Solid-State Stability Profiling of Ramipril to Optimize Its Quality Efficiency and Safety
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instruments
2.2.1. HPLC Method
2.2.2. HPLC-MS Method
2.2.3. Other Instruments
2.3. Procedures
2.3.1. Preparation of the Mobile Phase
2.3.2. Preparation of Pure RAM (Standard Solution)
2.3.3. Validation of HPLC for the Stability Assay of Pure RAM and RAM–Excipient Model Mixtures
Selectivity
Precision
Linearity
Sensitivity
2.3.4. Kinetic Study—Preparation of Samples
Pure RAM
RAM in Model Mixtures with Excipients
RAM in Tablets
2.3.5. Reaction Model Fitting
2.3.6. Calculation of Thermodynamic Parameters
2.3.7. Identification of RAM Degradation Impurities by HPLC–MS
3. Results
3.1. Validation of the Analytical Method
3.2. Kinetic Parameters
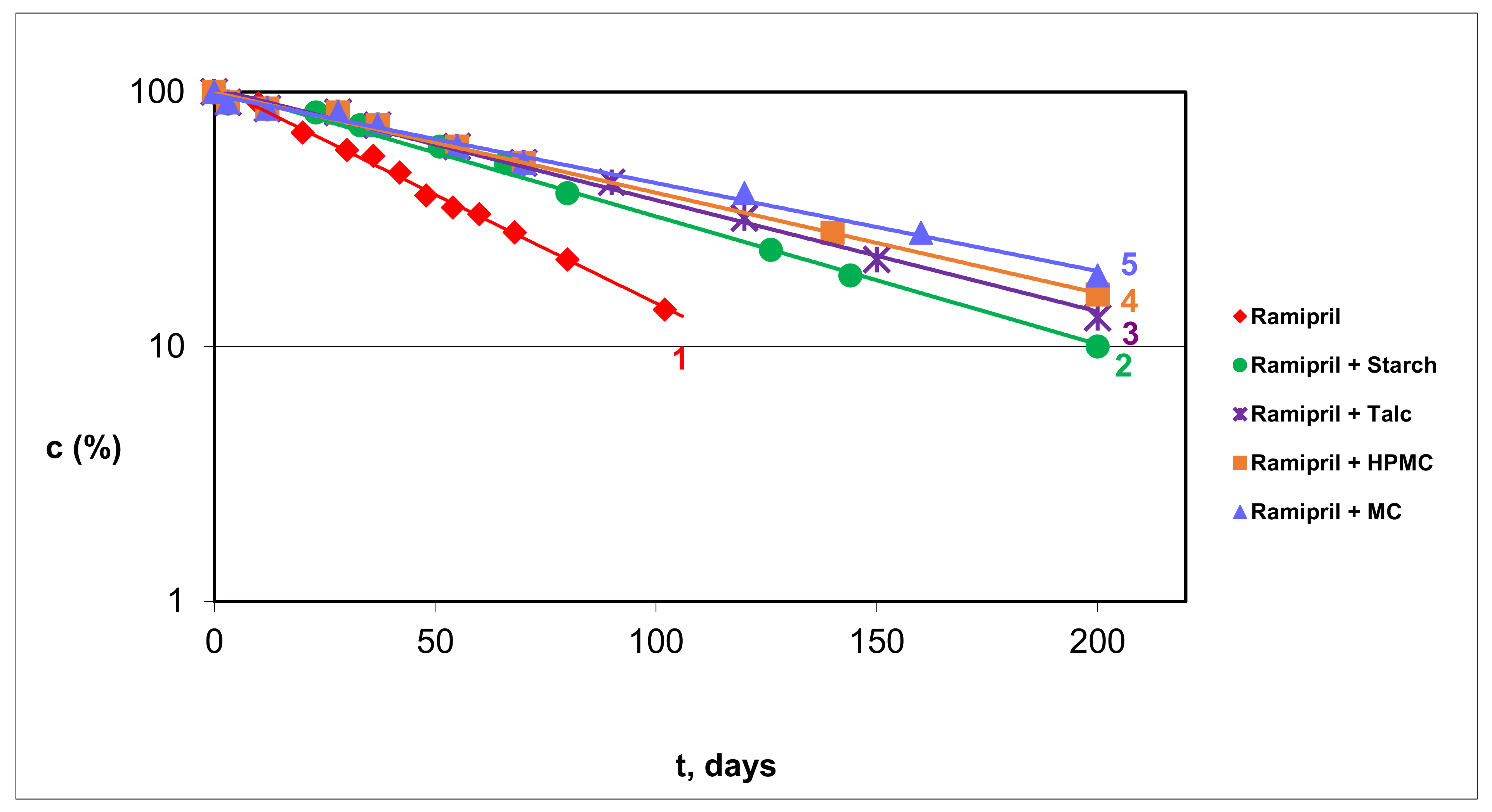
3.2.1. RAM in Pure Form and in Model Mixtures with S, T, HPMC and MC
3.2.2. RAM in Tablets
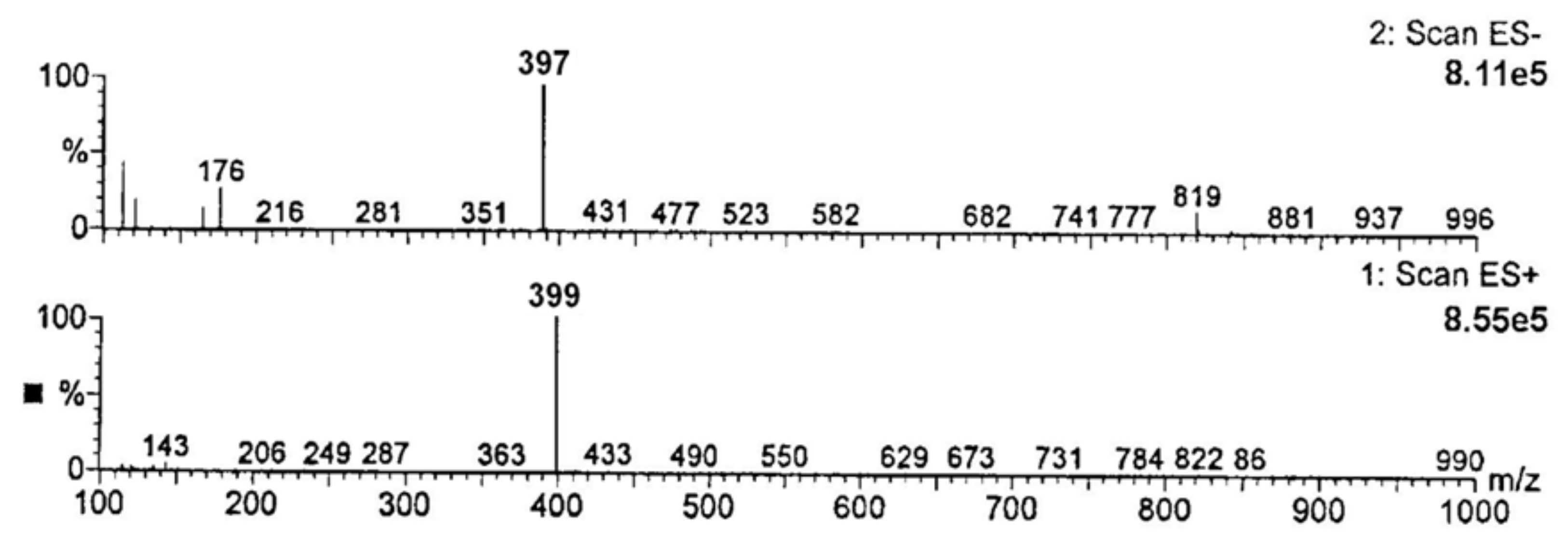
3.2.3. Identification of Degradation Impurities
4. Discussion
4.1. Validation Report
4.2. Kinetic Order of RAM Degradation
4.3. Effect of Temperature
4.4. Effect of RH
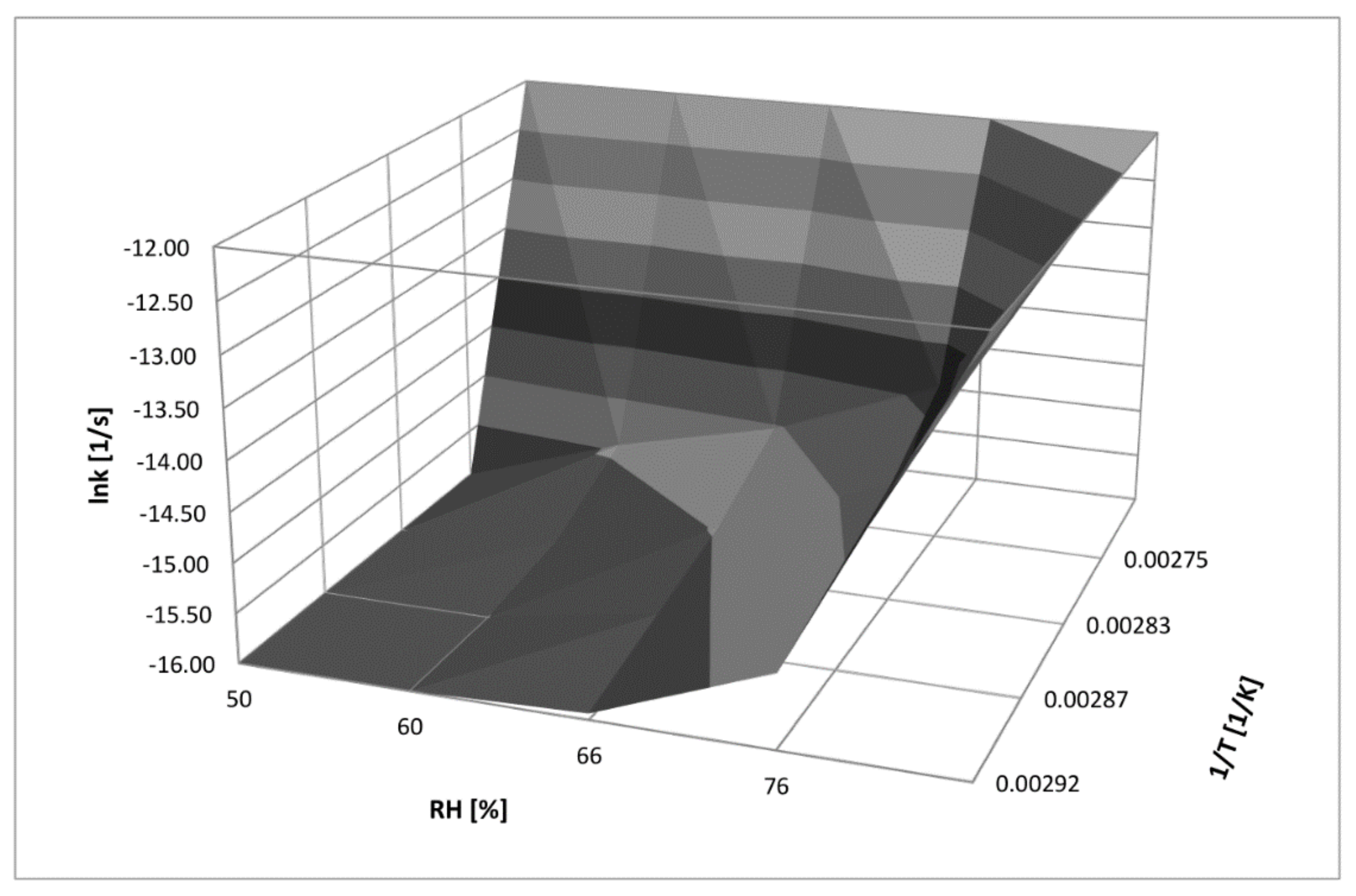
4.5. Three-Dimensional Correlation between T, RH, and k for RAM Degradation under Humid Conditions
4.6. RAM in Tablets
4.7. Degradants
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zilker, M.; Sörgel, F.; Holzgrabe, U. A systematic review of the stability of finished pharmaceutical products and drug substances beyond their labeled expiry dates. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 166, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, S.; Singla, D.; Sakhuja, N. Stability testing of pharmaceutical products. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2012, 2, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- The European Medicines Agency’s Scientific Guidelines on the Stability of Drug Substances and Drug Products Help Medicine Developers Prepare Marketing Authorisation Applications for Human Medicines. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory/research-development/scientific-guidelines/quality/quality-stability (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- The European Medicines Agency’s Scientific Guidelines on Impurities in Drug Products and Drug Substances Help Medicine Developers Prepare Marketing Authorisation Applications for Human Medicines. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory/research-development/scientific-guidelines/quality/quality-impurities (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- ICH M7 Assessment and Control of DNA Reactive (Mutagenic) Impurities in Pharmaceuticals to Limit Potential Carcinogenic Risk. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-guideline-m7r1-assessment-control-dna-reactive-mutagenic-impurities-pharmaceuticals-limit_en.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- Courtney, B.; Easton, J.; Inglesby, T.V.; SooHoo, C. Maximizing state and local medical countermeasure stockpile investments through the Shelf-LifeExtension Program. Biosecur. Bioterror. 2009, 7, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regulska, K.; Michalak, M.; Murias, M.; Stanisz, B. Genotoxic impurities in pharmaceutical products—Regulatory, toxicological and pharmaceutical considerations. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 90, 116–120. [Google Scholar]
- Regulski, M.; Regulska, K.; Stanisz, B.J.; Murias, M.; Gieremek, P.; Wzgarda, A.; Niznik, B. Chemistry and pharmacology of Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 1764–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Düsing, R. Mega clinical trials which have shaped the RAS intervention clinical practice. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 10, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evidence-Based Clinical Decision Support Tools and Calculators for Medical Professionals. Available online: https://clincalc.com/DrugStats/Drugs/Ramipril (accessed on 2 July 2021).
- Regulska, K.; Stanisz, B. Kinetics and mechanism of solid state imidapril hydrochloride degeneration and its degradation impurities identification. Centr. Eur. J. Chem. 2013, 11, 754–762. [Google Scholar]
- Stanisz, B. The influence of relative humidity and temperature on stability of moexipril hydrochloride in solid phase. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2004, 61, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stanisz, B. The stability of quinapril hydrochloride—a mixture of amorphous and crystalline forms (QHC-AC)—in solid phase. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2003, 60, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stanisz, B. Evaluation of stability of enalapril maleate in solid phase. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2003, 31, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanisz, B. Kinetics of lisinopril degradation in solid phase. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 2005, 85, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wzgarda, A.; Dettlaff, K.; Rostalska, M.; Pabian, E.; Regulska, K.; Stanisz, B. Thermo-, radio- and photostability of perindopril tert-butyloamine in the solid state. comparison to other angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. Iran J. Pharm. Res. 2017, 16, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- ICH Q2 (R1) Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/ich-q2-r1-validation-analytical-procedures-text-methodology (accessed on 5 September 2021).
- Khawam, A.; Flanagan, D.R. Solid-state kinetic models: Basics and mathematical fundamentals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 17315–17328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yu, L.; Mantri, R.V. Developing Solid Oral Dosage Forms Pharmaceutical Theory and Practice; Academic Press: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Stanisz, B.; Regulska, K.; Kolasa, K. UV derivative spectrophotometric and RP-HPLC methods for determination of imidapril hydrochloride in tablets and for its stability assessment in solid state. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2011, 68, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stanisz, B.; Regulska, K.; Ratajczak, T. First order derivative spectrophotometric and HPLC methods for determination of moexipril hydrochloride in the pure form, pharmeceutical formulations and evaluation of its stability. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2012, 69, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Regulska, K.; Stanisz, B.; Lisiecki, P. Optimization of storage and manufacture conditions for imidapril hydrochloride in solid state as a way to reduce costs of antihypertensive therapy. AAPS PharmSciTech 2013, 14, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stanisz, B.; Regulska, K.; Kania, J.; Garbacki, P. Effect of pharmaceutical excipients on the stability of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in their solid dosage formulations. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paszun, S.; Regulska, K.; Stanisz, B. Cilazapril decomposition kinetics and mechanism in the solid state versus stability of the other ester pro-drug angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. React. Kinet. Mech. Cat. 2013, 109, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanisz, B. Liquid chromatographic studies of the stability of benazepril in pure form and in tablets. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2004, 27, 3103–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
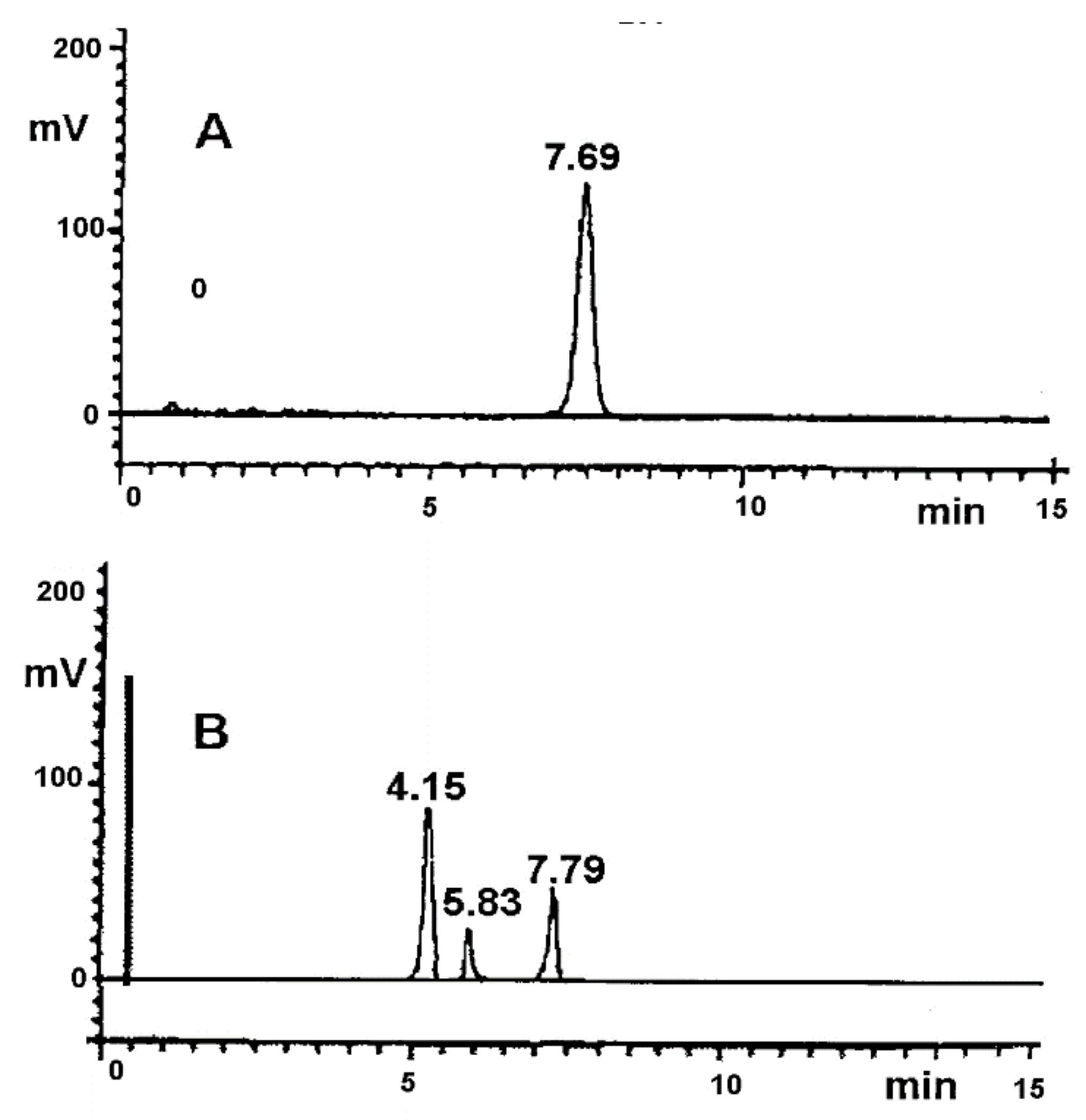
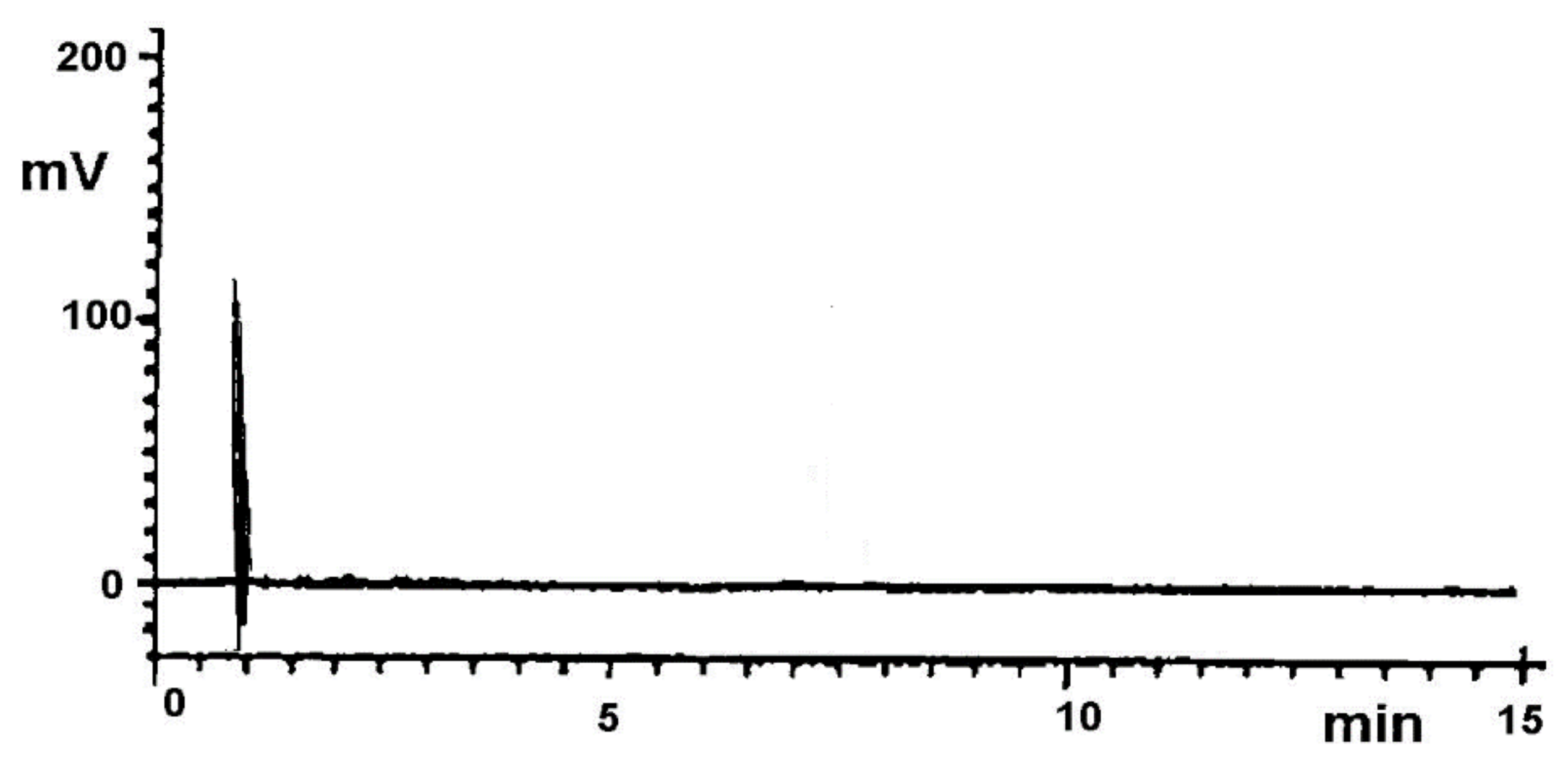



| Statistical Evaluation | Low Precision Level | High Precision Level |
|---|---|---|
| Arithmetic mean of the measured value, area | 3.4489 | 6.8340 |
| Standard deviation (SD) | 0.0505 | 0.0792 |
| Relative standard deviation (RSD) | 0.0146 | 0.0124 |
| Variation coefficient (CV%) | 1.2200 | 1.2410 |
| Statistical Analysis for y = ax + b | Statistical Analysis for y = ax |
|---|---|
| a ± Δa = 138.87 ± 7.62 | a ± Δa = 144.22 ± 7.05 |
| b ± Δb = 0.149 ± 0.189 | Sa = 3.119 |
| Sa = 3.308 | Sy = 0.113 |
| Sb = 0.0821 | r = 0.998 |
| Sy = 0.120 | |
| r = 0.998 |
