Safety and Efficacy of Combined Low-Dose Lithium and Low-Dose Aspirin: A Pharmacological and Behavioral Proof-of-Concept Study in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Chronic Treatment with Li and Aspirin
2.3. Toxicity Assessment
2.3.1. Assessment of Water Consumption
2.3.2. Determination of Urinary Output
2.3.3. Determination of Plasma Li, Creatinine, Urea and Cystatin C Levels
2.3.4. Determination of Nephrin and Podocin Levels
2.3.5. Determination of Renal Tubulointerstitial Damage
2.3.6. Assessment of Gastric Mucosal Damage and Bleeding
2.4. Behavioral Studies
2.4.1. Open Field Test (OFT)
2.4.2. Sucrose Consumption Test (SCT)
2.4.3. Elevated Plus-Maze Test (EPMT)
2.5. Statistical Analysis and Presentation of the Results
3. Results
3.1. Study Groups
3.2. Plasma Li Levels following the Various Regimens of Chronic Aspirin + Li Co-Treatment
3.3. Addition of Aspirin to Li Does Not Affect Water Consumption and Urinary Output
3.4. Effects of Chronic Aspirin plus Li Treatment on Kidney Parameters
3.4.1. Creatinine
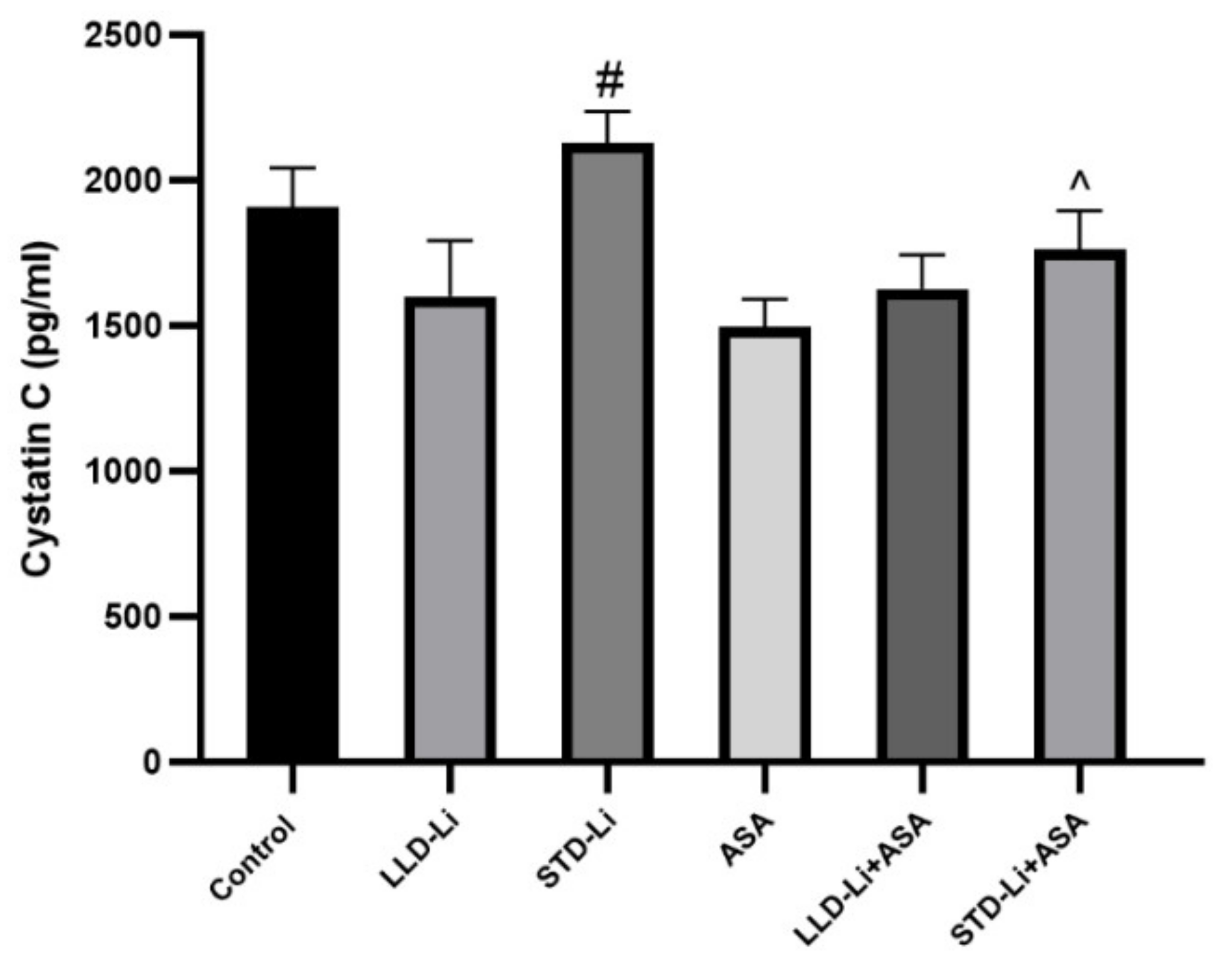
3.4.2. Cystatin C
3.4.3. Nephrin and Podocin
3.4.4. Kidney Weight
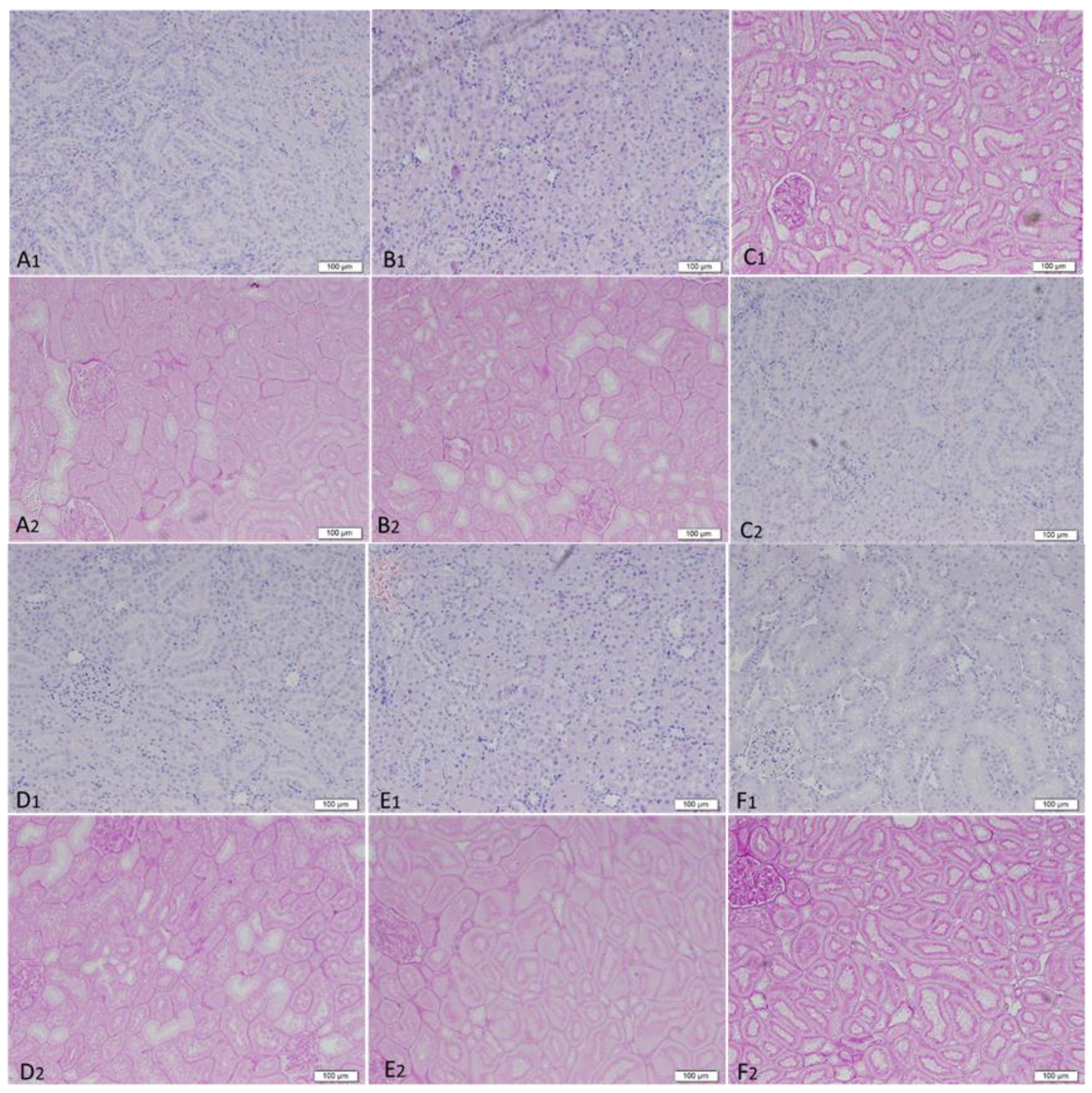
3.4.5. Renal Histopathology
3.5. Effects of Chronic Aspirin plus Li Treatment on Determinants of Gastric Mucosal Integrity
3.5.1. Macroscopic Examination of Stomachs
3.5.2. Gastric Mucosal PGE2 Levels
3.5.3. Gastrointestinal Bleeding
3.5.4. Plasma TXA2 Levels
3.6. Behavioral Effects of Chronic Low-Dose Aspirin Plus Li Treatment—Proof of Concept Experiments
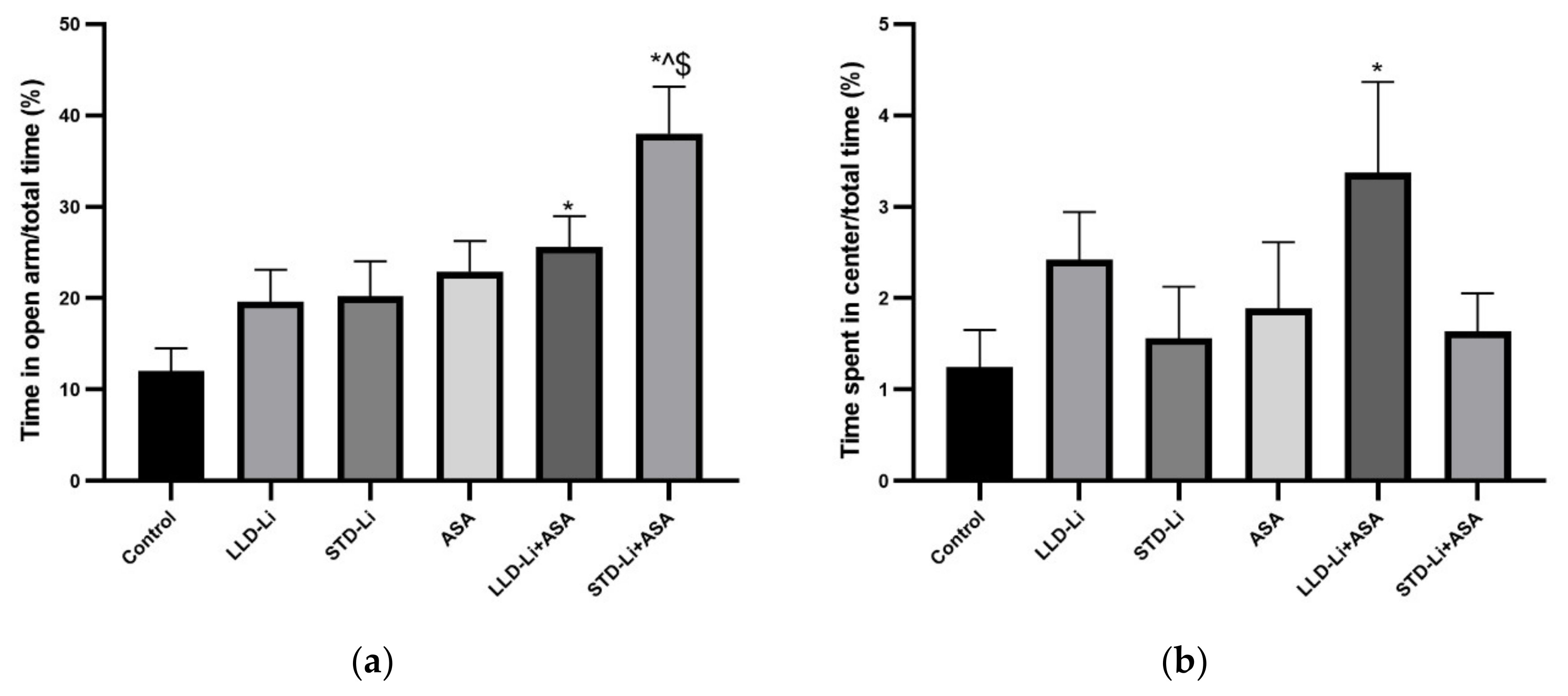
3.6.1. Anxiety-Like Behaviors
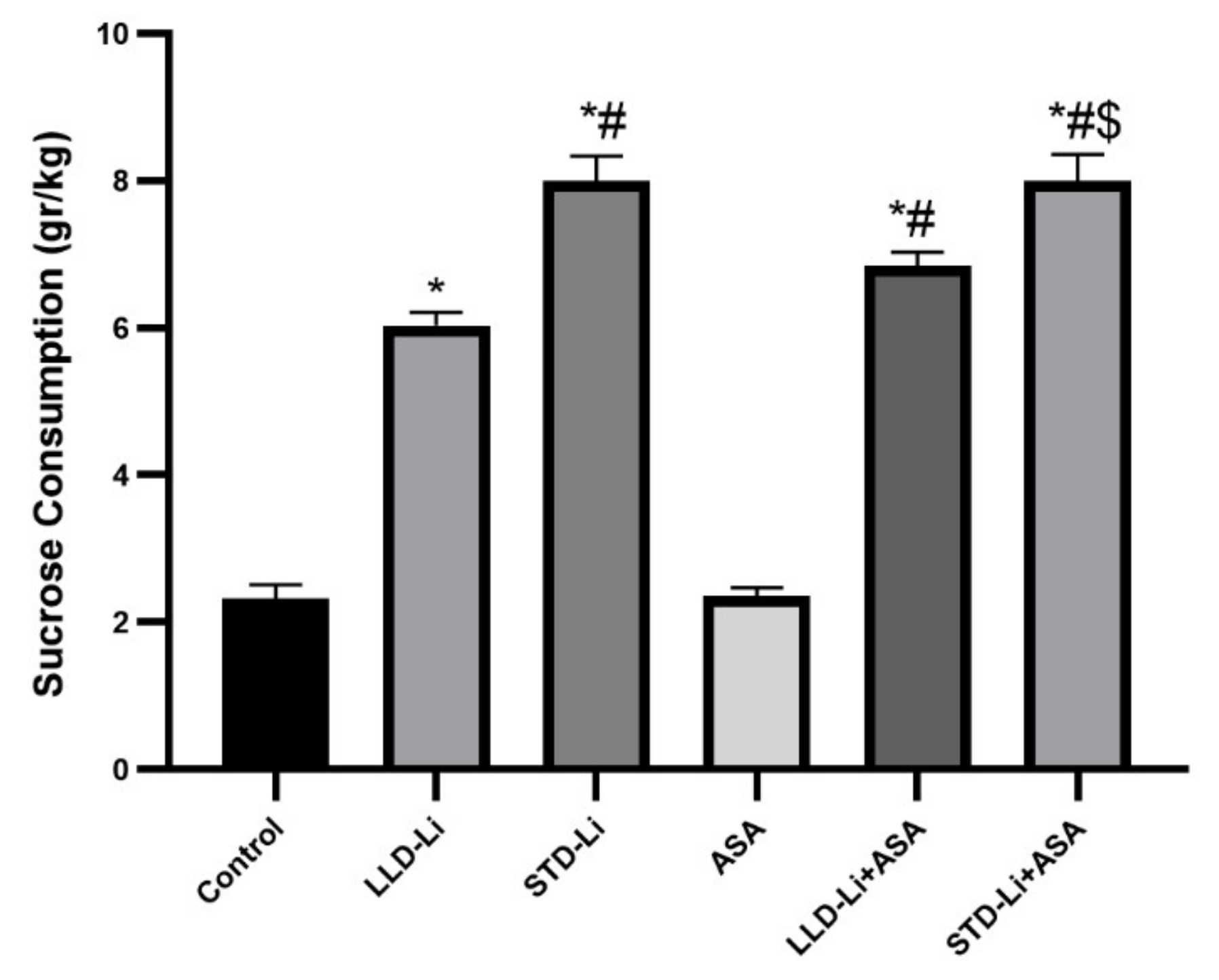
3.6.2. Depressive-Like Behavior
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fagiolini, A.; Forgione, R.; Maccari, M.; Cuomo, A.; Morana, B.; Dell’Osso, M.C.; Pellegrini, F.; Rossi, A. Prevalence, chronicity, burden and borders of bipolar disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2013, 148, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.J.; Stockings, E.; Khoo, J.P.; Erskine, H.E.; Degenhardt, L.; Vos, T.; Whiteford, H.A. The prevalence and burden of bipolar disorder: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Bipolar Disord. 2016, 18, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmaker, R.H. Bipolar disorder. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupfer, D.J. The increasing medical burden in bipolar disorder. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2005, 293, 2528–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande, I.; Berk, M.; Birmaher, B.; Vieta, E. Bipolar disorder. Lancet 2016, 387, 1561–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.L.R.; Van Meter, A.; Genzlinger, J.; Youngstrom, E.A. Review and meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies of adult bipolar disorder. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2017, 78, e1259–e1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, F.; van Ommeren, M.; Flaxman, A.; Cornett, J.; Whiteford, H.; Saxena, S. New WHO prevalence estimates of mental disorders in conflict settings: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2019, 394, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crump, C.; Sundquist, K.; Winkleby, M.A.; Sundquist, J. Comorbidities and mortality in bipolar disorder: A Swedish national cohort study. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Shariq, A.; Said, K.; Sharma, A.; Jeffrey Newport, D.; Salloum, I.M. Medical comorbidities in bipolar disorder. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2018, 20, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, M.L.; Schenck, L.A.; Kruse, J.L.; Klaas, J.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Bobo, W.V.; Bellivier, F.; Leboyer, M.; Roger, V.L.; Brown, R.D.; et al. Long-term risk of myocardial infarction and stroke in bipolar i disorder: A population-based Cohort Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 194, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Correll, C.U.; Solmi, M.; Veronese, N.; Bortolato, B.; Rosson, S.; Santonastaso, P.; Thapa-Chhetri, N.; Fornaro, M.; Gallicchio, D.; Collantoni, E.; et al. Prevalence, incidence and mortality from cardiovascular disease in patients with pooled and specific severe mental illness: A large-scale meta-analysis of 3,211,768 patients and 113,383,368 controls. World Psychiatry 2017, 16, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldstein, B.I.; Carnethon, M.R.; Matthews, K.A.; McIntyre, R.S.; Miller, G.E.; Raghuveer, G.; Stoney, C.M.; Wasiak, H.; McCrindle, B.W. Major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder predispose youth to accelerated atherosclerosis and early cardiovascular disease: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015, 132, 965–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayerbe, L.; Forgnone, I.; Addo, J.; Siguero, A.; Gelati, S.; Ayis, S. Hypertension risk and clinical care in patients with bipolar disorder or schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 225, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldstein, B.I. Bipolar disorder and the vascular system: Mechanisms and new prevention opportunities. Can. J. Cardiol. 2017, 33, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plans, L.; Barrot, C.; Nieto, E.; Rios, J.; Schulze, T.G.; Papiol, S.; Mitjans, M.; Vieta, E.; Benabarre, A. Association between completed suicide and bipolar disorder: A systematic review of the literature. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 242, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.N.; Black, D.W. Bipolar disorder and suicide: A review. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2020, 22, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, J.R.; Shelton, M.D.; Rapport, D.J.; Youngstrom, E.A.; Jackson, K.; Bilali, S.; Gaoocy, S.J.; Findling, R.L. A 20-month, double-blind, maintenance trial of lithium versus divalproex in rapid-cycling bipolar disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 2005, 162, 2152–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geddes, J.R.; Goodwin, G.M.; Rendell, J.; Morriss, R.; Alder, N.; Juszczak, E.; Azorin, J.M.; Cipriani, A.; Ostacher, M.J.; Lewis, S.; et al. Lithium plus valproate combination therapy versus monotherapy for relapse prevention in bipolar i disorder (BALANCE): A randomised open-label trial. Lancet 2010, 375, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severus, E.; Taylor, M.J.; Sauer, C.; Pfennig, A.; Ritter, P.; Bauer, M.; Geddes, J.R. Lithium for prevention of mood episodes in bipolar disorders: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Bipolar Disord. 2014, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berk, M.; Daglas, R.; Dandash, O.; Yücel, M.; Henry, L.; Hallam, K.; Macneil, C.; Hasty, M.; Pantelis, C.; Murphy, B.P.; et al. Quetiapine v. lithium in the maintenance phase following a first episode of mania: Randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Psychiatry 2017, 210, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joas, E.; Karanti, A.; Song, J.; Goodwin, G.M.; Lichtenstein, P.; Landén, M. Pharmacological treatment and risk of psychiatric hospital admission in bipolar disorder. Br. J. Psychiatry 2017, 210, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldessarini, R.J.; Tondo, L.; Vázquez, G.H. Pharmacological treatment of adult bipolar disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 198–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.F.; Pitman, A.; Marston, L.; Walters, K.; Geddes, J.R.; King, M.; Osborn, D.P.J. Self-harm, unintentional injury, and suicide in bipolar disorder during maintenance mood stabilizer treatment a UK population-based electronic health records study. JAMA Psychiatry 2016, 73, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, K.A.; Cipriani, A. Lithium and suicide in mood disorders: Updated meta-review of the scientific literature. Bipolar Disord. 2017, 19, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosser, T.; Smyth, E.; FitzGerald, G. Pharmacotherapy of inflammation, fever, pain, and gout. In Goodman & Gilman’s: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics; Brunton, L.L., Hilal-Dandan, R., Knollmann, B.C., Eds.; McGraw-Hill Medical: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Grandjean, E.M.; Aubry, J.M. Lithium: Updated human knowledge using an evidence-based approach: Part II: Clinical pharmacology and therapeutic monitoring. CNS Drugs 2009, 23, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhlund, L.; Ott, M.; Oja, S.; Bergqvist, M.; Lundqvist, R.; Sandlund, M.; Salander Renberg, E.; Werneke, U. Reasons for lithium discontinuation in men and women with bipolar disorder: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Psychiatry 2018, 18, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gitlin, M. Lithium side effects and toxicity: Prevalence and management strategies. Int. J. Bipolar Disord. 2016, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FitzGerald, G.A.; Patrono, C. The coxibs, selective inhibitors of cyclooxygenase-2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKnight, R.F.; Adida, M.; Budge, K.; Stockton, S.; Goodwin, G.M.; Geddes, J.R. Lithium toxicity profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2012, 379, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azab, A.N.; Shnaider, A.; Osher, Y.; Wang, D.; Bersudsky, Y.; Belmaker, R.H. Lithium nephrotoxicity. Int. J. Bipolar Disord. 2015, 3, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rej, S.; Herrmann, N.; Shulman, K.; Fischer, H.D.; Fung, K.; Harel, Z.; Gruneir, A. Lithium use, but not valproate use, is associated with a higher risk of chronic kidney disease in older adults with mental Illness. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2017, 78, e980–e985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; Desmond, M.; Berk, M. Lithium and nephrotoxicity: A literature review of approaches to clinical management and risk stratification. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahwa, M.; Joseph, B.; Nunez, N.A.; Jenkins, G.D.; Colby, C.L.; Kashani, K.B.; Marin, V.; Moore, K.M.; Betcher, H.K.; Ozerdem, A.; et al. Long-term lithium therapy and risk of chronic kidney disease in bipolar disorder: A historical cohort study. Bipolar Disord. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presne, C.; Fakhouri, F.; Noel, L.H.; Stengel, B.; Even, C.; Kreis, H.; Mignon, F.; Grünfeld, J.P. Lithium-induced nephropathy: Rate of progression and prognostic factors. Kidney Int. 2003, 64, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shine, B.; Mcknight, R.F.; Leaver, L.; Geddes, J.R. Long-term effects of lithium on renal, thyroid, and parathyroid function: A retrospective analysis of laboratory data. Lancet 2015, 386, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kessing, L.V.; Gerds, T.A.; Feldt-Rasmussen, B.; Andersen, P.K.; Licht, R.W. Use of lithium and anticonvulsants and the rate of chronic kidney disease a nationwide population-based study. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aiff, H.; Attman, P.O.; Aurell, M.; Bendz, H.; Ramsauer, B.; Schön, S.; Svedlund, J. Effects of 10 to 30 years of lithium treatment on kidney function. J. Psychopharmacol. 2015, 29, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowitz, G.S.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Kambham, N.; Valeri, A.M.; Hines, W.H.; D’Agati, V.D. Lithium nephrotoxicity: A progressive combined glomerular and tubulointerstitial nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000, 11, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Alphen, A.M.; Bosch, T.M.; Kupka, R.W.; Hoekstra, R. Chronic kidney disease in lithium-treated patients, incidence and rate of decline. Int. J. Bipolar Disord. 2021, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clos, S.; Rauchhaus, P.; Severn, A.; Cochrane, L.; Donnan, P.T. Long-term effect of lithium maintenance therapy on estimated glomerular filtration rate in patients with affective disorders: A population-based cohort study. Lancet Psychiatry 2015, 2, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiff, H.; Attman, P.O.; Aurell, M.; Bendz, H.; Schön, S.; Svedlund, J. The impact of modern treatment principles may have eliminated lithium-induced renal failure. J. Psychopharmacol. 