Cardiovascular and Respiratory Toxicity of Protamine Sulfate in Zebrafish and Rodent Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Housing
2.2. Materials
2.3. Zebrafish Experiment
2.4. hERG Channel Assay
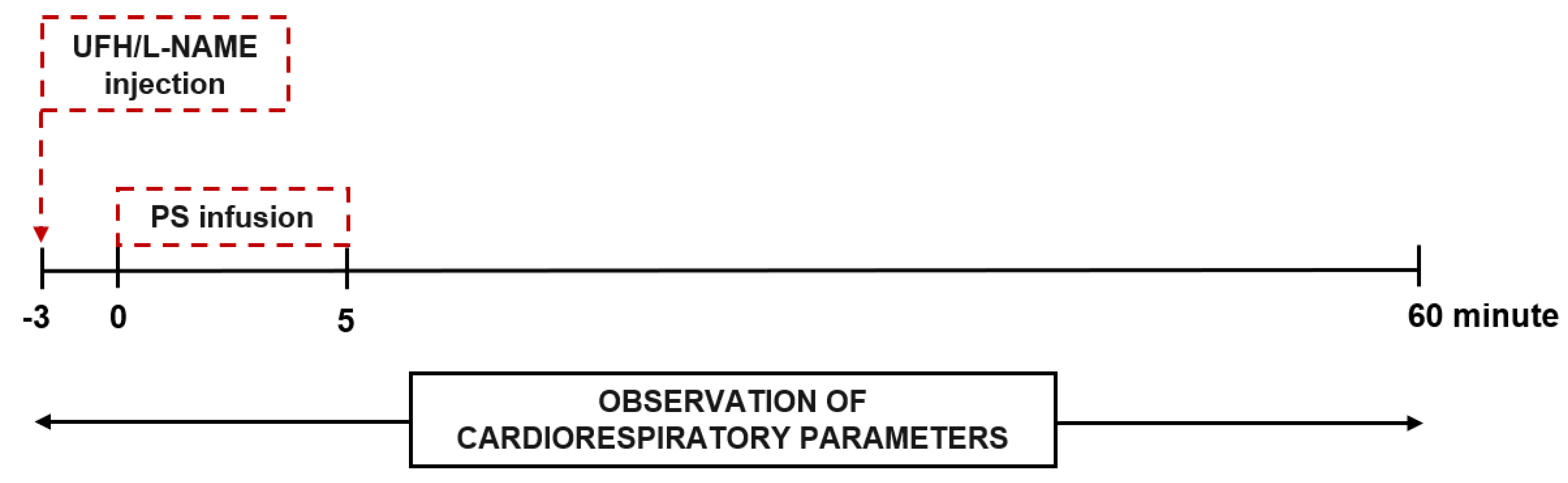
2.5. Cardiorespiratory Parameters up to 60 min after a Single Injection of Heparin and Protamine into Rats
2.6. Histopathology of the Heart and Cardiac Troponin Measurement 35 Days after the Repeated (Once a Week) Injection of Heparin and Protamine into Mice
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Effects of Protamine on Zebrafish Embryo Development and Cardiac Function during Chronic and 48-h Exposure
3.2. The Effects of Protamine, l–NAME, and Heparin on Cardiac Function of Zebrafish Embryos during 48–Hours Exposure
3.3. The Acute Effects of Protamine and Its Complexes with Heparin on Blood Pressure, Cardiac Function, and Respiratory Function in Rats
3.4. The Involvement of NO in Protamine–Induced Hypotension in Rats
3.5. The Chronic Effects of Protamine and Its Complexes with Heparin on Cardiac Biomarkers in Mice
3.6. The Effects of Protamine on hERG Channel Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yavari, M.; Becker, R.C. Anticoagulant therapy during cardiopulmonary bypass. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2008, 26, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.W.; Voelkel, N.F. Charge-related lung microvascular injury. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1989, 139, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefaniszyn, H.J.; Novick, R.J.; Salerno, T.A. Toward a better understanding of the hemodynamic effects of protamine and heparin interaction. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1984, 87, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiser, W.P.; Fewell, J.E.; Hill, D.E.; Barnes, R.W.; Read, R.C. Cardiovascular effects of protamine suIfate are dependent on the presence and type of circulating heparin. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1985, 89, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolowska, E.; Kalaska, B.; Miklosz, J.; Mogielnicki, A. The toxicology of heparin reversal with protamine: Past, present and future. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2016, 12, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nybo, M.; Madsen, J. Serious anaphylactic reactions due to protamine sulfate: A systematic literature review. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008, 103, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, W.J.; McSweeney, S.M.; Kellett, M.A.; Faxon, D.P.; Ryan, T.J. Increased risk of severe protamine reactions in NPH insulin-dependent diabetics undergoing cardiac catheterization. Circulation 1984, 70, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adourian, U.; Shampaine, E.L.; Hirshman, C.A.; Fuchs, E.; Adkinson, N.F., Jr. High-titer protamine-specific IgG antibody associated with anaphylaxis: Report of a case and quantitative analysis of antibody in vasectomized men. Anesthesiology 1993, 78, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.; O’Donnell, A. Does an allergy to fish pre-empt an adverse protamine reaction? A case report and a literature review. Perfusion 2008, 23, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoelting, R.K.; Henry, D.P.; Verburg, K.M.; McCammon, R.L.; King, R.D.; Brown, J.W. Haemodynamic changes and circulating histamine concentrations following protamine administration to patients and dogs. Can. J. Anaesth. 1984, 31, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frater, R.W.M.; Oka, Y.; Hong, Y.; Tsubo, T.; Loubser, P.G.; Masone, R. Protamine-induced circulatory changes. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1984, 87, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, D.R.; Zapol, W.M.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitain, E.M.; Robinson, D.R.; Moss, J.; Chenoweth, D.E.; Lowenstein, E. C5a and thromboxane generation associated with pulmonary vasa- and bronchoconstriction during protamine reversal with heparin. Anesthesiology 1987, 66, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, O.R.; Lowenstein, E.; Nguyenduy, T.; Robinson, D.R.; Repine, J.E.; Chenoweth, D.E.; Zapol, W.M. Acute pulmonary vasoconstriction and thromboxane release during protamine reversal of heparin anticoagulation in awake sheep. Circ. Res. 1988, 62, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rådegran, K.; Bergentz, S.E.; Lewis, D.H.; Ljungqvist, U.; Olsson, P. Pulmonary effects of induced platelet aggregation. Intravascular obstruction or vasoconstriction? Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 1971, 28, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastrzebski, J.; Sykes, M.K.; Woods, D.G. Cardiorespiratory effects of protamine after cardiopulmonary bypass in man. Thorax 1974, 29, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leung, L.W.M.; Gallagher, M.M.; Evranos, B.; Bolten, J.; Madden, B.P.; Wright, S.; Kaba, R.A. Cardiac arrest following protamine administration: A case series. Europace 2019, 21, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.W. Protamine and Protamine Reactions. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2004, 42, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viaro, F.; Dalio, M.B.; Evora, P.R.B. Catastrophic Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions to Protamine Are Nitric Oxide/Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate Dependent and Endothelium Mediated: Should Methylene Blue Be the Treatment of Choice? Chest 2002, 122, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakefield, T.W.; Lindblad, B.; Whitehouse, W.M., Jr.; Hantler, C.B.; Stanley, J.C. Attenuation of hemodynamic and hematologic effects of heparin-protamine sulfate interaction after aortic reconstruction in a canine model. Surgery 1986, 100, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield, T.W.; Whitehouse, W.M.; Stanley, J.C. Depressed cardiovascular function and altered platelet kinetics following protamine sulfate reversal of heparin activity. J. Vasc. Surg. 1984, 1, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butterworth, J.; Lin, Y.A.; Prielipp, R.; Bennett, J.; James, R. The pharmacokinetics and cardiovascular effects of a single intravenous dose of protamine in normal volunteers. Anesth. Analg. 2002, 94, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, J.; Lin, Y.A.; Prielipp, R.C.; Bennett, J.; Hammon, J.W.; James, R.L. Rapid disappearance of protamine in adults undergoing cardiac operation with cardiopulmonary bypass. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2002, 74, 1589–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaska, B.; Sokolowska, E.; Kaminski, K.; Szczubialka, K.; Kramkowski, K.; Mogielnicki, A.; Nowakowska, M.; Buczko, W. Cationic derivative of dextran reverses anticoagulant activity of unfractionated heparin in animal models of arterial and venous thrombosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 686, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, C.; Meesters, M.I.; Milojevic, M.; Benedetto, U.; Bolliger, D.; Heymann, C.; Jeppsson, A.; Koster, A.; Osnabrugge, R.L.; Ranucci, M.; et al. 2017 EACTS/EACTA guidelines on patient blood management for adult cardiac surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2018, 32, 88–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bang, C.J.; Berstad, A.; Talstad, I. Incomplete reversal of enoxaparin-induced bleeding by protamine sulfate. Haemostasis 1991, 21, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, Z.Z.; Benslimane, F.M.; Nasrallah, G.K.; Shurbaji, S.; Younes, N.N.; Mraiche, F.; Da’as, S.I.; Yalcin, H.C. Using Zebrafish for Investigating the Molecular Mechanisms of Drug-Induced Cardiotoxicity. Biomed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1642684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teijeiro-Valiño, C.; Yebra-Pimentel, E.; Guerra-Varela, J.; Csaba, N.; Alonso, M.J.; Sánchez, L. Assessment of the permeability and toxicity of polymeric nanocapsules using the zebrafish model. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 2069–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, W.; Chang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, A. Synthesis and antifungal activities of hydrophilic cationic polymers against Rhizoctonia solani. Fungal Biol. 2020, 124, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qinglian, H.; Fengliang, G.; Fenghui, Z.; Guping, T.; Zhengwei, F. Cardiovascular toxicity assessment of poly (ethylene imine)-based cationic polymers on zebrafish model. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2017, 28, 768–780. [Google Scholar]