| T (K) | Decomposition Rate Constants in Solid Phase ki (s−1) | Parameters of the Arrhenius Relationship ki = f(1/T) | Thermodynamic Parameters of RAM Decomposition (RH 76%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RAM in pure | |||
| 343 | (2.241 ± 0.185) × 10−7 | a = −5138.0 ± 561.2 | Ea = (96.39 ± 22.4) KJ/mol |
| 348 | (3.035 ± 0.293) × 10−7 | b = 1.032 ± 0.417 | ∆H≠ = (93.91 ± 24.8) KJ/mol |
| 353 | (5.145 ± 0.351) × 10−7 | Sa = 176.360 | ∆S≠ = (−92.01 ± 189.2) KJ/(K mol) |
| 363 | (1.343 ± 0.093) × 10−6 | Sb = 0.449 | T = 298 K |
| Sy = 0.449 | |||
| r = −0.998 | |||
| RAM–MC model mixture | |||
| 323 | (5.860 ± 0.122) × 10−9 | a = −13580.2 ± 4041.5 | Ea = (112.91± 33.6) KJ/mol |
| 328 | (9.900 ± 0.149) × 10−9 | b = 23.74 ± 10.72 | ∆H≠ = (110.43 ± 36.7) KJ/mol |
| 333 | (5.141 ± 0.168) × 10−8 | Sa = 1270.110 | ∆S≠ = (−47.57 ± 98.5) KJ/(K mol) |
| 343 | 1.151 ± 0.149) × 10−7 | Sb = 3.862 | T = 298 K |
| Sy = 0.223 | |||
| r = −0.991 | |||
| RAM–HPMC model mixture | |||
| 323 | (4.890 ± 0.480) × 10−9 | a = −13976.4 ± 3528.2 | Ea = (116.20 ± 29.3) KJ/mol |
| 328 | (9.168 ± 0.254) × 10−9 | b = 24.83 ± 9.36 | ∆H≠ = (113.71 ± 31.8) KJ/mol |
| 333 | (4.569 ± 0.388) × 10−8 | Sa = 1108.800 | ∆S≠ = (−38.47 ± 167.2) KJ/(K mol) |
| 343 | (1.090 ± 0.286) × 10−7 | Sb = 3.371 | T = 298 K |
| Sy = 0.195 | |||
| r = −0.993 | |||
| RAM–S model mixture | |||
| 323 | (4.660 ± 0.268) × 10−9 | a = −14824.4 ± 2433.1 | Ea = (123.25 ± 20.2) KJ/mol |
| 328 | (8.161 ± 0.396) × 10−9 | b = 27.38 ± 6.45 | ∆H≠ = (120.78 ± 22.7) KJ/mol |
| 333 | (4.154 ± 0.816) × 10−8 | Sa = 764.64 | ∆S≠ = (−17.26 ± 109.2) KJ/(K mol) |
| 343 | (1.268 ± 0.452) × 10−7 | Sb = 2.325 | T = 298 K |
| Sy = 0.134 | |||
