Development of [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-I&T for Targeted Alpha Therapy According to GMP Guidelines for Treatment of mCRPC
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Radiolabeling
2.3. Systems and Settings
2.4. Quality Control
2.5. Preparation Patient Solution
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rawla, P. Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Labriola, M.K.; Atiq, S.; Hirshman, N.; Bitting, R.L. Management of men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer following potent androgen receptor inhibition: A review of novel investigational therapies. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Body, A.; Pranavan, G.; Tan, T.H.; Slobodian, P. Medical management of metastatic prostate cancer. Aust. Prescr. 2018, 41, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruigrok, E.A.M.; van Weerden, W.M. The Future of PSMA-Targeted Radionuclide Therapy: An Overview of Recent Preclinical Research. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, A.; Heston, W.D.W. Tumor target prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) and its regulation in prostate cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 91, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatalic, K.L.; Heskamp, S.; Konijnenberg, M.; Molkenboer-Kuenen, J.D.; Franssen, G.M.; Groningen, M.C.C.-V.; Schottelius, M.; Wester, H.-J.; Van Weerden, W.M.; Boerman, O.C.; et al. Towards Personalized Treatment of Prostate Cancer: PSMA I&T, a Promising Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen-Targeted Theranostic Agent. Theranostics 2016, 6, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, S.; Thieme, A.; Allmann, J.; D’Alessandria, C.; Maurer, T.; Retz, M.; Tauber, R.; Heck, M.M.; Wester, H.-J.; Tamaki, N.; et al. Radiation Dosimetry for 177 Lu-PSMA I&T in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Absorbed Dose in Normal Organs and Tumor Lesions. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 58, 445. [Google Scholar]
- Kletting, P.; Thieme, A.; Eberhardt, N.; Rinscheid, A.; D’Alessandria, C.; Allmann, J.; Wester, H.-J.; Tauber, R.; Beer, A.J.; Glatting, G.; et al. Modeling and Predicting Tumor Response in Radioligand Therapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 60, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, N.J.; Thieme, A.; Eberhardt, N.; Tauber, R.; D’Alessandria, C.; Beer, A.J.; Glatting, G.; Eiber, M.; Kletting, P. The Effect of Total Tumor Volume on the Biologically Effective Dose to Tumor and Kidneys for177Lu-Labeled PSMA Peptides. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baum, R.P.; Kulkarni, H.R.; Schuchardt, C.; Singh, A.; Wirtz, M.; Wiessalla, S.; Schottelius, M.; Mueller, D.; Klette, I.; Wester, H.-J. 177Lu-Labeled Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen Radioligand Therapy of Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Safety and Efficacy. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heck, M.M.; Retz, M.; D’Alessandria, C.; Rauscher, I.; Scheidhauer, K.; Maurer, T.; Storz, E.; Janssen, F.; Schottelius, M.; Wester, H.