Aerosol Delivery of Surfactant Liposomes for Management of Pulmonary Fibrosis: An Approach Supporting Pulmonary Mechanics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Formulation of Naringin Liposomes
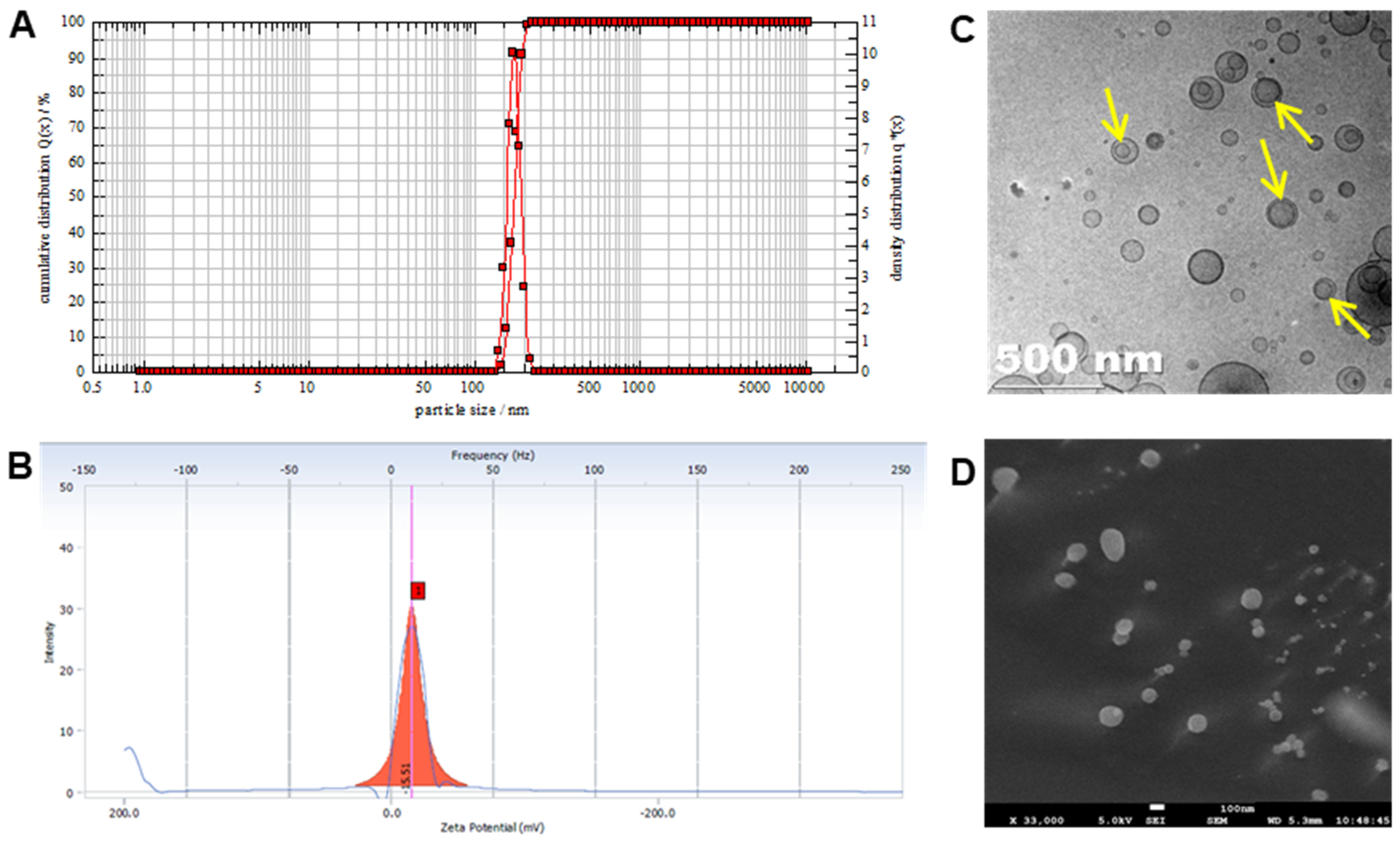
2.2.2. Physicochemical Characterization of Naringin Liposomes—Electron Microscopy, Zeta Potential, Particle Size, PDI, and Encapsulation Efficiency
2.2.3. RP-HPLC Analysis of Naringin
2.2.4. Analysis of Surfactant Functionality by Adsorption Studies
2.2.5. Measurement of Airway Patency
2.2.6. In Vitro Lung Deposition Experiments with the Anderson Twin Stage and the Impinger Cascade Impactor
2.2.7. In Vivo Pulmonary Fibrosis Induction in Rats and Treatment Regimen
Animals
Induction of Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats by Bleomycin and Therapy with Liposomal Naringin
2.2.8. BALF Total and Differential Cell Count, Protein Content, and Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Activity
2.2.9. Hydroxyproline Quantification in Lung Tissue
2.2.10. Study of Antioxidant Biomarkers and Oxidative Stress in Lung Tissues
2.2.11. Histopathological Analysis of Lung Tissues Stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H and E) and Masson’s Trichrome Stains and Other Vital Organs Stained with H and E
2.2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization
3.2. Surfactant Functionality
3.3. Airway Patency
3.4. In Vitro Lung Deposition
3.5. In Vivo Pharmacodynamic Efficacy of Liposomal Naringin in Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis Model in Rats
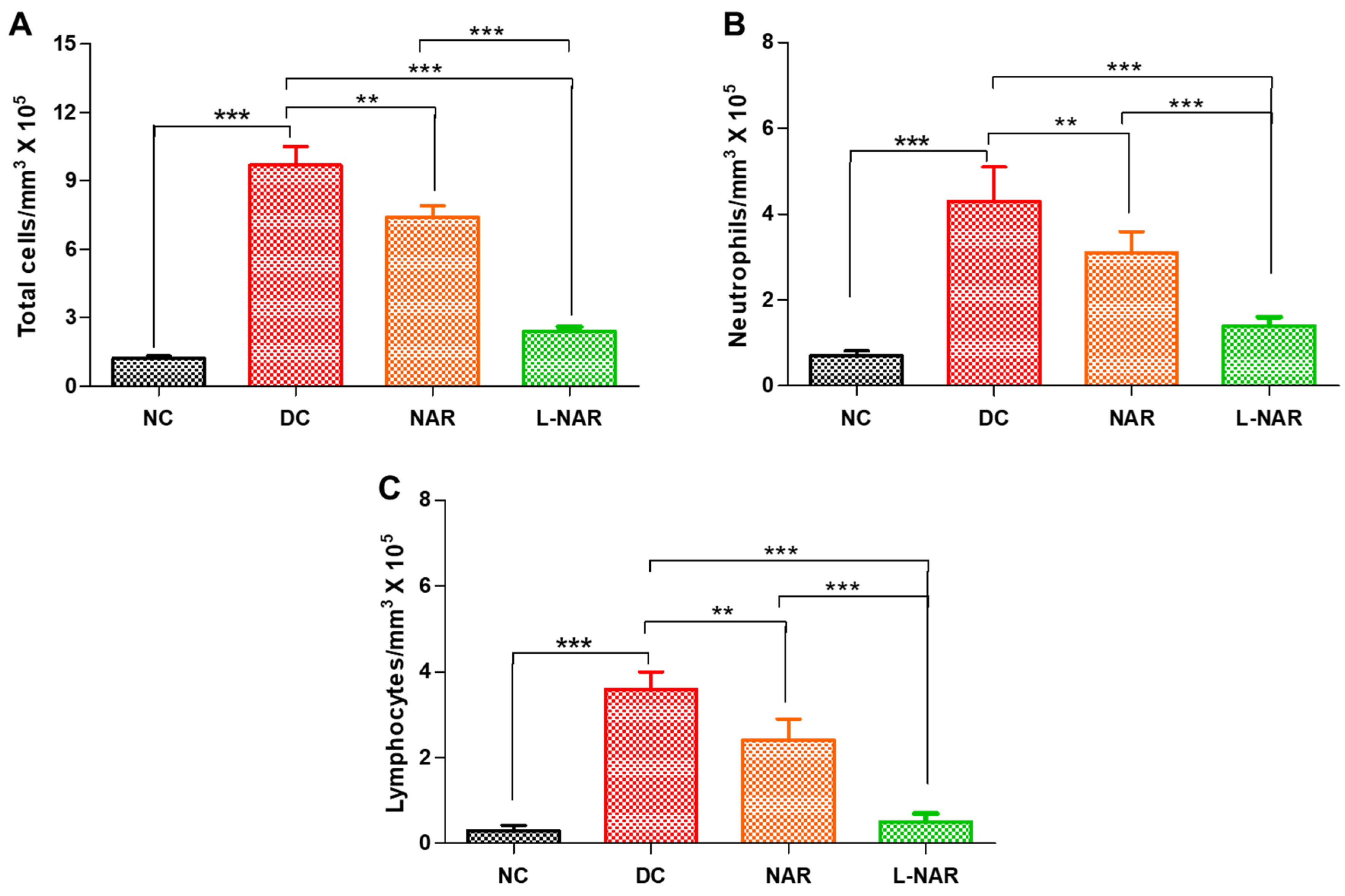
3.5.1. Total and Differential Cell Count, Protein Content and LDH
3.5.2. Hydroxyproline Content and Levels of Antioxidant Enzymes SOD and GPx
3.5.3. Tissue Histopathology
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ivanova, V.; Garbuzenko, O.B.; Reuhl, K.R.; Reimer, D.C.; Pozharov, V.P.; Minko, T. Inhalation treatment of pulmonary fibrosis by liposomal prostaglandin E2. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 84, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallace, W.A.H.; Fitch, P.M.; Simpson, A.J.; Howie, S.E.M. Inflammation-associated remodelling and fibrosis in the lung–A process and an end point. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2007, 88, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chennakesavulu, S.; Mishra, A.; Sudheer, A.; Sowmya, C.; Reddy, C.S.; Bhargav, E. Pulmonary delivery of liposomal dry powder inhaler formulation for effective treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotta, S.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Badr-Eldin, S.M.; Binmahfouz, L.S.; Bakhaidar, R.B.; Sreeharsha, N.; Nair, A.B.; Ramnarayanan, C. Lung Targeted Lipopolymeric Microspheres of Dexamethasone for the Treatment of ARDS. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.; Shirsath, N.; Singh, A.; Joshi, K.S.; Banerjee, R. Endogenous lung surfactant inspired pH responsive nanovesicle aerosols: Pulmonary compatible and site-specific drug delivery in lung metastases. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaur, R.; Dennison, S.R.; Burrow, A.J.; Rudramurthy, S.M.; Swami, R.; Gorki, V.; Katare, O.P.; Kaushik, A.; Singh, B.; Singh, K.K. Nebulised surface-active hybrid nanoparticles of voriconazole for pulmonary Aspergillosis demonstrate clathrin-mediated cellular uptake, improved antifungal efficacy and lung retention. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiara, S.; Antonella, C.; Harari, S. Recent advances in managing idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. F1000Research 2017, 6, 2052. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, G.; Toellner, H.; Morris, H.; Leonard, C.; Chaudhuri, N. Real world experiences: Pirfenidone and nintedanib are effective and well tolerated treatments for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.; Shin, D.; Min, D.; Kim, M.; Ryu, B.; Kim, H.W.; Bae, H. A standardized herbal extract PM014 ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis by suppressing the TGF-β1 pathway. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, N.H.; Kara, H.; Elagoz, S.; Deveci, K.; Gungor, H.; Arslanbas, E. The protective effect of naringin against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in Wistar rats. Pulm. Med. 2016, 2016, 7601393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagaraja, S.; Basavarajappa, G.M.; Karnati, R.K.; Bakir, E.M.; Pund, S. Ion-Triggered In Situ Gelling Nanoemulgel as a Platform for Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Small Lipophilic Molecules. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, A.; Aqil, M.; Imam, S.S.; Ahad, A.; Moolakkadath, T.; Ahmad, F.J. Lamotrigine encapsulated intra-nasal nanoliposome formulation for epilepsy treatment: Formulation design, characterization and nasal toxicity study. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 174, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, H.; Fathalla, Z.; Moharram, H.; Ali, T.F.S.; Pierscionek, B. Cyclodextrin Enhances Corneal Tolerability and Reduces Ocular Toxicity Caused by Diclofenac. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 5260976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagaraja, S.; Basavarajappa, G.M.; Attimarad, M.; Pund, S. Topical Nanoemulgel for the Treatment of Skin Cancer: Proof-of-Technology. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreeharsha, N.; Hiremath, J.G.; Kumar, P.R.; Meravanige, G.; Khan, S.; Karnati, R.K.; Attimarad, M.; Al-Dhubiab, B.; Nair, A.B.; Venugopala, K.N. Doxorubicin Hydrochloride Loaded Polyanhydride Nanoformulations and Cytotoxicity. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2021, 55, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, S.; Nair, A.B.; Al-Dhubiab, B.E. Preparation and evaluation of niosome gel containing acyclovir for enhanced dermal deposition. J. Liposome Res. 2017, 27, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akrawi, S.H.; Gorain, B.; Nair, A.B.; Choudhury, H.; Pandey, M.; Shah, J.N.; Venugopala, K.N. Development and Optimization of Naringenin-Loaded Chitosan-Coated Nanoemulsion for Topical Therapy in Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, M.A.; Nair, A.B. Prevention of rat liver fibrosis by selective targeting of hepatic stellate cells using hesperidin carriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 552, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.J.; Lohade, A.A.; Parmar, J.J.; Hegde, D.D.; Soni, P.; Samad, A.; Menon, M.D. Development of chitosan-based dry powder inhalation system of cisplatin for lung cancer. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 74, 521. [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugam, T.; Joshi, N.; Kaviratna, A.; Ahamad, N.; Bhatia, E.; Banerjee, R. Aerosol Delivery of Paclitaxel-Containing Self-Assembled Nanocochleates for Treating Pulmonary Metastasis: An Approach Supporting Pulmonary Mechanics. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 7, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbitts, A.J.; Ramsey, J.M.; Barlow, J.; MacLoughlin, R.; Cryan, S.-A. In vitro and in vivo assessment of PEGylated PEI for anti-IL-8/CxCL-1 siRNA delivery to the lungs. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, W.T.J.; Ho, S.L.; Coates, A.L. Comparison of nebulized particle size distribution with Malvern laser diffraction analyzer versus Andersen cascade impactor and low-flow Marple personal cascade impactor. J. Aerosol Med. 2000, 13, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvathaneni, V.; Kulkarni, N.S.; Shukla, S.K.; Farrales, P.T.; Kunda, N.K.; Muth, A.; Gupta, V. Systematic development and optimization of inhalable pirfenidone liposomes for non-small cell lung cancer treatment. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, W.; Liang, Y.; Meng, Z.; Chen, X.; Lu, M.; Han, X.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Fu, T. Inhalation of Tetrandrine-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes for pulmonary fibrosis treatment. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 1596–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.; Morsy, M.A.; Jacob, S. Dose translation between laboratory animals and human in preclinical and clinical phases of drug development. Drug Dev. Res. 2018, 79, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, M.A.; Abdel-Latif, R.G.; Nair, A.B.; Venugopala, K.N.; Ahmed, A.F.; Elsewedy, H.S.; Shehata, T.M. Preparation and evaluation of atorvastatin-loaded nanoemulgel on wound-healing efficacy. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kseibati, M.O.; Sharawy, M.H.; Salem, H.A. Chrysin mitigates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats through regulating inflammation, oxidative stress, and hypoxia. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 89, 107011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisseau, P.; Loubaton, B. Nanomedicine, nanotechnology in medicine. Comptes Rendus Phys. 2011, 12, 620–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knudsen, L.; Ruppert, C.; Ochs, M. Tissue remodelling in pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 367, 607–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnula, V.L.; Myllärniemi, M. Oxidant–antioxidant