Targeted Delivery of Epidermal Growth Factor to the Human Placenta to Treat Fetal Growth Restriction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Phage Screening
2.2. Peptide Localization
2.3. Liposome Formulation
2.4. Human Tissue
2.5. Explant Culture
2.6. Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Biochemical Assays
2.8. Measurement of System a Transporter Activity
2.9. Phosphokinase Array
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
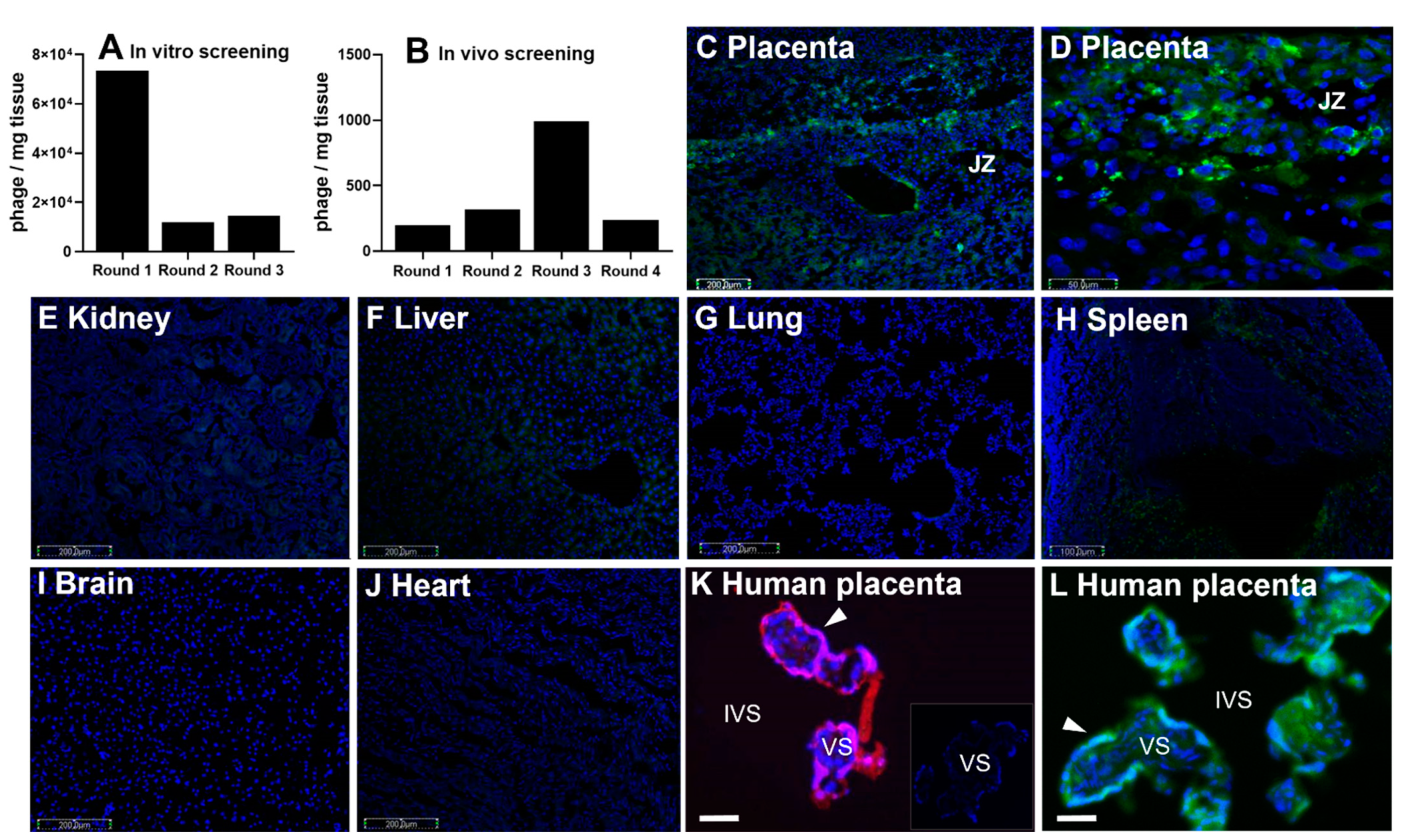
3.1. CCGPSARAPC Peptide Localizes to Human Placenta
3.2. Liposomal Preparation and Characterization
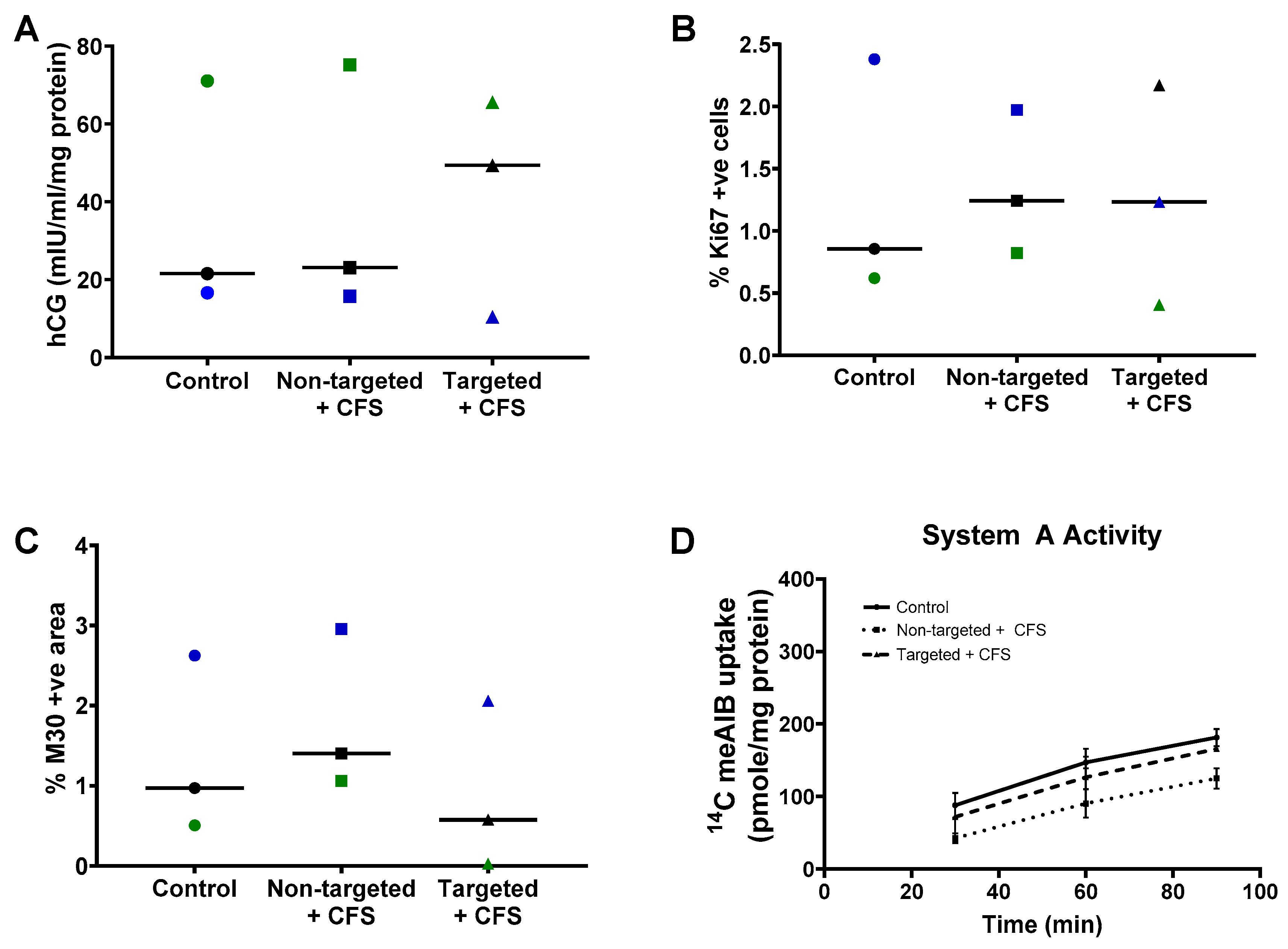
3.3. GPS-Liposomes Do Not Alter the Basal Rate of hCG Secretion, Cell Turnover or System a Transporter Activity
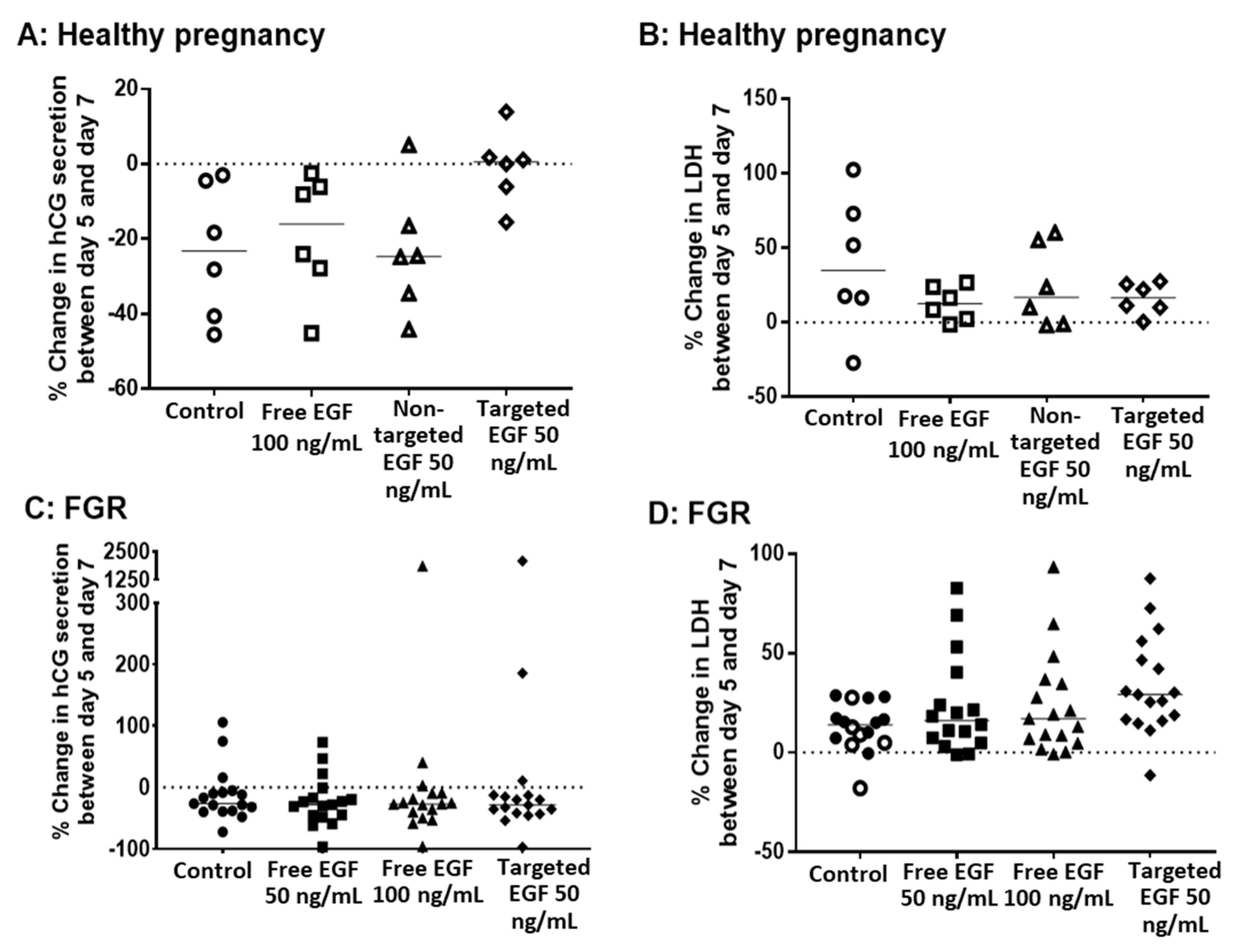
3.4. Delivery of EGF Does Not Alter hCG Secretion, LDH Release or Cell Turnover
3.5. EGF Significantly Increases System a Transporter Activity in Human Placental Explants
3.6. Phosphorylated Kinase Activity in Placental Explants in Response to EGF Delivery
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baschat, A.A. Neurodevelopment following fetal growth restriction and its relationship with antepartum parameters of placental dysfunction. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 37, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flenady, V.; Koopmans, L.; Middleton, P.; Froen, J.F.F.; Smith, G.; Gibbons, K.; Coory, M.; Gordon, A.; Ellwood, D.; McIntyre, H.; et al. Major risk factors for stillbirth in high-income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2011, 377, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brosens, I.; Pijnenborg, R.; Vercruysse, L.; Romero, R. The “Great Obstetrical Syndromes” are associated with disorders of deep placentation. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 204, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fisk, N.M.; Atun, R. Systematic analysis of research underfunding in maternal and perinatal health. BJOG 2009, 116, 347–356. [Google Scholar]
- Scaffidi, J.; Mol, B.W.; Keelan, J.A. The pregnant women as a drug orphan: A global survey of registered clinical trials of pharmacological interventions in pregnancy. BJOG 2017, 124, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015, 385, 117–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.; Ndifon, C.; Lui, S.; Widdows, K.; Kotamraju, V.R.; Agemy, L.; Teesalu, T.; Glazier, J.D.; Cellesi, F.; Tirelli, N.; et al. Tumor-homing peptides as tools for targeted delivery of payloads to the placenta. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600349. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, L.E.; De Castro, N.R.; Addo, N.; Wareing, M.; Greenwood, S.; Jones, R.L.; Sibley, C.P.; Johnstone, E.; Heazell, A. Placental Features of Late-Onset Adverse Pregnancy Outcome. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129117. [Google Scholar]
- Junaid, T.O.; Brownbill, P.; Chalmers, N.; Johnstone, E.D.; Aplin, J.D. Fetoplacental vascular alterations associated with fetal growth restriction. Placenta 2014, 35, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ptacek, I.; Smith, A.; Garrod, A.; Bullough, S.; Bradley, N.; Batra, G.; Sibley, C.P.; Jones, R.L.; Brownbill, P.; Heazell, A.E.P. Quantitative assessment of placental morphology may identify specific causes of stillbirth. BMC Clin. Pathol. 2016, 16, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, M.; Glazier, J.D.; Sibley, C.P.; Jansson, T.; Powell, T.L. Activity and protein expression of the Na+/H+ exchanger is reduced in syncytiotrophoblast microvillous plasma membranes isolated from preterm intrauterine growth restriction pregnancies. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 5686–5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glazier, J.D.; Cetin, I.; Perugino, G.; Ronzoni, S.; Grey, A.M.; Mahendran, D.; Marconi, A.M.; Pardi, G.; Sibley, C.P. Association between the Activity of the System A Amino Acid Transporter in the Microvillous Plasma Membrane of the Human Placenta and Severity of Fetal Compromise in Intrauterine Growth Restriction. Pediatr. Res. 1997, 42, 514–519. [Google Scholar]
- Izutsu, T.; Kudo, T.; Sato, T.; Nishiya, I.; Ohyashiki, K.; Nakagawara, K. Telomerase and Proliferative Activity in Placenta From Women With and Without Fetal Growth Restriction. Obstet. Gynecol. 1999, 93, 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Heazell, A.E.; Sharp, A.N.; Baker, P.N.; Crocker, I.P. Intra-uterine growth restriction is associated with increased apoptosis and altered expression of proteins in the p53 pathway in villous trophoblast. Apoptosis 2010, 16, 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, R.; Smith, S.D.; Yusuf, K.; Huettner, P.C.; Kraus, F.T.; Sadovsky, Y.; Nelson, D. Trophoblast apoptosis from pregnancies complicated by fetal growth restriction is associated with enhanced p53 expression. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2002, 186, 1056–1061. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dackor, J.; Caron, K.M.; Threadgill, D.W. Placental and Embryonic Growth Restriction in Mice With Reduced Function Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Alleles. Genetics 2009, 183, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fondacci, C.; Alsat, E.; Gabriel, R.; Blot, P.; Nessmann, C.; Evain-Brion, D. Alterations of human placental epidermal growth factor receptor in intrauterine growth retardation. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moll, S.J.; Jones, C.J.; Crocker, I.P.; Baker, P.N.; Heazell, A.E. Epidermal growth factor rescues trophoblast apoptosis induced by reactive oxygen species. Apoptosis 2007, 12, 1611–1622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, E.D.; Sibley, C.P.; Lowen, B.; Guilbert, L.J. Epidermal growth factor stimulation of trophoblast differentiation requires MAPK11/14 (p38 MAP kinase) activation. Biol. Reprod. 2005, 73, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.; Francis, R.; Guilbert, L.; Baker, P.N. Growth Factor Rescue of Cytokine Mediated Trophoblast Apoptosis. Placenta 2002, 23, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Teesalu, T.; Sugahara, K.N.; Kotamraju, V.R.; Ruoslahti, E. C-end rule peptides mediate neuropilin-1-dependent cell, vascular, and tissue penetration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16157–16162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teesalu, T.; Sugahara, K.N.; Ruoslahti, E. Mapping of Vascular ZIP Codes by Phage Display. Methods Enzymol. 2012, 503, 35–56. [Google Scholar]
- Matos, P.; Horn, J.A.; Beards, F.; Lui, S.; Desforges, M.; Harris, L.K. A role for the mitochondrial-associated protein p32 in regulation of trophoblast proliferation. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2014, 20, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greenwood, S.L.; Sibley, C.P. In vitro methods for studying human placental amino acid transport placental villous fragments. Methods Mol. Med. 2006, 122, 253–264. [Google Scholar]
- Simán, C.M.; Sibley, C.P.; Jones, C.J.; Turner, M.A.; Greenwood, S.L. The functional regeneration of syncytiotrophoblast in cultured explants of term placenta. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2001, 280, R1116–R1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muoth, C.; Aengenheister, L.; Kucki, M.; Wick, P.; Buerki-Thurnherr, T. Nanoparticle transport across the placental barrier: Pushing the field forward! Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 941–957. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, S.J.; Crompton, L.A.; Sood, A.; Saunders, M.; Boyle, N.T.; Buckley, A.; Minogue, A.M.; McComish, S.F.; Jiménez-Moreno, N.; Cordero-Llana, O.; et al. Nanoparticle-induced neuronal toxicity across placental barriers is mediated by autophagy and dependent on astrocytes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, M.A.; Roulstone, C.J.; Desforges, M.; Cretney, M.; Champion, E.; Lacey, H. The extent and variability of effects of culture conditions on the secretion of human chorionic gonadotrophin and interleukin-6 by human, term placental explants in culture. Placenta 2006, 27, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cureton, N.; Korotkova, I.; Baker, B.; Greenwood, S.; Wareing, M.; Kotamraju, V.R.; Teesalu, T.; Cellesi, F.; Tirelli, N.; Ruoslahti, E.; et al. Selective Targeting of a Novel Vasodilator to the Uterine Vasculature to Treat Impaired Uteroplacental Perfusion in Pregnancy. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3715–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, I.; Cartwright, J.E.; Lumicisi, B.; Wallace, A.E.; Whitley, G.S. Caffeine Inhibits EGF-Stimulated Trophoblast Cell Motility through the Inhibition of mTORC2 and Akt. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 4502–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, R.G.; Sonnenberg-Hirche, C.; Smith, S.D.; Hu, C.; Barton, A.; Sadovsky, Y.; Nelson, D.M. Epidermal Growth Factor Abrogates Hypoxia-Induced Apoptosis in Cultured Human Trophoblasts through Phosphorylation of BAD Serine 112. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 2131–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maruo, T.; Matsuo, H.; Otani, T.; Mochizuki, M. Role of epidermal growth factor (EGF) and its receptor in the development of the human placenta. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 1995, 7, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amemiya, K.; Kurachi, H.; Adachi, H.; Morishige, K.I.; Adachi, K.; Imai, T.; Miyake, A. Involvement of epidermal growth factor (EGF)/EGF receptor autocrine and paracrine mechanism in human trophoblast cells: Functional differentiation in vitro. J. Endocrinol. 1994, 143, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrish, D.W.; Dakour, J.; Li, H. Functional regulation of human trophoblast differentiation. J. Reprod. Immunol. 