Protein Loading into Spongelike PLGA Microspheres
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
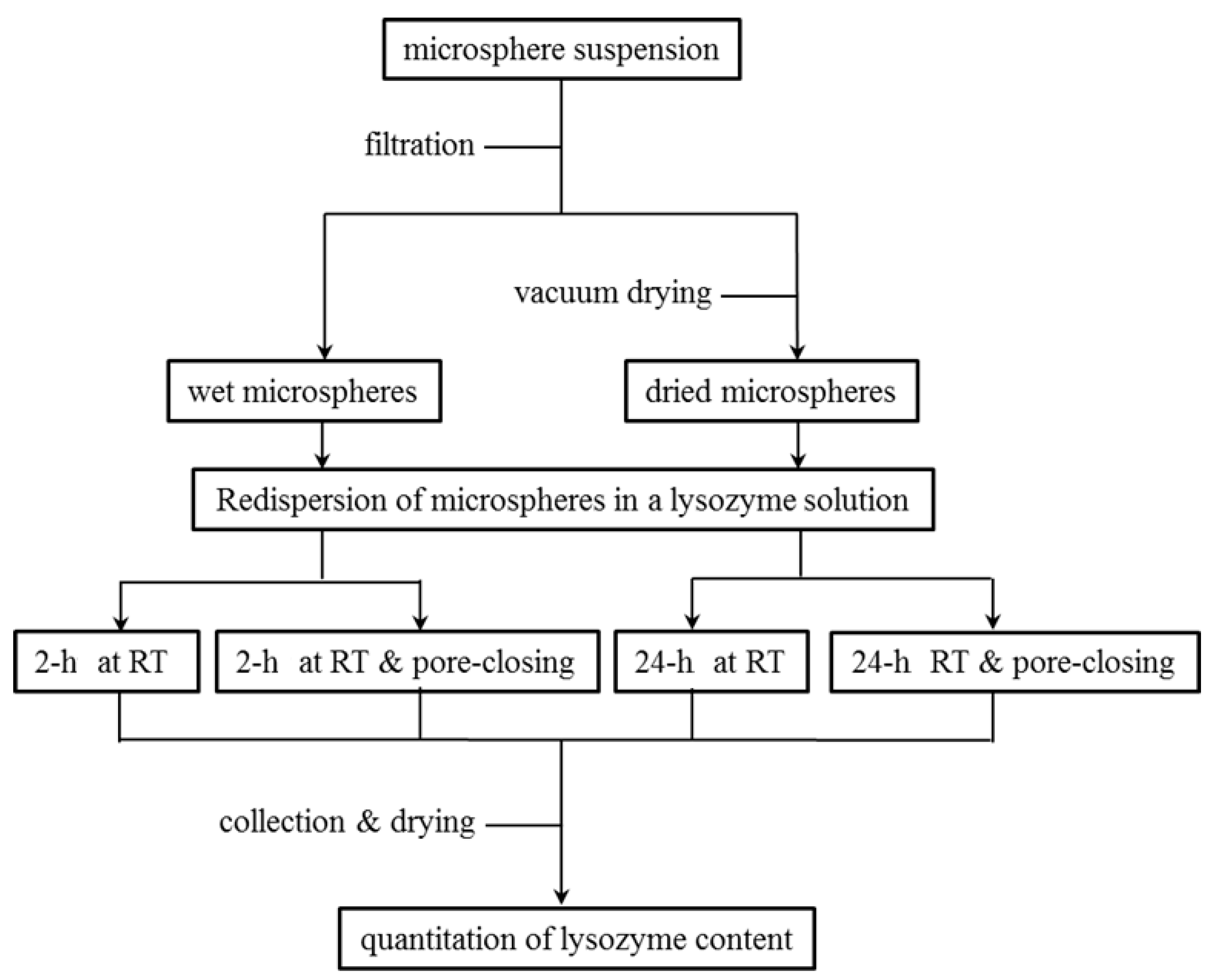
2.2. Preparation of Spongelike PLGA Microspheres
2.3. Encapsulation of Lysozyme Into Spongelike Microspheres
2.4. Determination of Lysozyme Content in PLGA Microspheres
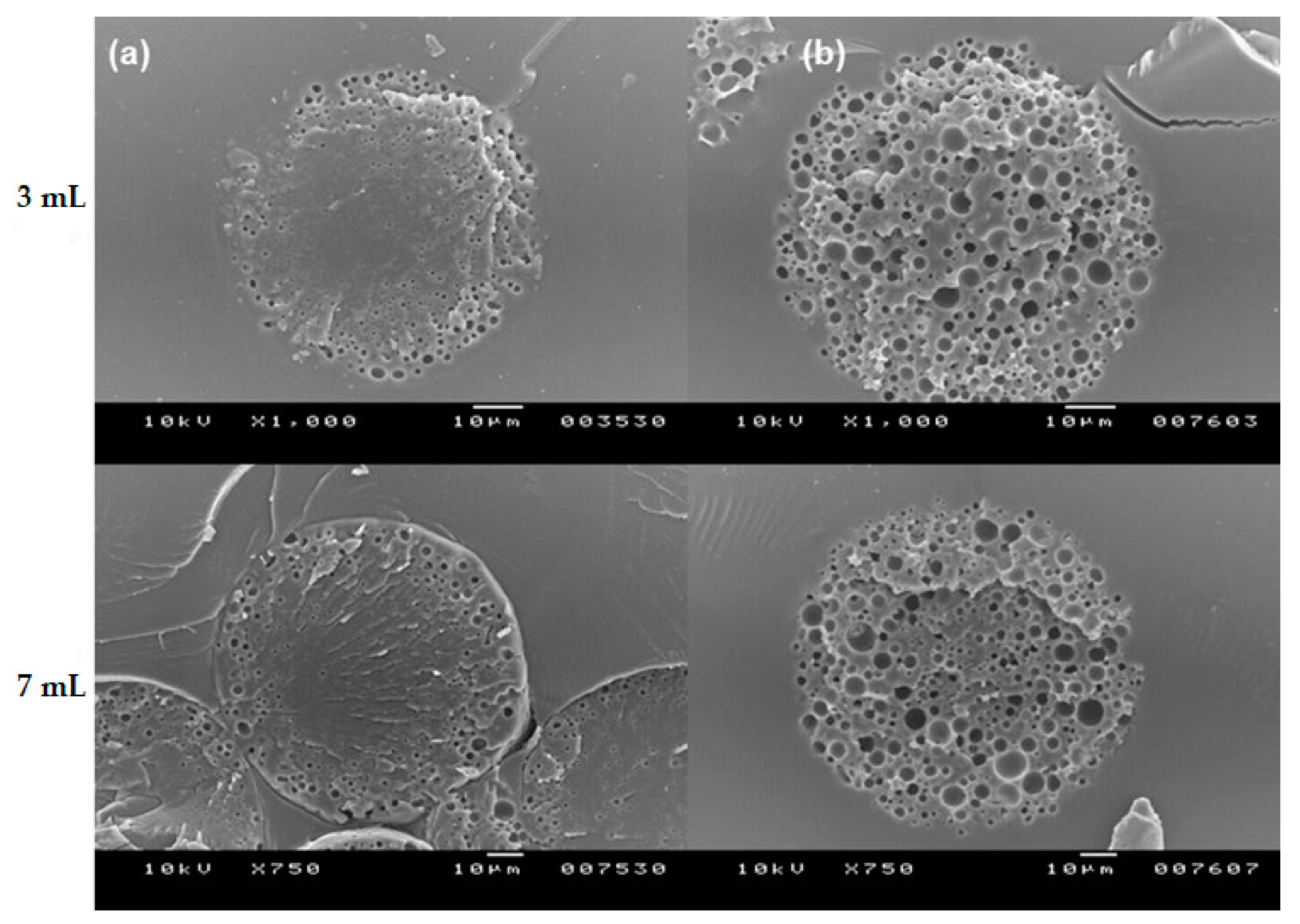
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.6. Pore Size Distribution
2.7. Encapsulation of Nile Red and FITC-Dextran into Porous PLGA Microspheres
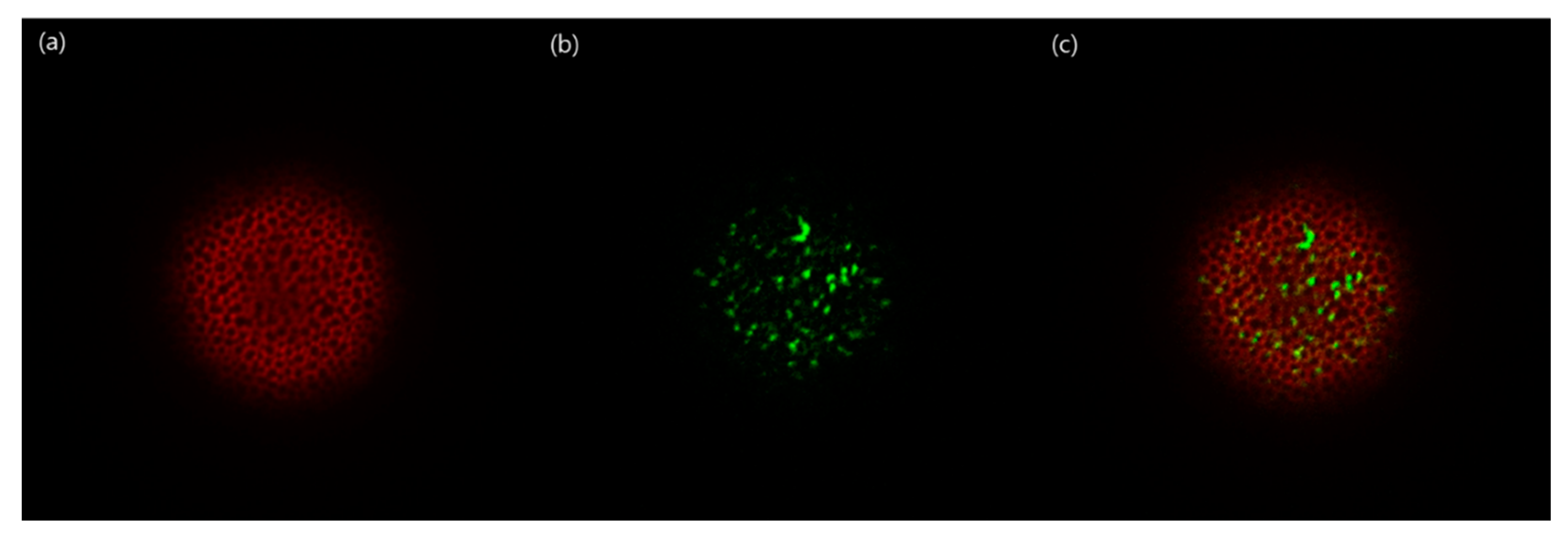
2.8. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
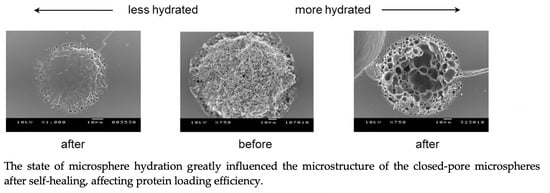
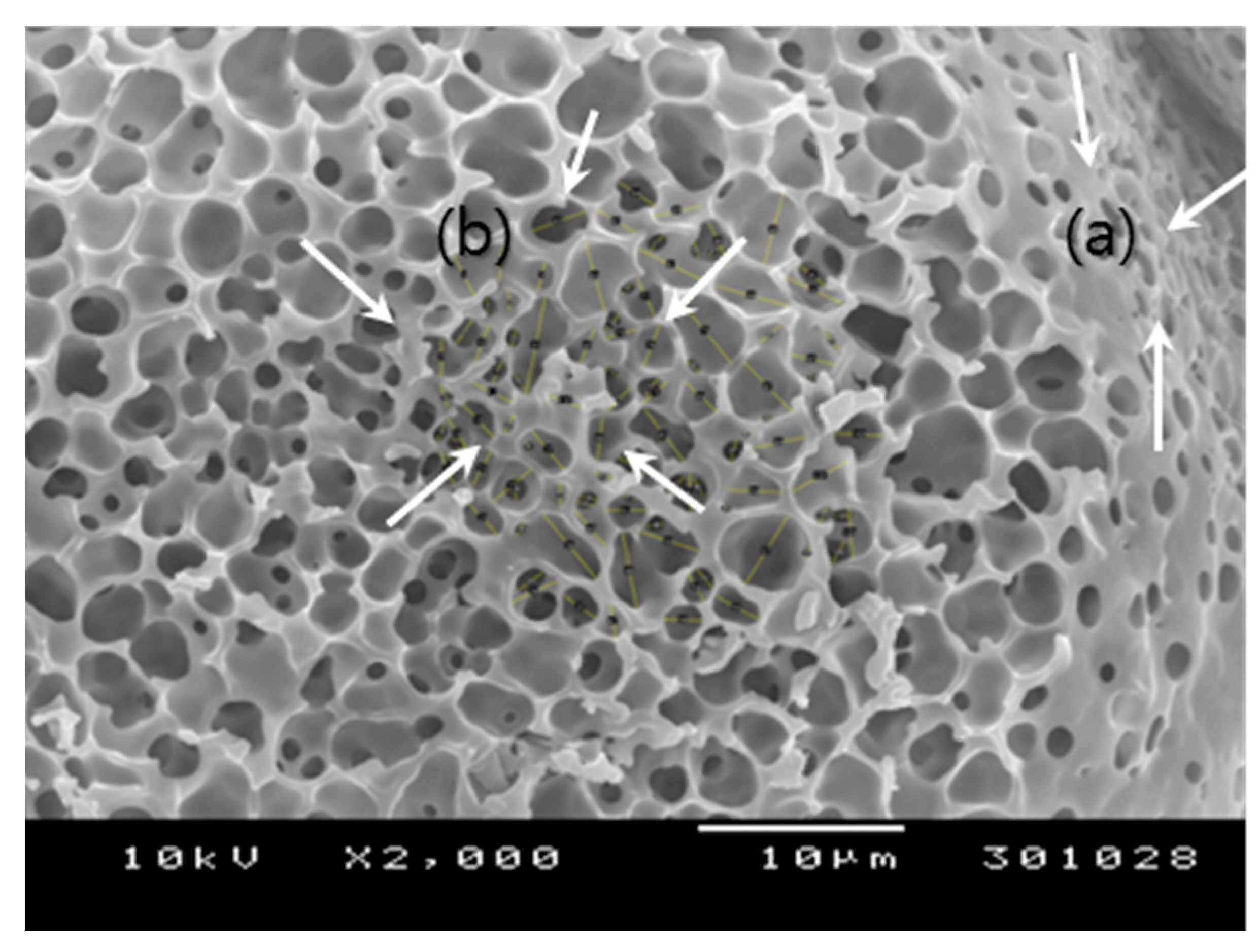
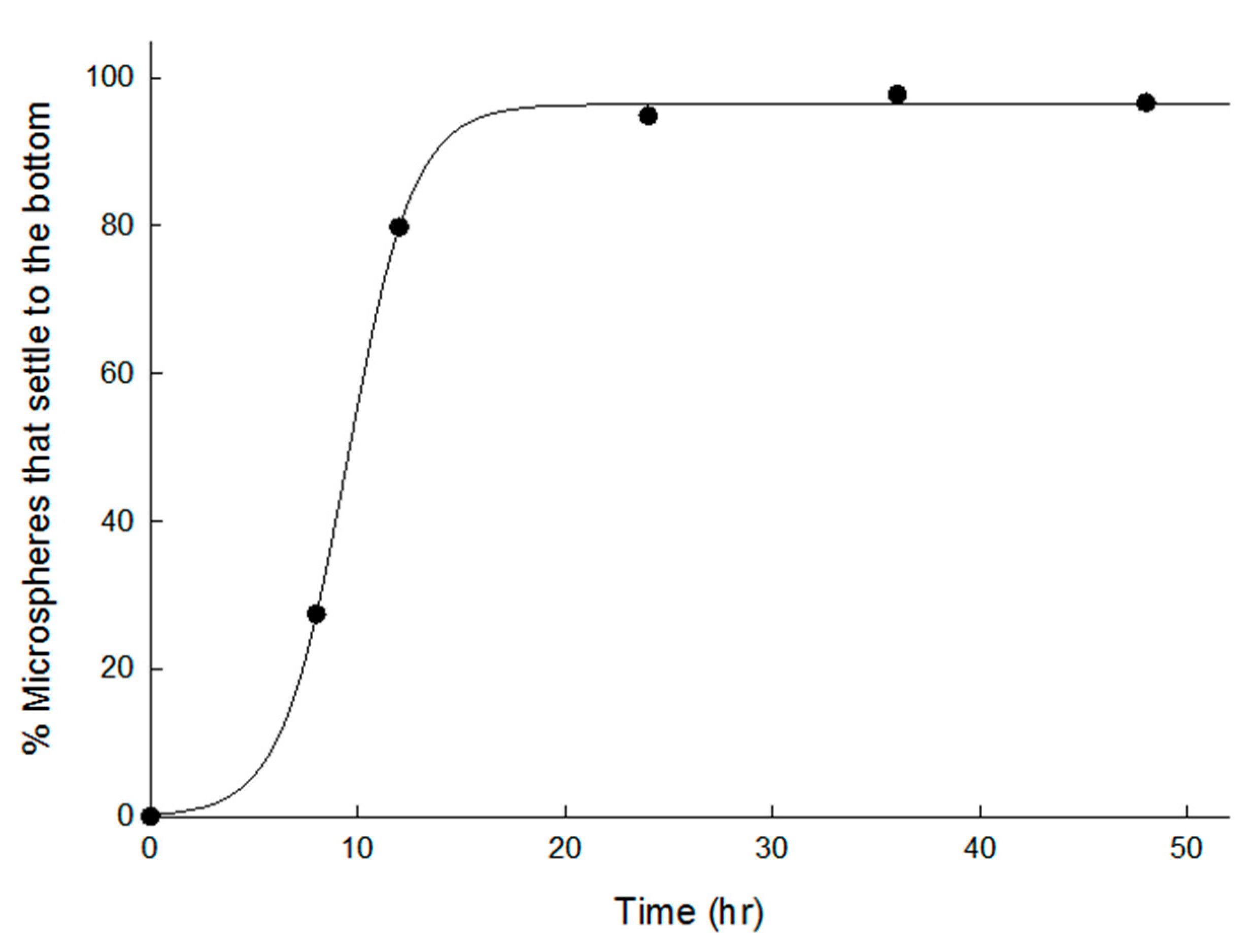
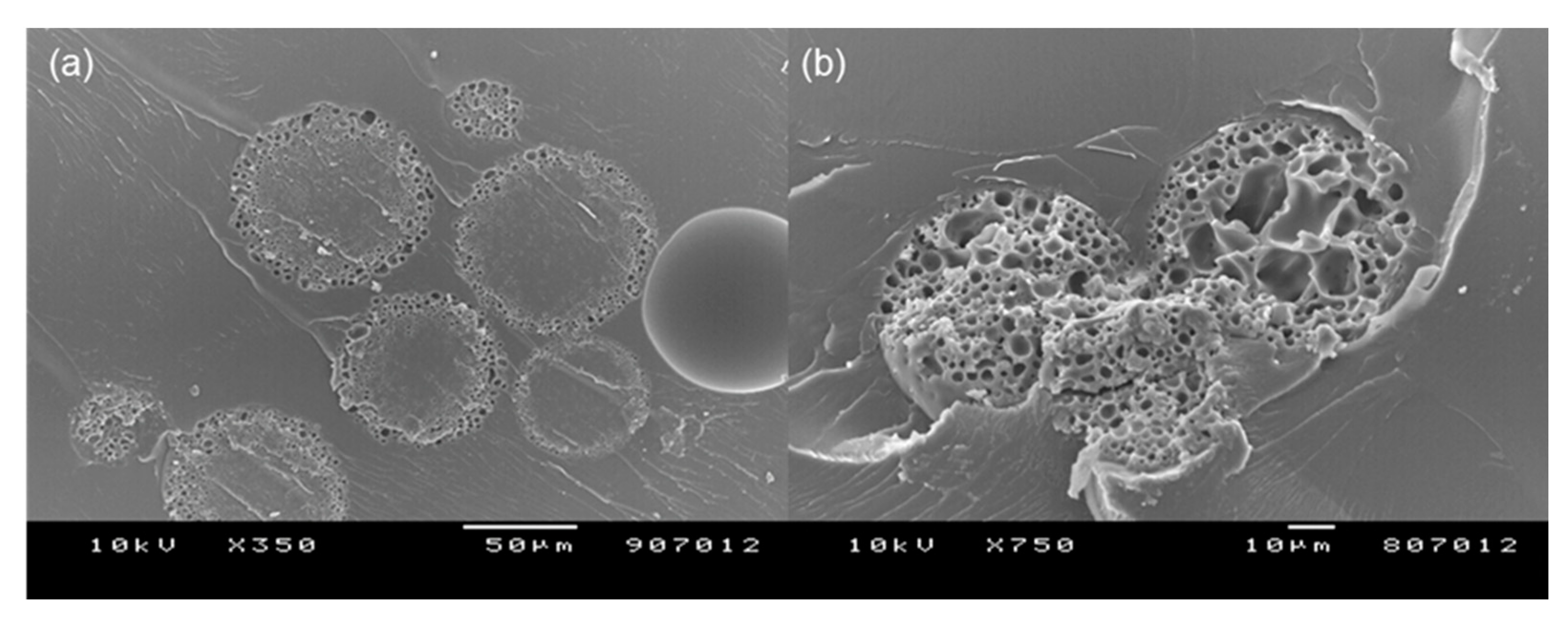
3.1. Spongelike Characteristics of Porous PLGA Microspheres
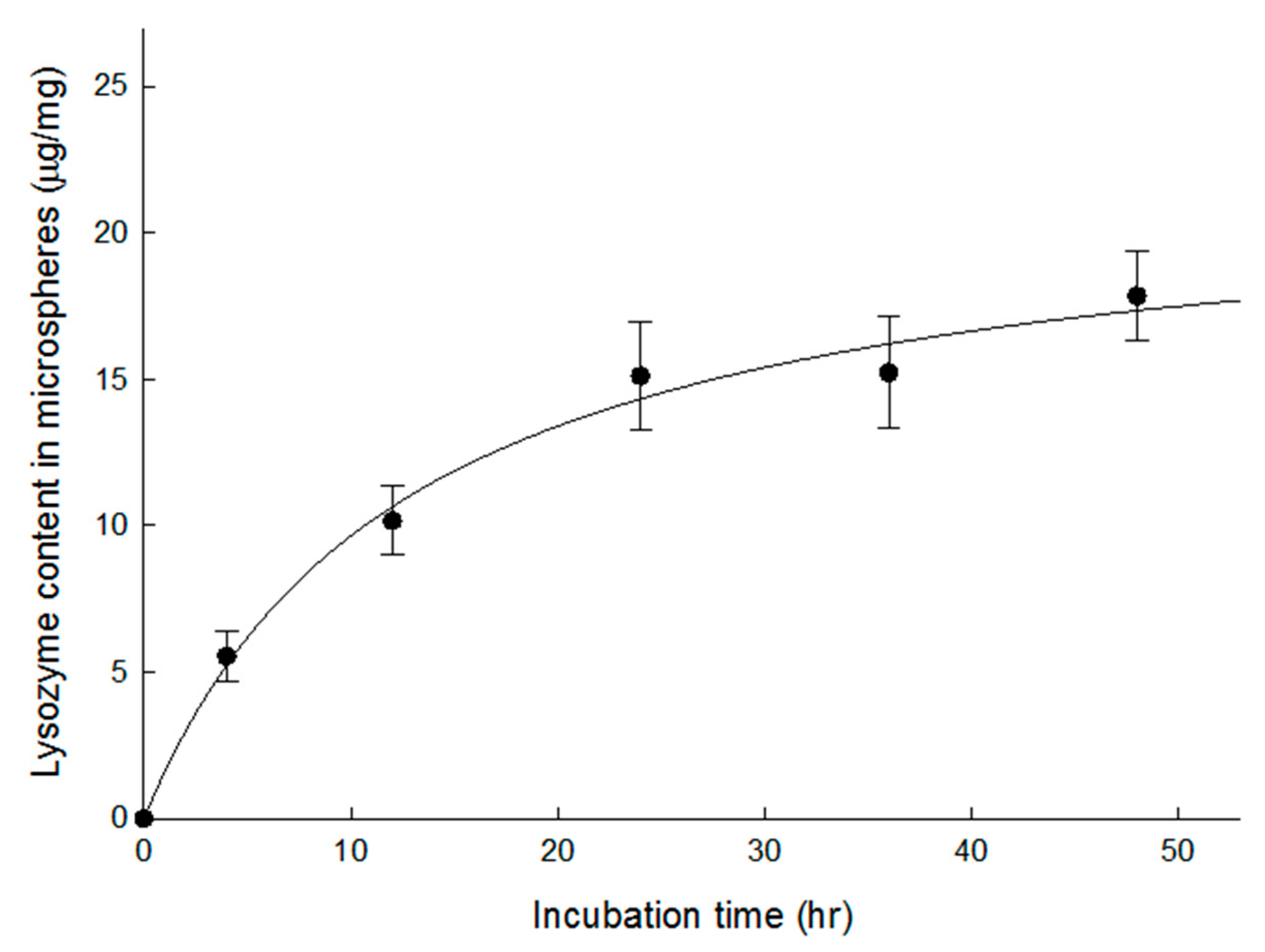
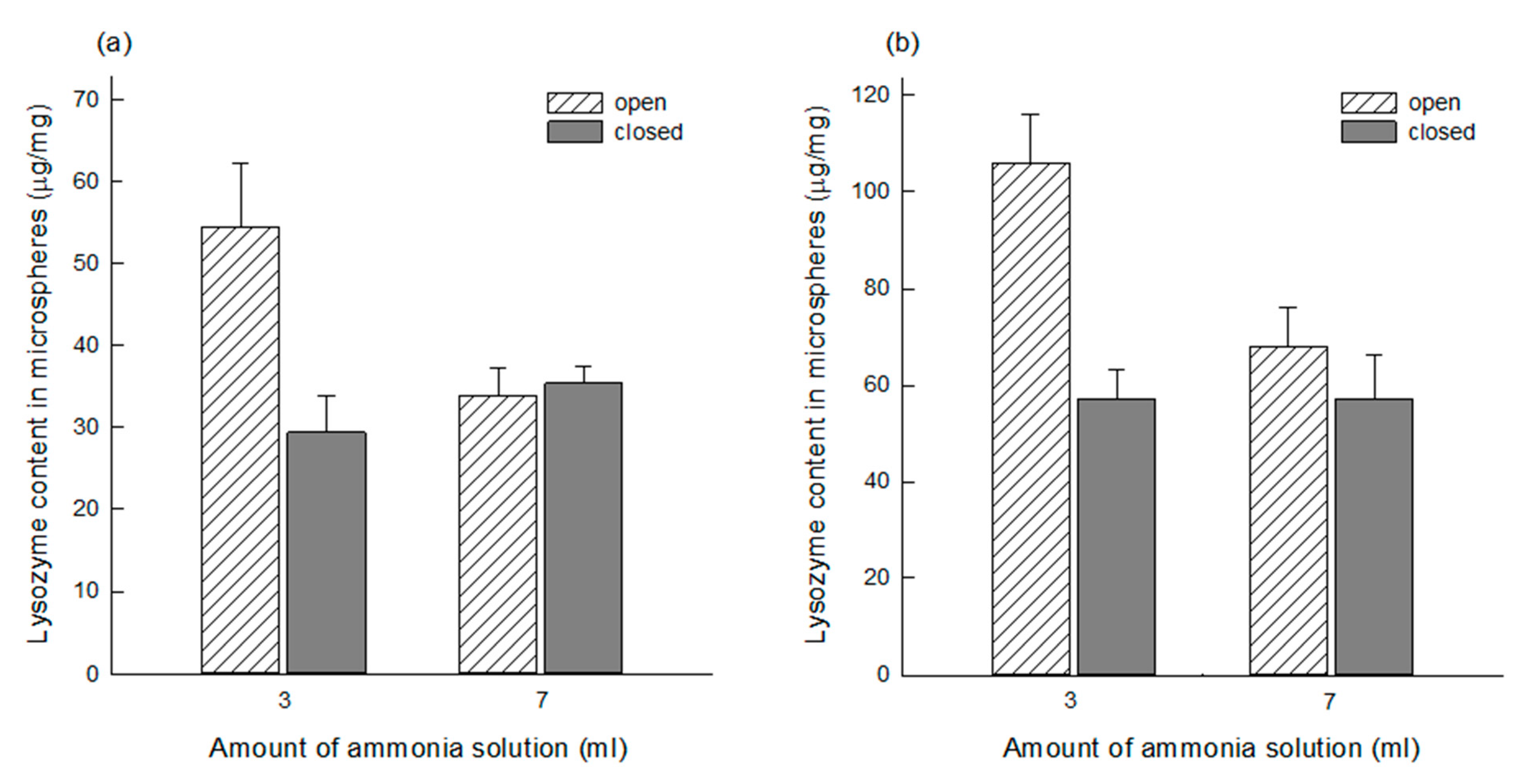
3.2. Lysozyme Loading into Open-Pore PLGA Microspheres
3.3. Comparison of Lysozyme Loadings before and after Self-Healing
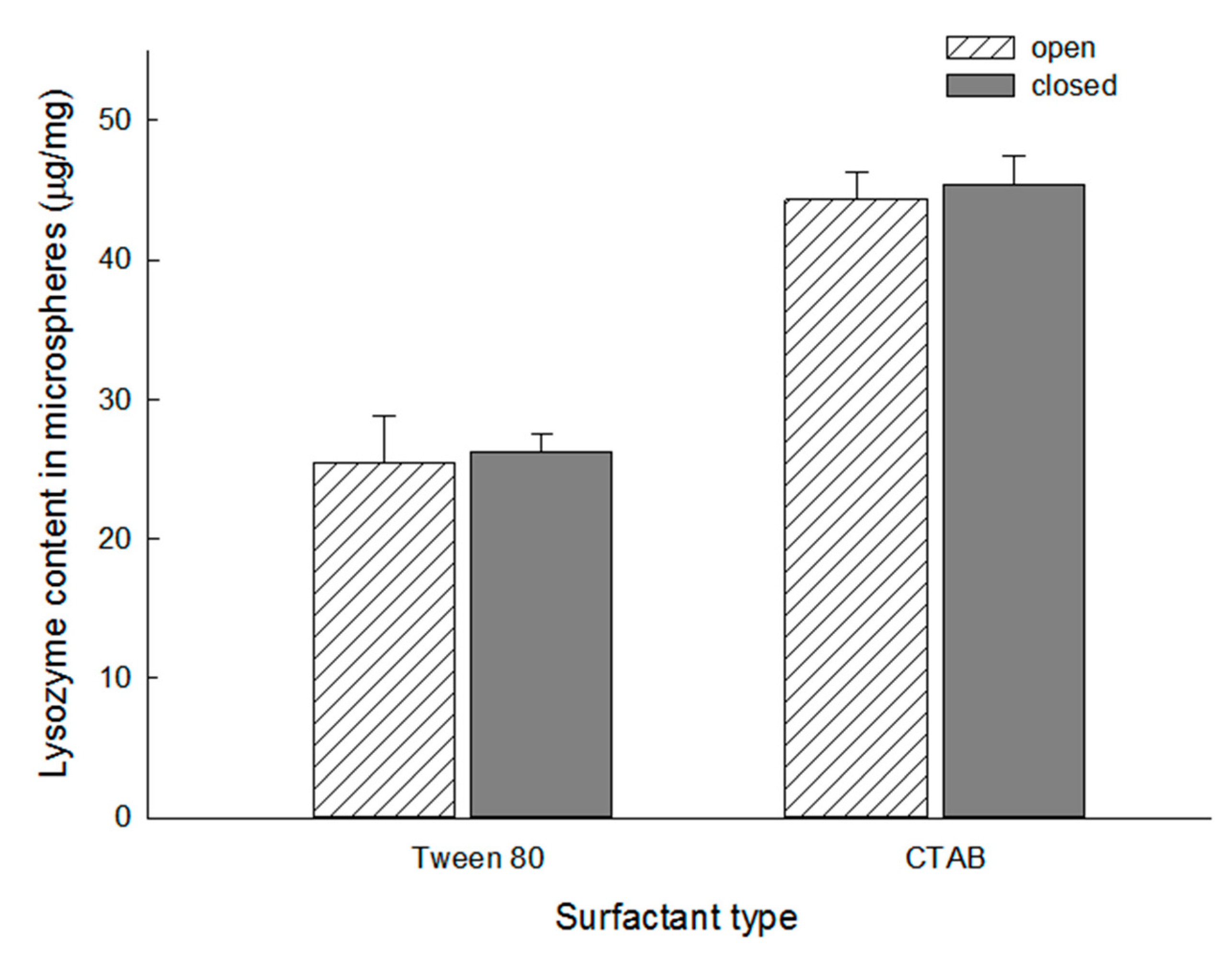
3.4. Effect of Surfactant Type upon Lysozyme Loading into Dried Microspheres