-J.; et al. Systemic Radioligand Therapy with 177 Lu Labeled Prostate Specific Membrane Antigen Ligand for Imaging and Therapy in Patients with Metastatic Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer. J. Urol. 2016, 196, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräuer, A.; Grubert, L.S.; Roll, W.; Schrader, A.J.; Schäfers, M.; Bögemann, M.; Rahbar, K. 177Lu-PSMA-617 radioligand therapy and outcome in patients with metastasized castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 44, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadzadehfar, H.; Wegen, S.; Yordanova, A.; Fimmers, R.; Kürpig, S.; Eppard, E.; Wei, X.; Schlenkhoff, C.; Hauser, S.; Essler, M. Overall survival and response pattern of castration-resistant metastatic prostate cancer to multiple cycles of radioligand therapy using [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 44, 1448–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathke, H.; Giesel, F.L.; Flechsig, P.; Kopka, K.; Mier, W.; Hohenfellner, M.; Haberkorn, U.; Kratochwil, C. Repeated177Lu-Labeled PSMA-617 Radioligand Therapy Using Treatment Activities of Up to 9.3 GBq. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 59, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- von Eyben, F.E.; Roviello, G. Third-line treatment and (177)Lu-PSMA radioligand therapy of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: A systematic review. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weineisen, M.; Schottelius, M.; Simecek, J.; Baum, R.P.; Yildiz, A.; Beykan, S.; Kulkarni, H.R.; Lassmann, M.; Klette, I.; Eiber, M.; et al. 68Ga- and 177Lu-Labeled PSMA I&T: Optimization of a PSMA-Targeted Theranostic Concept and First Proof-of-Concept Human Studies. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Scheinberg, D.A.; McDevitt, M.R. Actinium-225 in targeted alpha-particle therapeutic applications. Curr. Radiopharm. 2011, 4, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- chumann, S.; Eberlein, U.; Muhtadi, R.; Lassmann, M.; Scherthan, H. DNA damage in leukocytes after internal ex-vivo irradiation of blood with the α-emitter Ra-223. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sgouros, G. Alpha-particles for targeted therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1402–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenstern, A.; Apostolidis, C.; Kratochwil, C.; Sathekge, M.; Krolicki, L.; Bruchertseifer, F. An Overview of Targeted Alpha Therapy with 225Actinium and 213Bismuth. Curr. Radiopharm. 2018, 11, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochwil, C.; Bruchertseifer, F. 225Ac-PSMA-617 for PSMA-Targeted α-Radiation Therapy of Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1941–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kratochwil, C.; Bruchertseifer, F. Targeted α-Therapy of Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer with 225Ac-PSMA-617: Dosimetry Estimate and Empiric Dose Finding. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1624–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kratochwil, C.; Bruchertseifer, F.; Rathke, H.; Hohenfellner, M.; Giesel, F.L.; Haberkorn, U.; Morgenstern, A. Targeted α-Therapy of Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer with 225Ac-PSMA-617: Swimmer-Plot Analysis Suggests Efficacy Regarding Duration of Tumor Control. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zacherl, M.J.; Gildehaus, F.J.; Mittlmeier, L.; Boening, G.; Gosewisch, A.; Wenter, V.; Schmidt-Hegemann, N.