Bacterial Ghosts-Based Vaccine and Drug Delivery Systems
Abstract
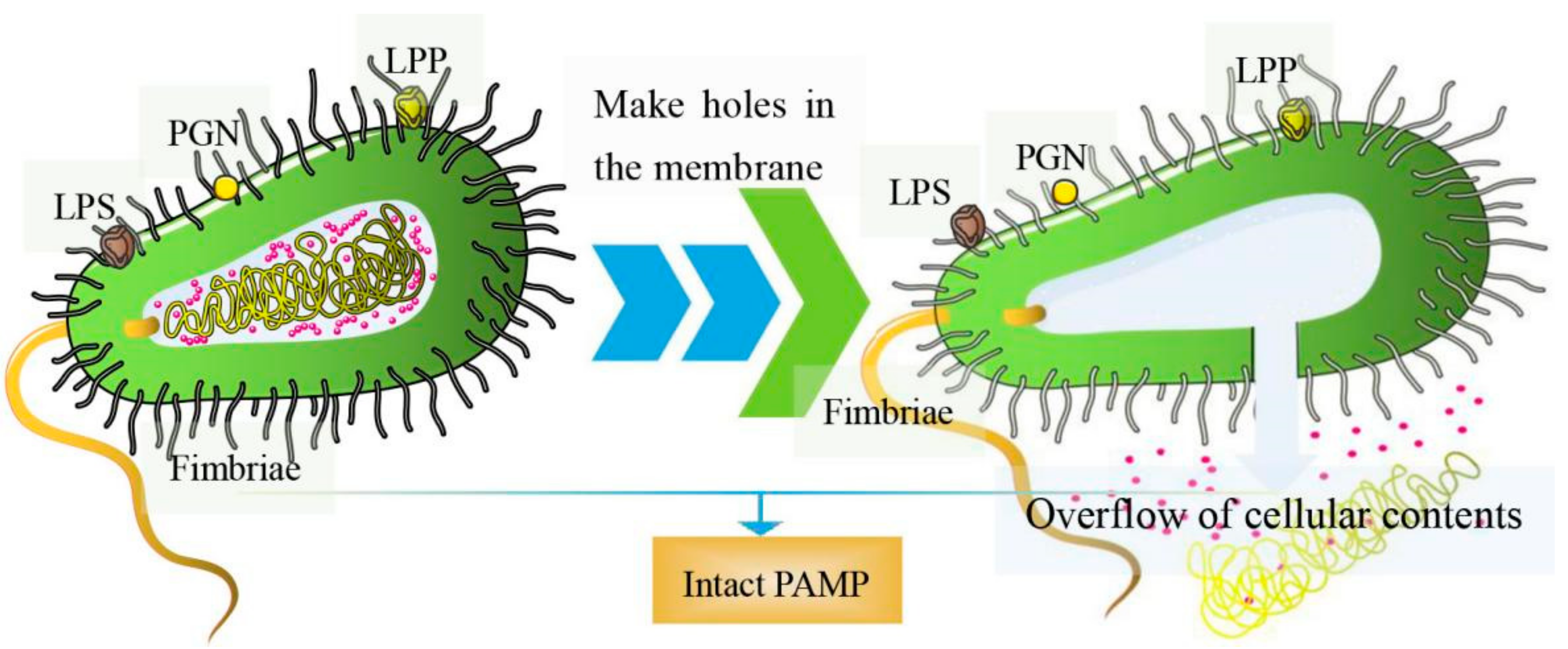
:1. Introduction
2. Methods for BGs Preparation
2.1. Genetic Engineering
2.2. The Chemical Method
3. The Association between BGs and Target Cells
4. BGs-Based Vaccine
4.1. DNA Vaccines
4.2. Protein Antigen Vaccines
5. Drug Delivery Systems Based on BGs
5.1. BGs for Delivery of Nucleic Acids
5.2. BGs Protein Delivery Systems
5.3. BGs for Delivery of Chemical Drugs
6. Drug Delivery Route for BGs
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BGs | Bacterial ghosts |
| MraY | Phospho-MurNAc-pentapeptide translocase |
| BPL | β-propiolactone |
| DAP | diaminopimelic acid |
| SNUC | staphylococcal nuclease |
| MAP | model amphipathic peptide |
| PAMPs | pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| LPP | lipoprotein |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| IFN-1 | I interferon |
| MIC | minimum inhibitory concentration |
| TLR2 | Toll-like receptor 2 |
| APCs | antigen-presenting cells |
| NLRC4 | Nod-like receptor card domain containing 4 |
| PGN | peptidoglycan |
| HCDECs | human conjunctiva-derived epithelial cells |
| BMDCs | bone marrow-derived DCs |
| Iclp | invariant chain-like protein |
| IBD | inflammatory bowel disease |
| OMVs | outer membrane vesicles |
| OMPA | outer membrane protein A |
| CIP | ciprofloxacin |
| ECN E | coli nissle 1917 |
| 5-FU | 5-fluorouridine |
| DC | dendritic cell |
References
- Peng, R.; Ji, H.; Jin, L.; Lin, S.; Huang, Y.; Xu, K.; Yang, Q.; Sun, D.; Wu, W. Macrophage-Based Therapies for Atherosclerosis Management. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, D.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Ji, H.; Peng, R.; Jin, L.; Wu, W. Advances in Refunctionalization of Erythrocyte-Based Nanomedicine for Enhancing Cancer-Targeted Drug Delivery. Theranostics 2019, 9, 6885–6900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghimipour, E.; Abedishirehjin, S.; Baghbadorani, M.A.; Handali, S. Bacteria and Archaea: A New Era of Cancer Therapy. J. Control. Release 2021, 338, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Cicuttini, F.; Li, J.; Jones, G. Targeting IL-6 in the Treatment of Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 18, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, S.; Li, X. Bacterial Navigation for Tumor Targeting and Photothermally-Triggered Bacterial Ghost Transformation for Spatiotemporal Drug Release. Acta Biomater. 2021, 131, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holay, M.; Guo, Z.; Pihl, J.; Heo, J.; Park, J.H.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Bacteria-Inspired Nanomedicine. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 3830–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinidoust, Z.; Mostaghaci, B.; Yasa, O.; Park, B.-W.; Singh, A.V.; Sitti, M. Bioengineered and Biohybrid Bacteria-Based Systems for Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 106, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senevirathne, A.; Hewawaduge, C.; Lee, J.H. Immunization of Chicken with Flagellin Adjuvanted Salmonella enteritidis Bacterial Ghosts Confers Complete Protection against Chicken Salmonellosis. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, S.B.; Peixoto, C.; Carrondo, M.J.T.; Silva, R.J.S. Downstream Processing for Influenza Vaccines and Candidates: An Update. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2021, 118, 2845–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbaghi, A.; Miri, S.M.; Keshavarz, M.; Zargar, M.; Ghaemi, A. Inactivation Methods for Whole Influenza Vaccine Production. Rev. Med. Virol. 