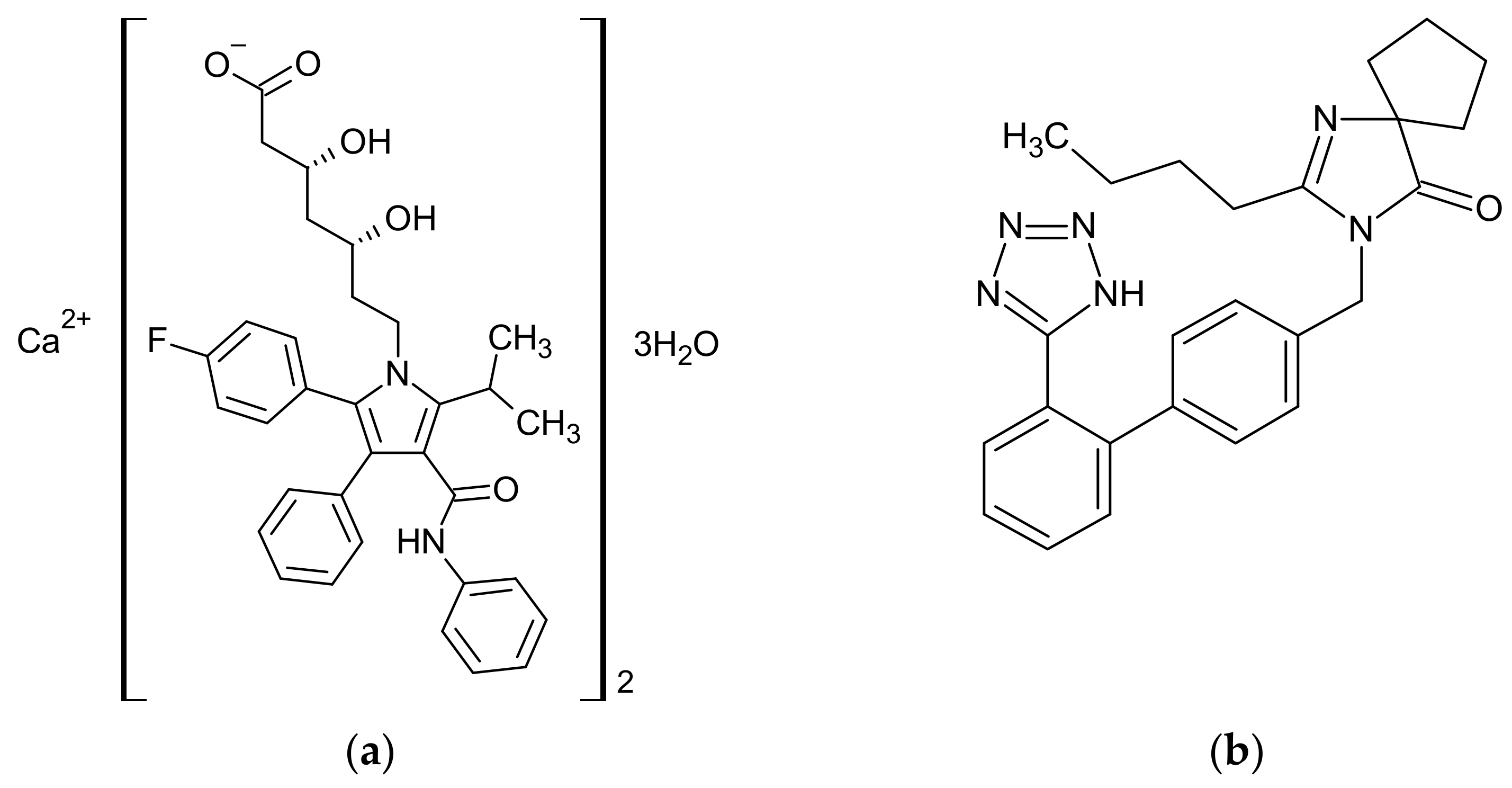
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Amorphous Binary Systems
2.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
2.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.5. Determination of the Theoretical Tg Value Using Couchman-Karasz Equation
2.6. Fourier Transform-Infrared Spectroscopy Measurements
2.7. Computational Section
2.8. Intrinsic Dissolution Testing
3. Results and Discussion
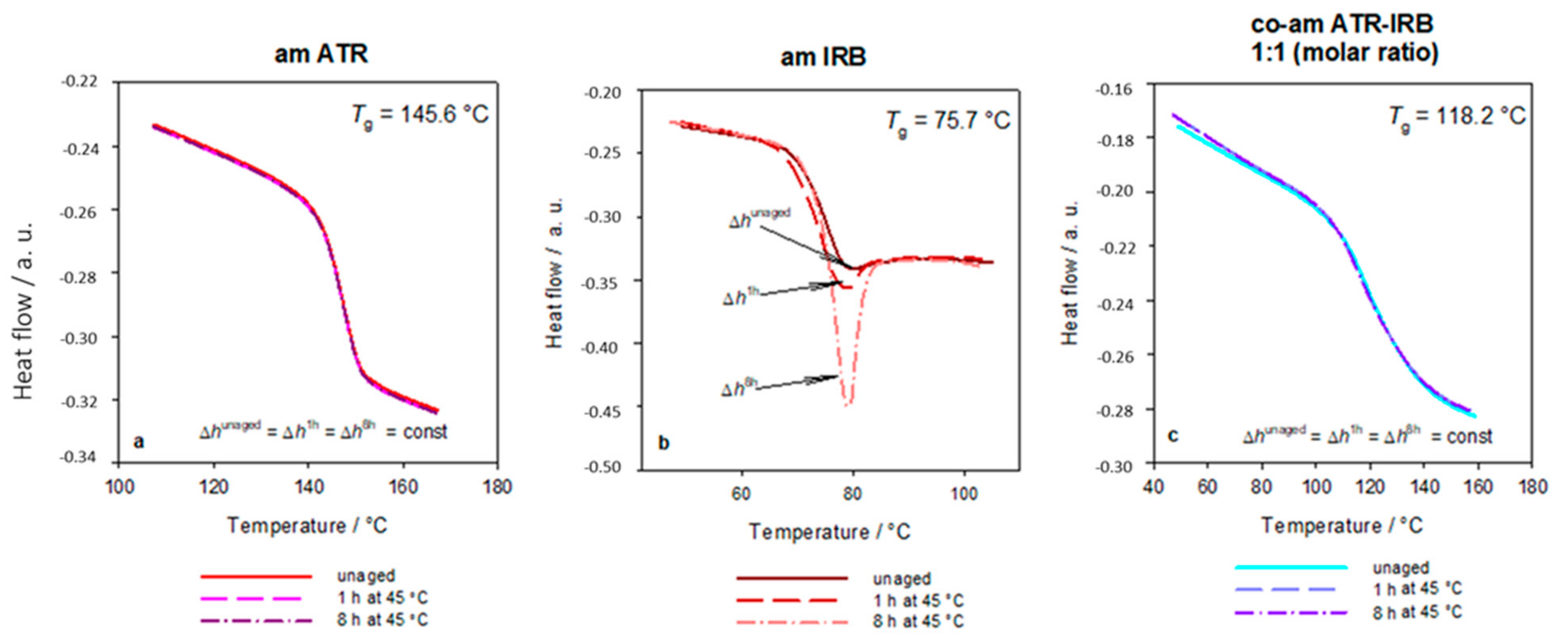
3.1. Thermal Analysis
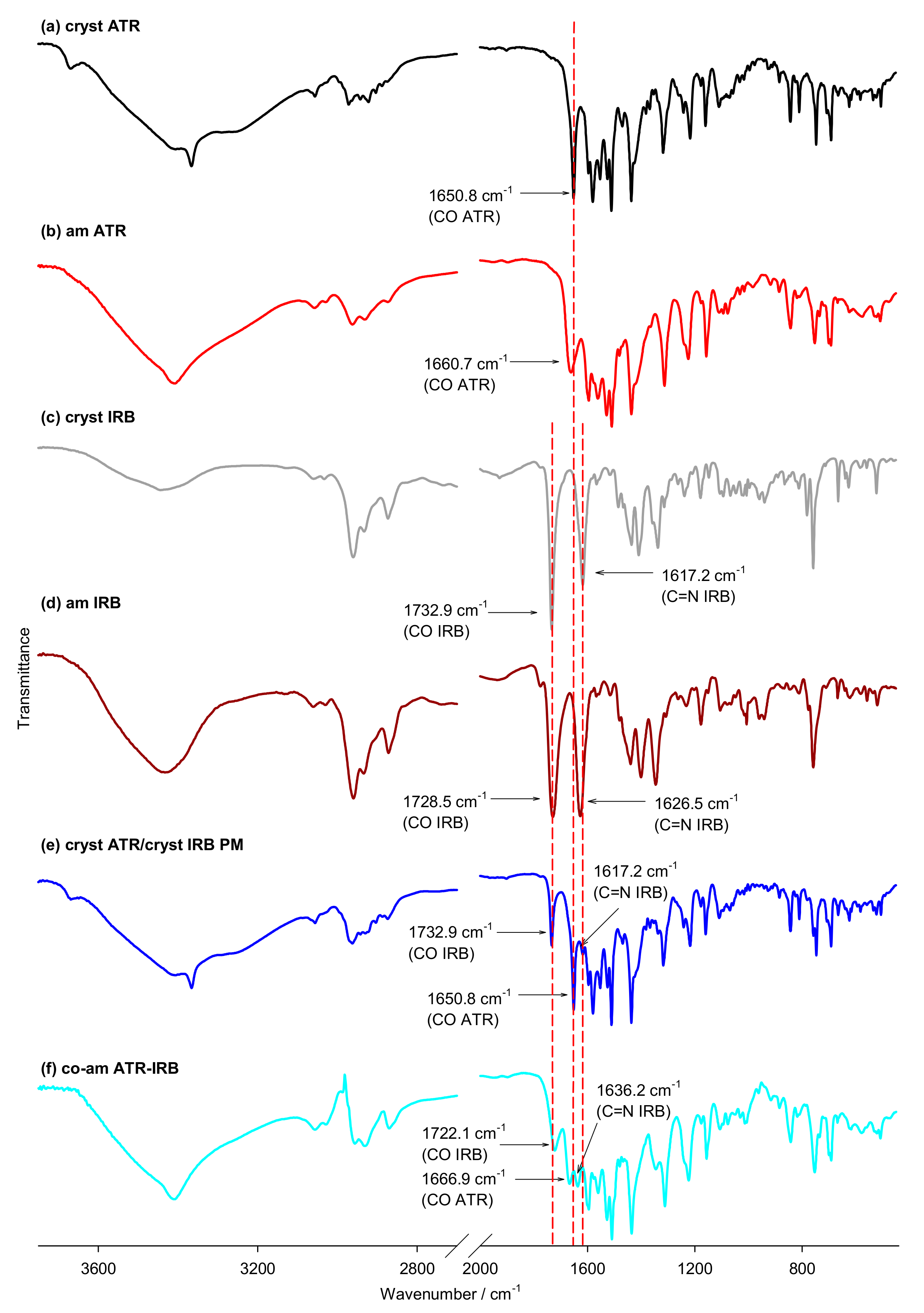
3.2. FT-IR Spectroscopy
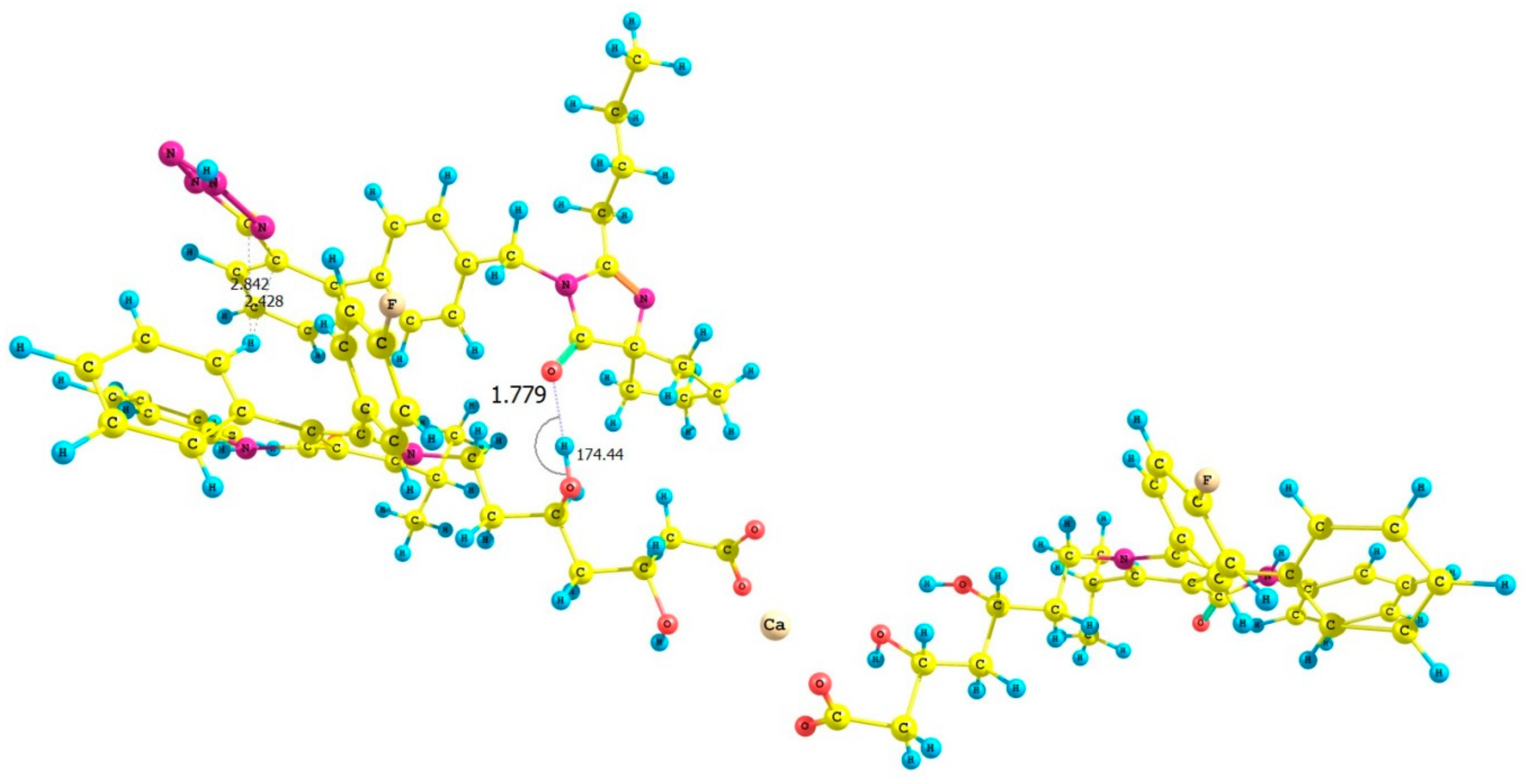
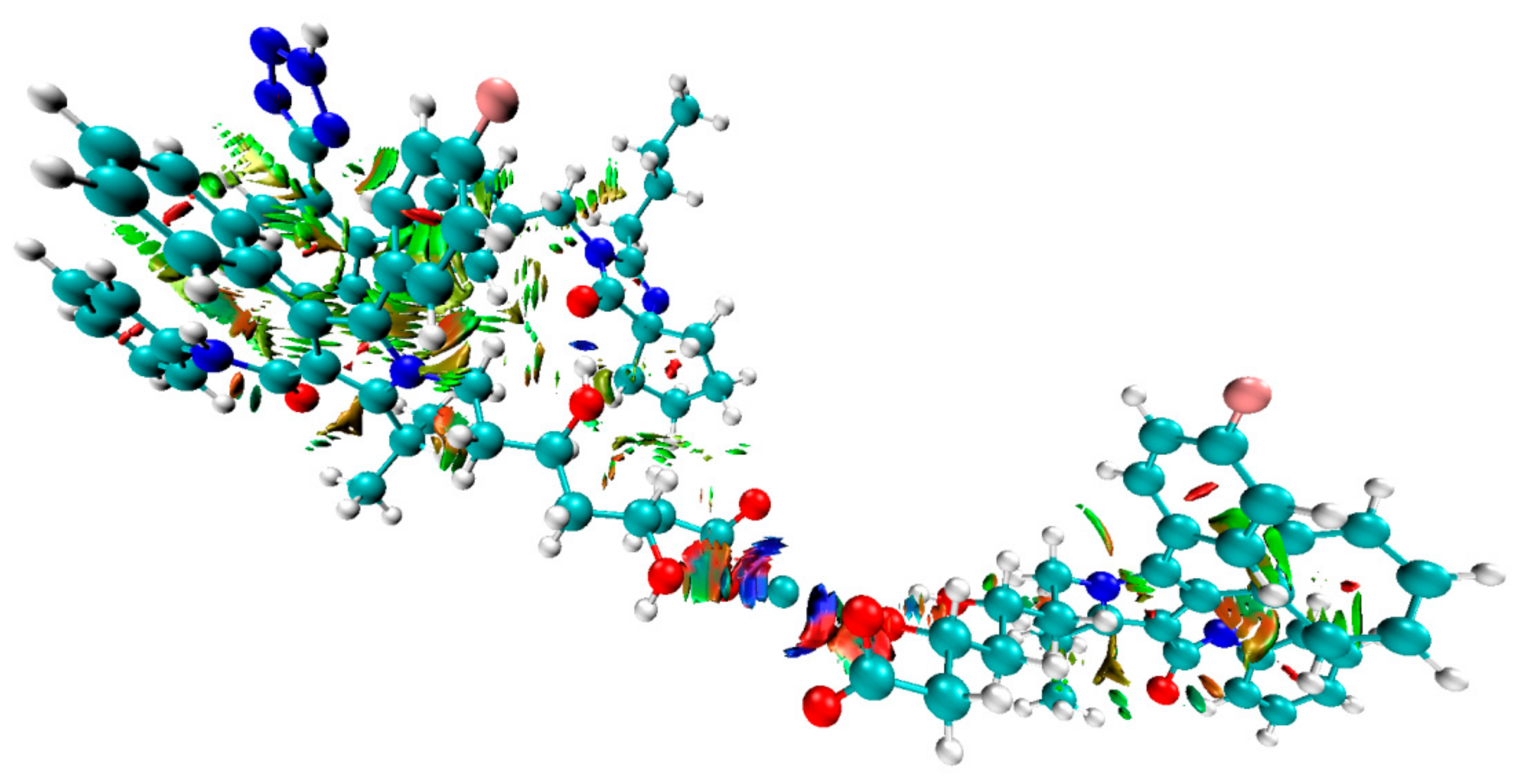
3.3. Computational Investigations
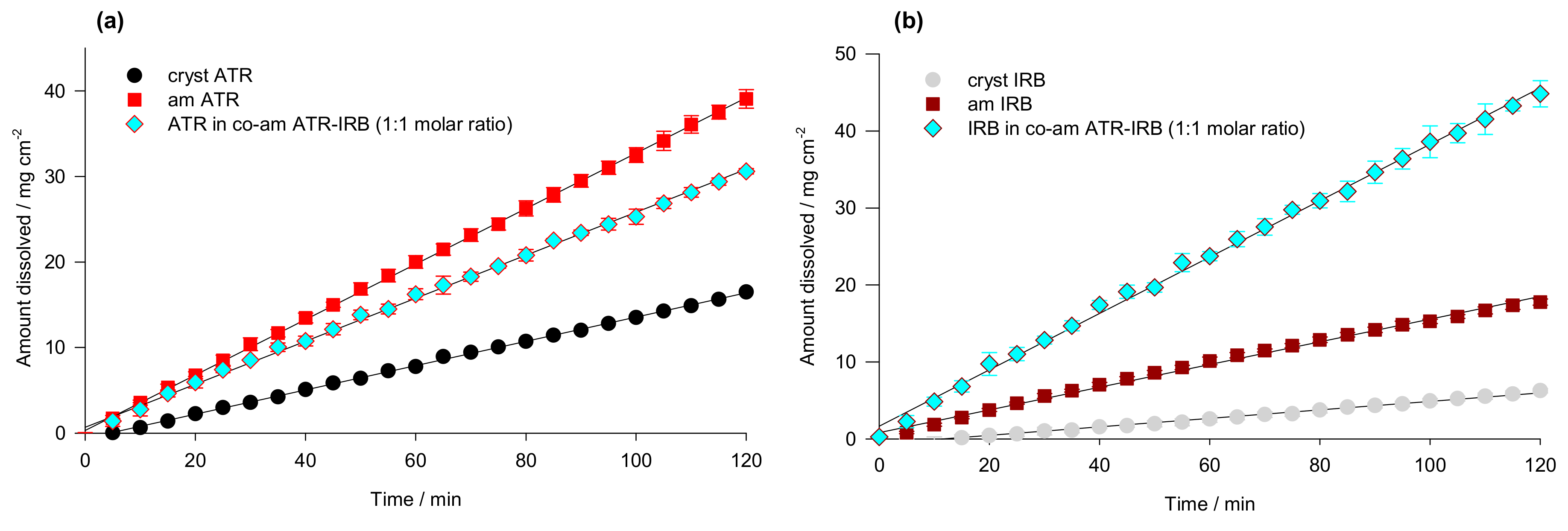
3.4. Intrinsic Dissolution Testing
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, V.; Prasad, B.; Singh, S. Pharmaceutical issues in the development of a polypill for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Drug Discov. Today Ther. Strateg. 2008, 5, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihm, S.H.; Shin, J.; Park, C.G.; Kim, C.H. Efficacy of a fixed dose combination of irbesartan and atorvastatin (Rovelito®) in Korean adults with hypertension and hypercholesterolemia. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2019, 13, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.S.; Jin, S.J.; Kim, J.S.; Park, H.J.; Song, H.S.; Neubert, R.H.H.; Hwang, S.J. Preparation, characterization and in vivo evaluation of amorphous atorvastatin calcium nanoparticles using supercritical antisolvent (SAS) process. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirlekar, R.; Kadam, V. Preformulation study of the inclusion complex irbesartan-β-cyclodextrin. AAPS PharmSciTech 2009, 10, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashwini Kumar, G.; Choudhary, R.K.; Chaitanya, C. Enhancement of solubility and dissolution rate of irbesartan by solid dispersion technique. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2011, 4, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Shete, G.; Puri, V.; Kumar, L.; Bansal, A.K. Solid state characterization of commercial crystalline and amorphous atorvastatin calcium samples. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, D.; Crull, G.; Yin, S.; Grosso, J. Low level drug product API form analysis—Avalide tablet NIR quantitative method development and robustness challenges. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 89, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedaya, M.A.; Helmy, S.A. Modeling of the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic interaction between irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide in normotensive subjects. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2015, 36, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalepu, S.; Nekkanti, V. Insoluble drug delivery strategies: Review of recent advances and business prospects. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, L. Amorphous pharmaceutical solids: Preparation, characterization and stabilization. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 48, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, B.C.; Zografi, G. Characteristics and significance of the amorphous state in pharmaceutical systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laitinen, R.; Löbmann, K.; Strachan, C.J.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T. Emerging trends in the stabilization of amorphous drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikiaris, D.N. Solid dispersions, Part I: Recent evolutions and future opportunities in manufacturing methods for dissolution rate enhancement of poorly water-soluble drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 1501–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, F.; Huang, J.; Hussain, M.A. Drug-polymer solubility and miscibility: Stability consideration and practical challenges in amorphous solid dispersion development. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 2941–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serajuddln, A.T.M. Solid dispersion of poorly water-soluble drugs: Early promises, subsequent problems, and recent breakthroughs. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 88, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, R.B.; Thipparaboina, R.; Kumar, D.; Shastri, N.R. Co amorphous systems: A product development perspective. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dengale, S.J.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T.; Löbmann, K. Recent advances in co-amorphous drug formulations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 100, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagianni, A.; Kachrimanis, K.; Nikolakakis, I. Co-amorphous solid dispersions for solubility and absorption improvement of drugs: Composition, preparation, characterization and formulations for oral delivery. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, J.; Wei, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Qian, S. Co-amorphous systems for the delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs: Recent advances and an update. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 1411–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Moinuddin, S.M.; Cai, T. Advances in coamorphous drug delivery systems. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Heng, W.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y. Coamorphous lurasidone hydrochloride-saccharin with charge-assisted hydrogen bonding interaction shows improved physical stability and enhanced dissolution with ph-independent solubility behavior. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 2920–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löbmann, K.; Laitinen, R.; Grohganz, H.; Strachan, C.; Rades, T.; Gordon, K.C. A theoretical and spectroscopic study of co-amorphous naproxen and indomethacin. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, K.; Chaitanya Mannava, M.K.C.; Nangia, A. A novel curcumin-artemisinin coamorphous solid: Physical properties and pharmacokinetic profile. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 58357–58361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, H.; Kadota, K.; Imono, M.; Ito, T.; Kunita, A.; Tozuka, Y. Co-amorphous formation induced by combination of tranilast and diphenhydramine hydrochloride. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Löbmann, K.; Strachan, C.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T.; Korhonen, O.; Laitinen, R. Co-amorphous simvastatin and glipizide combinations show improved physical stability without evidence of intermolecular interactions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löbmann, K.; Grohganz, H.; Laitinen, R.; Strachan, C.; Rades, T. Amino acids as co-amorphous stabilizers for poorly water soluble drugs—Part 1: Preparation, stability and dissolution enhancement. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayanfar, A.; Jouyban, A. Drug-drug coamorphous systems: Characterization and physicochemical properties of coamorphous atorvastatin with carvedilol and glibenclamide. J. Pharm. Innov. 2013, 8, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Rana, A.C.; Aggarwal, G.; Kumar, V.; Zakir, F. Development and characterization of an atorvastatin solid dispersion formulation using skimmed milk for improved oral bioavailability. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2012, 2, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anwar, M.; Warsi, M.H.; Mallick, N.; Akhter, S.; Gahoi, S.; Jain, G.K.; Talegaonkar, S.; Ahmad, F.J.; Khar, R.K. Enhanced bioavailability of nano-sized chitosan-atorvastatin conjugate after oral administration to rats. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 44, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeli, E. Irbesartan-loaded electrospun nanofibers-based PVP K90 for the drug dissolution improvement: Fabrication, in vitro performance assessment, and in vivo evaluation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meka, A.K.; Pola, S.; Tupally, K.R.; Abbaraju, P.L. Development, evaluation and characterization of surface solid dispersion for solubility and dissolution enhancement of Irbesartan. Int. J. Drug Dev. Res. 2012, 4, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.; Varma, R.; Gourishetti, K.; Bhat, K.; Dengale, S. Influence of preparation methods on physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties of co-amorphous formulations: The case of co-amorphous atorvastatin: Naringin. J. Pharm. Innov. 2020, 15, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayanfar, A.; Ghavimi, H.; Hamishehkar, H.; Jouyban, A. Coamorphous atorvastatin calcium to improve its physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 16, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cruz-Angeles, J.; Videa, M.; Martínez, L.M. Highly soluble glimepiride and irbesartan co-amorphous formulation with potential application in combination therapy. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneef, J.; Chadha, R. Drug-drug multicomponent solid forms: Cocrystal, coamorphous and eutectic of three poorly soluble antihypertensive drugs using mechanochemical approach. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 2279–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, G.; Bansal, A.K. Molecular mobility and physical stability of amorphous irbesartan. Sci. Pharm. 2009, 77, 695–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graeser, K.A.; Strachan, C.J.; Patterson, J.E.; Gordon, K.C.; Rades, T. Physicochemical properties and stability of two differently prepared amorphous forms of simvastatin. Cryst. Growth Des. 2008, 8, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikal, M.J.; Lukes, A.L.; Lang, J.E.; Gaines, K. Quantitative crystallinity determinations for β-lactam antibiotics by solution calorimetry: Correlations with stability. J. Pharm. Sci. 1978, 67, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukushi, I.; Yamamuro, O.; Suga, H. Heat capacities and glass transitions of ground amorphous solid and liquid-quenched glass of tri-O-methyl-ß-cyclodextrin. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 1994, 175, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, B. Thermal Analysis of Polymeric Materials; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2005; ISBN 3540236295. [Google Scholar]
- Couchman, P.R.; Karasz, F.E. A classical thermodynamic discussion of the effect of composition on glass-transition temperatures. Macromolecules 1978, 11, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böcskei, Z.; Simon, K.; Rao, R.; Caron, A.; Rodger, C.A.; Bauer, M. Irbesartan crystal form B. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Cryst. Struct. Commun. 1998, 54, 808–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.R.; Kim, D.; Bae, J.H.; Yeon, J.; Roshan, K.C.; Kang, S.K.; Lee, E.H. New category for active pharmaceutical ingredients, a low molecular weight organogelator: Crystal structure of atorvastatin calcium and its unusual phase transition behavior during dissolution. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 7198–7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenberg, P.; Kohn, W. Inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H. Gaussian 16, Revision C.01 2016; Computer Software; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chai, J.-D.; Head-Gordon, M. Long-range corrected hybrid density functionals with damped atom-atom dispersion corrections. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2008, 10, 6615–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boys, S.F.; Bernardi, F. The calculation of small molecular interactions by the differences of separate total energies. Some procedures with reduced errors. Mol. Phys. 1970, 19, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duijneveldt, F.B.; van Duijneveldt-van de Rijdt, J.G.C.M.; van Lenthe, J.H. State of the art in counterpoise theory. Chem. Rev. 1994, 94, 1873–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, T.A. AIMAll (Version 14.11.23), TK Gristmill Software, Overland Park, KS, USA. 2014. Available online: http://aim.tkgristmill.com/references.html (accessed on 26 November 2020).