-S.; Belka, C.; Kretschmer, A.; Casuscelli, J.; et al. First clinical results for PSMA targeted alpha therapy using 225Ac-PSMA-I&T in advanced mCRPC patients. J. Nucl. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathekge, M.; Bruchertseifer, F. (225)Ac-PSMA-617 in chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced prostate cancer: A pilot study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sathekge, M.; Bruchertseifer, F.; Vorster, M.; Lawal, I.; Knoesen, O.; Mahapane, J.; Davis, C.; Reyneke, F.; Maes, A.; Kratochwil, C.; et al. Predictors of Overall and Disease-Free Survival in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Patients Receiving 225Ac-PSMA-617 Radioligand Therapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 61, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuerecker, B.; Tauber, R.; Knorr, K.; Heck, M.; Beheshti, A.; Seidl, C.; Bruchertseifer, F.; Pickhard, A.; Gafita, A.; Kratochwil, C.; et al. Activity and Adverse Events of Actinium-225-PSMA-617 in Advanced Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer After Failure of Lutetium-177-PSMA. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suliman, G.; Pommé, S.; Marouli, M.; Van Ammel, R.; Stroh, H.; Jobbágy, V.; Paepen, J.; Dirican, A.; Bruchertseifer, F.; Apostolidis, C.; et al. Half-lives of 221Fr, 217At, 213Bi, 213Po and 209Pb from the 225Ac decay series. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2013, 77, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miederer, M.; Scheinberg, D.A.; McDevitt, M.R. Realizing the potential of the Actinium-225 radionuclide generator in targeted alpha particle therapy applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McDevitt, M.R.; Ma, D.; Simon, J.; Frank, R.; Scheinberg, D.A. Design and synthesis of 225Ac radioimmunopharmaceuticals. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2002, 57, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.K.H.; Ramogida, C.F.; Schaffer, P.; Radchenko, V. Development of 225Ac Radiopharmaceuticals: TRIUMF Perspectives and Experiences. Curr. Radiopharm. 2018, 11, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillings, N.; Todde, S.; Behe, M.; Decristoforo, C.; Elsinga, P.; Ferrari, V.; Hjelstuen, O.; Peitl, P.K.; Koziorowski, J.; Laverman, P.; et al. EANM guideline on the validation of analytical methods for radiopharmaceuticals. EJNMMI Radiopharm. Chem. 2020, 5, 7–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillings, N.; Hjelstuen, O.; Ballinger, J.; Behe, M.; Decristoforo, C.; Elsinga, P.; Ferrari, V.; Peitl, P.K.; Koziorowski, J.; Laverman, P.; et al. Guideline on current good radiopharmacy practice (cGRPP) for the small-scale preparation of radiopharmaceuticals. EJNMMI Radiopharm. Chem. 2021, 6, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coenen, H.H.; Gee, A.D.; Adam, M.; Antoni, G.; Cutler, C.S.; Fujibayashi, Y.; Jeong, J.M.; Mach, R.H.; Mindt, T.L.; Pike, V.W.; et al. Consensus nomenclature rules for radiopharmaceutical chemistry—Setting the record straight. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2017, 55, v–xi. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pramanick, S.; Chandel, V. Excipient Selection In Parenteral Formulation Development. Pharma Times 2013, 45, 65–77. [Google Scholar]