2019, 29, e2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheweita, S.A.; Batah, A.M.; Ghazy, A.A.; Hussein, A.; Amara, A.A. A New Strain of Acinetobacter Baumannii and Characterization of Its Ghost as a Candidate Vaccine. J. Infect. Public Health 2019, 12, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalek, J.; Hezova, R.; Turanek-Knötigova, P.; Gabkova, J.; Strioga, M.; Lubitz, W.; Kudela, P. Oncolysate-Loaded Escherichia Coli Bacterial Ghosts Enhance the Stimulatory Capacity of Human Dendritic Cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, G.; Chao, X.; Xie, L.; Wang, H. The Characteristic of Virulence, Biofilm and Antibiotic Resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, A.; Champeimont, J.; Mayr, U.B.; Lubitz, W.; Kudela, P. Bacterial Ghosts as Carriers of Protein Subunit and DNA-Encoded Antigens for Vaccine Applications. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2012, 11, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Nan, N.; Sun, Y.; He, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, F.; Li, T.; Ning, N.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; et al. Protective Immunity Elicited by VP1 Chimeric Antigens of Bacterial Ghosts against Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus. Vaccines 2020, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batah, A.M.; Ahmad, T.A. The Development of Ghost Vaccines Trials. Expert Rev Vaccines 2020, 19, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganeshpurkar, A.; Ganeshpurkar, A.; Pandey, V.; Agnihotri, A.; Bansal, D.; Dubey, N. Harnessing the Potential of Bacterial Ghost for the Effective Delivery of Drugs and Biotherapeutics. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2014, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Rawding, P.; Bu, J.; Hong, S.; Hu, Q. Chemically and Biologically Engineered Bacteria-Based Delivery Systems for Emerging Diagnosis and Advanced Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2102580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendel, S.; Holbourn, J.M.; Schouten, J.A.; Bugg, T.D.H. Interaction of the Transmembrane Domain of Lysis Protein E from Bacteriophage ΦX174 with Bacterial Translocase MraY and Peptidyl-Prolyl Isomerase SlyD. Microbiology 2006, 152, 2959–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langemann, T.; Koller, V.J.; Muhammad, A.; Kudela, P.; Mayr, U.B.; Lubitz, W. The Bacterial Ghost Platform System: Production and Applications. Bioeng. Bugs 2010, 1, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lubitz, P.; Mayr, U.B.; Lubitz, W. Applications of Bacterial Ghosts in Biomedicine. In Pharmaceutical Biotechnology; Guzmán, C.A., Feuerstein, G.Z., Eds.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 655, pp. 159–170. ISBN 978-1-4419-1131-5. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, T.-C.; Jones, C.H.; Gollakota, A.; Kamal Ahmadi, M.; Rane, S.; Zhang, G.; Pfeifer, B.A. Improved Escherichia Coli Bactofection and Cytotoxicity by Heterologous Expression of Bacteriophage ΦX174 Lysis Gene E. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1691–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szostak, M.P.; Hensel, A.; Eko, F.O.; Klein, R.; Auer, T.; Mader, H.; Haslberger, A.; Bunka, S.; Wanner, G.; Lubitz, W. Bacterial Ghosts: Non-Living Candidate Vaccines. J. Biotechnol. 1996, 44, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, A.; Wanner, G.; Sulzner, M.; Lubitz, W. Dynamics of PhiX174 Protein E-Mediated Lysis of Escherichia Coli. Arch. Microbiol. 1992, 157, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeusser, D.P.; Margolin, W. Splitsville: Structural and Functional Insights into the Dynamic Bacterial Z Ring. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Witte, A.; Brand, E.; Mayrhofer, P.; Narendja, F.; Lubitz, W. Mutations in Cell Division Proteins FtsZ and FtsA Inhibit ΦX174 Protein-E-Mediated Lysis of Escherichia Coli. Arch. Microbiol. 1998, 170, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchart, J.; Dropmann, G.; Lechleitner, S.; Schlapp, T.; Wanner, G.; Szostak, M.P.; Lubitz, W. Pasteurella Multocida- and Pasteurella Haemolytica-Ghosts: New Vaccine Candidates. Vaccine 2003, 21, 3988–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalava, K. Bacterial Ghosts as Vaccine Candidates for Veterinary Applications. J. Control. Release 2002, 85, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajam, I.A.; Dar, P.A.; Won, G.; Lee, J.H. Bacterial Ghosts as Adjuvants: Mechanisms and Potential. Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paukner, S.; Stiedl, T.; Kudela, P.; Bizik, J.; Al Laham, F.; Lubitz, W. Bacterial Ghosts as a Novel Advanced Targeting System for Drug and DNA Delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2006, 3, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barisani-Asenbauer, T.; Montanaro, J.; Inic-Kanada, A.; Ladurner, A.; Stein, E.; Belij, S.; Bintner, N.; Schlacher, S.; Schuerer, N.; Mayr, U.B.; et al. Escherichia Coli Nissle 1917 Bacterial Ghosts Retain Crucial Surface Properties and Express Chlamydial Antigen: An Imaging Study of a Delivery System for the Ocular Surface. DDDT 2015, 9, 3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farjadian, F.; Moghoofei, M.; Mirkiani, S.; Ghasemi, A.; Rabiee, N.; Hadifar, S.; Beyzavi, A.; Karimi, M.; Hamblin, M.R. Bacterial Components as Naturally Inspired Nano-Carriers for Drug/Gene Delivery and Immunization: Set the Bugs to Work? Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 968–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koller, V.J.; Dirsch, V.M.; Beres, H.; Donath, O.; Reznicek, G.; Lubitz, W.; Kudela, P. Modulation of Bacterial Ghosts—Induced Nitric Oxide Production in Macrophages by Bacterial Ghost-Delivered Resveratrol. FEBS J 2013, 280, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Efficient Production of Safety-Enhanced Escherichia Coli Ghosts by Tandem Expression of PhiX 174 Mutant Gene E and Staphylococcal Nuclease A Gene. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 176, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Zhou, W.; Si, W.; Yi, F.; Hua, X.; Yue, M.; Chen, L.; Liu, S.; Yu, S. Construction of Salmonella Pullorum Ghost by Co-Expression of Lysis Gene E and the Antimicrobial Peptide SMAP29 and Evaluation of Its Immune Efficacy in Specific-Pathogen-Free Chicks. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelm, A.; Söderström, B.; Vikström, D.; Jong, W.S.P.; Luirink, J.; de Gier, J.-W. Autotransporter-Based Antigen Display in Bacterial Ghosts. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senevirathne, A.; Hewawaduge, C.; Park, J.-Y.; Park, S.; Lee, J.H. Parenteral Immunization of Salmonella Typhimurium Ghosts with Surface-Displayed Escherichia Coli Flagellin EnhancesTLR-5 Mediated Activation of Immune Responses That Protect the Chicken against Salmonella Infection. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekong, E.E.; Okenu, D.N.; Mania-Pramanik, J.; He, Q.; Igietseme, J.U.; Ananaba, G.A.; Lyn, D.; Black, C.; Eko, F.O. A Vibrio Cholerae Ghost-Based Subunit Vaccine Induces Cross-Protective Chlamydial Immunity That Is Enhanced by CTA2B, the Nontoxic Derivative of Cholera Toxin. FEMS Immunol. Med Microbiol. 2009, 55, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatfaludi, T.; Liska, M.; Zellinger, D.; Ousman, J.P.; Szostak, M.; Jalava, K.; Lubitz, W. Bacterial Ghost Technology for Pesticide Delivery. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 5627–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, N.; She, F. Helicobacter Pylori Outer Inflammatory Protein DNA Vaccine-Loaded Bacterial Ghost Enhances Immune Protective Efficacy in C57BL/6 Mice. Vaccine 2014, 32, 6054–6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, A.; Kassmannhuber, J.; Rauscher, M.; Falcon, A.A.; Wheeler, D.W.; Zhang, A.A.; Lubitz, P.; Lubitz, W. Subcutaneous Immunization of Dogs With Bordetella bronchiseptica Bacterial Ghost Vaccine. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riedmann, E.M.; Lubitz, W.; McGrath, J.; Kyd, J.M.; Cripps, A.W. Effectiveness of Engineering the Nontypeable Haemophilus Influenzae Antigen Omp26 as an S-Layer Fusion in Bacterial Ghosts as a Mucosal Vaccine Delivery. Hum. Vaccines 2011, 7, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ran, X.; Meng, X.