- Bader, R.F.W. A quantum theory of molecular structure and its applications. Chem. Rev. 1991, 91, 893–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.R.; Keinan, S.; Mori-Sánchez, P.; Contreras-García, J.; Cohen, A.J.; Yang, W. Revealing noncovalent interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 6498–6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multiwfn. Available online: http://sobereva.com/multiwfn (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Marenich, A.V.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Universal solvation model based on solute electron density and on a continuum model of the solvent defined by the bulk dielectric constant and atomic surface tensions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Pharmacopeial Convention. United States Pharmacopeia and National Formulary (USP 32–NF27); United States Pharmacopeial Convention: Rockville, MD, USA, 2009; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelwahab, N.S.; El-Zeiny, B.A.; Tohamy, S.I. Two spectrophotometric methods for simultaneous determination of some antihyperlipidemic drugs. J. Pharm. Anal. 2012, 2, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, H.; Reddy, M.A.K.; Babu, C.N.; Bhatta, H.P.; Wagle, N.; Sapkota, H.P.; Dangi, N.B. Method development and validation of dual wavelength UV spectrophotometric method for simultaneous estimation of paracetamol and caffeine in combined dosage form by internal standard method. Asian J. Chem. 2015, 27, 4666–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogami, H.; Nagai, T.; Suzuki, A. Studies on powdered preparations. XVII. Dissolution rate of sulfonamides by rotating disk method.3,4. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1966, 14, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skotnicki, M.; Aguilar, J.A.; Pyda, M.; Hodgkinson, P. Bisoprolol and bisoprolol-valsartan compatibility studied by differential scanning calorimetry, nuclear magnetic resonance and X-Ray powder diffractometry. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 414–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Silva, E.P.; Pereira, M.A.V.; De Barros Lima, I.P.; Lima, N.G.P.B.; Barbosa, E.G.; Aragão, C.F.S.; Gomes, A.P.B. Compatibility study between atorvastatin and excipients using DSC and FTIR. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 123, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristea, M.; Baul, B.; Ledeţi, I.; Ledeţi, A.; Vlase, G.; Vlase, T.; Karolewicz, B.; Ştefănescu, O.; Dragomirescu, A.O.; Mureşan, C.; et al. Preformulation studies for atorvastatin calcium: An instrumental approach. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 138, 2799–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya-Sibaja, A.M.; Maduro de Campos, C.E.; Fandaruff, C.; Vega-Baudrit, J.R.; Guillén-Girón, T.; Navarro-Hoyos, M.; Cuffini, S.L. Irbesartan desmotropes: Solid-state characterization, thermodynamic study and dissolution properties. J. Pharm. Anal. 2019, 9, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura Ramos, J.J.; Diogo, H.P. Thermal behavior and molecular mobility in the glassy state of three anti-hypertensive pharmaceutical ingredients. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 10831–10840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruni, G.; Amici, L.; Berbenni, V.; Marini, A.; Orlandi, A. Drug-excipient compatibility studies: Search of interaction indicators. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2002, 68, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, G.; Berbenni, V.; Milanese, C.; Girella, A.; Marini, A. Drug-excipient compatibility studies in binary and ternary mixtures by physico-chemical techniques. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2010, 102, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharate, S.S.; Bharate, S.B.; Bajaj, A.N. Interactions and incompatibilities of pharmaceutical excipients with active pharmaceutical ingredients: A comprehensive review. J. Excipients Food Chem. 2010, 1, 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Rumondor, A.C.F.; Ivanisevic, I.; Bates, S.; Alonzo, D.E.; Taylor, L.S. Evaluation of drug-polymer miscibility in amorphous solid dispersion systems. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 2523–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, B.C.; Shamblin, S.L.; Zografi, G. Molecular mobility of amorphous pharmaceutical solids below their glass transition temperatures. Pharm. Res. An. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Pharm. Sci. 1995, 12, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, A.; Patel, S.B. Phase behavior, intermolecular interaction, and solid state characterization of amorphous solid dispersion of Febuxostat. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2017, 22, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoare, M. Stability and local order in simple amorphous packings. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1976, 279, 186–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, J.M. Physical aging of polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1995, 20, 703–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaev, E.; Zografi, G. The concept of “structure” in amorphous solids from the perspective of the pharmaceutical sciences. In Amorphous Food and Pharmaceutical Systems; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2007; pp. 11–30. ISBN 9781847550118. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Suryanarayanan, R. Local mobility in amorphous pharmaceuticals—Characterization and implications on stability. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 2935–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerniecka-Kubicka, A.; Zarzyka, I.; Pyda, M. Long-term physical aging tracked by advanced thermal analysis of Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide): A smart polymer for drug delivery system. Molecules 2020, 25, 3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skotnicki, M.; Drogoń, A.; Calvin, J.J.; Rosen, P.F.; Woodfield, B.F.; Pyda, M. Heat capacity and enthalpy of indapamide. Thermochim. Acta 2019, 674, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamblin, S.L.; Tang, X.; Chang, L.; Hancock, B.C.; Pikal, M.J. Characterization of the time scales of molecular motion in pharmaceutically important glasses. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 4113–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, R.L.; Kaduk, J.A.; Gindhart, A.M.; Blanton, T.N. Crystal structure of atorvastatin calcium trihydrate Form i (Lipitor®), (C33H34FN2O5)2 Ca(H2O)3. Powder Diffr. 2020, 35, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brus, J.; Urbanova, M.; Sedenkova, I.; Brusova, H. New perspectives of 19F MAS NMR in the characterization of amorphous forms of atorvastatin in dosage formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 409, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.; Harris, R.K.; Rao, R.C.; Apperley, D.C.; Rodger, C.A. NMR study of desmotropy in Irbesartan, a tetrazole-containing pharmaceutical compound. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 1998, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franca, C.A.; Etcheverry, S.B.; Diez, R.P.; Williams, P.A.M. Irbesartan: FTIR and Raman spectra. Density functional study on vibrational and NMR spectra. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2009, 40, 1296–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, E.; Molins, E.; Lecomte, C. Hydrogen bond strengths revealed by topological analyses of experimentally observed electron densities. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1998, 285, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spackman, M.A. Hydrogen bond energetics from topological analysis of experimental electron densities: Recognising the importance of the promolecule. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1999, 301, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, C.W. Statins in therapy: Understanding their hydrophilicity, lipophilicity, binding to 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase, ability to cross the blood brain barrier and metabolic stability based on electrostatic molecular orbital studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 85, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huq, F. Molecular modelling analysis of the metabolism of irbesartan. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 2, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