| r = −0.997 | |||
| RAM–T model mixture | |||
| 323 | (8.264 ± 0.268) × 10−9 | a = −11910.2 ± 2248.9 | Ea = (99.02 ± 18.7) KJ/mol |
| 328 | (1.264 ± 0.665) × 10−8 | b = 18.42 ± 5.96 | ∆H≠ = (101.51 ± 21.2) KJ/mol |
| 333 | (4.268 ± 0.426) × 10−8 | Sa = 706.760 | ∆S≠ = (−89.43 ± 105.2) KJ/(K mol) |
| 343 | (1.152 ± 0.338) × 10−7 | Sb = 2.149 | T = 298 K |
| Sy = 0.124 | |||
| r = −0.996 | |||
| RH (%) | Decomposition Rate Constants (k ± ∆k) s−1 for RAM in the Presence of Excipients | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC | HPMC | S | T | |
| 50 | (7.158 ± 0.461) 10−8 | (5.998 ± 0.328) 10−8 | (7.234 ± 0.234) 10−8 | (8.518 ± 0.398) 10−8 |
| 60 | (8.145 ± 0.435) 10−8 | (7.129 ± 0.569) 10−8 | (8.657 ± 0.781) 10−8 | (9.551 ± 0.670) 10−8 |
| 66 | (9.216 ± 0.541) 10−8 | (8.161 ± 0.871) 10−8 | (9.551 ± 0.443) 10−8 | (1.005 ± 0.981) 10−7 |
| 76 | (1.157 ± 0.781) 10−7 | (1.097 ± 0.563) 10−7 | (1.268 ± 0.542) 10−7 | (1.149 ± 0.894) 10−7 |
| Regression Parameters ln ki = a (RH%) + b | ||||
| a ± ∆a | 0.0187 ± 0.0053 | 0.0234 ± 0.0068 | 0.0215 ± 0.0068 | 0.0116 ± 0.0022 |
| b ± ∆b | −17.43 ± 0.35 | −17.86 ± 0.43 | −17.56 ± 0.44 | −16.89 ± 0.14 |
| Sa | 0.0017 | 0.0021 | 0.0022 | 0.0007 |
| Sb | 0.108 | 0.137 | 0.136 | 0.045 |
| r | 0.992 | 0.991 | 0.990 | 0.996 |
| RH (%) | Decomposition rate constants (k ± ∆k) s−1 for pure RAM | Regression parametersln ki = a(RH%) + b | ||
| 50 | (4.166 ± 0.885) 10−8 | A ± ∆a | 0.0646 ± 0.0152 | |
| 60 | (8.169 ± 0.982) 10−8 | B ± ∆b | −20.29 ± 0.98 | |
| 66 | (1.022 ± 0.465) 10−7 | Sa | 0.0048 | |
| 76 | (2.248 ± 0.664) 10−7 | Sb | 0.307 | |
| r | 0.995 | |||