- (PCT) IAPUTPCT. Ascorbate Formulations and Methods of Use as Contrast Agents. Patent Application No. WO/2017/059092, 6 April 2017.
- Múčka, V.; Blaha, P.; Čuba, V.; Červenák, J. Influence of various scavengers of OH radicals on the radiation sensitivity of yeast and bacteria. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2013, 89, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Good Manufacturing Practice, Medicinal Products for Human and Veterinary Use, Annex 13, Investigational Medicinal Products; EudraLex: Brussels, Belgium, 2010; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Good Manufacturing Practice, Medicinal Products for Human and Veterinary Use, Annex 15, Qualification and Validation; EudraLex: Brussels, Belgium, 2015; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & Healthcare. European Pharmacopoeia (Ph Eur), European Commission, Strasbourg, France; European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & Healthcare: Strasbourg, France, 2021; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Verbruggen, A.; Coenen, H.H.; Deverre, J.-R.; Guilloteau, D.; Langstrom, B.; Salvadori, P.A.; Halldin, C. Guideline to regulations for radiopharmaceuticals in early phase clinical trials in the EU. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 35, 2144–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todde, S.; Windhorst, A.D.; Behe, M.; Bormans, G.; Decristoforo, C.; Faivre-Chauvet, A.; Ferrari, V.; Gee, A.D.; Gulyas, B.; Halldin, C.; et al. EANM guideline for the preparation of an Investigational Medicinal Product Dossier (IMPD). Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 2175–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, E.C.; Humm, J.L.; Ljungberg, M. Accuracy and Precision of Radioactivity Quantification in Nuclear Medicine Images. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2012, 42, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Ellars, C.E.; Edwards, D.S. Ascorbic Acid: Useful as a Buffer Agent and Radiolytic Stabilizer for Metalloradiopharmaceuticals. Bioconjugate Chem. 2003, 14, 1052–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Zanger, R.M.S.; Chan, H.S. Maintaining radiochemical purity of [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-PSMA-617 for PRRT by reducing radiolysis. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2019, 321, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Blois, E.; Chan, H.S. Application of single-vial ready-for-use formulation of 111In- or 177Lu-labelled somatostatin analogs. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2014, 85, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Blois, E.; Chan, H.S. Effectiveness of quenchers to reduce radiolysis of (111)In- or (177)Lu-labelled methionine-containing regulatory peptides. Maintaining radiochemical purity as measured by HPLC. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 2677–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kruijff, R.M.; Wolterbeek, H.T. A Critical Review of Alpha Radionuclide Therapy-How to Deal with Recoiling Daughters? Pharmaceuticals 2015, 8, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozempel, J.; Mokhodoeva, O.; Vlk, M. Progress in Targeted Alpha-Particle Therapy. What We Learned about Recoils Release from In Vivo Generators. Molecules 2018, 23, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Brechbiel, M.W. An overview of targeted alpha therapy. Tumor Biol. 2012, 33, 573–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, Y.; Imobersteg, S.; Blanc, A.; Frank, S.; Schibli, R.; Béhé, M.P.; Grzmil, M. Evaluation of Actinium-225 Labeled Minigastrin Analogue [225Ac]Ac-DOTA-PP-F11N for Targeted Alpha Particle Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruijff, R.M.d.; Raavé, R. The in vivo fate of 225Ac daughter nuclides using polymersomes as a model carrier. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Jaraquemada-Peláez, M.G. Functionally Versatile and Highly Stable Chelator for (111)In and (177)Lu: Proof-of-Principle Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen Targeting. Bioconjug. Chem. 2019, 30, 1539–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, J.M.; Amor-Coarasa, A.; Nikolopoulou, A.; Kim, D.; Williams, C.; Vallabhajosula, S.; Babich, J.W. Assessment of PSMA targeting ligands bearing novel chelates with application to theranostics: Stability and complexation kinetics of 68Ga 3+, 111In 3+, 177Lu 3+ and 225Ac 3+. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2017, 55, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenstern, A.; Lilley, L.M.; Stein, B.W.; Kozimor, S.A.; Batista, E.R.; Yang, P. Computer-Assisted Design of Macrocyclic Chelators for Actinium-225 Radiotherapeutics. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiele, N.A.; Wilson, J.J. Actinium-225 for Targeted α Therapy: Coordination Chemistry and Current Chelation Approaches. Cancer Biotherapy Radiopharm. 2018, 33, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Rousseau, J.; Jaraquemada-Peláez, M.D.G.; Wang, X.; Robertson, A.; Radchenko, V.; Schaffer, P.; Lin, K.-S.; Bénard, F.; Orvig, C. 225Ac-H4py4pa for Targeted Alpha Therapy. Bioconjugate Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, M.K.; Alejandro, A.-C. A Consensus Time for Performing Quality Control of 225Ac-Labeled Radiopharmaceuticals. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




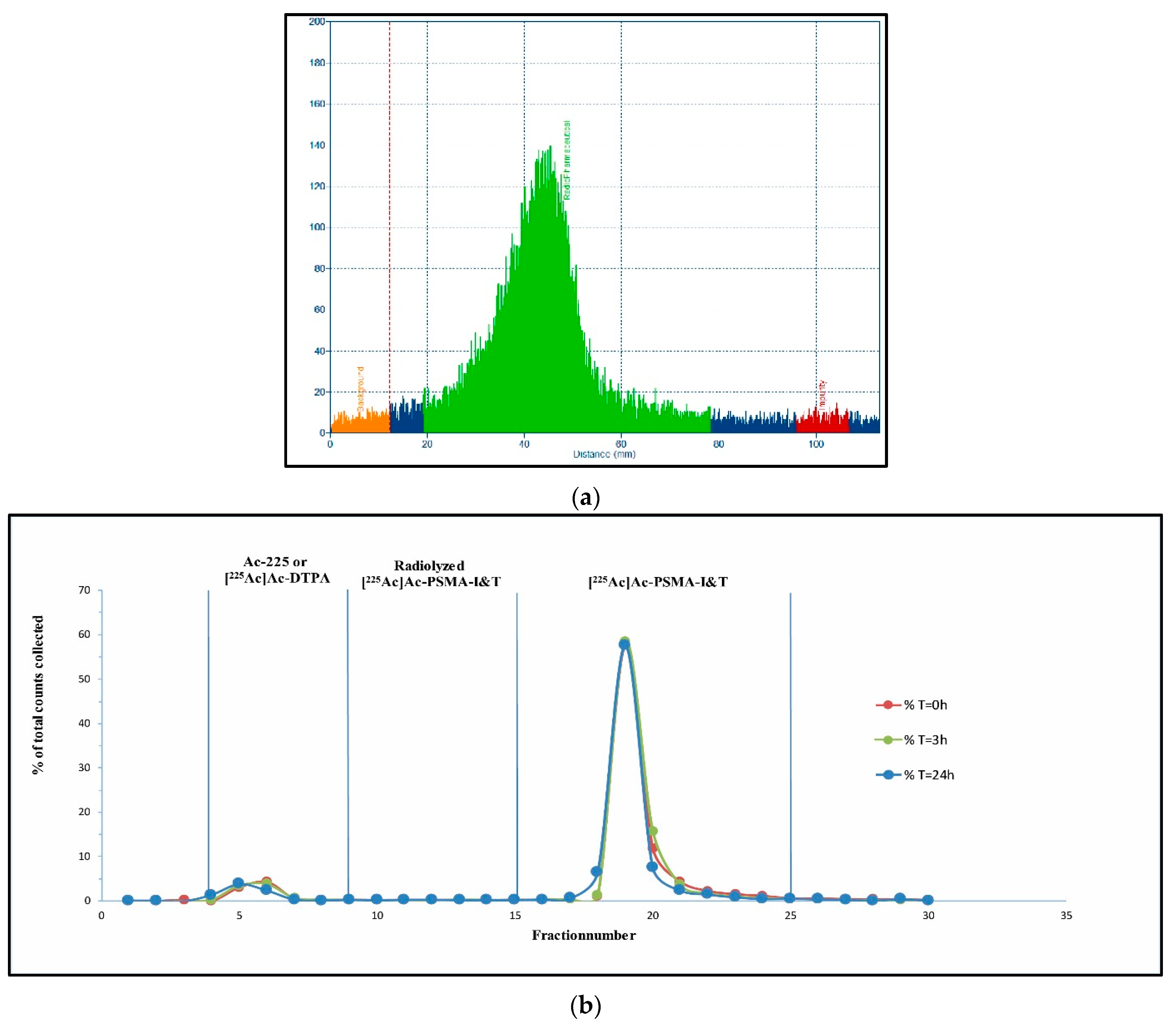
| Radio-(i)TLC-scanner | Strips (ITLC-SG, 0.5 × 10 cm), activity spotted at RF 0.1, sealed with parafilm after separation was performed |
| HPGe-detector | ITLC strip cut at RF 0.7, top and bottom measured in borosilicate glass tube (Pyrex 12 × 7.5 mm) in 10 mL reaction tube (8.5 mL, 75 × 15.7 mm) |
| Gamma counter | Activity concentration of <10 kBq, (5 µL radiolabeling solution) in Milliq water (total volume of 1 mL) |
| Dose calibrator | 8–12 MBq, 3–8 mL final solution in 10 mL syringe (Luer Lock) with stopper |
| Reaction Component | Amount (µL) | |
|---|---|---|
| During labeling | PSMA-I&T (0.1 M TRIS) | 300 |
| Ac-225 + 0.1 M HCl | 25 (15, 17, 19 MBq) | |
| Milliq water | 80 | |
| 1 M ascorbate | 200 | |
| Directly after labeling | DTPA | 15 |
| 1 M ascorbate | 500 |
| No Addition of Ascorbate 90 µg PSMA-I&T | T = 0 h (%) | T = 1 h (%) | T = 2 h (%) | T = 3 h (%) |
| Ac-225, [225Ac]Ac-DTPA | 8.9 | 13.2 | 13.3 | 12.4 |
| Radiolyzed [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-I&T | 7.5 | 8.2 | 8.1 | 7.6 |
| [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-I&T | 83.6 | 78.6 | 78.6 | 79.9 |
