The Biological Effects of Novel Nutraceuticals with Curcuminoids and Other Plant-Derived Immunomodulators and Pre-Probiotics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Phytochemical Screening of Selected Plant Actives for Novel Nutraceuticals
2.2. Formulas of the Novel Nutraceuticals with Immunomodulatory Properties
2.3. Health Claims and Nutritional Status
2.4. Evaluation of Key Physico-Chemical Parameters and Antioxidative Status
2.5. Assessment of Antimicrobial Activity
2.6. Determination of Intracellular Toxicity
2.7. Evaluation of Immunomodulatory Activity
2.8. Statistical Assesment of Data
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Key Physico-Chemical Parameters and Antioxidative Status
3.2. Antimicrobial Activity
3.3. Determination of Intracellular Toxicity
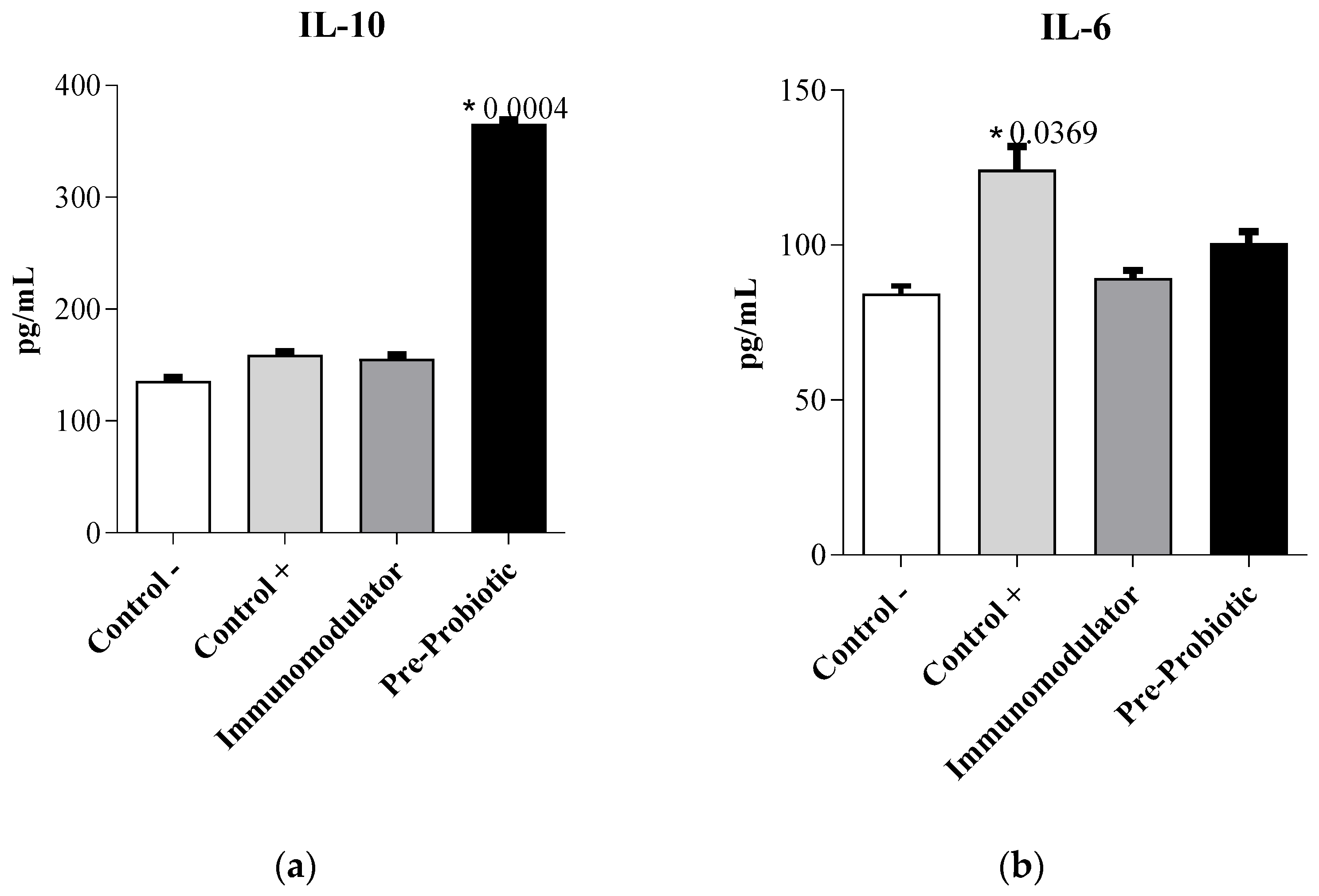
3.4. Evaluation of Immunomodulatory Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, J.; de Vos, P. Immunomodulatory Functions of Nutritional Ingredients in Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High, K.P. Nutritional Strategies to Boost Immunity and Prevent Infection in Elderly Individuals. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 1892–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, F.; Nadeem, M.; Ahmed, R.S.; Tahir Nadeem, M.; Arshad, M.S.; Ullah, A. Studying the Impact of Nutritional Immunology Underlying the Modulation of Immune Responses by Nutritional Compounds – a Review. Food Agric. Immunol. 2016, 27, 205–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos, A.; Nova, E.; Montero, A. Changes in the Immune System Are Conditioned by Nutrition. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 57, S66–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, G.; Xie, J.; Chen, Q.; Hu, Z. How Functional Foods Play Critical Roles in Human Health. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2012, 1, 26–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Lewis, E.D.; Pae, M.; Meydani, S.N. Nutritional Modulation of Immune Function: Analysis of Evidence, Mechanisms, and Clinical Relevance. Front. Immunol. 2019, 9, 3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, A.M.C.; Gomes-Santos, A.C.; Gonçalves, J.L.; Moreira, T.G.; Medeiros, S.R.; Dourado, L.P.A.; Cara, D.C. Food Components and the Immune System: From Tonic Agents to Allergens. Frontiers in Immunology 2013, 4, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rosa, V.; Galgani, M.; Santopaolo, M.; Colamatteo, A.; Laccetti, R.; Matarese, G. Nutritional Control of Immunity: Balancing the Metabolic Requirements with an Appropriate Immune Function. Seminars in Immunology 2015, 27, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasri, H.; Baradaran, A.; Shirzad, H.; Kopaei, M.R. New Concepts in Nutraceuticals as Alternative for Pharmaceuticals. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2014, 5, 1487–1499. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gulati, O.P.; Berry Ottaway, P. Legislation Relating to Nutraceuticals in the European Union with a Particular Focus on Botanical-Sourced Products. Toxicology 2006, 221, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andlauer, W.; Fürst, P. Nutraceuticals: A Piece of History, Present Status and Outlook. Food Res. Int. 2002, 35, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, A. History and Overview of DSHEA. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, I.S. Dietary Supplement Regulation: A Comprehensive Guide; FDLI: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- DeFelice, S.L. The Nutraceutical Revolution: Its Impact on Food Industry R&D. Trends in Food Science and Technology 1995, 6, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Abood, W.N. Immunomodulatory and Natural Immunomodulators. J. Allergy Inflamm. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Childs, C.E.; Calder, P.C.; Miles, E.A. Diet and Immune Function. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichers, H. Immunomodulation by Food: Promising Concept for Mitigating Allergic Disease? Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminogawa, S.; Nanno, M. Modulation of Immune Functions by Foods. Complement. Altern. Med. 2004, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ló Pez-Varela, S.; González-Gross, M.; Marcos, A. Functional Foods and the Immune System: A Review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 56, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachimura, S.; Totsuka, M.; Hosono, A. Immunomodulation by Food: Impact on Gut Immunity and Immune Cell Function. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 82, 584–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, E.; Stępień, A.E.; Gol, O.; Tabarkiewicz, J. Potential Immunomodulatory Effects from Consumption of Nutrients in Whole Foods and Supplements on the Frequency and Course of Infection: Preliminary Results. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toumi, R.; Samer, A.; Soufli, I.; Rafa, H.; Touil-Boukoffa, C. Role of Probiotics and Their Metabolites in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBDs). Gastroenterol. Insights 2021, 12, 56–66. [Google Scholar]
- Toumi, R.; Soufli, I.; Rafa, H.; Belkhelfa, M.; Biad, A.; Touil-Boukoffa, C. Probiotic Bacteria Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium Attenuate Inflammation in Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Experimental Colitis in Mice. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2014, 27, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciupercă Oana, T.; Ţebrencu Carmen, E.; Onisei Tatiana, R.A. Innovative Association of Medicinal Species with Potential for Use in Food Supplements with Immunomodulatory Effects. In Proceedings of the International Symposium ISB-INMA Agricultural and Mechanical Engineering, Bucharest, Romania, 31 October–1 November 2019; pp. 684–694. [Google Scholar]
- Ciupercă Oana, T.; Ţebrencu Carmen, E.; Răducanu, A.; Pop Anca Lucia, O.T. Phytochemical Evaluation of Some Herbal Prebiotics and Their Ptential Use in Food Supplements. In Proceedings of the Inaugural Edition of the Virtual Congresswith International Participation Nutrition, Diet Therapy &Food Safety in the Context of the Covid-19 NutriTerra, Bucharest, Romania, 28–29 May 2020; pp. 305–312. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.H.; Lee, J.H.; Park, S.; Oh, S.s.