2014, 28, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aprahamian, I.; Santos, F.S.; Dos Santos, B.; Talib, L.; Diniz, B.S.; Radanovic, M.; Gattaz, W.F.; Forlenza, O.V. Long-term, low-dose lithium treatment does not impair renal function in the elderly: A 2-year randomized, placebo-controlled trial followed by single-blind extension. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2014, 75, e672–e678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovvuru, K.; Kanduri, S.R.; Thongprayoon, C.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Lithium and nephrotoxicity: Nephrology’s perspectives. Bipolar Disord. 2020, 22, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Bosmans, E.; Suy, E.; Vandervorst, C.; De Jonckheere, C.; Raus, J. Immune disturbances during major depression: Upregulated expression of interleukin-2 receptors. Neuropsychobiology 1990, 24, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, D.R.; Rapaport, M.H.; Miller, B.J. A meta-analysis of blood cytokine network alterations in psychiatric patients: Comparisons between schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1696–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhaik, E.; Zandi, P. Dysregulation of the NF-κB pathway as a potential inducer of bipolar disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2015, 70, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.M.; Scully, P.; Scott, L.V.; Dinan, T.G. Cytokine profiles in bipolar affective disorder: Focus on acutely ill patients. J. Affect. Disord. 2006, 90, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappelmann, N.; Lewis, G.; Dantzer, R.; Jones, P.B.; Khandaker, G.M. Antidepressant activity of anti-cytokine treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials of chronic inflammatory conditions. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kupka, R.W.; Nolen, W.A.; Post, R.M.; McElroy, S.L.; Altshuler, L.L.; Denicoff, K.D.; Frye, M.A.; Keck, P.E.; Leverich, G.S.; Rush, A.J.; et al. High rate of autoimmune thyroiditis in bipolar disorder: Lack of association with lithium exposure. Biol. Psychiatry 2002, 51, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modabbernia, A.; Taslimi, S.; Brietzke, E.; Ashrafi, M. Cytokine alterations in bipolar disorder: A meta-analysis of 30 studies. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayana, P.; Colpo, G.D.; Simões, L.R.; Giridharan, V.V.; Teixeira, A.L.; Quevedo, J.; Barichello, T. A systemic review of evidence for the role of inflammatory biomarkers in bipolar patients. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2017, 92, 160–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, W.W.; Pedersen, M.G.; Nielsen, P.R.; Mortensen, P.B. Autoimmune diseases, bipolar disorder, and non-affective psychosis. Bipolar Disord. 2010, 12, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perugi, G.; Quaranta, G.; Belletti, S.; Casalini, F.; Mosti, N.; Toni, C.; Dell’Osso, L. General medical conditions in 347 bipolar disorder patients: Clinical correlates of metabolic and autoimmune-allergic diseases. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 170, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.C.; Chen, S.C.; Liu, C.J.; Lu, T.; Shen, C.C.; Hu, Y.W.; Yeh, C.M.; Chen, P.M.; Chen, T.J.; Hu, L.Y. Rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of bipolar disorder: A nationwide population-based study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachen, E.A.; Chesney, M.A.; Criswell, L.A. Prevalence of mood and anxiety disorders in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Care Res. 2009, 61, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Lofland, J.H.; Zhao, N.; Schenkel, B. Increased prevalence of psychiatric disorders and health care-associated costs among patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2011, 10, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Edwards, L.J.; Constantinescu, C.S. A prospective study of conditions associated with multiple sclerosis in a cohort of 658 consecutive outpatients attending a multiple sclerosis clinic. Mult. Scler. 2004, 10, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, R.S.; Konarski, J.Z.; Misener, V.L.; Kennedy, S.H. Bipolar disorder and diabetes mellitus: Epidemiology, etiology, and treatment implications. Ann. Clin. Psychiatry 2005, 17, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.W.; Rapoport, S.I.; Rao, J.S. Altered arachidonic acid cascade enzymes in postmortem brain from bipolar disorder patients. Mol. Psychiatry 2011, 16, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, J.S.; Harry, G.J.; Rapoport, S.I.; Kim, H.W. Increased excitotoxicity and neuroinflammatory markers in postmortem frontal cortex from bipolar disorder patients. Mol. Psychiatry 2010, 15, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderlund, J.; Olsson, S.K.; Samuelsson, M.; Walther-Jallow, L.; Johansson, C.; Erhardt, S.; Landén, M.; Engberg, G. Elevation of cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-1β in bipolar disorder. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2011, 36, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isgren, A.; Jakobsson, J.; Pålsson, E.; Ekman, C.J.; Johansson, A.G.M.; Sellgren, C.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Landén, M. Increased cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-8 in bipolar disorder patients associated with lithium and antipsychotic treatment. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2015, 43, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.K.; Miller, B.J. Meta-analysis of cerebrospinal fluid cytokine and tryptophan catabolite alterations in psychiatric patients: Comparisons between schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and depression. Schizophr. Bull. 2018, 44, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olsson, S.K.; Sellgren, C.; Engberg, G.; Landén, M.; Erhardt, S. Cerebrospinal fluid kynurenic acid is associated with manic and psychotic features in patients with bipolar I disorder. Bipolar Disord. 