| Addition of 50 µL Ascorbate 90 µg PSMA-I&T | ||||
| Ac-225, [225Ac]Ac-DTPA | 2.3 | 4.0 | 5.2 | 4.2 |
| Radiolyzed [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-I&T | 4.3 | 5.2 | 6.9 | 7.3 |
| [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-I&T | 93.5 | 90.9 | 88.0 | 88.5 |
| Addition of 100 µL Ascorbate (n = 3) 90 µg PSMA-I&T | ||||
| Ac-225, [225Ac]Ac-DTPA | 3.1 ± 1.3 | 3.2 ± 1.5 | 3.8 ± 1.3 | 3.5 ± 2.2 |
| Radiolyzed [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-I&T | 3.9 ± 0.2 | 4.3 ± 0.6 | 4.8 ± 1.0 | 5.2 ± 0.6 |
| [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-I&T | 93.1 ± 1.1 | 92.6 ± 1.5 | 91.6 ± 1.6 | 91.5 ± 1.6 |
| Addition of 200 µL Ascorbate and Injection Solution (n = 3) 180 µg PSMA-I&T | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| T = 0 h (%) | T = 3 h (%) | T = 24 h (%) | |
| Ac-225, [225Ac]Ac-DTPA | 7.5 ± 1.0 | 7.3 ± 1.5 | 9.6 ± 2.9 |
| Radiolyzed [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-I&T | 1.8 ± 0.9 | 1.9 ± 1.0 | 1.5 ± 0.3 |
| [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-I&T | 90.2 ± 0.2 | 90.3 ± 0.3 | 89.1 ± 3.5 |
| Release Criteria | Acceptance Limit | Batch 1 | Batch 2 | Batch 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCY (Radio-(i)TLC-scanner) | >95% | 97.0% | 97.2% | 96.3% |
| RCY (HPGe-detector) | >95% | 99.9% | 99.7% | 99.7% |
| RCP/stability (HPLC) | >90% | |||
| T0h | 90.0% | 90.1% | 90.4% | |
| T3h | 90.1% | 90.6% | 90.2% | |
| Bacterial endotoxins | <5 EU/mL | Conform | Conform | Conform |
| pH | 5.5–9 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hooijman, E.L.; Chalashkan, Y.; Ling, S.W.; Kahyargil, F.F.; Segbers, M.; Bruchertseifer, F.; Morgenstern, A.; Seimbille, Y.; Koolen, S.L.W.; Brabander, T.; et al. Development of [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-I&T for Targeted Alpha Therapy According to GMP Guidelines for Treatment of mCRPC. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050715
Hooijman EL, Chalashkan Y, Ling SW, Kahyargil FF, Segbers M, Bruchertseifer F, Morgenstern A, Seimbille Y, Koolen SLW, Brabander T, et al. Development of [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-I&T for Targeted Alpha Therapy According to GMP Guidelines for Treatment of mCRPC. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(5):715. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050715
Chicago/Turabian StyleHooijman, Eline L., Yozlem Chalashkan, Sui Wai Ling, Figen F. Kahyargil, Marcel Segbers, Frank Bruchertseifer, Alfred Morgenstern, Yann Seimbille, Stijn L. W. Koolen, Tessa Brabander, and et al. 2021. "Development of [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-I&T for Targeted Alpha Therapy According to GMP Guidelines for Treatment of mCRPC" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 5: 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050715
APA StyleHooijman, E. L., Chalashkan, Y., Ling, S. W., Kahyargil, F. F., Segbers, M., Bruchertseifer, F., Morgenstern, A., Seimbille, Y., Koolen, S. L. W., Brabander, T., & de Blois, E. (2021). Development of [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-I&T for Targeted Alpha Therapy According to GMP Guidelines for Treatment of mCRPC. Pharmaceutics, 13(5), 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050715






