Formulation and In Vitro Evaluation of Pellets Containing Sulfasalazine and Caffeine to Verify Ileo-Colonic Drug Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extrusion–Spheronization
2.3. ColoPulse Coating
2.4. Particle Size Analysis
2.5. Tensile Strength Analysis
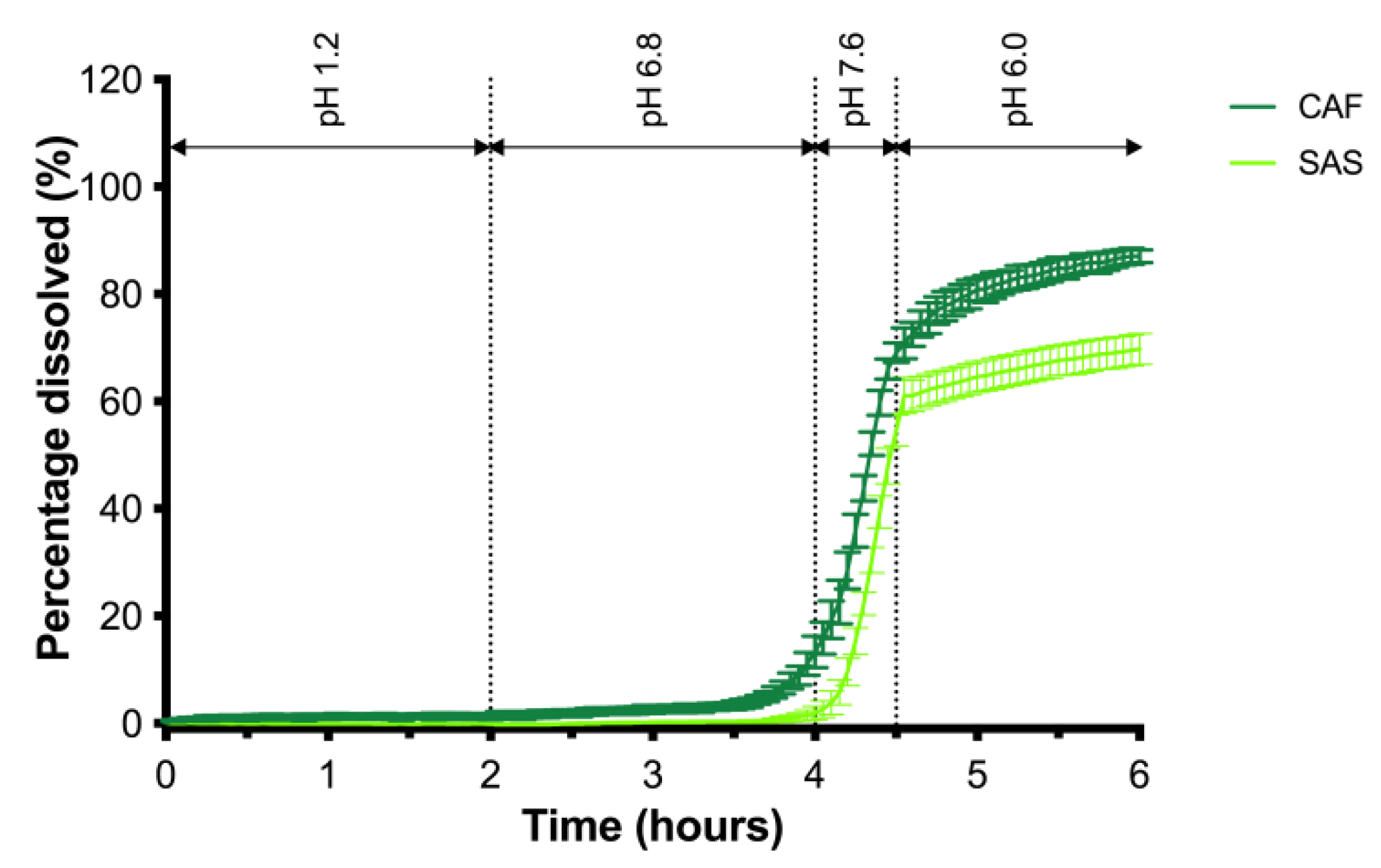
2.6. In Vitro Dissolution
2.7. Swelling Behavior Disintegrants
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Uncoated Pellets
3.2. ColoPulse Coated Pellets
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
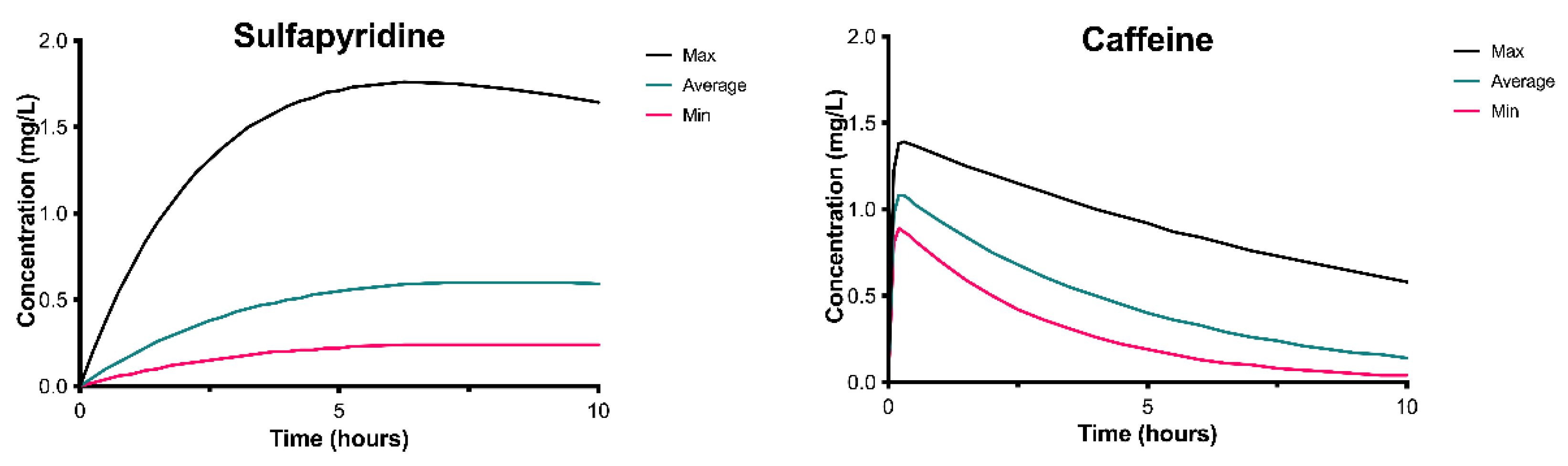
Appendix B
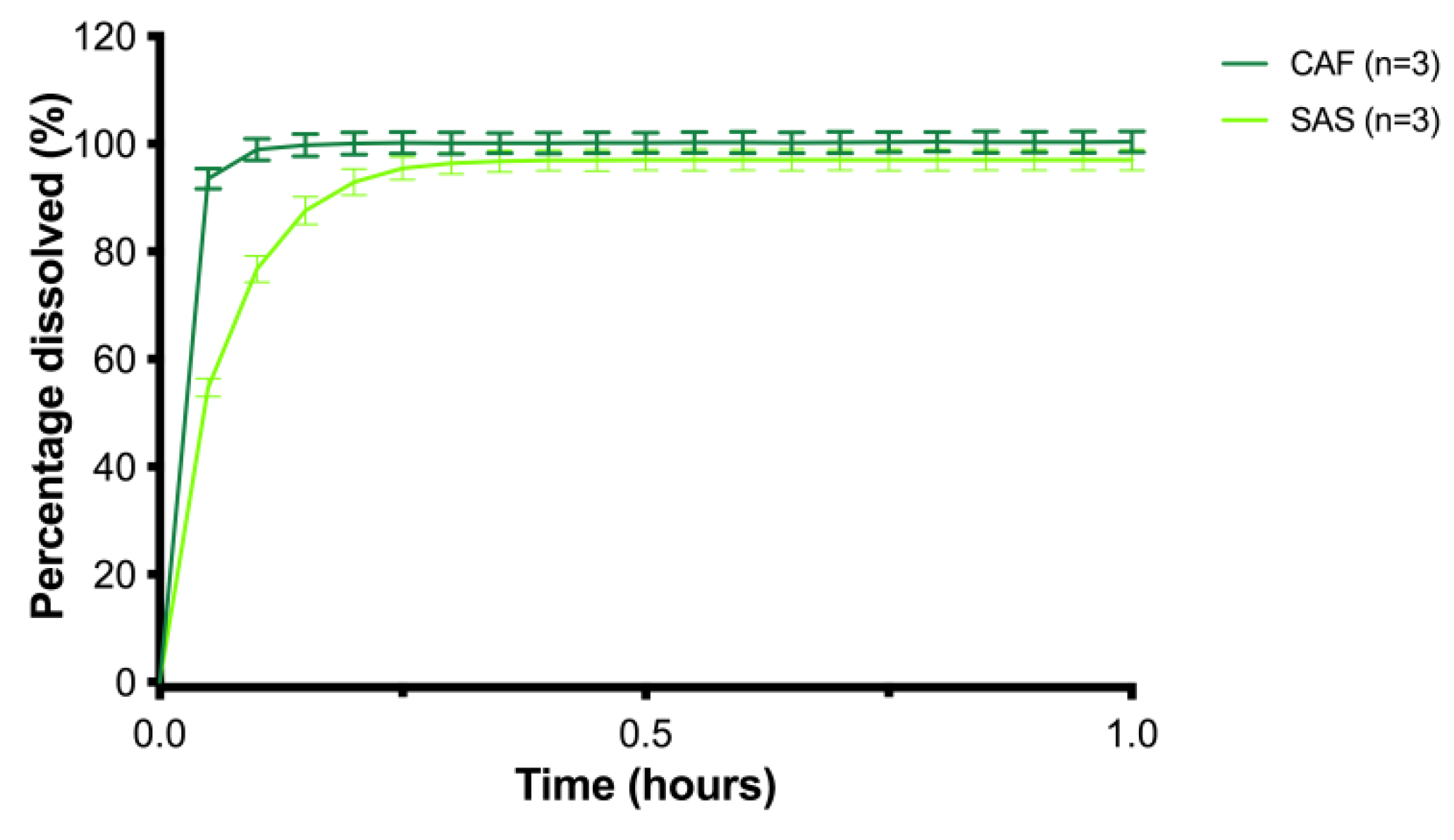
| Batch | Release (%) at t = 30 min | Time (Min) ≥ 80% Release | Particle Size x50 (μm) | Span | Sphericity s50 | Tensile Strength (MPa) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAS | CAF | SAS | CAF | |||||
| MCC_CCS4_EtOH_1 | 94.8 ± 0.4 | 98.0 ± 0.8 | 9 | 3 | 1088.3 ± 2.9 | 0.38 | 0.937 ± 0.000 | 10.5 ± 0.9 |
| MCC_CCS4_EtOH_2 | 98.5 ± 0.6 | 101.5 ± 1.2 | 9 | 3 | 1073.1 ± 1.2 | 0.42 | 0.938 ± 0.000 | 10.8 ± 3.6 |
| MCC_CCS4_EtOH_3 | 97.7 ± 0.6 | 101.1 ± 0.7 | 9 | 3 | 1082.7 ± 2.4 | 0.39 | 0.938 ± 0.000 | 9.4 ± 1.8 |
References
- Schellekens, R.C.A.; Stellaard, F.; Mitrovic, D.; Stuurman, F.E.; Kosterink, J.G.W.; Frijlink, H.W. Pulsatile drug delivery to ileo-colonic segments by structured incorporation of disintegrants in pH-responsive polymer coatings. J. Control. Release 2008, 132, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broesder, A.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; Prins, G.H.; Nguyen, D.N.; Frijlink, H.W.; Hinrichs, W.L.J. pH-dependent ileocolonic drug delivery, part I: In vitro and clinical evaluation of novel systems. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1362–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evonik. EUDRAGIT® Application Guidelines, 13th ed.; Skalsky, B., Ed.; Evonik Nutrition & Care GmbH: Darmstadt, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Schellekens, R.C.A.; Stellaard, F.; Olsder, G.G.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; Frijlink, H.W.; Kosterink, J.G.W. Oral ileocolonic drug delivery by the colopulse-system: A bioavailability study in healthy volunteers. J. Control. Release 2010, 146, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, J.M.; Schellekens, R.C.A.; van Rieke, H.M.; Stellaard, F.; Wutzke, K.D.; Buurman, D.J.; Dijkstra, G.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; Frijlink, H.W.; Kosterink, J.G.W. ColoPulse tablets perform comparably in healthy volunteers and Crohn’s patients and show no influence of food and time of food intake on bioavailability. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMEA. Note for Guidance on Quality of Modified Release Products: A: Oral Dosage Forms B: Transdermal Dosage Forms Section I (Quality); CPMP/QWP/6.; EMEA: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, P.; Shahiwala, A. Multiparticulate formulation approach to pulsatile drug delivery: Current perspectives. J. Control. Release 2009, 134, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, S.S.; Hardy, J.G.; Fara, J.W. Transit of pharmaceutical dosage forms through the small intestine. Gut 1986, 27, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abuhelwa, A.Y.; Foster, D.J.R.; Upton, R.N. A quantitative review and meta-models of the variability and factors affecting oral drug absorption—part II: Gastrointestinal transit time. AAPS J. 2016, 18, 1322–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Shi, C.; Fang, J.; Wang, W. Approaches to developing fast release pellets via wet extrusion-spheronization. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2018, 23, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervaet, C.; Baert, L.; Remon, J.P. Extrusion-spheronisation A literature review. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 116, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman-Boer, Y.; Fenton-May, V.; Le Brun, P. (Eds.) Practical Pharmaceutics, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-15813-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi, T.; Ikegami, K.; Kubo, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Mizobe, M.; Yoshino, H. Evaluation of colonic absorbability of drugs in dogs using a novel colon-targeted delivery capsule (CTDC). J. Control. Release 1999, 59, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, J.; Alves, M.G.; Oliveira, P.F.; Silva, B.M. Pharmacological potential of methylxanthines: Retrospective analysis and future expectations. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2597–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellow, J.E.; Borody, T.J.; Phillips, S.F.; Haddad, A.C.; Brown, M.L. Sulfapyridine appearance in plasma after salicylazosulfapyridine. Gastroenterology 1986, 91, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.; Chinwah, P.; Wade, D. A pharmacological method of measuring mouth caecal transit time in man. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1979, 8, 372–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Sanchez, R.D.C.; Lara-Diaz, V.J.; Aranda-Gutierrez, A.; Martinez-Cardona, J.A.; Hernandez, J.A. HPLC Method for Quantification of Caffeine and Its Three Major Metabolites in Human Plasma Using Fetal Bovine Serum Matrix to Evaluate Prenatal Drug Exposure. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2018, 2018, 2085059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broesder, A.; Kosta, A.-M.M.A.C.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; Nguyen, D.N.; Frijlink, H.W.; Hinrichs, W.L.J. pH-dependent ileocolonic drug delivery, part II: Preclinical evaluation of novel drugs and novel excipients. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1374–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejchal, V.; Žagar, G.; Charvet, R.; Dénéréaz, C.; Mortensen, A. Compression testing spherical particles for strength: Theory of the meridian crack test and implementation for microscopic fused quartz. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2017, 99, 70–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schellekens, R.C.A.; Stuurman, F.E.; van der Weert, F.H.J.; Kosterink, J.G.W.; Frijlink, H.W. A novel dissolution method relevant to intestinal release behaviour and its application in the evaluation of modified release mesalazine products. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 30, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalkowksy, S.H.; He, Y.; Jain, P. Handbook of Aqueous Solubility Data; Taylor & Francis Group: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- da Costa, M.A.B.; Villa, A.L.V.; Barros, R.C.S.A.; Ricci-Júnior, E.; Santos, E.P. Development, characterization and evaluation of the dissolution profile of sulfasalazine suspensions. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 51, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quadir, A.; Kolter, K. A comparative study of current superdisintegrants. Pharm. Technol. 2006, 30, s38–s42. [Google Scholar]
- Bisharat, L.; AlKhatib, H.S.; Muhaissen, S.; Quodbach, J.; Blaibleh, A.; Cespi, M.; Berardi, A. The influence of ethanol on superdisintegrants and on tablets disintegration. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 129, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, C.; Rodríguez, A.; Parajes, S.; Martínez-Pacheco, R. A comparative study of the utility of two superdisintegrants in microcrystalline cellulose pellets prepared by extrusion–spheronization. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2005, 61, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves-Silva, I.; Marreto, R.N.; Gelfuso, G.M.; Sá-Barreto, L.C.L.; Lima, E.M.; Cunha-Filho, M.S.S. Preparation of benznidazole pellets for immediate drug delivery using the extrusion spheronization technique. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manda, A.; Walker, R.; Khamanga, S. An Artificial Neural Network Approach to Predict the Effects of Formulation and Process Variables on Prednisone Release from a Multipartite System. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Debunne, A.; Vervaet, C.; Remon, J.-P. Development and in vitro evaluation of an enteric-coated multiparticulate drug delivery system for the administration of piroxicam to dogs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2002, 54, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.E.; Pharmacists, A.S.H.-S. Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 6th ed.; ASHP: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Klotz, U. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Sulphasalazine, Its Metabolites and Other Prodrugs of 5-Aminosalicylic Acid. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1985, 10, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsabri, S.G.; Mari, W.O.; Younes, S.; Alsadawi, M.A.; Oroszi, T.L. Kinetic and Dynamic Description of Caffeine. J. Caffeine Adenosine Res. 2018, 8, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

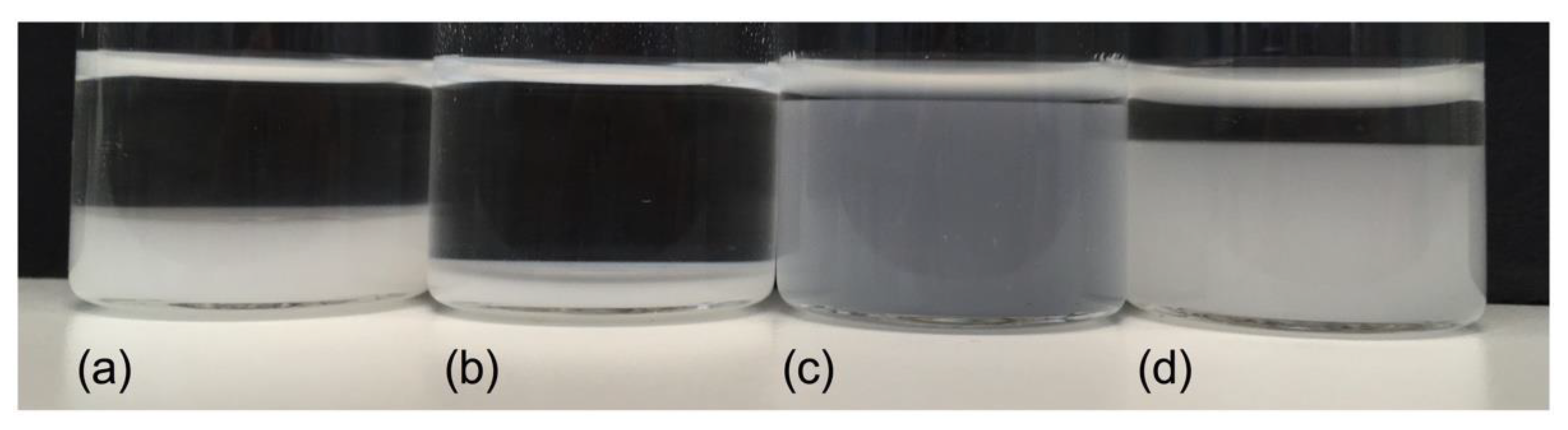
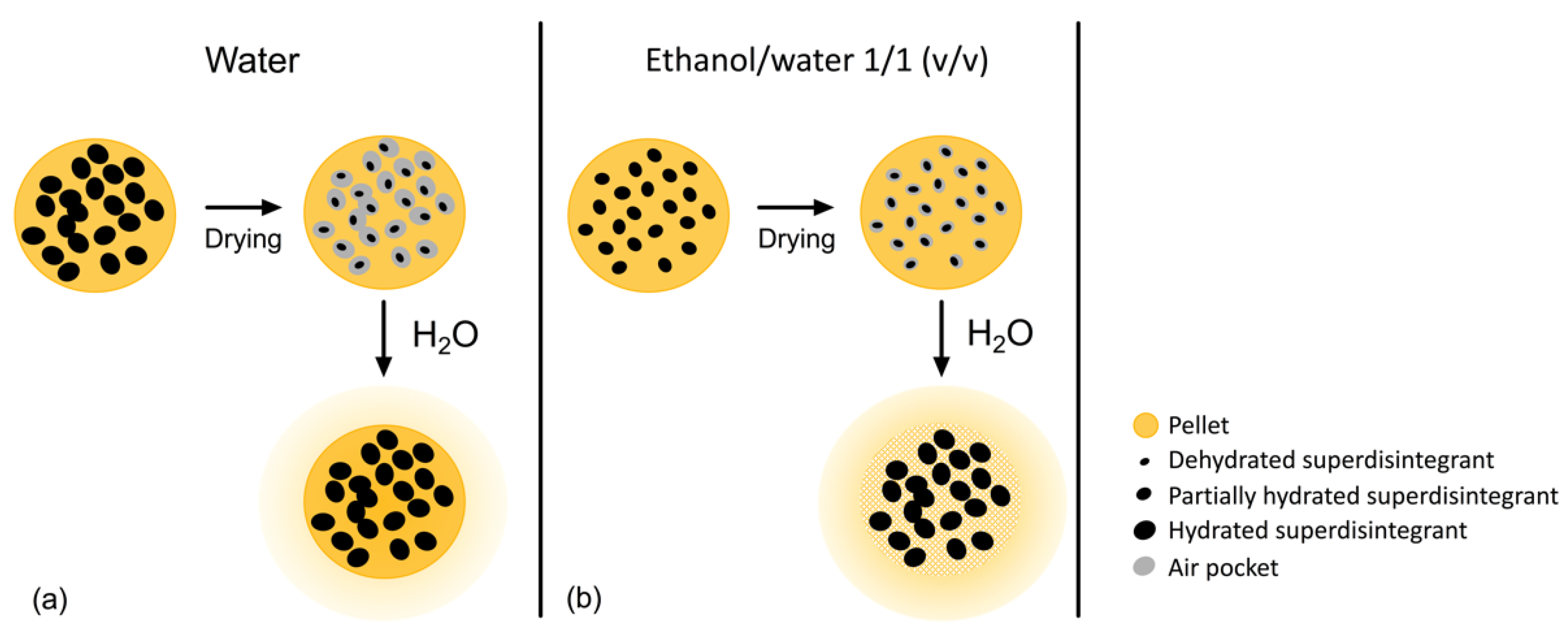
| Formulations | Composition (g) | Pelletizing Liquid (mL) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAS | CAF | MCC | CCS | SSG | Water | Ethanol/Water 1/1 (v/v) | |
| MCC_H2O | 3.571 | 1.429 | 5 | 7 | |||
| MCC_EtOH | 3.571 | 1.429 | 5 | 7.75 | |||
| MCC_CCS4_H2O | 3.571 | 1.429 | 5 | 0.4 | 9 | ||
| MCC_SSG4_H2O | 3.571 | 1.429 | 5 | 0.4 | 9 | ||
| MCC_CCS4_EtOH | 3.571 | 1.429 | 5 | 0.4 | 8 | ||
| MCC_SSG4_EtOH | 3.571 | 1.429 | 5 | 0.4 | 8 | ||
| Formulation | Release at t = 30 min (%) | Time at 80% Release (min) | Particle Size x50 (μm) | Span | Sphericity s50 | Tensile Strength (MPa) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAS | CAF | SAS | CAF | |||||
| MCC_H2O | 59.3 ± 0.4 | 101.5 ± 0.7 | 66 | 12 | 1126.2 ± 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.943 ± 0.000 | 14.0 ± 3.5 |
| MCC_EtOH | 57.8 ± 0.7 | 99.6 ± 0.7 | 66 | 9 | 1094.6 ± 2.2 | 0.38 | 0.938 ± 0.000 | 8.2 ± 1.1 |
| MCC_CCS_H2O | 67.9 ± 0.2 | 98.8 ± 0.8 | 48 | 9 | 982.6± 2.6 | 0.60 | 0.920 ± 0.001 | 8.4 ± 1.3 * |