-Z.; Geng, H.-L.; Chang, C.; Chen, X.; Wen, X.; Ni, H. Generation of Porcine Pasteurella Multocida Ghost Vaccine and Examination of Its Immunogenicity against Virulent Challenge in Mice. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 132, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xi, L.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. A Safe Non-Toxic Brucella Abortus Ghosts Induce Immune Responses and Confer Protection in BALB/c Mice. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 124, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Luo, L.; Xing, W.; Li, T.; Yuan, D.; Xu, G.; Li, W.; Ma, Z.; Jin, L.; Ji, M. Generation and Immunity Effect Evaluation of Biotechnology-Derived Aeromonas Veronii Ghost by PhiX174 Gene E-Mediated Inactivation in Koi (Cyprinus Carprio Koi). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panoff, J.M.; Chuiton, C. Horizontal Gene Transfer: A Universal Phenomenon. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2004, 10, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleymani, S.; Tavassoli, A.; Hashemi Tabar, G.; Kalidari, G.A.; Dehghani, H. Design, Development, and Evaluation of the Efficacy of a Nucleic Acid-Free Version of a Bacterial Ghost Candidate Vaccine against Avian Pathogenic E. Coli (APEC) O78:K80 Serotype. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchel, M.C.; Molina, L.; Witte, A.; Lutbiz, W.; Molin, S.; Ramos, J.L.; Ramos, C. Characterization of Cell Lysis in Pseudomonas Putida Induced upon Expression of Heterologous Killing Genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 4904–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kloos, D.U.; Strätz, M.; Güttler, A.; Steffan, R.J.; Timmis, K.N. Inducible Cell Lysis System for the Study of Natural Transformation and Environmental Fate of DNA Released by Cell Death. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 7352–7361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amara, A.A.; Salem-Bekhit, M.M.; Alanazi, F.K. Sponge-Like: A New Protocol for Preparing Bacterial Ghosts. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabea, S.; Salem-Bekhit, M.M.; Alanazi, F.K.; Yassin, A.S.; Moneib, N.A.; Hashem, A.E.M. A Novel Protocol for Bacterial Ghosts’ Preparation Using Tween 80. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Dong, H.; Fu, L.; Zuo, J.; Hu, S. Comparison of Three Methods for Preparation of Bacterial Ghosts from Avian Pathogenic Escherichia Coli. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao = Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm-Apergi, C.; Hällbrink, M. A New Rapid Cell-Penetrating Peptide Based Strategy to Produce Bacterial Ghosts for Plasmid Delivery. J. Control. Release 2008, 132, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Peng, W.; Si, W.; Yin, L.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Zhao, H.; Wang, C.; Chang, Y.; Lin, Y. Enhancement of Bacteriolysis of Shuffled Phage PhiX174 Gene E. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vinod, N.; Oh, S.; Park, H.J.; Koo, J.M.; Choi, C.W.; Kim, S.C. Generation of a Novel Staphylococcus Aureus Ghost Vaccine and Examination of Its Immunogenicity against Virulent Challenge in Rats. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 2957–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dobrovolskaia, M.A. Dendrimers Effects on the Immune System: Insights into Toxicity and Therapeutic Utility. CPD 2017, 23, 3134–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, K.; Martinon, F.; Esslinger, C.; Pahl, H.; Schneider, P.; Bodmer, J.