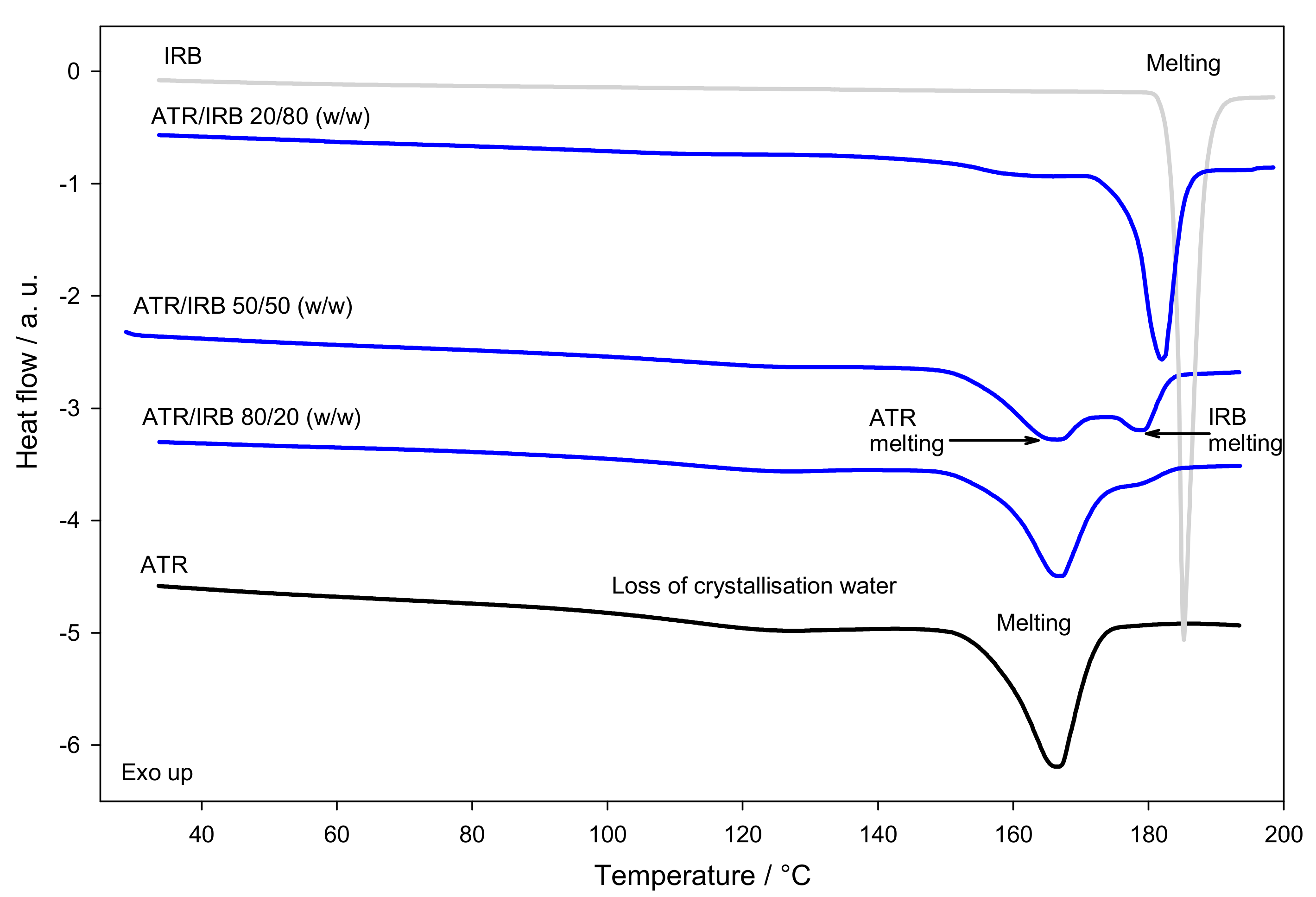
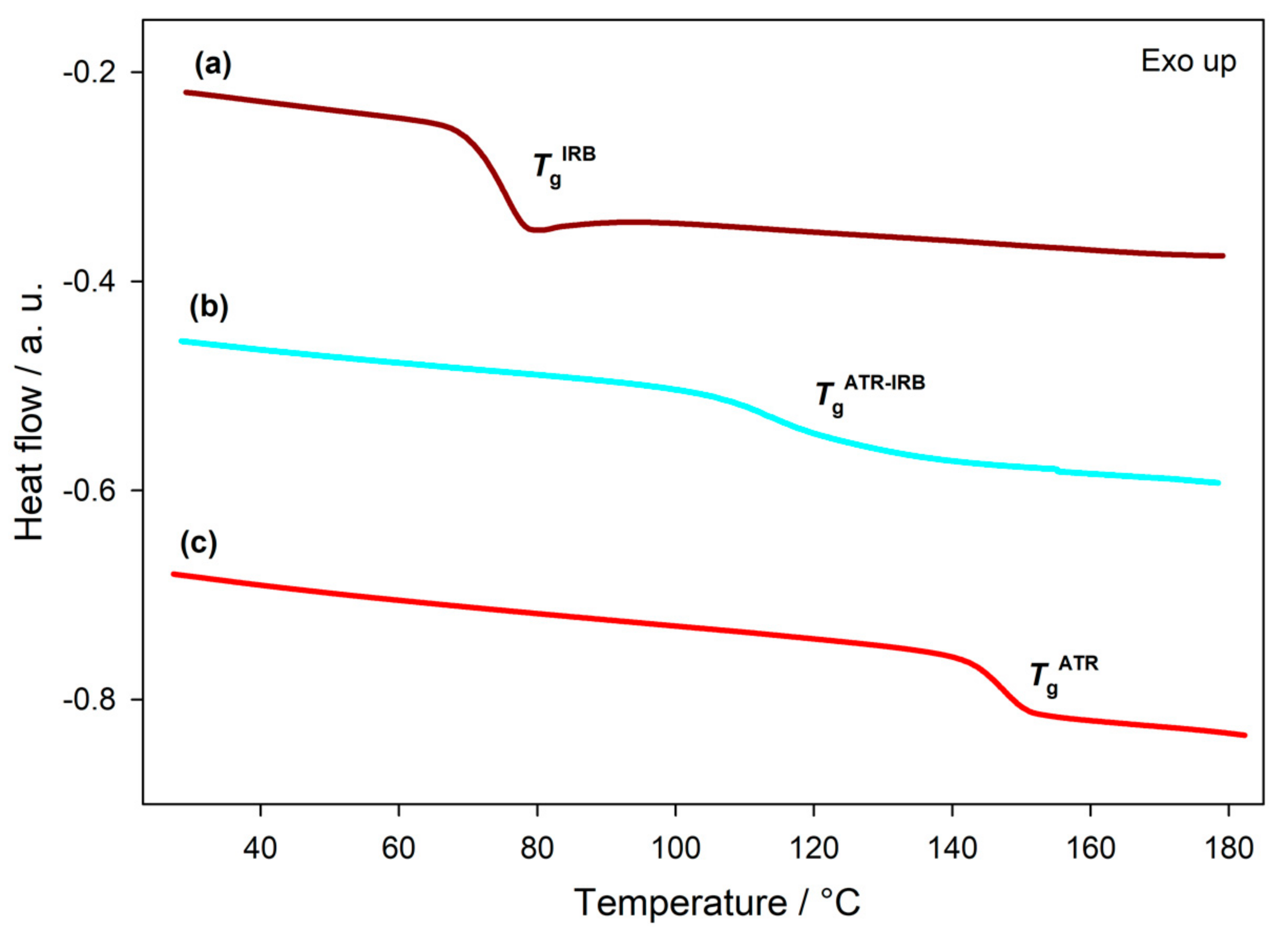


| Sample | Tfus ± SD/°C | Tfus | Δfushexp ± SD/J g−1 | Δfushtheor/J g−1 | Δfushexp − Δfushtheor/J g−1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATR | IRB | ATR | IRB | ATR | IRB | ATR + IRB | ATR + IRB | ||
| ATR | 150.2 ± 0.9 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 81 ± 3 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| IRB | N/A | 183.8 ± 0.2 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 94.1 ± 0.5 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| ATR/IRB 80/20 PM | 158.0 ± 0.7 | NPE * | −7.8 | NPE * | NPE * | NPE * | 72 ± 1 | 83.7 | −11.7 |
| ATR/IRB 50/50 PM | 153.8 ± 0.6 | 173 ± 2 | −3.6 | 10.8 | NPE * | NPE * | 72 ± 5 | 87.6 | −15.6 |
| ATR/IRB 20/80 PM | 151 ± 1 | 177.9 ± 0.6 | −0.8 | 5.9 | NPE * | NPE * | 70 ± 4 | 91.5 | −21.5 |
| Sample | Tg ± SD/°C | Δcp ± SD/J g−1 °C−1 | TgCK/°C | ΔTg(Tg − TgCK)/°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATR | 145.6 ± 0.9 | 0.39 ± 0.04 | N/A | N/A |
| IRB | 75.7 ± 0.2 | 0.50 ± 0.01 | N/A | N/A |
| Co-am ATR-IRB | 118 ± 2 | 0.34 ± 0.01 | 122.9 | −4.9 |
| ATR-IRB Complex | Interaction Energy (ΔE) Calculated for ATR-IRB Complexes kcal mol−1 |
|---|---|
| Level of Theory—B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p)//B3LYP/6-31Gd,p) | |
| I | −1.46 |
| II | −25.17 |
| III | −34.44 |
| IV | −17.00 |
| Level of Theory—B97D3/6-311++G(d,p)//B97D3/6-31Gd,p) | |
| V | −3.24 |
| VI | −22.11 |
| VII | −33.20 |
| VIII | −10.65 |
| Group | Wavenumber/cm−1 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental | Calculated | ||||||||||
| cryst ATR | am ATR | am IRB | cryst IRB | co-am ATR-IRB | ATRa | ATRb | IRBa | IRBb | III | VII | |
| C=OATR | 1650.8 | 1660.7 | N/A | N/A | 1666.9 | 1633.3 | 1641.7 | N/A | N/A | 1727.6 * | 1649.3 * |
| C=OIRB | N/A | N/A | 1732.9 | 1728.5 | 1722.1 | N/A | N/A | 1886.3 | 1821.4 | 1765.9 | 1719.8 |
| C=Nar(IRB) | N/A | N/A | 1617.2 | 1626.5 | 1636.2 | N/A | N/A | 1745.5 | 1650.1 | 1711.3 | 1651.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skotnicki, M.; Jadach, B.; Skotnicka, A.; Milanowski, B.; Tajber, L.; Pyda, M.; Kujawski, J. Physicochemical Characterization of a Co-Amorphous Atorvastatin-Irbesartan System with a Potential Application in Fixed-Dose Combination Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13010118
Skotnicki M, Jadach B, Skotnicka A, Milanowski B, Tajber L, Pyda M, Kujawski J. Physicochemical Characterization of a Co-Amorphous Atorvastatin-Irbesartan System with a Potential Application in Fixed-Dose Combination Therapy. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(1):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13010118
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkotnicki, Marcin, Barbara Jadach, Agnieszka Skotnicka, Bartłomiej Milanowski, Lidia Tajber, Marek Pyda, and Jacek Kujawski. 2021. "Physicochemical Characterization of a Co-Amorphous Atorvastatin-Irbesartan System with a Potential Application in Fixed-Dose Combination Therapy" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 1: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13010118
APA StyleSkotnicki, M., Jadach, B., Skotnicka, A., Milanowski, B., Tajber, L., Pyda, M., & Kujawski, J. (2021). Physicochemical Characterization of a Co-Amorphous Atorvastatin-Irbesartan System with a Potential Application in Fixed-Dose Combination Therapy. Pharmaceutics, 13(1), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13010118