- Fadali, M.A.; Ledbetter, M.; Papacostas, C.A.; Duke, L.J.; Lemole, G.M. Mechanism responsible for the cardiovascular depressant effect of protamine sulfate. Ann. Surg. 1974, 180, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speth, M.; Seibold, K.; Katz, N. Interaction between heparin and cardiac troponin T and troponin I from patients after coronary bypass surgery. Clin. Biochem. 2002, 35, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priest, B.T.; Bell, I.M.; Garcia, M.L. Role of hERG potassium channel assays in drug development. Channels 2008, 2, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanguinetti, M.C.; Jiang, C.; Curran, M.E.; Keating, M.T. A mechanistic link between an inherited and an acquired cardiac arrhythmia: HERG encodes the IKr potassium channel. Cell 1995, 81, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gintant, G.A.; Su, Z.; Martin, R.L.; Cox, B.F. Utility of hERG assays as surrogate markers of delayed cardiac repolarization and QT safety. Toxicol. Pathol. 2006, 34, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iteg, M.; Log, G.; Gunay, I.; Ulus, T. Electromechanical effects of protamine and verapamil in rat papillary muscle. Asian Cardiovasc. Thorac. Ann. 1999, 7, 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Pevni, D.; Gurevich, J.; Frolkis, I.; Keren, G.; Shapira, I.; Paz, J.; Kramer, A.; Locker, C.; Mohr, R. Protamine induces vasorelaxation of human internal thoracic artery by endothelial NO-synthase pathway. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2000, 70, 2050–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, R.M.; Rees, D.D.; Ashton, D.S.; Moncada, S. L-arginine is the physiological precursor for the formation of nitric oxide in endothelium-dependent relaxation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1988, 153, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsche, R.; Schwerte, T.; Pelster, B. Nitric oxide and vascular reactivity in developing zebrafish, Danio rerio. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2000, 279, R2200–R2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lepiller, S.; Laurens, V.; Bouchot, A.; Herbomel, P.; Solary, E.; Chluba, J. Imaging of nitric oxide in a living vertebrate using a diamino-fluorescein probe. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, F.B.; McGovern, L.; McGeer, J.C. Effect of a nitric oxide releasing compound isosorbide dinitrate on development and cardiovascular physiology of rainbow trout (Oncorhyncus mykiss). Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 1999, 21, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conzen, P.F.; Habazettl, H.; Gutmann, R.; Hobbhahn, J.; Goetz, A.E.; Peter, K.; Brendel, W. Thromboxane mediation of pulmonary hemodynamic responses after neutralization of heparin by protamine in pigs. Anesth. Analg. 1989, 68, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miklosz, J.; Kalaska, B.; Kaminski, K.; Rusak, M.; Szczubialka, K.; Nowakowska, M.; Pawlak, D.; Mogielnicki, A. The Inhibitory Effect of Protamine on Platelets is Attenuated by Heparin without Inducing Thrombocytopenia in Rodents. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hobbhahn, J.; Conzen, P.F.; Zenker, B.; Goetz, A.E.; Peter, K.; Brendel, W. Beneficial effect of cyclooxygenase inhibition on adverse hemodynamic responses after protamine. Anesth. Analg. 1988, 67, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambam, J.; Meszaros, R.; Merrill, W.; Stewart, J.; Smith, B.E.; Bender, H. Prophylactic administration of histamine1 and histamine2 receptor blockers in the prevention of protamine related haemodynamic effects. Can. J. Anaesth. 1990, 37, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akata, T.; Kodama, K.; Yoshite, J.; Takahashi, S. Heparin prevents the vasodilatating action of protamine on human small mesenteric arteries. Anesth. Analg. 1993, 76, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairman, R.P.; Sessler, C.N.; Bierman, M.; Glauser, F.L. Protamine sulfate causes pulmonary hypertension and edema in isolated rat lungs. J. Appl. Physiol. 