-L.; Di Marco, F.; French, L.; Tschopp, J. MyD88, an Adapter Protein Involved in Interleukin-1 Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 12203–12209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piras, V.; Selvarajoo, K. Beyond MyD88 and TRIF Pathways in Toll-Like Receptor Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tough, D.F.; Sun, S.; Sprent, J. T Cell Stimulation In Vivo by Lipopolysaccharide (LPS). J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 2089–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Qi, C.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y. Toll-like Receptor 4-Related Immunostimulatory Polysaccharides: Primary Structure, Activity Relationships, and Possible Interaction Models. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 149, 186–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.; Wang, H.; Hajishengallis, G.N.; Martin, M. TLR-Signaling Networks: An Integration of Adaptor Molecules, Kinases, and Cross-Talk. J. Dent. Res. 2011, 90, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; Kagan, J.C. Toll-like Receptors and the Control of Immunity. Cell 2020, 180, 1044–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, P.; Wu, Y.; Lian, S.; Yan, L.; Meng, X.; Duan, Q.; Zhu, G. Research Progress on Toll-like Receptor Signal Transduction and Its Roles in Antimicrobial Immune Responses. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 5341–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAleer, J.P.; Vella, A.T. Educating CD4 T Cells with Vaccine Adjuvants: Lessons from Lipopolysaccharide. Trends Immunol. 2010, 31, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Razim, A.; Pacyga, K.; Naporowski, P.; Martynowski, D.; Szuba, A.; Gamian, A.; Górska, S. Identification of Linear Epitopes on the Flagellar Proteins of Clostridioides Difficile. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gries, C.M.; Mohan, R.R.; Morikis, D.; Lo, D.D. Crosslinked Flagella as a Stabilized Vaccine Adjuvant Scaffold. BMC Biotechnol. 2019, 19, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, H.C.; Rumbo, M.; Sirard, J.C. Bacterial Flagellins: Mediators of Pathogenicity and Host Immune Responses in Mucosa. Trends Microbiol. 2004, 12, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, J.; Xuan, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; He, L.; Meng, X.; Zhou, T.; Wang, Y. Updating the NLRC4 Inflammasome: From Bacterial Infections to Autoimmunity and Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 702527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Zhou, X.; Wen, S.; Xiao, Q. Flagellin/TLR5 Responses Induce Mucus Hypersecretion by Activating EGFR via an Epithelial Cell Signaling Cascades. Exp. Cell Res. 2012, 318, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, E.A.; Andersen-Nissen, E.; Warren, S.E.; Aderem, A. TLR5 and Ipaf: Dual Sensors of Bacterial Flagellin in the Innate Immune System. Semin. Immunopathol. 2007, 29, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buwitt-Beckmann, U.; Heine, H.; Wiesmuller, K.-H.; Jung, G.; Brock, R.; Ulmer, A.J. Lipopeptide Structure Determines TLR2 Dependent Cell Activation Level. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 6354–6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, H.; Mohajeri, M.; La Fata, G. Toll-Like Receptors: Regulators of the Immune Response in the Human Gut. Nutrients 2018, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warshakoon, H.J.; Hood, J.D.; Kimbrell, M.R.; Malladi, S.; Wu, W.Y.; Shukla, N.; Agnihotri, G.; Sil, D.; David, S.A. Potential Adjuvantic Properties of Innate Immune Stimuli. Hum. Vaccines 2009, 5, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, L.a.M.; Travassos, L.H.; Philpott, D.J. Innate Immune Recognition of Microbes through Nod1 and Nod2: Implications for Disease. Microbes Infect. 2004, 6, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, C.E.; Ernst, R.K. Bacterial Lipids: Powerful Modifiers of the Innate Immune Response. F1000Research 2017, 6, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kudela, P.; Koller, V.J.; Mayr, U.B.; Nepp, J.; Lubitz, W.; Barisani-Asenbauer, T. Bacterial Ghosts as Antigen and Drug Delivery System for Ocular Surface Diseases: Effective Internalization of Bacterial Ghosts by Human Conjunctival Epithelial Cells. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 153, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombetta, E.S.; Mellman, I. Cell Biology of Antigen Processing In Vitro and In Vivo. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 23, 975–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felnerova, D.; Kudela, P.; Bizik, J.; Haslberger, A.; Lubitz, W. T Cell-Specific Immune Response Induced by Bacterial Ghosts. Med. Sci. Monit. 2004, 10, BR362–BR370. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Wu, H.; Chen, S.; Bai, Q.; Chen, X.; Chen, L.; Zeng, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, L. MOMP and MIP DNA-Loaded Bacterial Ghosts Reduce the Severity of Lung Lesions in Mice after Chlamydia Psittaci Respiratory Tract Infection. Immunobiology 2019, 224, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, H.; Yang, H.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, D.; Li, G. Enhancement of Immune Responses by Co-administration of Bacterial Ghosts-mediated Neisseria Gonorrhoeae DNA Vaccines. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 130, 1770–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhu, X.-C.; Liu, X.-Y.; Yuan, K.; Zhang, J.-J.; Gao, H.-H.; Li, J.-N. An Oral Double-Targeted DNA Vaccine Induces Systemic and Intestinal Mucosal Immune Responses and Confers High Protection against Vibrio Mimicus in Grass Carps. Aquaculture 2019, 504, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groza, D.; Gehrig, S.; Kudela, P.; Holcmann, M.; Pirker, C.; Dinhof, C.; Schueffl, H.H.; Sramko, M.; Hoebart, J.; Alioglu, F.; et al. Bacterial Ghosts as Adjuvant to Oxaliplatin Chemotherapy in Colorectal Carcinomatosis. OncoImmunology 2018, 7, 1424676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuntufye, H.N.; Ons, E.; Pham, A.D.N.; Luyten, T.; Van Gerven, N.; Bleyen, N.; Goddeeris, B.M. Escherichia Coli Ghosts or Live E. coli Expressing the Ferri-Siderophore Receptors FepA, FhuE, IroN and IutA Do Not Protect Broiler Chickens against Avian Pathogenic E. Coli (APEC). Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 159, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraśko, J.A.; Žilionytė, K.; Darinskas, A.; Strioga, M.; Rjabceva, S.; Zalutsky, I.; Derevyanko, M.; Kulchitsky, V.; Lubitz, W.; Kudela, P.; et al. Bacterial Ghosts as Adjuvants in Syngeneic Tumour Cell Lysate-Based Anticancer Vaccination in a Murine Lung Carcinoma Model. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Hao, L.; Liu, X.; Borrás-Hidalgo, O.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced Anti-Proliferative Efficacy of Epothilone B Loaded with Escherichia Coli Nissle 1917 Bacterial Ghosts on the HeLa Cells by Mitochondrial Pathway of Apoptosis. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 1328–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paukner, S.; Kohl, G.; Lubitz, W. Bacterial Ghosts as Novel Advanced Drug Delivery Systems: Antiproliferative Activity of Loaded Doxorubicin in Human Caco-2 Cells. J. Control. Release 2004, 94, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssof, A.M.E.; Alanazi, F.K.; Salem-Bekhit, M.M.; Shakeel, F.; Haq, N. Bacterial Ghosts Carrying 5-Fluorouracil: A Novel Biological Carrier for Targeting Colorectal Cancer. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, S. Harnessing the Immunomodulatory Properties of Bacterial Ghosts to Boost the Anti-Mycobacterial Protective Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, M.; Ran, P.; Li, X. Bacterial Ghosts for Targeting Delivery and Subsequent Responsive Release of T Ciprofloxacin to Destruct Intracellular Bacteria. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 399, 125700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Pak-Wai, Y.; Jenny, L. Intranasal DNA Vaccine for Protection against Respiratory Infectious Diseases: The Delivery Perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2014, 6, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stein, E.; Inic-Kanada, A.; Belij, S.; Montanaro, J.; Bintner, N.; Schlacher, S.; Mayr, U.B.; Lubitz, W.; Stojanovic, M.; Najdenski, H.; et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Uptake Study of Escherichia Coli Nissle 1917 Bacterial Ghosts: Cell-Based Delivery System to Target Ocular Surface Diseases. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kudela, P.; Paukner, S.; Mayr, U.B.; Cholujova, D.; Schwarczova, Z.; Sedlak, J.; Bizik, J.; Lubitz, W. Bacterial Ghosts as Novel Efficient Targeting Vehicles for DNA Delivery to the Human Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells. J. Immunother. 2005, 28, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haslberger, A.G.; Kohl, G.; Felnerova, D.; Mayr, U.B.; Fürst-Ladani, S.; Lubitz, W. Activation, Stimulation and Uptake of Bacterial Ghosts in Antigen Presenting Cells. J. Biotechnol. 2000, 83, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walcher, P.; Mayr, U.B.; Azimpour-Tabrizi, C.; Eko, F.O.; Jechlinger, W.; Mayrhofer, P.; Alefantis, T.; Mujer, C.V.; DelVecchio, V.G.; Lubitz, W. Antigen Discovery and Delivery of Subunit Vaccines by Nonliving Bacterial Ghost Vectors. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2004, 3, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, H.; Yang, H.; Zhao, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, J.; Yin, Y.; Kong, G.; Li, G. Design and Immune Characterization of a Novel Neisseria Gonorrhoeae DNA Vaccine Using Bacterial Ghosts as Vector and Adjuvant. Vaccine 2018, 36, 4532–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sührer, I.; Langemann, T.; Lubitz, W.; Weuster-Botz, D.; Castiglione, K. A Novel One-Step Expression and Immobilization Method for the Production of Biocatalytic Preparations. Microb Cell Fact 2015, 14, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paukner, S.; Kohl, G.; Jalava, K.; Lubitz, W. Sealed Bacterial Ghosts—Novel Targeting Vehicles for Advanced Drug Delivery of Water-Soluble Substances. J. Drug Target. 2003, 11, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Li, X.; Zhou, W.; Chu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, H.; Liu, P.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Sequentially Triggered Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles for Macrophage Metabolism Modulation and Tumor Metastasis Suppression. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 13826–13838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, B.; Yang, Y.; Tham, W.L.; Chen, L.; Guo, J.; Zhu, G. Genetic Engineering of Probiotic Escherichia Coli Nissle 1917 for Clinical Application. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 8693–8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabea, S.; Alanazi, F.K.; Ashour, A.E.; Salem-Bekhit, M.M.; Yassin, A.S.; Moneib, N.A.; Hashem, A.E.M.; Haq, N. Salmonella-Innovative Targeting Carrier: Loading with Doxorubicin for Cancer Treatment. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, H.J. Microfold Cells-Targeting Antigen Delivery: A Promising Strategy to Enhance the Efficacy of Mucosal Vaccines. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandra, I.K.; Marijana, S.; Simone, S.; Elisabeth, S.; Sandra, B.R.; Emilija, M.; Ivana, L.; Jacqueline, M.; Nadine, S.; Nora, B. Delivery of a Chlamydial Adhesin N-PmpC Subunit Vaccine to the Ocular Mucosa Using Particulate Carriers. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eko, F.O.; Barisani-Asenbauer, T. Development of a Chlamydia Trachomatis Bacterial Ghost Vaccine to Fight Human Blindness. Hum. Vaccines 2008, 4, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Han, Y.; Huang, W.; Jin, M.; Gao, Z. The Influence of the Gut Microbiota on the Bioavailability of Oral Drugs. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 1789–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, S.; Gong, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, J.; Peng, B.; Yang, M. Recombinant Vibrio Parahaemolyticus Ghosts Protect Zebrafish against Infection by Vibrio Species. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 107, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S. Whether Viable and Dead Probiotic Are Equally Efficacious? NFS 2018, 48, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahtinen, S.J. Probiotic Viability—Does It Matter? Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2012, 23, 18567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plovier, H.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Depommier, C.; Van Hul, M.; Geurts, L.; Chilloux, J.; Ottman, N.; Duparc, T.; Lichtenstein, L.; et al. A Purified Membrane Protein from sAkkermansia Muciniphila or the Pasteurized Bacterium Improves Metabolism in Obese and Diabetic Mice. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Lysis Plasmid | Contents | Strain Name of BGs | Application | Reference | Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| / | pcDNA of Macrophage infectivity potentiator (MIP) and pcDNA of C. psittaci major outer membrane protein (MOMP) | E. coli JM109 | DNA vaccine for Preventing C. psittaci infection | [79] | mice |
| pBBR1MCS-E | Recombinant plasmid pVAX1-nspA | S.enteritidis | DNA vaccine for Preventing Gonococcal | [80] | mice |
| pBV220-E | DNA of Vibrio mimicus epitopes OmpU and VMH in tandem | E. coli DH5α | Oral DNA vaccine for Preventing Vibrio mimicus infection | [81] | grass carps |
| / | Oxaliplatin | ECN | Injection of oxaliplatin@BGs to induce immunogenic cell death (ICD) for therapy of colon cancer | [82] | mice |
| pML1, pDKL01 | NTHi antigen OMP26 | E. coli pop2135 | Mucosal delivery of OMP26@BGs for immunization against NTHi infection | [42] | rat |
| pBAD-E | Ferri-siderophore receptors FepA, FhuE, IroN and IutA | E. coli APEC | Recombinant BGs vaccine mucosal vaccine to prevent APEC infection | [83] | chicken |
| / | Lewis tumour cell lysate | ECN | BGs carries tumor lysates to enhance tumor immunogenicity, induce immune cells to mature and attack cancer cells | [84] | mice |
| pBV-mELS | Epothilone B | ECN | Epothilone B@BGs as an anticancer drug to treat cancer | [85] | HeLa cell |
| pSON1 | DOX | Mannheimia haemolytica | DOX@BGs is targeted to human colon adenocarcinoma cells for the treatment of cancer | [86] | Caco-2 |
| pLysS | 5-FU | E. coli BL21 (DE3) | 5-FU@BGs treatment of various types of colorectal cancer | [87] | Caco-2 |
| / | Bedaquiline and delamanid | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Bedaquiline/delamanid@BGs stimulate the immune system to kill bacteria and treat tuberculosis | [88] | mice |
| pBV220-E | CIP | ECN | CIP@BGs is used to destroy Staphylococcus aureus in macrophages | [89] | macrophage RAW264.7/mice |
| pBV220-E | ZOL/5-FU | ECN | ZOL/5-FU@BGs promote macrophage polarization and kill tumor | [5] | mice |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Ji, H.; Kong, X.; Lei, P.; Yang, Q.; Wu, W.; Jin, L.; Sun, D. Bacterial Ghosts-Based Vaccine and Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111892
Chen H, Ji H, Kong X, Lei P, Yang Q, Wu W, Jin L, Sun D. Bacterial Ghosts-Based Vaccine and Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(11):1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111892
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Haojie, Hao Ji, Xiangjun Kong, Pengyu Lei, Qinsi Yang, Wei Wu, Libo Jin, and Da Sun. 2021. "Bacterial Ghosts-Based Vaccine and Drug Delivery Systems" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 11: 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111892
APA StyleChen, H., Ji, H., Kong, X., Lei, P., Yang, Q., Wu, W., Jin, L., & Sun, D. (2021). Bacterial Ghosts-Based Vaccine and Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics, 13(11), 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111892









