Nanoantibiotics Based in Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: New Formulations for Bacterial Infection Treatment
Abstract
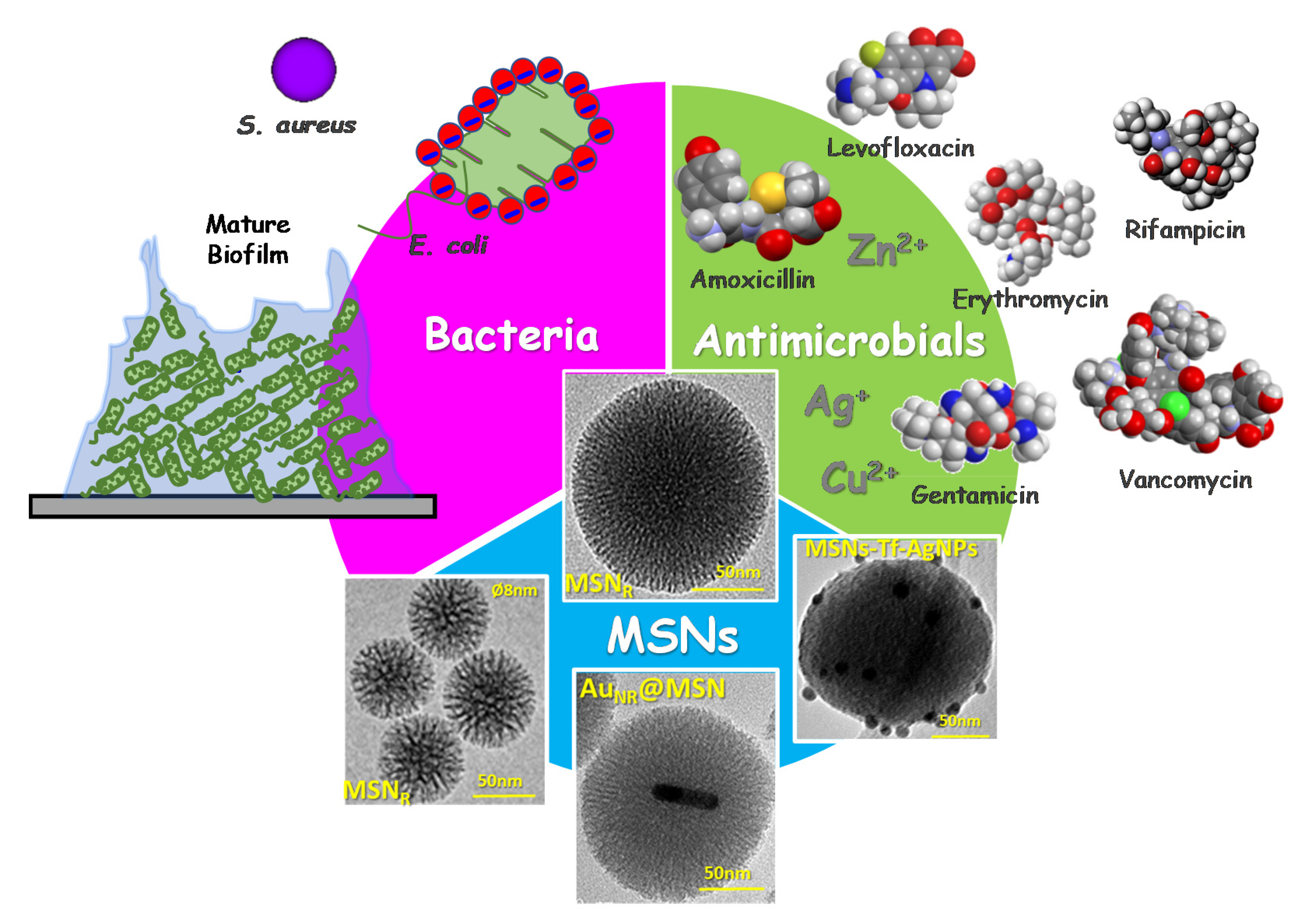
:1. Introduction
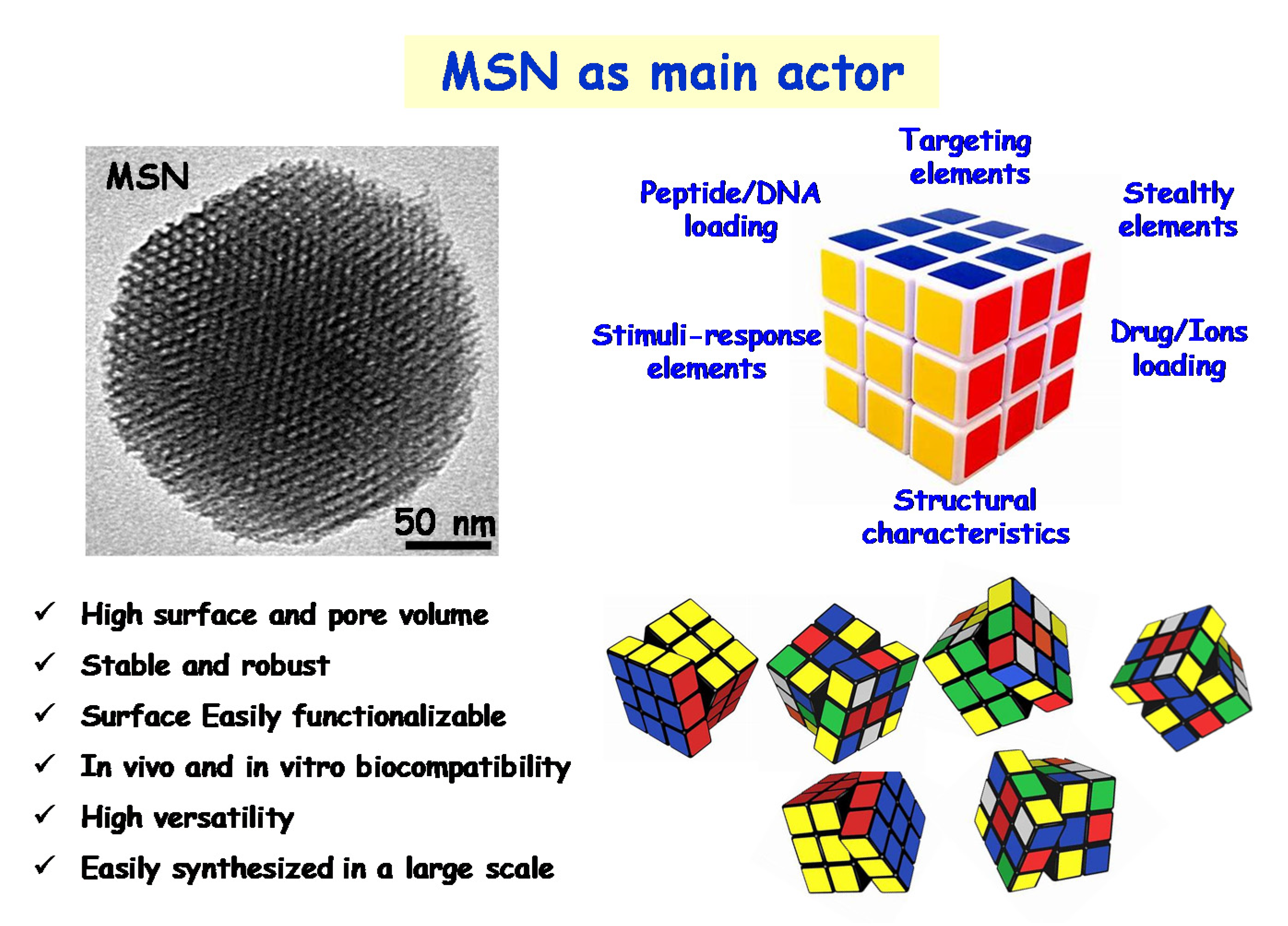
2. Engineering Mesoporous Materials as Antimicrobial Delivery Systems
3. A New Era of the Nanoantibiotics
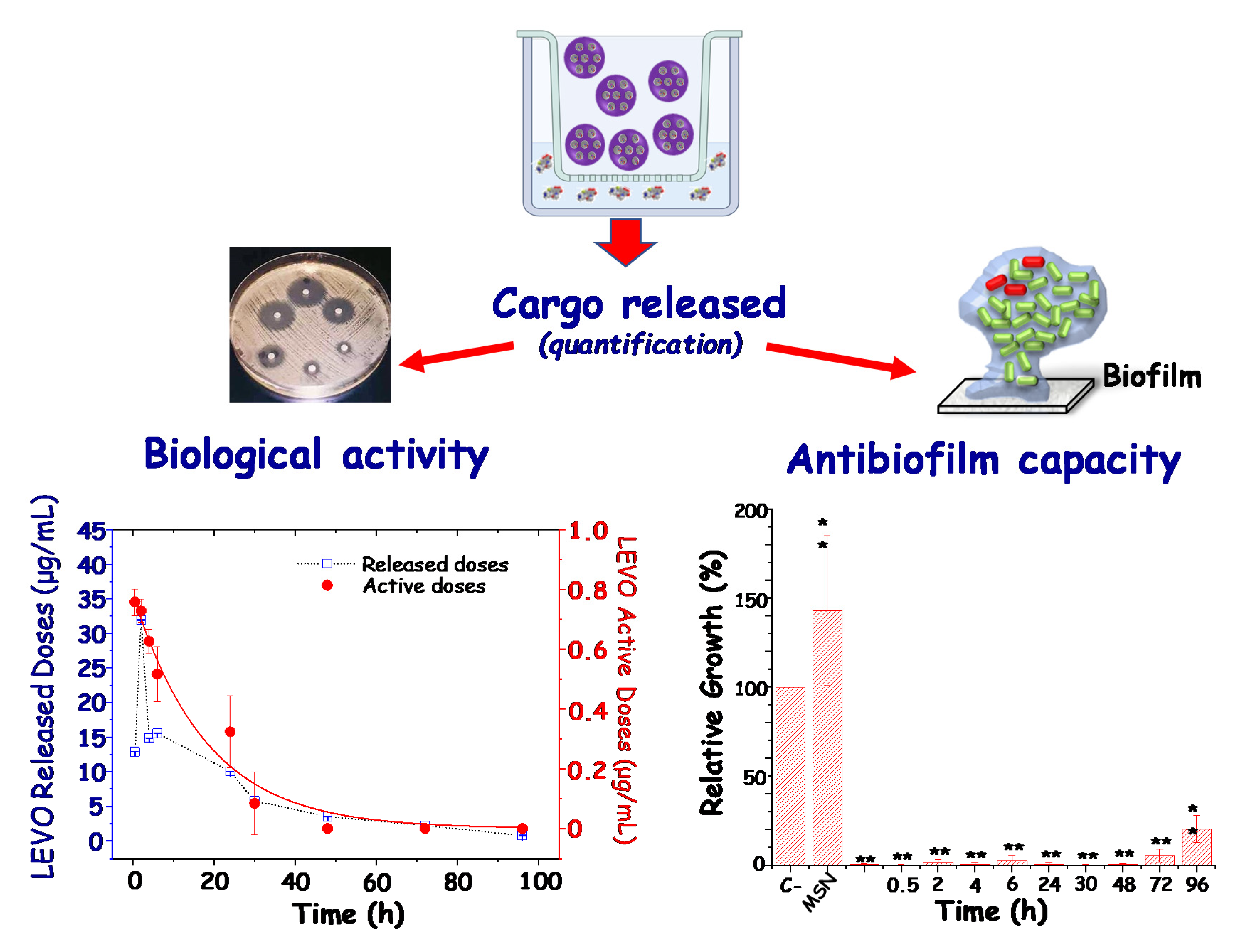
3.1. Antimicrobial Doses as Key Factor for Custom-Made Therapies
3.2. MSNs for Targeted Delivery of Antimicrobials
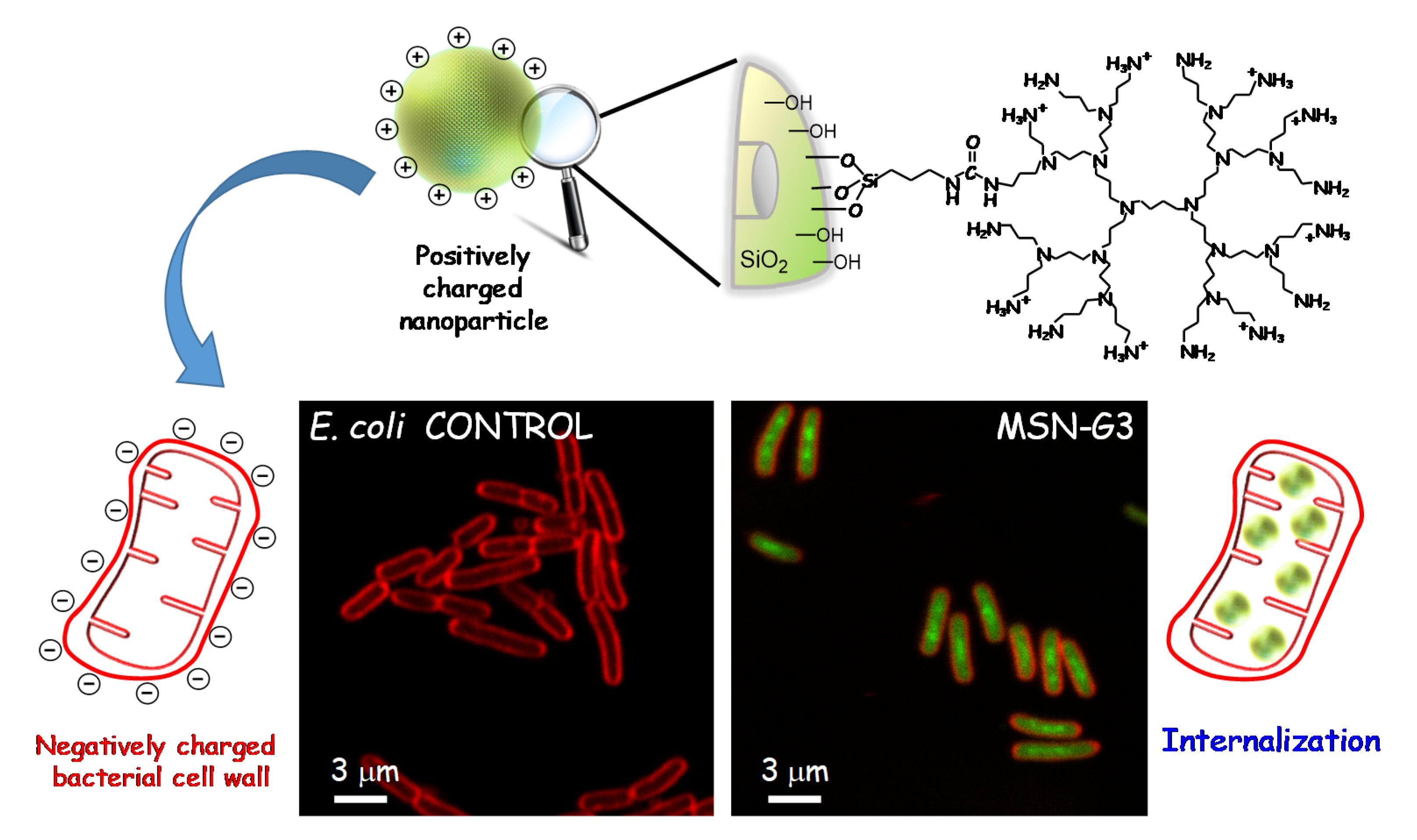
3.2.1. Targeting Bacteria
3.2.2. Targeting Biofilm
3.3. Combined Therapies
3.4. Stimuli-Responsive
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maradit Kremers, H.; Larson, D.R.; Crowson, C.S.; Kremers, W.K.; Washington, R.E.; Steiner, C.A.; Jiranek, W.A.; Berry, D.J. Prevalence of Total Hip and Knee Replacement in the United States. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2015, 97, 1386–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Lozano, D.; González, B.; Izquierdo-Barba, I. Biomaterials against Bone Infection. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2020, 9, 2000310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. New Report Calls for Urgent Action to Avert Antimicrobial Resistance Crisis. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/29-04-2019-new-report-calls-for-urgent-action-to-avert-antimicrobial-resistance-crisis (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Saeed, K.; McLaren, A.C.; Schwarz, E.M.; Antoci, V.; Arnold, W.V.; Chen, A.F.; Clauss, M.; Esteban, J.; Gant, V.; Hendershot, E.; et al. 2018 international consensus meeting on musculoskeletal infection: Summary from the biofilm workgroup and consensus on biofilm related musculoskeletal infections. J. Orthop. Res. 2019, 37, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, E.M.; Parvizi, J.; Gehrke, T.; Aiyer, A.; Battenberg, A.; Brown, S.A.; Callaghan, J.J.; Citak, M.; Egol, K.; Garrigues, G.E.; et al. 2018 International Consensus Meeting on Musculoskeletal Infection: Research Priorities from the General Assembly Questions. J. Orthop. Res. 2019, 37, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas, S.; Ong, A.C.; Buller, L.T.; Sabeh, K.G.; Law, T.Y.; Roche, M.W.; Hernandez, V.H. Season of the year influences infection rates following total hip arthroplasty. World J. Orthop. 2017, 8, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, S.L. Recent lessons for the management of bone and joint infections. J. Infect. 2014, 68 (Suppl. 1), S51–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; Costerton, J.W.; Stoodley, P. Bacterial biofilms: From the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D. Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Alam, A.; Rani, M.; Ehtesham, N.Z.; Hasnain, S.E. Biofilms: Survival and defense strategy for pathogens. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 307, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S.; Ciofu, O. Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masters, E.A.; Trombetta, R.P.; de Mesy Bentley, K.L.; Boyce, B.F.; Gill, A.L.; Gill, S.R.; Nishitani, K.; Ishikawa, M.; Morita, Y.; Ito, H.; et al. Evolving concepts in bone infection: Redefining “biofilm”, “acute vs. chronic osteomyelitis”, “the immune proteome” and “local antibiotic therapy”. Bone Res. 2019, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redlich, K.; Smolen, J.S. Inflammatory bone loss: Pathogenesis and therapeutic intervention. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnam, N.E.; Fulbright, L.E.; Curry, J.M.; Ford, C.A.; Petronglo, J.R.; Hendrix, A.S.; Cassat, J.E. MyD88 and IL-1R signaling drive antibacterial immunity and osteoclast-driven bone loss during Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arciola, C.R.; Campoccia, D.; Montanaro, L. Implant infections: Adhesion, biofilm formation and immune evasion. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J. Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a crisis for the health and wealth of nations. Rev. Antimicrob. Resist. 2014, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Campoccia, D.; Montanaro, L.; Arciola, C.R. A review of the biomaterials technologies for infection-resistant surfaces. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8533–8554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, K.; Slay, B.; Knackstedt, M.; Gaharwar, A.K. Antimicrobial Activity of Metal and Metal-Oxide Based Nanoparticles. Adv. Ther. 2018, 1, 1700033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garino, N.; Sanvitale, P.; Dumontel, B.; Laurenti, M.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Cauda, V.; Vallet-Regì, M. Zinc oxide nanocrystals as a nanoantibiotic and osteoinductive agent. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 11312–11321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdușel, A.-C.; Gherasim, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Mogoantă, L.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E. Biomedical Applications of Silver Nanoparticles: An Up-to-Date Overview. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huh, A.J.; Kwon, Y.J. “Nanoantibiotics”: A new paradigm for treating infectious diseases using nanomaterials in the antibiotics resistant era. J. Control. Release 2011, 156, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.M.; Sorinolu, A.J.; Munir, M.; Vejerano, E.P. Nanoantibiotics: Functions and Properties at the Nanoscale to Combat Antibiotic Resistance. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 687660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M. Our Contributions to Applications of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, A.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Advances in mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted stimuli-responsive drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, A.; Manzano, M.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Recent advances in mesoporous silica nanoparticles for antitumor therapy: Our contribution. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carvalho, G.C.; Sábio, R.M.; de Cássia Ribeiro, T.; Monteiro, A.S.; Pereira, D.V.; Ribeiro, S.J.L.; Chorilli, M. Highlights in Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as a Multifunctional Controlled Drug Delivery Nanoplatform for Infectious Diseases Treatment. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, R.R.; Lozano, D.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Carriers for Therapeutic Biomolecules. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, R.R.; Vallet-Regí, M. Recent Advances Toward the Use of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Bacterial Infections. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 4409–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Targeted Stimuli-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Bacterial Infection Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisbert-Garzarán, M.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Complex Bone Diseases: Bone Cancer, Bone Infection and Osteoporosis. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. New developments in ordered mesoporous materials for drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 5593–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Manzano, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery: Current Insights. Molecules 2018, 23, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sábio, R.M.; Meneguin, A.B.; Martins dos Santos, A.; Monteiro, A.S.; Chorilli, M. Exploiting mesoporous silica nanoparticles as versatile drug carriers for several routes of administration. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 312, 110774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valetti, S.; Thomsen, H.; Wankar, J.; Falkman, P.; Manet, I.; Feiler, A.; Ericson, M.B.; Engblom, J. Can mesoporous nanoparticles promote bioavailability of topical pharmaceutics? Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 602, 120609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, A.; Sancenón, F.; Martínez-Máñez, R. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for pulmonary drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 177, 113953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M. Infection. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kssRgcEfiW4 (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Rámila, A.; del Real, R.P.; Pérez-Pariente, J. A New Property of MCM-41: Drug Delivery System. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; González, B.; Izquierdo-Barba, I. Nanomaterials as Promising Alternative in the Infection Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Carmona, M.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Silica Materials as Drug Delivery: “The Nightmare” of Bacterial Infection. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernardos, A.; Piacenza, E.; Sancenón, F.; Hamidi, M.; Maleki, A.; Turner, R.J.; Martínez-Máñez, R. Mesoporous Silica-Based Materials with Bactericidal Properties. Small 2019, 15, 1900669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarajan, V.; Obuobi, S.; Ee, P.L.R. Silica Nanoparticles-A Versatile Tool for the Treatment of Bacterial Infections. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Colilla, M.; González, B. Medical applications of organic–inorganic hybrid materials within the field of silica-based bioceramics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 596–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Balas, F.; Arcos, D. Mesoporous Materials for Drug Delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7548–7558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Colilla, M. Structure and functionalization of mesoporous bioceramics for bone tissue regeneration and local drug delivery. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2012, 370, 1400–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravlev, L.T. Concentration of hydroxyl groups on the surface of amorphous silicas. Langmuir 1987, 3, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravlev, L.T. The Surface Chemistry of Amorphous Silica. Zhuravlev Model. Colloids Surf. A 2000, 173, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vallet-Regí, M. Ordered Mesoporous Materials in the Context of Drug Delivery Systems and Bone Tissue Engineering. Chem. Eur. J. 2006, 12, 5934–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, F.; Cornelius, M.; Morell, J.; Fröba, M. Silica-Based Mesoporous Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 3216–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Gaib, S.; Lin, J. Functionalized mesoporous silica materials for controlled drug delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3679–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Shen, Y.-W.; Guan, Y.-Y.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Wu, Y.; Rahman, K.; Zhang, L.-J.; Liu, H.-J.; Luan, X. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Facile surface functionalization and versatile biomedical applications in oncology. Acta Biomater. 2020, 116, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.W.; Hidajat, K.; Kawi, S. Functionalized SBA-15 Materials as Carriers for Controlled Drug Delivery: Influence of Surface Properties on Matrix−Drug Interactions. Langmuir 2005, 21, 9568–9575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, A.; Colilla, M.; Balas, F.; Vallet-Regí, M. Surface Electrochemistry of Mesoporous Silicas as a Key Factor in the Design of Tailored Delivery Devices. Langmuir 2010, 26, 5038–5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Colomer, A.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Jiménez-Jiménez, C.; Mahillo, I.; Esteban, J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Impact of the antibiotic-cargo from MSNs on gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial biofilms. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2021, 311, 110681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balas, F.; Manzano, M.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. L-Trp adsorption into silica mesoporous materials to promote bone formation. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, B.; Colilla, M.; Díez, J.; Pedraza, D.; Guembe, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles decorated with polycationic dendrimers for infection treatment. Acta Biomater. 2018, 68, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedraza, D.; Díez, J.; Isabel Izquierdo, B.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Amine-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A New Nanoantibiotic for Bone Infection Treatment. Biomed. Glass. 2018, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Encinas, N.; Angulo, M.; Astorga, C.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mixed-charge pseudo-zwitterionic mesoporous silica nanoparticles with low-fouling and reduced cell uptake properties. Acta Biomater. 2019, 84, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arca, H.; Mosquera-Giraldo, L.I.; Pereira, J.M.; Sriranganathan, N.; Taylor, L.S.; Edgar, K.J. Rifampin Stability and Solution Concentration Enhancement Through Amorphous Solid Dispersion in Cellulose ω-Carboxyalkanoate Matrices. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doadrio, A.L.; Doadrio, J.C.; Sánchez-Montero, J.M.; Salinas, A.J.; Vallet-Regí, M. A rational explanation of the vancomycin release from SBA-15 and its derivative by molecular modelling. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2010, 132, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusev, V.Y.; Feng, X.; Bu, Z.; Haller, G.L.; O’Brien, J.A. Mechanical stability of pure silica mesoporous MCM-41 by nitrogen adsorption and small-angle X-ray diffraction measurements. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 1985–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doadrio, A.; Salinas, A.; Montero, J.M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Drug Release from Ordered Mesoporous Silicas. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salviano, A.B.; Santos, M.R.D.; de Araújo, L.M.; Ardisson, J.D.; Lago, R.M.; Araujo, M.H. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Supported on Mesoporous MCM-41 for Efficient Adsorption of Hazardous β-Lactamic Antibiotics. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Doadrio, J.; Doadrio, A.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Pérez-Pariente, J. Hexagonal ordered mesoporous material as a matrix for the controlled release of amoxicillin. Solid State Ion. 2004, 172, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Tehrani, Z.M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MCM-41) coated PEGylated chitosan as a pH-responsive nanocarrier for triggered release of erythromycin. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2014, 63, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbeci, C.; Stănescu, R.; Negoescu, D.; Parvulescu, V. Synthesis, characterization and functionalization of MCM-41 for the removal of organic compounds from wastewaters. EEMJ 2017, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doadrio, J.C.; Sousa, E.M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Doadrio, A.L.; Perez-Pariente, J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Functionalization of mesoporous materials with long alkyl chains as a strategy for controlling drug delivery pattern. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Martinez, Á.; Doadrio, A.L.; Pérez-Pariente, J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Release evaluation of drugs from ordered three-dimensional silica structures. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 26, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, S.; Rahim, A.; Muhammad, N.; Rahman, S.U.; Azhar, U.; Sultana, K.; Sharif, F.; Siddiqi, S.A.; Zaman, M.; Rehman, F. Controllable delivery from gentamicin loaded polycaprolactone/grafted silica nanoparticles composite mats. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doadrio, A.; Sousa, E.; Doadrio, J.; Pariente, J.P.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous SBA-15 HPLC evaluation for controlled gentamicin drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2004, 97, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Yuan, W.; Xue, Y.; Wei, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, K. Co-modified MCM-41 as an effective adsorbent for levofloxacin removal from aqueous solution: Optimization of process parameters, isotherm, and thermodynamic studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 5238–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siafaka, P.; Okur, M.E.; Ayla, Ş.; Er, S.; Cağlar, E.Ş.; Okur, N.Ü. Design and characterization of nanocarriers loaded with Levofloxacin for enhanced antimicrobial activity; physicochemical properties, in vitro release and oral acute toxicity. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adristya, I.; Suryaningtyas, A.D.; Wijaya, J.; Pangestu, F.C.; Hartono, S.B.; Soewignyo, L.; Irawaty, W. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as vehicles for drug delivery. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; p. 012021. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Huang, Y.; Yan, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.Y.; Yuan, P.; Ding, X. Bacterial Outer Membrane-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery of Antibiotic Rifampicin against Gram-Negative Bacterial Infection In Vivo. Adv. Funct. Mater 2021, 31, 2103442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doadrio, A.L.; Sánchez-Montero, J.M.; Doadrio, J.C.; Salinas, A.J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a new carrier methodology in the controlled release of the active components in a polypill. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 97, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jijie, R.; Barras, A.; Teodorescu, F.; Boukherroub, R.; Szunerits, S. Advancements on the molecular design of nanoantibiotics: Current level of development and future challenges. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2017, 2, 349–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castillo, R.R.; Lozano, D.; González, B.; Manzano, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Vallet-Regí, M. Advances in mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted stimuli-responsive drug delivery: An update. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 415–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I. Drug Delivery and Bone Infection. Enzymes 2018, 44, 35–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Shu, Y.; Parra-Robert, M.; Desai, D.; Zhou, H.; Li, Q.; Rong, Z.; Karaman, D.; Yang, H.; Peng, J.; et al. Scalable synthesis of multicomponent multifunctional inorganic core@mesoporous silica shell nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 128, 112272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, R.R.; de la Torre, L.; García-Ochoa, F.; Ladero, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Production of MCM-41 Nanoparticles with Control of Particle Size and Structural Properties: Optimizing Operational Conditions during Scale-Up. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragoneses-Cazorla, G.; Serrano-Lopez, J.; Martinez-Alfonzo, I.; Vallet-Regí, M.; González, B.; Luque-Garcia, J.L. A novel hemocompatible core@shell nanosystem for selective targeting and apoptosis induction in cancer cells. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 2697–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, D.L.; Lee, B.-Y.; Xue, M.; Thomas, C.R.; Meng, H.; Ferris, D.; Nel, A.E.; Zink, J.I.; Horwitz, M.A. Targeted intracellular delivery of antituberculosis drugs to mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages via functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2535–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, A.A.; Lee, B.-Y.; Clemens, D.L.; Dillon, B.J.; Zink, J.I.; Horwitz, M.A. pH-Responsive Isoniazid-Loaded Nanoparticles Markedly Improve Tuberculosis Treatment in Mice. Small 2015, 11, 5066–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montalvo-Quirós, S.; Gómez-Graña, S.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Prados-Rosales, R.C.; González, B.; Luque-Garcia, J.L. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles containing silver as novel antimycobacterial agents against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 197, 111405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beitzinger, B.; Gerbl, F.; Vomhof, T.; Schmid, R.; Noschka, R.; Rodriguez, A.; Wiese, S.; Weidinger, G.; Ständker, L.; Walther, P.; et al. Delivery by Dendritic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Enhances the Antimicrobial Activity of a Napsin-Derived Peptide Against Intracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, e2100453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarre, W.W.; Schneewind, O. Surface proteins of gram-positive bacteria and mechanisms of their targeting to the cell wall envelope. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1999, 63, 174–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beveridge, T.J. Structures of gram-negative cell walls and their derived membrane vesicles. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 4725–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruehle, B.; Clemens, D.L.; Lee, B.-Y.; Horwitz, M.A.; Zink, J.I. A Pathogen-Specific Cargo Delivery Platform Based on Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 6663–6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Jin, Y.; Wang, R. Integration of diagnosis and treatment in the detection and kill of S.aureus in the whole blood. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavruk, M.; Celikbicak, O.; Ozalp, V.C.; Borsa, B.A.; Hernandez, F.J.; Bayramoglu, G.; Salih, B.; Arica, M.Y. Antibiotic loaded nanocapsules functionalized with aptamer gates for targeted destruction of pathogens. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 8492–8495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Han, X.; Yang, Y.; Qiao, H.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Tang, T. Bacteria-Targeting Nanoparticles with Microenvironment-Responsive Antibiotic Release To Eliminate Intracellular Staphylococcus aureus and Associated Infection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 14299–14311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, K.; Patel, U.; Pham, C.; McAlpin, A.; Budisalich, T.; Jayawardena, S.N. Targeted Delivery of Antibiotic Therapy to Inhibit Pseudomonas aeruginosa Using Lipid-Coated Mesoporous Silica Core–Shell Nanoassembly. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2020, 3, 6708–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, N.; Chen, X.; Jeon, S.; Yan, M. Carbohydrate-Conjugated Hollow Oblate Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Nanoantibiotics to Target Mycobacteria. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 2797–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Jayawardana, K.W.; Kong, N.; Ren, Y.; Hao, N.; Yan, M.; Ramström, O. Trehalose-Conjugated, Photofunctionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Efficient Delivery of Isoniazid into Mycobacteria. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 1250–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudakavi, R.J.; Vanamali, S.; Chakravortty, D.; Raichur, A.M. Development of arginine based nanocarriers for targeting and treatment of intracellular Salmonella. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 7022–7032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Lin, A.; Huang, N.; Long, L.; Gang, Y.; Liu, J. Folic acid-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles with pH-responsiveness loaded with Amp for an enhanced effect against anti-drug-resistant bacteria by overcoming efflux pump systems. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 1923–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, G.; Li, L.; Yu, F.; Wang, H. Vancomycin-Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Selective Recognition and Killing of Pathogenic Gram-Positive Bacteria Over Macrophage-Like Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 10874–10881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesniak, A.; Salvati, A.; Santos-Martinez, M.J.; Radomski, M.W.; Dawson, K.A.; Åberg, C. Nanoparticle Adhesion to the Cell Membrane and Its Effect on Nanoparticle Uptake Efficiency. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Häffner, S.M.; Parra-Ortiz, E.; Browning, K.L.; Jørgensen, E.; Skoda, M.W.; Montis, C.; Li, X.; Berti, D.; Zhao, D.; Malmsten, M. Membrane Interactions of Virus-like Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 6787–6800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Luo, Q.; Lin, J.; Hu, L.; Liu, X.; Xue, F. Virus-like mesoporous silica-coated plasmonic Ag nanocube with strong bacteria adhesion for diabetic wound ulcer healing. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2021, 34, 102381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; McCarthy, K.A.; Kelly, M.A.; Gao, J. Targeting bacteria via iminoboronate chemistry of amine-presenting lipids. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, S.J.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Pantarat, N.; Sulistio, A.; Wong, E.H.H.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Lenzo, J.C.; Holden, J.A.; Blencowe, A.; Reynolds, E.C.; et al. Combating multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria with structurally nanoengineered antimicrobial peptide polymers. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovic-Moreno, A.F.; Lu, T.K.; Puscasu, V.A.; Yoon, C.J.; Langer, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Surface Charge-Switching Polymeric Nanoparticles for Bacterial Cell Wall-Targeted Delivery of Antibiotics. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 4279–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Rico, M.; Pérez-Esteve, É.; de la Torre, C.; Jiménez-Belenguer, A.I.; Quiles, A.; Marcos, M.D.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Barat, J.M. Improving the Antimicrobial Power of Low-Effective Antimicrobial Molecules Through Nanotechnology. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 2140–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, N.; Galiana, I.; Mondragón, L.; Aznar, E.; Climent, E.; Cabedo, N.; Sancenón, F.; Murguía, J.R.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Marcos, M.D.; et al. Enhanced Efficacy and Broadening of Antibacterial Action of Drugs via the Use of Capped Mesoporous Nanoparticles. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 11167–11171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikova, N.; Mas, N.; Miguel-Romero, L.; Polo, L.; Stolte, E.; Zaccaria, E.; Cao, R.; Taverne, N.; Murguía, J.R.; Martinez-Manez, R.; et al. Broadening the antibacterial spectrum of histidine kinase autophosphorylation inhibitors via the use of ε-poly-L-lysine capped mesoporous silica-based nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, T.F.; O’Toole, G.A. Mechanisms of biofilm resistance to antimicrobial agents. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, K.K. What drives bacteria to produce a biofilm? FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 236, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; He, Y.; Li, Z.; Ahmad Nor, Y.; Ye, Q. Nanoengineered hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the delivery of antimicrobial proteins into biofilms. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 1899–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasia, W.; Lei, C.; Cao, Y.; Ye, Q.; He, Y.; Xu, C. Enhanced eradication of bacterial biofilms with DNase I-loaded silver-doped mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 2328–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulaz, S.; Devlin, H.; Vitale, S.; Quinn, L.; O’Gara, J.P.; Casey, E. Tailoring Nanoparticle-Biofilm Interactions to Increase the Efficacy of Antimicrobial Agents Against Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 4779–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carmona, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Concanavalin A-targeted mesoporous silica nanoparticles for infection treatment. Acta Biomater. 2019, 96, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera-Correa, J.J.; Gisbert-Garzarán, M.; Mediero, A.; Carias-Cálix, R.A.; Jiménez-Jiménez, C.; Esteban, J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Arabic gum plus colistin coated moxifloxacin-loaded nanoparticles for the treatment of bone infection caused by Escherichia coli. Acta Biomater. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounani, Z.; Asadollahi, M.A.; Pedersen, J.N.; Lyngsø, J.; Pedersen, J.S.; Arpanaei, A.; Meyer, R.L. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles carrying multiple antibiotics provide enhanced synergistic effect and improved biocompatibility. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces. 2019, 175, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebert, A.M.; Aimé, C.; Álvarez, G.S.; Shi, Y.; Flor, S.A.; Lucangioli, S.I.; Desimone, M.F.; Coradin, T. Silica core-shell particles for the dual delivery of gentamicin and rifamycin antibiotics. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 3135–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, W.; Hu, J. Antibacterial and anticancer activities of asymmetric lollipop-like mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with curcumin and gentamicin sulfate. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 186, 110744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Radovic-Moreno, A.F.; Wu, J.; Langer, R.; Shi, J. Nanomedicine in the management of microbial infection—Overview and perspectives. Nano Today 2014, 9, 478–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perelshtein, I.; Lipovsky, A.; Perkas, N.; Gedanken, A.; Moschini, E.; Mantecca, P. The influence of the crystalline nature of nano-metal oxides on their antibacterial and toxicity properties. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.; Lim, J.Z.Z.; Ng, C.T.; Li, J.J.; Yung, L.Y.L.; Bay, B.H. Silver Nanoparticles in Cancer: Therapeutic Efficacy and Toxicity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AshaRani, P.V.; Low Kah Mun, G.; Hande, M.P.; Valiyaveettil, S. Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of Silver Nanoparticles in Human Cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.N.; Muñoz-Olivas, R.; Luque-Garcia, J.L. SILAC-based quantitative proteomics identifies size-dependent molecular mechanisms involved in silver nanoparticles-induced toxicity. Nanotoxicology 2019, 13, 812–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Sun, L.; Luo, H. Preparation of AgBr@SiO2 core@shell hybrid nanoparticles and their bactericidal activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2013, 33, 1808–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvo-Quiros, S.; Aragoneses-Cazorla, G.; Garcia-Alcalde, L.; Vallet-Regí, M.; González, B.; Luque-Garcia, J.L. Cancer cell targeting and therapeutic delivery of silver nanoparticles by mesoporous silica nanocarriers: Insights into the action mechanisms using quantitative proteomics. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 4531–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, X.; Chen, Y.; Guo, M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Gu, H. Antibiotic-loaded, silver core-embedded mesoporous silica nanovehicles as a synergistic antibacterial agent for the treatment of drug-resistant infections. Biomaterials 2016, 101, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Qi, J.; Zhang, W.; Cai, Q.; Jiang, X. Facile, One-Pot Synthesis, and Antibacterial Activity of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Decorated with Well-Dispersed Silver Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 12038–12045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liong, M.; France, B.; Bradley, K.A.; Zink, J.I. Antimicrobial activity of silver nanocrystals encapsulated in mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 1684–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.-M.; Wang, Z.; Lu, M.M.; Shao, D.; Yue, J.; Yang, D.; Li, M.-Q.; Dong, W.-F. Janus silver mesoporous silica nanobullets with synergistic antibacterial functions. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 157, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cai, L.; Tian, Z.; Wu, Y. Phytochemical Curcumin-Coformulated, Silver-Decorated Melanin-like Polydopamine/Mesoporous Silica Composites with Improved Antibacterial and Chemotherapeutic Effects against Drug-Resistant Cancer Cells. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 15083–15094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, E.; Estévez, M.; Jiménez-Jiménez, C.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; González, B.; Vallet-Regí, M. A versatile multicomponent mesoporous silica nanosystem with dual antimicrobial and osteogenic effects. Acta Biomater. 2021, 136, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera-Correa, J.J.; Esteban, J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Inorganic and Polymeric Nanoparticles for Human Viral and Bacterial Infections Prevention and Treatment. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Yang, K.; Liu, F.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Sun, S. Diverse gatekeepers for mesoporous silica nanoparticle based drug delivery systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 6024–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Ghasemi, A.; Zangabad, P.S.; Rahighi, R.; Basri, S.M.M.; Mirshekari, H.; Amiri, M.; Pishabad, Z.S.; Aslani, A.; Bozorgomid, M.; et al. Smart micro/nanoparticles in stimulus-responsive drug/gene delivery systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 1457–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, M.; Gu, Z.; Ottewell, T.; Yu, C. Silica-based nanoparticles for therapeutic protein delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 3241–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I. Bioactive Mesoporous Silicas as Controlled Delivery Systems: Application in Bone Tissue Regeneration. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2008, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaverde, G.; Alfranca, A.; Gonzalez-Murillo, Á.; Melen, G.J.; Castillo, R.R.; Ramírez, M.; Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Molecular Scaffolds as Double-Targeting Agents for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Neuroblastoma. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 3067–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mora-Raimundo, P.; Lozano, D.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Nanoparticles to Knockdown Osteoporosis-Related Gene and Promote Osteogenic Marker Expression for Osteoporosis Treatment. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 5451–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mora-Raimundo, P.; Lozano, D.; Benito, M.; Mulero, F.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Osteoporosis Remission and New Bone Formation with Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2101107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cai, X.; Ji, J.; He, S.; Zhai, G. Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanocarriers for stimuli-responsive target delivery of anticancer drugs. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 92073–92091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemichez, E.; Barbieri, J.T. General aspects and recent advances on bacterial protein toxins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a013573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, B.Y.; Li, Z.; Clemens, D.L.; Dillon, B.J.; Hwang, A.A.; Zink, J.I.; Horwitz, M.A. Redox-Triggered Release of Moxifloxacin from Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Functionalized with Disulfide Snap-Tops Enhances Efficacy Against Pneumonic Tularemia in Mice. Small 2016, 12, 3690–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, H.; Ha, D.-G.; Markopoulos, G.; Chae, H.S.; Baldo, M.A.; Swager, T.M. Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence and Aggregation Induced Emission with Through-Space Charge Transfer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 4894–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, F.; Xiao, F. A multifunctional nanoplatform based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles for imaging-guided chemo/photodynamic synergetic therapy. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 31133–31141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, J.; Ren, L. Self-enriched mesoporous silica nanoparticle composite membrane with remarkable photodynamic antimicrobial performances. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 559, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Carmona, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Advances in Laser Ablation Synthesized Silicon-Based Nanomaterials for the Prevention of Bacterial Infection. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Hao, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Tao, B.; Chen, M.; Lin, C.; Liu, P.; Cai, K. A dual-functional implant with an enzyme-responsive effect for bacterial infection therapy and tissue regeneration. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 1840–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.M.; Ge, Y.; Qiu, J.; Shao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, J.; Zheng, X.; Chang, Z.M.; Wang, Z.; Dong, W.F.; et al. Redox/pH dual-controlled release of chlorhexidine and silver ions from biodegradable mesoporous silica nanoparticles against oral biofilms. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 7697–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuchs, S.; Pané-Farré, J.; Kohler, C.; Hecker, M.; Engelmann, S. Anaerobic Gene Expression in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 4275–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bistrian, B. Systemic response to inflammation. Nutr. Rev. 2007, 65, S170–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmen, H.P.; Blaser, J. Analysis of pH and pO2 in abscesses, peritoneal fluid, and drainage fluid in the presence or absence of bacterial infection during and after abdominal surgery. Am. J. Surg. 1993, 166, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.; Monteiro, F.J.; Ferraz, M.P. Infection of orthopedic implants with emphasis on bacterial adhesion process and techniques used in studying bacterial-material interactions. Biomatter 2012, 2, 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gisbert-Garzarán, M.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. pH-Responsive Mesoporous Silica and Carbon Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gisbert-Garzaran, M.; Lozano, D.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Manzano, M. Self-immolative polymers as novel pH-responsive gate keepers for drug delivery. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Carmona, M.; Lozano, D.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Lectin-conjugated pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted bone cancer treatment. Acta Biomater. 2018, 65, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carmona, M.; Ho, Q.P.; Morand, J.; García, A.; Ortega, E.; Erthal, L.C.S.; Ruiz-Hernandez, E.; Santana, M.D.; Ruiz, J.; Vallet-Regí, M.; et al. Amino-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle-Encapsulated Octahedral Organoruthenium Complex as an Efficient Platform for Combatting Cancer. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 10275–10284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert-Garzarán, M.; Lozano, D.; Matsumoto, K.; Komatsu, A.; Manzano, M.; Tamanoi, F.; Vallet-Regí, M. Designing Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles to Overcome Biological Barriers by Incorporating Targeting and Endosomal Escape. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 9656–9666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.L.; de la Torre, P.; Cabañas, M.V.; Manzano, M.; Flores, A.I.; Vallet-Regí, M. Suicide-gene transfection of tumor-tropic placental stem cells employing ultrasound-responsive nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2019, 83, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.L.; Cabañas, M.V.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Polymer-Grafted Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Ultrasound-Responsive Drug Carriers. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11023–11033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paris, J.L.; Villaverde, G.; Cabañas, M.V.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. From proof-of-concept material to PEGylated and modularly targeted ultrasound-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 2785–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paris, J.L.; Manzano, M.; Cabañas, M.V.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles engineered for ultrasound-induced uptake by cancer cells. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 6402–6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guisasola, E.; Baeza, A.; Talelli, M.; Arcos, D.; Moros, M.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Magnetic-Responsive Release Controlled by Hot Spot Effect. Langmuir 2015, 31, 12777–12782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisasola, E.; Asín, L.; Beola, L.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Beyond Traditional Hyperthermia: In Vivo Cancer Treatment with Magnetic-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanocarriers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 12518–12525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villaverde, G.; Gómez-Graña, S.; Guisasola, E.; García, I.; Hanske, C.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Targeted Chemo-Photothermal Therapy: A Nanomedicine Approximation to Selective Melanoma Treatment. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2018, 35, 1800148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carmona, M.; Lozano, D.; Baeza, A.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. A novel visible light responsive nanosystem for cancer treatment. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 15967–15973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villaverde, G.; Nairi, V.; Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Double Sequential Encrypted Targeting Sequence: A New Concept for Bone Cancer Treatment. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 7174–7179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, J.L.; Villaverde, G.; Gómez-Graña, S.; Vallet-Regí, M. Nanoparticles for multimodal antivascular therapeutics: Dual drug release, photothermal and photodynamic therapy. Acta Biomater. 2020, 101, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, A.; González, B.; Harvey, C.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Vallet-Regí, M. Effective reduction of biofilm through photothermal therapy by gold core@shell based mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2021, 328, 111489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, T.E.; Roper, M.; Kolter, R.; Weitz, D.A.; Brenner, M.P. Bacillus subtilis spreads by surfing on waves of surfactant. PNAS 2009, 106, 18109–18113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whitchurch, C.B.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Ragas, P.C.; Mattick, J.S. Extracellular DNA required for bacterial biofilm formation. Science 2002, 295, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Liu, L.S.; Lau, C.H.; Han Chang, T.J.; Tam, D.Y.; Leung, H.M.; Tin, C.; Lo, P.K. Synthetic α-l-Threose Nucleic Acids Targeting BcL-2 Show Gene Silencing and in Vivo Antitumor Activity for Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 38510–38518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi-Polyachenko, N.; Young, C.; MacNeill, C.; Braden, A.; Argenta, L.; Reid, S. Eradicating group A streptococcus bacteria and biofilms using functionalised multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Int. J. Hyperth. 2014, 30, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Ju, E.; Gao, N.; Wang, Z.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Synergistic eradication of antibiotic-resistant bacteria based biofilms in vivo using a NIR-sensitive nanoplatform. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 5312–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, R.N.; Kelso, M.J.; Rineh, A.; Yepuri, N.R.; Feelisch, M.; Soren, O.; Brito-Mutunayagam, S.; Salib, R.J.; Stoodley, P.; Clarke, S.C.; et al. Cephalosporin-NO-donor prodrug PYRRO-C3D shows β-lactam-mediated activity against Streptococcus pneumoniae biofilms. Nitric Oxide 2017, 65, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Antibiotic/Host Matrix/ Antibiotic Family | Docking * | Computed Properties Drug ** | H-Bonds Count ** |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin MCM-41 [62] SBA-15 [63] Semisynthetic penicillin | 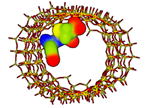 Ecomplex −227.65 kJ/mol | Mw = 365.4 amu XlogP3 = −2.0 Length = 10.63 Å Width = 7.90 Å | Donor drug 4 Aceptor drug 7 Complex 5 |
| Erythromycin MCM-41 [64], MCM-41-Ti [65], SBA-15 [66], LP-Ia3d [67] Broad-spectrum macrolide | 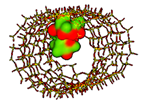 Ecomplex −315.45 kJ/mol | Mw = 733.9 amu XlogP3 = 2.7 Length = 14.01 Å Width = 9.70 Å | Donor drug 5 Aceptor drug 14 Complex 1 |
| Gentamicin MCM-41 [68], SBA-15 [69] Broad-spectrum aminoglycoside | 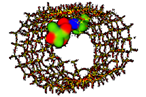 Ecomplex −256.08 kJ/mol | Mw = 477.6 amu XlogP3 = −4.1 Length = 14.10 Å Width = 8.90 Å | Donor drug 8 Aceptor drug 12 Complex 6 |
| Levofloxacin MCM-41 [70], SBA-15 [71] Broad-spectrum, third-generation fluoroquinolone | 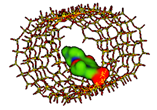 Ecomplex −241.96 kJ/mol | Mw = 361.4 amu XlogP3 = −0.4 Length = 14.20 Å Width = 7.50 Å | Donor drug 1 Aceptor drug 8 Complex 1 |
| Rifampicin MCM-41 [72], MSNs [73] Semisynthetic amycolatopsis rifamycinica |  Ecomplex −349.59 kJ/mol | Mw = 822.9 amu XlogP3 = 4.9 Length = 14.50 Å Width = 11.50 Å | Donor drug 5 Aceptor drug 15 Complex 5 |
| Vancomycin SBA-15 [59] Branched tricyclic glycosylated peptide | 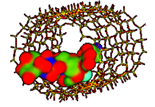 Ecomplex −486.39 kJ/mol | Mw = 1449.2 amu XlogP3 = −2.6 Length = 19.74 Å Width = 18.70 Å | Donor drug 19 Aceptor drug 26 Complex 4 |
 ; Ecomplex is the electrostatic potential energy in the model complex, where MCM-41 was used as receptor and the antibiotic as ligand. ** XlogP3 (for the fast calculation of partition coefficient, logP), donor and acceptor drug H-bonds have been obtained from PubChem DataBank. Complex H-bonds have been obtained from Hex 8.0 docking software.
; Ecomplex is the electrostatic potential energy in the model complex, where MCM-41 was used as receptor and the antibiotic as ligand. ** XlogP3 (for the fast calculation of partition coefficient, logP), donor and acceptor drug H-bonds have been obtained from PubChem DataBank. Complex H-bonds have been obtained from Hex 8.0 docking software.Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Álvarez, E.; González, B.; Lozano, D.; Doadrio, A.L.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I. Nanoantibiotics Based in Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: New Formulations for Bacterial Infection Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122033
Álvarez E, González B, Lozano D, Doadrio AL, Colilla M, Izquierdo-Barba I. Nanoantibiotics Based in Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: New Formulations for Bacterial Infection Treatment. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(12):2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122033
Chicago/Turabian StyleÁlvarez, Elena, Blanca González, Daniel Lozano, Antonio L. Doadrio, Montserrat Colilla, and Isabel Izquierdo-Barba. 2021. "Nanoantibiotics Based in Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: New Formulations for Bacterial Infection Treatment" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 12: 2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122033
APA StyleÁlvarez, E., González, B., Lozano, D., Doadrio, A. L., Colilla, M., & Izquierdo-Barba, I. (2021). Nanoantibiotics Based in Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: New Formulations for Bacterial Infection Treatment. Pharmaceutics, 13(12), 2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122033