| MCC_SSG_H2O | 63.7 ± 0.6 | 101.4 ± 0.4 | 57 | 12 | 1137.9 ± 15.5 | 0.80 | 0.931 ± 0.001 | 8.4 ± 1.4 * |
| MCC_CCS_EtOH | 97.7 ± 0.6 | 101.1 ± 0.7 | 9 | 3 | 1082.7 ± 2.4 | 0.39 | 0.938 ± 0.000 | 9.4 ± 1.8 |
| MCC_SSG_EtOH | 94.4 ± 0.6 | 98.4 ± 0.6 | 12 | 6 | 1073.8 ± 1.0 | 0.39 | 0.936 ± 0.000 | 11.0 ± 1.1 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Broesder, A.; Bircan, S.Y.; de Waard, A.B.; Eissens, A.C.; Frijlink, H.W.; Hinrichs, W.L.J. Formulation and In Vitro Evaluation of Pellets Containing Sulfasalazine and Caffeine to Verify Ileo-Colonic Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1985. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13121985
Broesder A, Bircan SY, de Waard AB, Eissens AC, Frijlink HW, Hinrichs WLJ. Formulation and In Vitro Evaluation of Pellets Containing Sulfasalazine and Caffeine to Verify Ileo-Colonic Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(12):1985. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13121985
Chicago/Turabian StyleBroesder, Annemarie, Said Y. Bircan, Anneko B. de Waard, Anko C. Eissens, Henderik W. Frijlink, and Wouter L. J. Hinrichs. 2021. "Formulation and In Vitro Evaluation of Pellets Containing Sulfasalazine and Caffeine to Verify Ileo-Colonic Drug Delivery" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 12: 1985. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13121985
APA StyleBroesder, A., Bircan, S. Y., de Waard, A. B., Eissens, A. C., Frijlink, H. W., & Hinrichs, W. L. J. (2021). Formulation and In Vitro Evaluation of Pellets Containing Sulfasalazine and Caffeine to Verify Ileo-Colonic Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics, 13(12), 1985. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13121985