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.W.; Park, K.H.; Kim, K.D. 6-Acetonyl-5,6-Dihydrosanguinarine (ADS) from Chelidonium Majus L. Triggers Proinflammatory Cytokine Production via ROS-JNK/ERK-NFκB Signaling Pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 58, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.-S.; An, H.-J.; Jeong, H.-J.; Won, J.-H.; Hong, S.-H.; Kim, H.-M. Water Extract Isolated from Chelidonium Majus Enhances Nitric Oxide and Tumour Necrosis Factor-α Production via Nuclear Factor-ΚB Activation in Mouse Peritoneal Macrophages. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2004, 56, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.Y.; Yang, H.O.; Pyo, S.N.; Jung, I.S.; Yi, S.Y.; Yun, Y.S. Immunomodulatory Activity of Protein-Bound Polysaccharide Extracted from Chelidonium Majus. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2002, 25, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kour, K.; Bani, S.; Sangwan, P.L.; Singh, A. Upregulation of Th1 Polarization by Taraxacum Officinale in Normal and Immune Suppressed Mice. Curr. Sci. 2016, 111, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramendra, P.; Pandey; Chanchal, A.; Vohra, R.; Elesela, S.; Bhushan, L.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Ahmad, S.; Ramendra, C.; et al. Gelatin Biopolymer: A Journey from Micro to Nano. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 8, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar]
- Szewczyk, A.; Zagaja, M.; Bryda, J.; Kosikowska, U.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Winiarczyk, S.; Andres-Mach, M. Topinambur—New Possibilities for Use in a Supplementation Diet. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2019, 26, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalanka, J.; Major, G.; Murray, K.; Singh, G.; Nowak, A.; Kurtz, C.; Silos-Santiago, I.; Johnston, J.M.; de Vos, W.M.; Spiller, R. The Effect of Psyllium Husk on Intestinal Microbiota in Constipated Patients and Healthy Controls. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA/HMPC/199775/2012. Assessment Report on Plantago Ovata Forssk., Seminis Tegumentum; European Medicine Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013.
- European Medicines Agency. European Medicines Agency Post-Authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use; EMA Website: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013.
- EUR-Lex—32006R1924—RO—EUR-Lex. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=celex%3A32006R1924 (accessed on 3 April 2021).
- Botanicals|European Food Safety Authority. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/topics/topic/botanicals (accessed on 3 April 2021).
- Nistico, S.; Tamburi, F.; Bennardo, L.; Dastoli, S.; Schipani, G.; Caro, G.; Fortuna, M.C.; Rossi, A. Treatment of Telogen Effluvium Using a Dietary Supplement Containing Boswellia Serrata, Curcuma Longa, and Vitis Vinifera: Results of an Observational Study. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e12842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUR-Lex—32012R0432—RO—EUR-Lex. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32012R0432 (accessed on 3 April 2021).