1987, 62, 1363–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winata, C.L.; Korzh, S.; Kondrychyn, I.; Zheng, W.; Korzh, V.; Gong, Z. Development of zebrafish swimbladder: The requirement of Hedgehog signaling in specification and organization of the three tissue layers. Dev. Biol. 2009, 331, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winata, C.L.; Korzh, S.; Kondrychyn, I.; Korzh, V.; Gong, Z. The role of vasculature and blood circulation in zebrafish swimbladder development. BMC Dev. Biol. 2010, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, M.S.; Peterson, R.E.; Heideman, W. Dioxin inhibition of swim bladder development in zebrafish: Is it secondary to heart failure? Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 162, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeLucia, A.; Wakefield, T.W.; Kadell, A.M.; Wrobleski, S.K.; VanDort, M.; Stanley, J.C. Tissue distribution, circulating half-life, and excretion of intravenously administered protamine sulfate. ASAIO J. 1993, 39, 715–718. [Google Scholar]
- Sokolowska, E.; Kalaska, B.; Kaminski, K.; Lewandowska, A.; Blazejczyk, A.; Wietrzyk, J.; Kasacka, I.; Szczubialka, K.; Pawlak, D.; Nowakowska, M.; et al. The Toxicokinetic Profile of Dex40-GTMAC3-a Novel Polysaccharide Candidate for Reversal of Unfractionated Heparin. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jastrzebski, J.; Hilgard, P.; Sykes, M.K. Pulmonary vasoconstriction produced by protamine and protamine-heparin complex in the isolated cat lung per fused with blood or dextran. Cardiovasc. Res. 1975, 9, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigma-Aldrich. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/united-kingdom.html (accessed on 8 March 2021).
- Mogielnicki, A.; Kalaska, B.; Pawlak, D.; Sokolowska, E.; Nowakowska, M.; Szczubiałka, K.; Kaminsk, K. Use of a Block Polymer Comprising a Block of Poly(3-(methacryloylamino)propyltrimethylammonium chloride) (Pmaptac) for the Neutralization of Heparin. U.S. Patent 10052347B2, 21 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Maurer, J.; Haselbach, S.; Klein, O.; Baykut, D.; Vogel, V.; Mäntele, W. Analysis of the complex formation of heparin with protamine by light scattering and analytical ultracentrifugation: Implications for blood coagulation management. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsley, M.J. Structure and composition of pulmonary arteries, capillaries and veins. Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2, 675–709. [Google Scholar]
- Hislop, A.; Reid, L. Normal structure and dimensions of the pulmonary arteries in the rat. J. Anat. 1978, 125, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reid, L.M. Structure and function in pulmonary hypertension. New perceptions. Chest 1986, 89, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miklosz, J.; Kalaska, B.; Podlasz, P.; Chmielewska-Krzesińska, M.; Zajączkowski, M.; Kosiński, A.; Pawlak, D.; Mogielnicki, A. Cardiovascular and Respiratory Toxicity of Protamine Sulfate in Zebrafish and Rodent Models. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13030359
Miklosz J, Kalaska B, Podlasz P, Chmielewska-Krzesińska M, Zajączkowski M, Kosiński A, Pawlak D, Mogielnicki A. Cardiovascular and Respiratory Toxicity of Protamine Sulfate in Zebrafish and Rodent Models. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(3):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13030359
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiklosz, Joanna, Bartlomiej Kalaska, Piotr Podlasz, Małgorzata Chmielewska-Krzesińska, Miłosz Zajączkowski, Adam Kosiński, Dariusz Pawlak, and Andrzej Mogielnicki. 2021. "Cardiovascular and Respiratory Toxicity of Protamine Sulfate in Zebrafish and Rodent Models" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 3: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13030359
APA StyleMiklosz, J., Kalaska, B., Podlasz, P., Chmielewska-Krzesińska, M., Zajączkowski, M., Kosiński, A., Pawlak, D., & Mogielnicki, A. (2021). Cardiovascular and Respiratory Toxicity of Protamine Sulfate in Zebrafish and Rodent Models. Pharmaceutics, 13(3), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13030359