2012, 14, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourjman, V.; Kouassi, É.; Koué, M.È.; Rocchetti, M.; Fortin-Fournier, S.; Fusar-Poli, P.; Potvin, S. Antipsychotics’ effects on blood levels of cytokines in schizophrenia: A meta-analysis. Schizophr. Res. 2013, 151, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troib, A.; Azab, A.N. Effects of psychotropic drugs on Nuclear Factor kappa B. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Nassar, A.; Sharon-Granit, Y.; Azab, A.N. Psychotropic drugs attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced hypothermia by altering hypothalamic levels of inflammatory mediators in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 626, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boufidou, F.; Nikolaou, C.; Alevizos, B.; Liappas, I.A.; Christodoulou, G.N. Cytokine production in bipolar affective disorder patients under lithium treatment. J. Affect. Disord. 2004, 82, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, J.S.; Lee, H.J.; Rapoport, S.I.; Bazinet, R.P. Mode of action of mood stabilizers: Is the arachidonic acid cascade a common target? Mol. Psychiatry 2008, 13, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.J.; Ertley, R.N.; Rapoport, S.I.; Bazinet, R.P.; Rao, J.S. Chronic administration of lamotrigine downregulates COX-2 mRNA and protein in rat frontal cortex. Neurochem. Res. 2008, 33, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, B.I.; Kemp, D.E.; Soczynska, J.K.; McIntyre, R.S. Inflammation and the phenomenology, pathophysiology, comorbidity, and treatment of bipolar disorder: A systematic review of the literature. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2009, 70, 1078–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, A.; Azab, A.N. Effects of lithium on inflammation. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2014, 5, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bosetti, F.; Rintala, J.; Seemann, R.; Rosenberger, T.A.; Contreras, M.A.; Rapoport, S.I.; Chang, M.C. Chronic lithium downregulates cyclooxygenase-2 activity and prostaglandin E2 concentration in rat brain. Mol. Psychiatry 2002, 7, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Husain, M.I.; Chaudhry, I.B.; Khoso, A.B.; Husain, M.O.; Hodsoll, J.; Ansari, M.A.; Naqvi, H.A.; Minhas, F.A.; Carvalho, A.F.; Meyer, J.H.; et al. Minocycline and celecoxib as adjunctive treatments for bipolar depression: A multicentre, factorial design randomised controlled trial. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, M.G.; Centonze, A.; Miciaccia, M.; Ferorelli, S.; Scilimati, A. Cyclooxygenase inhibition safety and efficacy in inflammation-based psychiatric disorders. Molecules 2020, 25, 5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arana, G.W.; Forbes, R.A. Dexamethasone for the treatment of depression: A preliminary report. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1991, 52, 304–306. [Google Scholar]
- Wolkowitz, O.M.; Reus, V.I.; Keebler, A.; Nelson, N.; Friedland, M.; Brizendine, L.; Roberts, E. Double-blind treatment of major depression with dehydroepiandrosterone. Am. J. Psychiatry 1999, 156, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBattista, C.; Posener, J.A.; Kalehzan, B.M.; Schatzberg, A.F. Acute antidepressant effects of intravenous hydrocortisone and CRH in depressed patients: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Am. J. Psychiatry 2000, 157, 1334–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, F.G.; Monkul, E.S.; Hatch, J.P.; Fonseca, M.; Zunta-Soares, G.B.; Frey, B.N.; Bowden, C.L.; Soares, J.C. Celecoxib as an adjunct in the treatment of depressive or mixed episodes of bipolar disorder: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Hum. Psychopharmacol. 2008, 23, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.H.; Hosseini, F.; Modabbernia, A.; Ashrafi, M.; Akhondzadeh, S. Effect of celecoxib add-on treatment on symptoms and serum IL-6 concentrations in patients with major depressive disorder: Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 141, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabzadeh, S.; Ameli, N.; Zeinoddini, A.; Rezaei, F.; Farokhnia, M.; Mohammadinejad, P.; Ghaleiha, A.; Akhondzadeh, S. Celecoxib adjunctive therapy for acute bipolar mania: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Bipolar Disord. 2015, 17, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, C.; Drye, L.; Vaidya, V.; Lyketsos, C. Celecoxib or naproxen treatment does not benefit depressive symptoms in persons age 70 and older: Findings from a randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2012, 20, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vane, J.R.; Botting, R.M. The mechanism of action of aspirin. Thromb. Res. 2003, 110, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargiulo, G.; Windecker, S.; Vranckx, P.; Gibson, C.M.; Mehran, R.; Valgimigli, M. A critical appraisal of aspirin in secondary prevention. Circulation 2016, 134, 1881–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antithrombotic Trialists’ Collaboration. Collaborative meta-analysis of randomised trials of antiplatelet therapy for prevention of death, myocardial infarction, and stroke in high risk patients. Br. Med. J. 2002, 324, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baigent, C.; Blackwell, L.; Collins, R.; Peto, R.; Hennekens, C.; Doll, R.; Bubes, V.; Buring, J.; Dushkesas, R.; Gaziano, M.; et al. Aspirin in the primary and secondary prevention of vascular disease: Collaborative meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised trials. Lancet 2009, 373, 1849–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capodanno, D.; Angiolillo, D.J. Aspirin for primary cardiovascular risk prevention and beyond in diabetes mellitus. Circulation 2016, 134, 1579–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biondi-Zoccai, G.G.L.; Lotrionte, M.; Agostoni, P.; Abbate, A.; Fusaro, M.; Burzotta, F.; Testa, L.; Sheiban, I.; Sangiorgi, G. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the hazards of discontinuing or not adhering to aspirin among 50 279 patients at risk for coronary artery disease. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 2667–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abraham, N.S.; Hlatky, M.A.; Antman, E.M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Bjorkman, D.J.; Clark, C.B.; Furberg, C.D.; Johnson, D.A.; Kahi, C.J.; Laine, L.; et al. ACCF/ACG/AHA 2010 expert consensus document on the concomitant use of proton pump inhibitors and thienopyridines: A focused update of the ACCF/ACG/AHA 2008 expert consensus document on reducing the gastrointestinal risks of antiplatelet therapy and NSAID. Circulation 2010, 122, 2619–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkun, A.; Bardou, M.; Kuipers, E.J.; Sung, J.; Hunt, R.H.; Martel, M.; Sinclair, P. International concensus recommendations on the management of patients with nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Ann. Intern. Med. 2010, 152, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, O.P.; Flicker, L.; Yeap, B.B.; Alfonso, H.; McCaul, K.; Hankey, G.J. Aspirin decreases the risk of depression in older men with high plasma homocysteine. Transl. Psychiatry 2012, 2, e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sepehrmanesh, Z.; Fahimi, H.; Akasheh, G.; Davoudi, M.; Gilasi, H.; Ghaderi, A. The effects of combined sertraline and aspirin therapy on depression severity among patients with major depressive disorder: A randomized clinical trial. Electron. Physician 2017, 9, 5770–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savitz, J.B.; Teague, T.K.; Misaki, M.; Macaluso, M.; Wurfel, B.E.; Meyer, M.; Drevets, D.; Yates, W.; Gleason, O.; Drevets, W.C.; et al. Treatment of bipolar depression with minocycline and/or aspirin: An adaptive, 2×2 double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase IIA clinical trial. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kessing, L.V.; Rytgaard, H.C.; Gerds, T.A.; Berk, M.; Ekstrøm, C.T.; Andersen, P.K. New drug candidates for bipolar disorder—A nation-wide population-based study. Bipolar Disord. 2019, 21, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stolk, P.; Souverein, P.C.; Wilting, I.; Leufkens, H.G.M.; Klein, D.F.; Rapoport, S.I.; Heerdink, E.R. Is aspirin useful in patients on lithium? A pharmacoepidemiological study related to bipolar disorder. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2010, 82, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uwai, Y.; Yamaguchi, R.; Nabekura, T. Analysis of sex difference in the tubular reabsorption of lithium in rats. Physiol. Res. 2021, 70, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, T.; Morinobu, S.; Okamoto, Y.; Kagaya, A.; Yamawaki, S. Chronic lithium treatment increases the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the rat brain. Psychopharmacology 2001, 158, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimon, G.; Sidhu, R.S.; Lauver, D.A.; Lee, J.Y.; Sharma, N.P.; Yuan, C.; Frieler, R.A.; Trievel, R.C.; Lucchesi, B.R.; Smith, W.L. Coxibs interfere with the action of aspirin by binding tightly to one monomer of cyclooxygenase-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quinn, R. Comparing rat’s to human’s age: How old is my rat in people years? Nutrition 2005, 21, 775–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, P. The laboratory rat: Relating its age with human’s. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, 624–630. [Google Scholar]
- Einat, H.; Yuan, P.; Gould, T.D.; Li, J.; Du, J.H.; Zhang, L.; Manji, H.K.; Chen, G. The role of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway in mood modulation. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 7311–7316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, M.; Kavraal, A.; Art, A.S.; Süer, C. Effects of chronic and acute lithium treatment on the long-term potentiation and spatial memory in adult rats. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2019, 17, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocjar, C.; Hammonds, M.D.; Shim, S.S. Chronic lithium treatment magnifies learning in rats. Neuroscience 2007, 150, 774–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, S.; Kusano, E.; Yusufi, A.N.K.; Murayama, N.; Dousa, T.P. Pathogenesis of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus due to chronic administration of lithium in rats. J. Clin. Invest. 1985, 75, 1869–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmer, R.T.; Sands, J.M. Lithium intoxication. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, K. The effect of sodium chloride on kidney function in rats with lithium intoxication. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1973, 33, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seggie, J.; Werstiuk, E.S.; Grota, L. Effect of chronic lithium treatment on twenty four hour variation in plasma and red blood cell lithium and sodium concentrations, drinking behavior, body weight, kidney weight, and corticosterone levels. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 1982, 6, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterle, F.; Perentes, E.; Cordier, A.; Roth, D.R.; Verdes, P.; Grenet, O.; Pantano, S.; Moulin, P.; Wahl, D.; Mahl, A.; et al. Urinary clusterin, cystatin C, Β2-microglobulin and total protein as markers to detect drug-induced kidney injury. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; Paglialunga, S.; Islam, R. Cystatin C is a more reliable biomarker for determining eGFR to support drug development studies. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 58, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavenstädt, H.; Kriz, W.; Kretzler, M. Cell biology of the glomerular podocyte. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 253–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kestilä, M.; Lenkkeri, U.; Männikkö, M.; Lamerdin, J.; McCready, P.; Putaala, H.; Ruotsalainen, V.; Morita, T.; Nissinen, M.; Herva, R.; et al. Positionally cloned gene for a novel glomerular protein—Nephrin—Is mutated in congenital nephrotic syndrome. Mol. Cell 1998, 1, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assady, S.; Alter, J.; Axelman, E.; Zohar, Y.; Sabo, E.; Litvak, M.; Kaplan, M.; Ilan, N.; Vlodavsky, I.; Abassi, Z. Nephroprotective effect of heparanase in experimental nephrotic syndrome. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, T.H.; Laursen, U.H.; Marples, D.; Maunsbach, A.B.; Knepper, M.A.; Frokiær, J.; Nielsen, S. Altered expression of renal acid-base transporters in rats with lithium-induced NDI. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2000, 279, F552–F564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christensen, B.M.; Kim, Y.H.; Kwon, T.H.; Nielsen, S. Lithium treatment induces a marked proliferation of primarily principal cells in rat kidney inner medullary collecting duct. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2006, 291, F39–F48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flaisher-Grinberg, S.; Einat, H. Strain-specific battery of tests for domains of mania: Effects of valproate, lithium and imipramine. Front. Psychiatry 2010, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellow, S.; Chopin, P.; File, S.E.; Briley, M. Validation of open: Closed arm entries in an elevated plus-maze as a measure of anxiety in the rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 1985, 14, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita-De Croft, P.; Bedford, J.J.; Leader, J.P.; Walker, R.J. Amiloride modifies the progression of lithium-induced renal interstitial fibrosis. Nephrology 2018, 23, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, T.; Stables, M.; Hobbs, A.; de Souza, P.; Colville-Nash, P.; Warner, T.; Newson, J.; Bellingan, G.; Gilroy, D.W. Effects of low-dose aspirin on acute inflammatory responses in humans. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 2089–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroesen, V.M.; Rodríguez-Martínez, P.; García, E.; Rosales, Y.; Díaz, J.; Martín-Céspedes, M.; Tapia, G.; Sarrias, M.R.; Cardona, P.J.; Vilaplana, C. A beneficial effect of low-dose aspirin in a murine model of active tuberculosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jankowski, J.; Floege, J.; Fliser, D.; Böhm, M.; Marx, N. Cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease: Pathophysiological insights and therapeutic options. Circulation 2021, 143, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, D.E.; Dad, T. Stroke and chronic kidney disease: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management across kidney disease stages. Semin. Nephrol. 2015, 35, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reimann, I.W.; Golbs, E.; Fischer, C.; Frölich, J.C. Influence of intravenous acetylsalicylic acid and sodium salicylate on human renal function and lithium clearance. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1985, 29, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendz, H.; Feinberg, M. Aspirin increases serum lithium ion levels. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1984, 41, 310–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragheb, M.A. Aspirin does not significantly affect patients’ serum lithium levels. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1987, 48, 425. [Google Scholar]
- Szirmai, E.; Sachs, V. Experimental investigation of the effect of a combination of quinine, lithium and salicylic acid by means of various methods. Arzneim.-Forsch./Drug Res. 1974, 24, 1322–1325. [Google Scholar]
- Schaffler, K.; Reeh, P.W.; Zentzis, K.; Hamperl, W. Analgesic effect of acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) versus a lithium-ASA combination: An evoked potential study employing radiant heat stimulation with a CO2 laser. Pharmacopsychiatry 1987, 20, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandragiri, S.S.; Pasol, E.; Gallagher, R.M. Lithium, ACE inhibitors, NSAIDs, and verapamil. A possible fatal combination. Pharmacopsychiatry 1987, 20, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.G.; Seideman, P.; Day, R.O. Adverse drug interactions with Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Recognition, management and avoidance. Drug Saf. 1993, 8, 99–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, K.M.; Mosholder, A.D.; Lu, S. Lithium interaction with the cyclooxygenase 2 Inhibitors rofecoxib and celecoxib and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2003, 64, 1328–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroukhani, S.; Emami-Parsa, M.; Modabbernia, A.; Ashrafi, M.; Farokhnia, M.; Hajiaghaee, R.; Akhondzadeh, S. Aspirin for treatment of lithium-associated sexual dysfunction in men: Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Bipolar Disord. 2013, 15, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fond, G.; Hamdani, N.; Kapczinski, F.; Boukouaci, W.; Drancourt, N.; Dargel, A.; Oliveira, J.; Le Guen, E.; Marlinge, E.; Tamouza, R.; et al. Effectiveness and tolerance of anti-inflammatory drugs’ add-on therapy in major mental disorders: A systematic qualitative review. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2014, 129, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Greene, T.; Li, L.; Beck, G.J.; Joffe, M.M.; Froissart, M.; Kusek, J.W.; Zhang, Y.; Coresh, J.; et al. Factors other than glomerular filtration rate affect serum cystatin C levels. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dastych, M.; Synek, O.; Gottwaldová, J. Impact of long-term lithium treatment on renal function in patients with bipolar disorder based on novel biomarkers. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 39, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Stolz, D.B.; Kiss, L.P.; Monga, S.P.; Holzman, L.B.; Liu, Y. Wnt/β-catenin signaling promotes podocyte dysfunction and albuminuria. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1997–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Groot, T.; Damen, L.; Kosse, L.; Alsady, M.; Doty, R.; Baumgarten, R.; Sheehan, S.; Van Der Vlag, J.; Korstanje, R.; Deen, P.M.T. Lithium reduces blood glucose levels, but aggravates albuminuria in BTBR-ob/ob mice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuure, S.; Popsueva, A.; Jakobson, M.; Sainio, K.; Sariola, H. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inactivation and stabilization of β-catenin induce nephron differentiation in isolated mouse and rat kidney mesenchymes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plotnikov, E.Y.; Grebenchikov, O.A.; Babenko, V.A.; Pevzner, I.B.; Zorova, L.D.; Likhvantsev, V.V.; Zorov, D.B. Nephroprotective effect of GSK-3β inhibition by lithium ions and δ-opioid receptor agonist dalargin on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 220, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, H.; Ge, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhuang, S.; Dworkin, L.; Peng, A.; Gong, R. Delayed administration of a single dose of lithium promotes recovery from AKI. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, W.; Ge, Y.; Liu, Z.; Gong, R. Glycogen synthase kinase 3β dictates podocyte motility and focal adhesion turnover by modulating paxillin activity implications for the protective effect of low-dose lithium in podocytopathy. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 2742–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, H.; Ge, Y.; Peng, A.; Gong, R. Fine-tuning of NFκB by glycogen synthase kinase 3β directs the fate of glomerular podocytes upon injury. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, H.; Ge, Y.; Zhuang, S.; Dworkin, L.D.; Liu, Z.; Gong, R. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3Β prevents NSAID-induced acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinha, S.; Dwivedi, N.; Woodgett, J.; Tao, S.; Howard, C.; Fields, T.A.; Jamadar, A.; Rao, R. Glycogen synthase kinase-3β inhibits tubular regeneration in acute kidney injury by a FoxM1-dependent mechanism. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 13597–13608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Xia, Y.; Xiong, C.; Shao, X.; Zou, H. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3β alleviates chronic renal allograft dysfunction in rats. Transplantation 2021, 105, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, R.; Minay, J.; Cardwell, C.; Fogarty, D.; Kelly, C. Review: Meta-analysis of the effects of lithium usage on serum creatinine levels. J. Psychopharmacol. 2010, 24, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.M.; Rosenbaum, A.; Shahinian, V.; Brosius, F.C. Prevention of lithium-associated renal failure: Recent evidence. Lancet Psychiatry 2015, 2, 1045–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hestbech, J.; Hansen, H.E.; Amdisen, A.; Olsen, S. Chronic renal lesions following long-term treatment with lithium. Kidney Int. 1977, 12, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, R.J.; Leader, J.P.; Bedford, J.J.; Gobe, G.; Davis, G.; Vos, F.E.; DeJong, S.; Schollum, J.B.W. Chronic interstitial fibrosis in the rat kidney induced by long-term (6-mo) exposure to lithium. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2013, 304, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, R.G.; Bennett, W.M.; Davies, B.M.; Kincaid-Smith, P. Structural and functional effects of long-term lithium therapy. Kidney Int. 1982, 21, S13–S19. [Google Scholar]
- Young, R.C.; Gyulai, L.; Mulsant, B.H.; Flint, A.; Beyer, J.L.; Shulman, K.I.; Reynolds, C.F. Pharmacotherapy of bipolar disorder in old age: Review and recommendations. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2004, 12, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngs, R.M.; Chu, M.S.; Meloni, E.G.; Naydenov, A.; Carlezon, W.A.; Konradi, C. Lithium administration to preadolescent rats causes long-lasting increases in anxiety-like behavior and has molecular consequences. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 6031–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnaider, A.; Azab, A.N. Lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus-a case report and discussion on the pathophysiological mechanism. Int. J. Nephrol. Kidney Fail. 2015, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünfeld, J.P.; Rossier, B.C. Lithium nephrotoxicity revisited. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2009, 5, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batlle, D.C.; von Riotte, A.B.; Gaviria, M.; Grupp, M. Amelioration of polyuria by amiloride in patients receiving long-term lithium therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 312, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurcombe, J.A.; Hartley, P.; Lay, A.C.; Ni, L.; Bedford, J.J.; Leader, J.P.; Singh, S.; Murphy, A.; Scudamore, C.L.; Marquez, E.; et al. Podocyte GSK3 is an evolutionarily conserved critical regulator of kidney function. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stambolic, V.; Ruel, L.; Woodgett, J.R. Lithium inhibits glycogen synthase kinase-3 activity and mimics wingless signalling in intact cells. Curr. Biol. 1996, 6, 1664–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Huang, L.D.; Jiang, Y.M.; Manji, H.K. The mood-stabilizing agent valproate inhibits the activity of glycogen synthase kinase-3. J. Neurochem. 2000, 72, 1327–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, F.; Phiel, C.J.; Spece, L.; Gurvich, N.; Klein, P.S. Inhibitory phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) in response to lithium: Evidence for autoregulation of GSK-3. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 33067–33077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polakis, P. Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 1837–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bos, C.L.; Kodach, L.L.; Van Den Brink, G.R.; Diks, S.H.; Van Santen, M.M.; Richel, D.J.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Hardwick, J.C.H. Effect of aspirin on the Wnt/β-catenin pathway is mediated via protein phosphatase 2A. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6447–6456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dovizio, M.; Bruno, A.; Tacconelli, S.; Patrignani, P. Mode of action of aspirin as a chemopreventive agent. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2013, 191, 39–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, M.; Klawonn, A.M.; Nilsson, A.; Singh, A.K.; Zajdel, J.; Wilhelms, D.B.; Lazarus, M.; Löfberg, A.; Jaarola, M.; Kugelberg, U.