1998, 39, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bajoria, R.; Fisk, N.M.; Contractor, S.F. Liposomal Thyroxine: A Noninvasive Model for Transplacental Fetal Therapy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 3271–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajoria, R.; Sooranna, S.; Chatterjee, R. Effect of lipid composition of cationic SUV liposomes on materno-fetal transfer of warfarin across the perfused human term placenta. Placenta 2013, 34, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barzago, M.M.; Bortolotti, A.; Stellari, F.F.; Diomede, L.; Algeri, M.; Efrati, S.; Salmona, M.; Bonati, M. Placental transfer of valproic acid after liposome encapsulation during in vitro human placenta perfusion. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1996, 277, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Refuerzo, J.S.; Leonard, F.; Bulayeva, N.; Gorenstein, D.; Chiossi, G.; Ontiveros, A.; Longo, M.; Godin, B. Uterus-targeted liposomes for preterm labor management: Studies in pregnant mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34710. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paul, J.W.; Hua, S.; Ilicic, M.; Tolosa, J.M.; Butler, T.; Robertson, S.; Smith, R. Drug delivery to the human and mouse uterus using immunoliposomes targeted to the oxytocin receptor. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 216, 283.e1–283.e14. [Google Scholar]
- Alfaifi, A.A.; Heyder, R.S.; Bielski, E.R.; Almuqbil, R.M.; Kavdia, M.; Gerk, P.M.; da Rocha, S.R. Megalin-targeting liposomes for placental drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 324, 366–378. [Google Scholar]
- Valero, L.; Alhareth, K.; Gil, S.; Simasotchi, C.; Roques, C.; Scherman, D.; Mignet, N.; Fournier, T.; Andrieux, K. Assessment of dually labelled PEGylated liposomes transplacental passage and placental penetration using a combination of two ex-vivo human models: The dually perfused placenta and the suspended villous explants. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhareth, K.; Valero, L.; Mohamed, K.E.; Fliedel, L.; Roques, C.; Gil, S.; Mignet, N.; Fournier, T.; Andrieux, K. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the uptake of lipoplexes by villous placenta explants. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 567, 118479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, K.; Westwood, M. Maternal growth factor regulation of human placental development and fetal growth. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 207, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rejman, J.; Oberle, V.; Zuhorn, I.S.; Hoekstra, D. Size-dependent internalization of particles via the pathways of clathrin- and caveolae-mediated endocytosis. Biochem. J. 2004, 377 Pt 1, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, J.L.; Maihle, N.J. Characterization and expression of novel 60-kDa and 110-kDa EGFR isoforms in human placenta. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 995, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Demographic | Normal Pregnancy (n = 6) | FGR (n = 15) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal age (years) | 35 (31–37) | 29 (24–48) | NS |
| Parity | 2 (1–2) | 0 (0–2) | NS |
| Smoker | 0/6 | 4/15 | |
| BMI | 25 (19–29) | 24 (19–47) | NS |
| Gestation (days) | 273 (272–280) | 250 (209–268) | p = 0.002 |
| Male sex | 6/6 | 3/15 | |
| Individualized birthweight centile | 52 (14–80) | 0.2 (0–3) | p < 0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Renshall, L.J.; Beards, F.; Evangelinos, A.; Greenwood, S.L.; Brownbill, P.; Stevens, A.; Sibley, C.P.; Aplin, J.D.; Johnstone, E.D.; Teesalu, T.; et al. Targeted Delivery of Epidermal Growth Factor to the Human Placenta to Treat Fetal Growth Restriction. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111778
Renshall LJ, Beards F, Evangelinos A, Greenwood SL, Brownbill P, Stevens A, Sibley CP, Aplin JD, Johnstone ED, Teesalu T, et al. Targeted Delivery of Epidermal Growth Factor to the Human Placenta to Treat Fetal Growth Restriction. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(11):1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111778
Chicago/Turabian StyleRenshall, Lewis J., Frances Beards, Angelos Evangelinos, Susan L. Greenwood, Paul Brownbill, Adam Stevens, Colin P. Sibley, John D. Aplin, Edward D. Johnstone, Tambet Teesalu, and et al. 2021. "Targeted Delivery of Epidermal Growth Factor to the Human Placenta to Treat Fetal Growth Restriction" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 11: 1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111778
APA StyleRenshall, L. J., Beards, F., Evangelinos, A., Greenwood, S. L., Brownbill, P., Stevens, A., Sibley, C. P., Aplin, J. D., Johnstone, E. D., Teesalu, T., & Harris, L. K. (2021). Targeted Delivery of Epidermal Growth Factor to the Human Placenta to Treat Fetal Growth Restriction. Pharmaceutics, 13(11), 1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111778