| (k ± ∆k) s−1 | t0.1 (days) | t0.5 (days) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RAM in pure form | (1.449 ± 0.156) × 10−8 | 84.2 | 553.5 |
| RAM tablets in blisters | (0.993 ± 0.846) × 10−8 | 123.2 | 810.2 |
| RAM in whole blisterless tablets | (1.865 ± 0.795) × 10−8 | 65.2 | 428.8 |
| RAM in halved blisterless tablets | (4.395 ± 0.328) × 10−8 | 27.8 | 182.7 |
| Compound | Molecular Formula | Molecular Mass | m/z in ES+ [M-H]+ Ion | m/z in ES− [M-H]− Ion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAM | C23H32N2O5 | 416 | 417 | 415 |
|
Product n°1 (RAMat *) | C21H28N2O5 | 388 | 387 | 389 |
|
Product n°2 (DKP-RAM) ** | C23H30N2O4 | 398 | 397 | 399 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Regulska, K.; Musiał, J.; Stanisz, B.J. Solid-State Stability Profiling of Ramipril to Optimize Its Quality Efficiency and Safety. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13101600
Regulska K, Musiał J, Stanisz BJ. Solid-State Stability Profiling of Ramipril to Optimize Its Quality Efficiency and Safety. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(10):1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13101600
Chicago/Turabian StyleRegulska, Katarzyna, Joanna Musiał, and Beata J. Stanisz. 2021. "Solid-State Stability Profiling of Ramipril to Optimize Its Quality Efficiency and Safety" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 10: 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13101600
APA StyleRegulska, K., Musiał, J., & Stanisz, B. J. (2021). Solid-State Stability Profiling of Ramipril to Optimize Its Quality Efficiency and Safety. Pharmaceutics, 13(10), 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13101600