3.5. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bao, T.Q.; Hiep, N.T.; Kim, Y.H.; Yang, H.M.; Lee, B.T. Fabrication and characterization of porous poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) microspheres for use as a drug delivery system. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 2510–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Ou, Z.; Zhong, L.; Wang, Y.E.; Cao, L.P.; Guan, S. Exenatide-loaded inside-porous poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres as a long-acting drug delivery system with improved release characteristics. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 1667–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G. Microencapsulation of protein drugs for drug delivery: Strategy, preparation, and applications. J. Control. Release 2014, 193, 324–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diana, J.N.; Tao, Y.; Du, Q.; Wang, M.; Kumar, C.U.; Wu, F.; Jin, T. PLGA microspheres of hGH of preserved native state prepared using a self-regulated process. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolnik, B.S.; Burgess, D.J. Effect of acidic pH on PLGA microsphere degradation and release. J. Control. Release 2007, 122, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houchin, M.L.; Topp, E.M. Chemical degradation of peptides and proteins in PLGA: A review of reactions and mechanisms. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2395–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hong, X.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, W. Porous microsphere and its applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, J.; Won, Y.Y. Phenomenology of the initial burst release of drugs from PLGA microparticles. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 6053–6062. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.D.; Sun, P.J.; Gan, Z.H. Preparation of porous polylactide microspheres and their application in tissue engineering. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 36, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoyav, B.; Benny, O. Microfluidic based fabrication and characterization of highly porous polymeric microspheres. Polymers 2019, 11, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, L.; Li, M.; Liu, X.; Jin, Y. Drug-loaded PLGA electrospraying porous microspheres for the local therapy of primary lung cancer via pulmonary delivery. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 2273–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lagreca, E.; Onesto, V.; Di Natale, C.; La Manna, S.; Netti, P.A.; Vecchione, R. Recent advances in the formulation of PLGA microparticles for controlled drug delivery. Prog. Biomater. 2020, 9, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Bajaj, N.; Xu, P.; Ohn, K.; Tsifansky, M.D.; Yeo, Y. Development of highly porous large PLGA microparticles for pulmonary drug delivery. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 1947–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Han, T.H.; Hong, S.C.; Park, S.J.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, H.; Park, M.; Lee, J. PLGA microspheres with alginate-coated large pores for the formulation of an injectable depot of donepezil hydrochloride. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhamecha, D.; Le, D.; Movsas, R.; Gonsalves, A.; Menon, J.U. Porous polymeric microspheres with controllable pore diameters for tissue engineered lung tumor model development. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.W.; Yeh, Y.C.; Zhang, Y.; Sung, H.W.; Xia, Y. Uniform beads with controllable pore sizes for biomedical applications. Small 2010, 6, 1492–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Jeong, J.H.; Woo, H.C.; Kim, M.H. Synthesis of highly porous polymer microspheres with interconnected open pores for catalytic microreactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 127628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Ngai, T.; Tong, Z. Hierarchical porous polymeric microspheres as efficient adsorbents and catalyst scaffolds. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 8761–8763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qutachi, O.; Vetsch, J.R.; Gill, D.; Cox, H.; Scurr, D.J.; Hofmann, S.; Müller, R.; Quirk, R.A.; Shakesheff, K.M.; Rahman, C.V. Injectable and porous PLGA microspheres that form highly porous scaffolds at body temperature. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 5090–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinhold, S.E.; Desai, K.G.H.; Zhang, L.; Olsen, K.F.; Schwendeman, S.P. Self-healing microencapsulation of biomacromolecules without organic solvents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2012, 51, 10800–10803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhold, S.E.; Schwendeman, S.P. Effect of polymer porosity on aqueous self-healing encapsulation of proteins in PLGA microspheres. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 1700–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Na, X.M.; Gao, F.; Zhang, L.Y.; Su, Z.G.; Ma, G.H. Biodegradable microcapsules prepared by self-healing of porous microspheres. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzara, J.M.; Ochyl, L.J.; Hong, J.K.Y.; Moon, J.J.; Prausnitz, M.R.; Schwendeman, S.P. Self-healing encapsulation and controlled release of vaccine antigens from PLGA microparticles delivered by microneedle patches. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2018, 4, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odonchimeg, M.; Kim, S.C.; Shim, Y.K.; Lee, W.K. Preparation of “open/closed” pores of PLGA-microsphere for controlled release of protein drug. Mong. J. Chem. 2018, 18, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, B.A.; Ochyl, L.J.; Schwendeman, S.P.; Moon, J.J. Toward a single-dose vaccination strategy with self-encapsulating PLGA microspheres. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, X.; Ye, T.; Wang, S.; Na, Z.; Wang, J.; Qing, S.; Gao, X.; Wang, C.; Li, F.; Wei, W.; et al. Self-healing microcapsules synergetically modulate immunization microenvironments for potent cancer vaccination. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay7735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Sah, H. Simple emulsion technique as an innovative template for preparation of porous, spongelike poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres with pore-closing capability. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 6257–6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, H. A new strategy to determine the actual protein content of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 68, 1315–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Yang, J. Controlling internal nanostructures of porous microspheres prepared via electrospraying. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2010, 288, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, O.; McGuire, J. Adsorption behavior of lysozyme and Tween 80 at hydrophilic and hydrophobic silica-water interfaces. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2009, 152, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, C.; Blume, A.; Miller, I.; Garidel, P. Insights into protein–polysorbate interactions analysed by means of isothermal titration and differential scanning calorimetry. Eur. Biophys. J. 2009, 38, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, J.M.; Malik, A.; Ahmed, A.; Rehman, T.; AlAjmi, M.F.; Khan, R.H.; Fatima, S.; Alamery, S.F.; Abdullah, E.M. Effect of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) on the conformation of a hen egg white lysozyme: A spectroscopic and molecular docking study. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 219, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.H.; Singh, M.; O’Hagan, D.; Hora, M. Microparticle Compositions and Methods for the Manufacture Thereof. US Patent 7,846,479B2, 7 December 2010. [Google Scholar]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.; Sah, H. Protein Loading into Spongelike PLGA Microspheres. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13020137
Kim Y, Sah H. Protein Loading into Spongelike PLGA Microspheres. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(2):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13020137
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yuyoung, and Hongkee Sah. 2021. "Protein Loading into Spongelike PLGA Microspheres" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 2: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13020137
APA StyleKim, Y., & Sah, H. (2021). Protein Loading into Spongelike PLGA Microspheres. Pharmaceutics, 13(2), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13020137