Ö.; et al. Prostaglandin-dependent modulation of dopaminergic neurotransmission elicits inflammation-induced aversion in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2016, 126, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Din, F.V.N.; Valanciute, A.; Houde, V.P.; Zibrova, D.; Green, K.A.; Sakamoto, K.; Alessi, D.R.; Dunlop, M.G. Aspirin inhibits mTOR signaling, activates AMP-activated protein kinase, and induces autophagy in colorectal cancer cells. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1504–1515.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wu, L.; Zhang, W. Aspirin may inhibit angiogenesis and induce autophagy by inhibiting mTOR signaling pathway in murine hepatocarcinoma and sarcoma models. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 2804–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Liao, B.; Qi, H.; Xie, L.J.; Huang, L.; Tan, W.J.; Zhai, N.; Yuan, L.B.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, L.J.; et al. Autophagy contributes to regulation of the hypoxia response during submergence in Arabidopsis thaliana. Autophagy 2015, 11, 2233–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hernández, C.; Barrachina, M.D.; Vallecillo-Hernández, J.; Álvarez, Á.; Ortiz-Masiá, D.; Cosín-Roger, J.; Esplugues, J.V.; Calatayud, S. Aspirin-induced gastrointestinal damage is associated with an inhibition of epithelial cell autophagy. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, L.; Mafham, M.; Wallendszus, K.; Stevens, W.; Buck, G.; Barton, J. Effects of aspirin for primary prevention in persons with diabetes mellitus: The ASCEND study collaborative group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1529–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahmoud, A.N.; Gad, M.M.; Elgendy, A.Y.; Elgendy, I.Y.; Bavry, A.A. Efficacy and safety of aspirin for primary prevention of cardiovascular events: A meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.L.; Roddick, A.J. Association of aspirin use for primary prevention with cardiovascular events and bleeding events: A Systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2019, 321, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rothwell, P.M.; Fowkes, F.G.R.; Belch, J.F.; Ogawa, H.; Warlow, C.P.; Meade, T.W. Effect of daily aspirin on long-term risk of death due to cancer: Analysis of individual patient data from randomised trials. Lancet 2011, 377, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibbins-Domingo, K.; Grossman, D.C.; Curry, S.J.; Davidson, K.W.; Epling, J.W.; García, F.A.R.; Gillman, M.; Harper, D.M.; Kemper, A.R.; Krist, A.H.; et al. Aspirin use for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and colorectal cancer: U.S. preventive services task force recommendation statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016, 164, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.; Nishihara, R.; Wu, K.; Wang, M.; Ogino, S.; Willett, W.C.; Spiegelman, D.; Fuchs, C.S.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Chan, A.T. Population-wide impact of long-term use of aspirin and the risk for cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bosetti, C.; Santucci, C.; Gallus, S.; Martinetti, M.; La Vecchia, C. Aspirin and the risk of colorectal and other digestive tract cancers: An updated meta-analysis through 2019. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abnet, C.C.; Freedman, N.D.; Kamangar, F.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Schatzkin, A. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of gastric and oesophageal adenocarcinomas: Results from a cohort study and a meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simon, T.G.; Duberg, A.S.; Aleman, S.; Chung, R.T.; Chan, A.T.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Association of aspirin with hepatocellular carcinoma and liver-related mortality. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risch, H.A.; Lu, L.; Streicher, S.A.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Ni, Q.; Kidd, M.S.; Yu, H.; Gao, Y.T. Aspirin use and reduced risk of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2017, 26, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Title 1 | Control | LLD-Li | STD-Li | Aspirin | LLD-Li + Aspirin | STD-Li + Aspirin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 23 | 25 | 27 | 24 | 27 | 27 |
| Mild gastritis, n (%) | 11 (48) | 12 (48) | 18 (67) | 10 (42) | 16 (59) | 19 (70) |
| Severe gastritis, n (%) | 0 | 0 | 1 (3.7) | 2 (8.3) | 0 | 1 (3.7) |
| Gastric bleeding | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Gastric ulcer | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shvartsur, R.; Agam, G.; Shnaider, A.; Uzzan, S.; Nassar, A.; Jabarin, A.; Abu-Freha, N.; Meir, K.; Azab, A.N. Safety and Efficacy of Combined Low-Dose Lithium and Low-Dose Aspirin: A Pharmacological and Behavioral Proof-of-Concept Study in Rats. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111827
Shvartsur R, Agam G, Shnaider A, Uzzan S, Nassar A, Jabarin A, Abu-Freha N, Meir K, Azab AN. Safety and Efficacy of Combined Low-Dose Lithium and Low-Dose Aspirin: A Pharmacological and Behavioral Proof-of-Concept Study in Rats. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(11):1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111827
Chicago/Turabian StyleShvartsur, Rachel, Galila Agam, Alla Shnaider, Sarit Uzzan, Ahmad Nassar, Adi Jabarin, Naim Abu-Freha, Karen Meir, and Abed N. Azab. 2021. "Safety and Efficacy of Combined Low-Dose Lithium and Low-Dose Aspirin: A Pharmacological and Behavioral Proof-of-Concept Study in Rats" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 11: 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111827
APA StyleShvartsur, R., Agam, G., Shnaider, A., Uzzan, S., Nassar, A., Jabarin, A., Abu-Freha, N., Meir, K., & Azab, A. N. (2021). Safety and Efficacy of Combined Low-Dose Lithium and Low-Dose Aspirin: A Pharmacological and Behavioral Proof-of-Concept Study in Rats. Pharmaceutics, 13(11), 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111827