- Kim, D.O.; Jeong, S.W.; Lee, C.Y. Antioxidant Capacity of Phenolic Phytochemicals from Various Cultivars of Plums. Food Chem. 2003, 81, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of Total Phenolics with Phosphomolybdic-Phosphotungstic Acid Reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar]
- Formagio, A.S.N.; Kassuya, C.A.L.; Neto, F.F.; Volobuff, C.R.F.; Iriguchi, E.K.K.; Vieira, M.d.C.; Foglio, M.A. The Flavonoid Content and Antiproliferative, Hypoglycaemic, Anti-Inflammatory and Free Radical Scavenging Activities of Annona Dioica St. Hill. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhu, G.; Bose, V.C.; Aiswaryaraj, A.S.; Maniammal, K.; Biju, V. Defect Dependent Antioxidant Activity of Nanostructured Nickel Oxide Synthesized through a Novel Chemical Method. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 429, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Chen, S.; Xu, T.; Ren, Z.; Han, G.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Capacity of Chinese Raisins Produced in Xinjiang Province. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2830–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.F.; Strain, J.J. Ferric Reducing/Antioxidant Power Assay: Direct Measure of Total Antioxidant Activity of Biological Fluids and Modified Version for Simultaneous Measurement of Total Antioxidant Power and Ascorbic Acid Concentration. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 299, 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Thaipong, K.; Boonprakob, U.; Crosby, K.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Hawkins Byrne, D. Comparison of ABTS, DPPH, FRAP, and ORAC Assays for Estimating Antioxidant Activity from Guava Fruit Extracts. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2006, 19, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tihăuan, B.-M.; Berca, L.M.; Adascalului, M.; Sanmartin, A.M.; Nica, S.; Cimponeriu, D.; Duță, D. Experimental in Vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Plant Bioactive Compounds and Phytoagents: A Review. Rom Biotechnol Lett. 2020, 25, 1832–1842. [Google Scholar]
- Bopp, S.K.; Lettieri, T. Comparison of Four Different Colorimetric and Fluorometric Cytotoxicity Assays in a Zebrafish Liver Cell Line. BMC Pharmacol. 2008, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojdyło, A.; Oszmiański, J.; Czemerys, R. Antioxidant Activity and Phenolic Compounds in 32 Selected Herbs. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Es-Safi, N.E.; Gómez-Cordovés, C. Characterization of Flavonoid Glycosides from Fenugreek (Trigonella Foenum-Graecum) Crude Seeds by HPLC-DAD-ESI/MS Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 20668–20685. [Google Scholar]
- Sabir, S.M.; Zeb, A.; Mahmood, M.; Abbas, S.R.; Ahmad, Z.; Iqbal, N. Phytochemical Analysis and Biological Activities of Ethanolic Extract of Curcuma Longa Rhizome. Brazilian J. Biol. 2021, 81, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Showkat, M.M.; Falck-Ytter, A.B.; Strætkvern, K.O. Phenolic Acids in Jerusalem Artichoke (Helianthus Tuberosus L.): Plant Organ Dependent Antioxidant Activity and Optimized Extraction from Leaves. Molecules 2019, 24, 3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, P.; Talapatra, S.; Ghoshal, N.; Sen Raychaudhuri, S. Antioxidant Activity and High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Analysis of Phenolic Compounds during in Vitro Callus Culture of Plantago Ovata Forsk. and Effect of Exogenous Additives on Accumulation of Phenolic Compounds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinzade, A.; Sadeghi, O.; Biregani, A.N.; Soukhtehzari, S.; Brandt, G.S.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Immunomodulatory Effects of Flavonoids: Possible Induction of T CD4+ Regulatory Cells through Suppression of MTOR Pathway Signaling Activity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francenia Santos-Sánchez, N.; Salas-Coronado, R.; Villanueva-Cañongo, C.; Hernández-Carlos, B. Antioxidant Compounds and Their Antioxidant Mechanism. In Antioxidants; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Koley, T.K.; Maurya, A.; Tripathi, A.; Singh, B.K.; Singh, M.; Bhutia, T.L.; Tripathi, P.C.; Singh, B. Antioxidant Potential of Commonly Consumed Underutilized Leguminous Vegetables. Int. J. Veg. Sci. 2019, 25, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.L. Modulation of Antibiotic Efflux in Bacteria. Curr. Med. Chem. Anti Infective Agents 2002, 1, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simion, I.M.; Moț, A.C.; Găceanu, R.D.; Pop, H.F.; Sârbu, C. Characterization and Classification of Medicinal Plant Extracts According to Their Antioxidant Activity Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Multivariate Analysis. Stud. Univ. Babeș-Bolyai Chem. 2020, 65, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tsao, R. Dietary Polyphenols, Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 8, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, W.K.E.; Hoshi, N.; Shouval, D.S.; Snapper, S.; Medzhitov, R. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of IL-10 Mediated by Metabolic Reprogramming of Macrophages. Science 2017, 356, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenvinkel, P.; Ketteler, M.; Johnson, R.J.; Lindholm, B.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Riella, M.; Heimbürger, O.; Cederholm, T.; Girndt, M. IL-10, IL-6, and TNF-α: Central Factors in the Altered Cytokine Network of Uremia—The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 1216–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuster, J.J.; Walsh, K. The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly of Interleukin-6 Signaling. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 1425–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, T.; Koido, Y.; Aiboshi, J.; Yamashita, T.; Suzaki, S.; Kurokawa, A. The Ratio of Interleukin-6 to Interleukin-10 Correlates with Severity in Patients with Chest and Abdominal Trauma. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 1999, 17, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, M.A.K.; Sarker, M.; Wan, D. Immunomodulatory Effects of Probiotics on Cytokine Profiles. BioMed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado Galdeano, C.; De Moreno De Leblanc, A.; Vinderola, G.; Bibas Bonet, M.E.; Perdigón, G. Proposed Model: Mechanisms of Immunomodulation Induced by Probiotic Bacteria. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2007, 14, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Lin, H.C.; Lai, C.H.; Lu, J.J.Y.; Wu, S.F.; Fang, S.H. Immunomodulatory Effects of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium on Both Murine and Human Mitogen-Activated T Cells. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 156, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Total Polyphenols (mg GAE/g) | Total Flavonoids (mg QE/g) | % Flavonoids from Total Polyphenols |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immunomodulator | 144.07 ± 4.21 | 20.472 ± 2.005 | 14.21 |
| Pre-Probiotic | 1.13 ± 0.26 | 0.032 ± 0.009 | 2.85 |
| Sample | DPPH (μM Trolox/mg) | CUPRAC (μM Trolox/mg) | FRAP (μM Trolox/mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immunomodulator | 2956.63 ± 292.12 | 1001.13 ± 30.82 | 918.91 ± 2.97 |
| Pre-Probiotic | 7.47 ± 0.04 | 33.59 ± 0.76 | 18.25 ± 0.55 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Răducanu, A.E.; Tihăuan, B.-M.; Marinaș, I.C.; Ciupercă, O.T.; Țebrencu, C.E.; Ionescu, E.; Onisei, T. The Biological Effects of Novel Nutraceuticals with Curcuminoids and Other Plant-Derived Immunomodulators and Pre-Probiotics. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050666
Răducanu AE, Tihăuan B-M, Marinaș IC, Ciupercă OT, Țebrencu CE, Ionescu E, Onisei T. The Biological Effects of Novel Nutraceuticals with Curcuminoids and Other Plant-Derived Immunomodulators and Pre-Probiotics. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(5):666. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050666
Chicago/Turabian StyleRăducanu, Adina Elena, Bianca-Maria Tihăuan, Ioana Cristina Marinaș, Oana Teodora Ciupercă, Carmen Elena Țebrencu, Elena Ionescu, and Tatiana Onisei. 2021. "The Biological Effects of Novel Nutraceuticals with Curcuminoids and Other Plant-Derived Immunomodulators and Pre-Probiotics" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 5: 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050666
APA StyleRăducanu, A. E., Tihăuan, B.-M., Marinaș, I. C., Ciupercă, O. T., Țebrencu, C. E., Ionescu, E., & Onisei, T. (2021). The Biological Effects of Novel Nutraceuticals with Curcuminoids and Other Plant-Derived Immunomodulators and Pre-Probiotics. Pharmaceutics, 13(5), 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050666