imbalance as a potential contributor to the progression of human pulmonary fibrosis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, D.; Gazdhar, A.; Lopez-Rodriguez, E.; Ruppert, C.; Mahavadi, P.; Günther, A.; Klepetko, W.; Bates, J.H.; Smith, B.; Geiser, T. Alveolar derecruitment and collapse induration as crucial mechanisms in lung injury and fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 52, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Rodriguez, E.; Gay-Jordi, G.; Knudsen, L.; Ochs, M.; Serrano-Mollar, A. Improved Alveolar Dynamics and Structure After Alveolar Epithelial Type II Cell Transplantation in Bleomycin Induced Lung Fibrosis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukamp, C.; Hidalgo, A.; Cruz, A.; Perez-Gil, J.; Ochs, M.; Knudsen, L.; Lopez-Rodriguez, E. New approach to the treatment of bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis using pulmonary surfactant as pirfenidone carrier into the lung. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, PA3910. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Nie, Y.; Luo, Y.; Lin, F.; Zheng, Y.; Cheng, G.; Wu, H.; Zhang, K.; Su, W.; Shen, J. Protective effects of naringin against paraquat-induced acute lung injury and pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 58, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorain, B.; Al-Dhubiab, B.E.; Nair, A.; Kesharwani, P.; Pandey, M.; Choudhury, H. Multivesicular Liposome: A Lipid-based Drug Delivery System for Efficient Drug Delivery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 4404–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudokas, M.; Najlah, M.; Alhnan, M.A.; Elhissi, A. Liposome delivery systems for inhalation: A critical review highlighting formulation issues and anticancer applications. Med. Princ. Pract. 2016, 25, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clancy, J.P.; Dupont, L.; Konstan, M.W.; Billings, J.; Fustik, S.; Goss, C.H.; Lymp, J.; Minic, P.; Quittner, A.L.; Rubenstein, R.C. Phase II studies of nebulised Arikace in CF patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Thorax 2013, 68, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trucillo, P.; Campardelli, R.; Reverchon, E. Liposomes: From bangham to supercritical fluids. Processes 2020, 8, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schürch, S.; Bachofen, H.; Possmayer, F. Surface activity in situ, in vivo, and in the captive bubble surfactometer. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2001, 129, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beike, L.; Wrede, C.; Hegermann, J.; Lopez-Rodriguez, E.; Kloth, C.; Gauldie, J.; Kolb, M.; Maus, U.A.; Ochs, M.; Knudsen, L. Surfactant dysfunction and alveolar collapse are linked with fibrotic septal wall remodeling in the TGF-β1-induced mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis. Lab. Investig. 2019, 99, 830–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akella, A.; Deshpande, S.B. Pulmonary surfactants and their role in pathophysiology of lung disorders. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 51, 5–22. [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett, J.A.; Wert, S.E.; Weaver, T.E. Diseases of Pulmonary Surfactant Homeostasis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2015, 10, 371–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hallworth, G.W.; Westmoreland, D.G. The twin impinger: A simple device for assessing the delivery of drugs from metered dose pressurized aerosol inhalers. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1987, 39, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almurshedi, A.S.; Aljunaidel, H.A.; Alquadeib, B.; Aldosari, B.N.; Alfagih, I.M.; Almarshidy, S.S.; Eltahir, E.K.D.; Mohamoud, A.Z. Development of Inhalable Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Ciprofloxacin for Noncystic Fibrosis Bronchiectasis Treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drent, M.; Cobben, N.A.; Henderson, R.F.; Wouters, E.F.; van Dieijen-Visser, M. Usefulness of lactate dehydrogenase and its isoenzymes as indicators of lung damage or inflammation. Eur. Respir. J. 1996, 9, 1736–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, B.; Wei, F.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Duan, B.; Shi, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, W.; Mu, W. Measurement of hydroxyproline in collagen with three different methods. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prabhakar, O. Naringin Attenuates Aluminum Induced Cognitive Deficits in Rats. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2020, 54, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kotta, S.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Badr-Eldin, S.M.; Binmahfouz, L.S.; Bakhaidar, R.B.; Sreeharsha, N.; Nair, A.B.; Ramnarayanan, C. Aerosol Delivery of Surfactant Liposomes for Management of Pulmonary Fibrosis: An Approach Supporting Pulmonary Mechanics. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111851
Kotta S, Aldawsari HM, Badr-Eldin SM, Binmahfouz LS, Bakhaidar RB, Sreeharsha N, Nair AB, Ramnarayanan C. Aerosol Delivery of Surfactant Liposomes for Management of Pulmonary Fibrosis: An Approach Supporting Pulmonary Mechanics. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(11):1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111851
Chicago/Turabian StyleKotta, Sabna, Hibah Mubarak Aldawsari, Shaimaa M. Badr-Eldin, Lenah S. Binmahfouz, Rana Bakur Bakhaidar, Nagaraja Sreeharsha, Anroop B. Nair, and Chandramouli Ramnarayanan. 2021. "Aerosol Delivery of Surfactant Liposomes for Management of Pulmonary Fibrosis: An Approach Supporting Pulmonary Mechanics" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 11: 1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111851
APA StyleKotta, S., Aldawsari, H. M., Badr-Eldin, S. M., Binmahfouz, L. S., Bakhaidar, R. B., Sreeharsha, N., Nair, A. B., & Ramnarayanan, C. (2021). Aerosol Delivery of Surfactant Liposomes for Management of Pulmonary Fibrosis: An Approach Supporting Pulmonary Mechanics. Pharmaceutics, 13(11), 1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111851






